紫黑链霉菌进化枝菌株Streptomyces solisilvae HNM0141T的全基因组分析
2022-03-25周奕帆李陈贵许云吴文嫱夏薇黄小龙黄东益周双清
周奕帆 李陈贵 许云 吴文嫱 夏薇 黄小龙 黄东益 周双清

摘 要:鏈霉菌属放线菌是最重要的抗生素产生菌,也是包含放线菌种类最多的放线菌属。链霉菌属的有效发表种的模式菌株在16S rRNA基因序列系统发育树上分散归簇于不同的进化分枝。紫黑链霉菌16S rRNA 基因进化枝( 16S rRNA gene clade)是其中的一个分枝。该分枝菌株在燕麦培养基上基内菌丝淡黄色,气生菌丝发育成灰色,表面皱纹的螺旋状孢子丝,培养后期呈黑色。该分枝中的菌株普遍具有丰富的生物活性,能产生抗菌、抗寄生虫、抗肿瘤、免疫抑制等多种活性物质,是新型抗生素开发与利用的重要菌源。HNM0141是紫黑链霉菌16S rRNA基因进化枝放线菌的模式菌株。采用第三代全基因组测序技术,首次获得了菌株 HNM0141的基因组完成图,其线状基因组长度11 639 536 bp,GC含量为71.03%,包含9363个蛋白编码基因(CDS),18个rRNA基因和67个tRNA基因。其中有6376、5886、3246个CDS分别在COG、GO和KEGG数据库中得到功能注释。除了一般功能预测之外,有大部分基因参与转录、氨基酸转运和代谢、碳水化合物转运和代谢以及次级代谢生物合成和代谢,基因数占比分别为12.91%、10.25%、8.89%、7.59%。利用antiSMASH软件,预测到48个次级代谢产物合成基因簇,其类型包括8个聚酮(PKS)型、7个非核糖体肽(NRPS)型、14个杂合型、6个terpene、3个siderophore、2个butyrolactone,其余NAPAA、ectoine、lanthipeptide-class-i、ladderane、indole、RiPP-like、hserlactone、redox-cofactor各1个。其中聚酮类(PKS)和非核糖体肽(NRPS)类(包括杂合类型)的基因簇含量丰富,占总基因簇的50%以上。7个基因簇与已知代谢物(pristinol、ectoine、geosmin、desferrioxamin B、echoside A/B/C/D/E、nigericin、coelichelin)基因簇的相似性为100%,34个基因簇的相似性在2%~96%之间,剩余的7个基因簇无法匹配到已知基因簇。全基因组分析表明菌株 HNM0141具有强大次级代谢产物合成的能力,预示该菌株在新颖抗生素的挖掘上具有良好的研究潜力。
关键词:紫黑链霉菌;16S rRNA基因进化枝;基因组测序;次级代谢合成基因簇中图分类号:Q933 文献标识码:A
Analysis of Complete Genome Sequence of HNM0141of the Clade
ZHOU Yifan, LI Chengui, XU Yun, WU Wenqiang, XIA Wei, HUANG Xiaolong, HUANG Dongyi, ZHOU Shuangqing
1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Biological Resources of Ministry of Education, Haikou, Hainan 570228, China; 2. College of Tropical Crops, Hainan University, Haikou, Hainan 570228, China; 3. Pharmacy School of Guilin Medical University, Guilin, Guangxi 541199, China
Actinomycetes belonging to are the most important antibiotic producing bacteria and also the actinomycete genus with the largest number of species. Many streptomycete type strains can be assigned to distinct evolutionary clades on the 16S rRNA gene phylogenetic tree, and the 16S rRNA gene clade is one of them. Members of the clade form a greyish yellow substrate mycelium and a grayish aerial hyphae on oatmeal agar that develop into spiral chains of rugose ornamented spores that become black on prolonged incubation. Members of the violaceusniger 16S rRNA gene clade have abundant biological activities and produce antibacterial metabolites, antiparasitic metabolites, antitumour compounds and immunosuppressants as important sources for the development and utilization of new antibiotics. HNM0141is a type strain assigned to the 16S rRNA gene clade. Here, we present the complete genome sequence of it, which is generated using the third sequencing technology and consists of a linear chromosome of 11 639 536 bp with a GC content of 71.3%, 9363 protein coding genes(CDS), 18 rRNA genes, and 67 tRNA genes. The identified CDS were classified into 6376, 5886, and 3246 categories based on clusters of orthologous genes of proteins (COG), gene ontology (GO), and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) designation, respectively. In addition to the general function prediction only, most of the genes involved in transcription, amino acid transport and metabolism, carbohydrate transport and metabolism and secondary metabolic biosynthesis and metabolism were accounted for 12.91%,10.25%, 8.89% and 7.59% respectively. Forty-eight putative secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters were found in the genome using the online antiSMASH software, including eight PKS, seven NRPS, fourteen hybrid gene clusters, six terpenes, three siderophores, two butyrolactones, one NAPAA, one ectoine, one lanthipeptide-class-i, one ladderane, one indole, one RiPP-like, one hserlactone and one redox-cofactor. Polyketone (PKS) and non-ribosomal peptide (NRPS) gene clusters (including heterozygous types) were abundant and accounted for more than 50% of the total gene clusters. Seven putative gene clusters showed 100% similarities to known gene clusters: pristinol, ectoine, geosmin, desferrioxamin B, echoside A/B/C/D/E, nigericin, and coelichelin gene clusters. Thirty-four putative gene clusters showed 2%–96% similarities to known gene clusters. The remaining seven gene clusters could not be matched to known gene clusters. Genome-wide analysis showed that HNM0141 had strong ability of the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, indicated that it should be good research potential for mining of the novel antibiotics.
; 16S rRNA gene clade; genome sequence; secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters
10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.03.003
链霉菌属是放线菌门种类最多的放线菌属,是最重要的抗生素产生菌。当前该属含有效发表种677个(http://www.bacterio.net/streptomyces. html)。链霉菌属的有效发表种的模式菌株在16S rRNA基因序列系统发育树上分散归簇于不同的进化分枝(clade)[,处在同一进化分枝上的菌株亲缘关系较近,通常表现出某些共同的生理特征。紫黑链霉菌16S rRNA基因进化枝( 16S rRNA gene clade)是其中的一个分枝(clade),由SEMBIRING等[推荐建立。该分枝菌株在ISP3培养基上具有明显的特征:基内菌丝淡黄色,孢子丝早期灰色,后期黑褐色,孢子链呈螺旋状,表面不光滑,有褶皱[1-2]。利用特异性引物可以扩增到该分枝菌株16S rRNA基因序列中的部分特异性片段[。目前,该分枝包含正式发表的有效种共17个[,在这些报道的有效种菌株中,许多菌株已经是知名的抗生素产生菌,如和。该分枝中的菌株普遍具有丰富的生物活性,能产生抗菌、抗虫、抗肿瘤、免疫抑制等多种活性物质,在抗生素的开发上得到了广泛的利用[4。因此,紫黑链霉菌16S rRNA基因进化枝菌株被认为是链霉菌属中利用价值极高的一类放线菌资源,是寻找新型抗生素的重要菌源。
研究发现该类菌在植物根际、非根际土壤、落叶堆、淡水沉积物、海洋沉积物等环境均具有分布,菌种的分布与环境具有相关性,特殊的环境蕴藏新颖的菌株[3]。也有研究者从植物的种子、叶鞘等内生环境分离到该分枝的菌株[。本实验室前期研究证实,紫黑链霉菌16S rRNA基因进化枝菌株在我国热带地区也有分布,不仅从海南药用植物根际分离到此类放线菌[,也从热带雨林森林土壤中分离到此类放线菌的新种HNM0141[4]。为了深入地了解该分枝新种菌株HNM0141的生物学功能和次生代谢合成潜力,本研究采用Pacific BioscienceRS II系统上的SMRT对其进行全基因组测序,获得了菌株HNM0141的基因组全序列,同时进行了基因预测、功能注释与次级代谢合成基因簇分析,为该菌株的进一步研究和开发利用奠定基础。
材料与方法
材料
菌株 HNM0141由实验室前期分离于海南霸王岭热带雨林土壤,保存于本实验室–20℃冰箱甘油管中。
方法
1.2.1 菌株HNM0141 DNA的提取与基因组测序 菌株HNM0141使用ISP2液体培养基28℃,摇瓶培养5 d,离心收集菌体,使用Promega(美国)Wizard基因组DNA提取试剂盒进行总DNA的提取。送北京百迈客科技有限公司,利用Pacific BioscienceRS II系统上的SMRT进行全基因组测序。获得的数据用HGAP 2.3软件[进行拼接组装获得基因组完全图,采用Circos version 0.62软件[绘制基因组圈图。
1.2.2 基因预测、功能注释与次级代谢合成基因簇分析 将拼接好的基因组序列采用Glimmer 3.02软件[预测其开放阅读框(ORF);使用tRNAscan-SE[软件预测tRNA,采用软件Infernal 1.1[基于Rfam[数据库预测基因组中的rRNA以及除了tRNA和rRNA之外的其他ncRNA。将所有的ORF预测的蛋白序列采用BLAST软件完
成比对及功能注释。CDS和Genes的功能注釋分别采用COG(Clusters of orthologous groups)、GO(Gene ontology)和KEGG(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes)数据库完成。采用antiSMASH 6.0(http://antismash.secondarymetabolites.org)在线软件预测菌株HNM0141的次级代谢生物合成基因簇。
1.2.3 基因组系统发育树构建 将获得的菌株HNM0141的基因组序列,利用Type Strain Genome Server(https://tygs.dsmz.de/)在线软件构建基因组水平的系统发育树,从基因组水平判断菌株的系统发育地位。
结果与分析
基因组的组装与功能注释
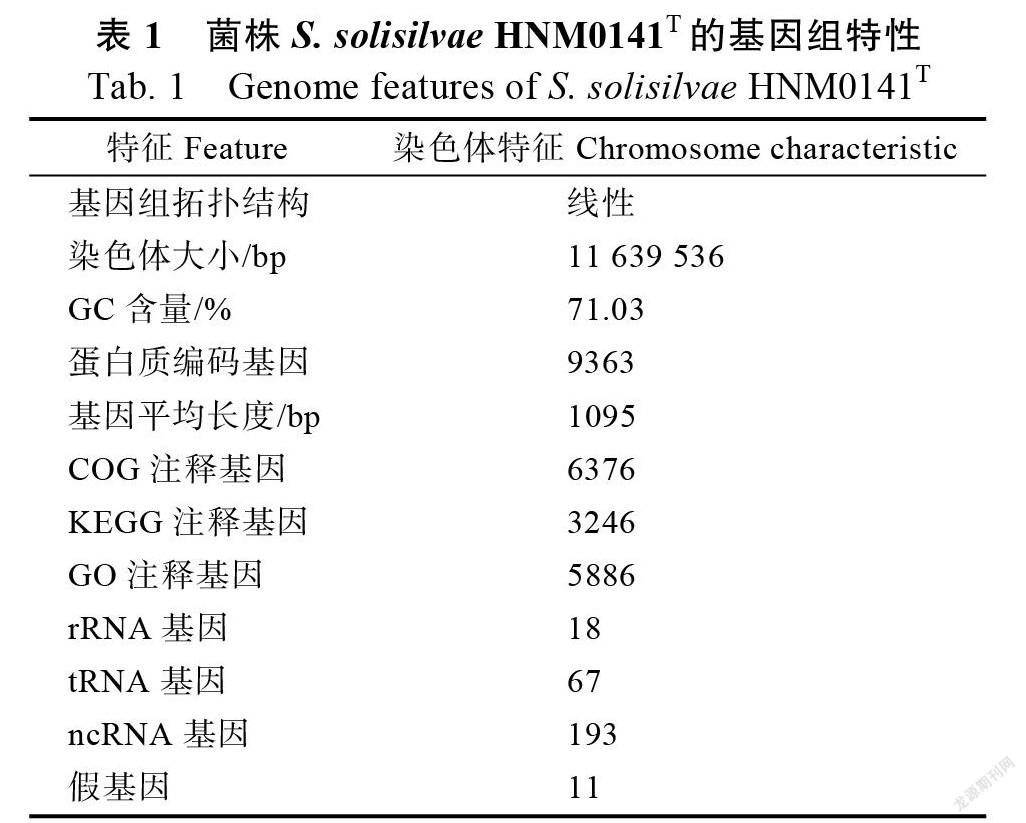
菌株HNM0141经测序、组装获得完整的基因组,长度为11 639 536 bp,GC含量71.03%的线形染色体(GenBank登录号:CP065050)。基因组预测获得总共9363个蛋白编码基因,18个rRNA,67个tRNA基因和193 ncRNA基因(图1和表1)。其中,9363个CDS(蛋白质编码序列)中有6376、5886、3246个CDS分别在COG、GO和KEGG数据库中得到功能注释。
最外面一圈为基因组大小的标示,每个刻度为0.1 Mb;第二圈和第三圈分别为基因组正链和负链的基因,不同颜色代表不同的COG功能分类;第四圈为重复序列;第五圈为tRNA 和rRNA;第六圈为GC含量,浅黄色部分表示该区域GC含量高于基因组的平均GC含量,蓝色部分则表示该区域GC含量低于基因组的平均GC含量;最内圈是GC-skew,深灰色代表G含量大于C的区域,红色代表C含量大于G的区域。
The outermost circle is the mark of genome size, with each scale of 0.1 MB; The second and third circles are the positive and negative genes of genome respectively, Different colors represent different COG functional classification; The fourth circle is repetitive sequence; The fifth circle is tRNA and rRNA genes; The sixth circle is the GC percentage plot, pale yellow above average, blue below average; The innermost layer is the GC skew, dark gray represents areas with more G than C, and red represents areas with more C than G.
功能分類
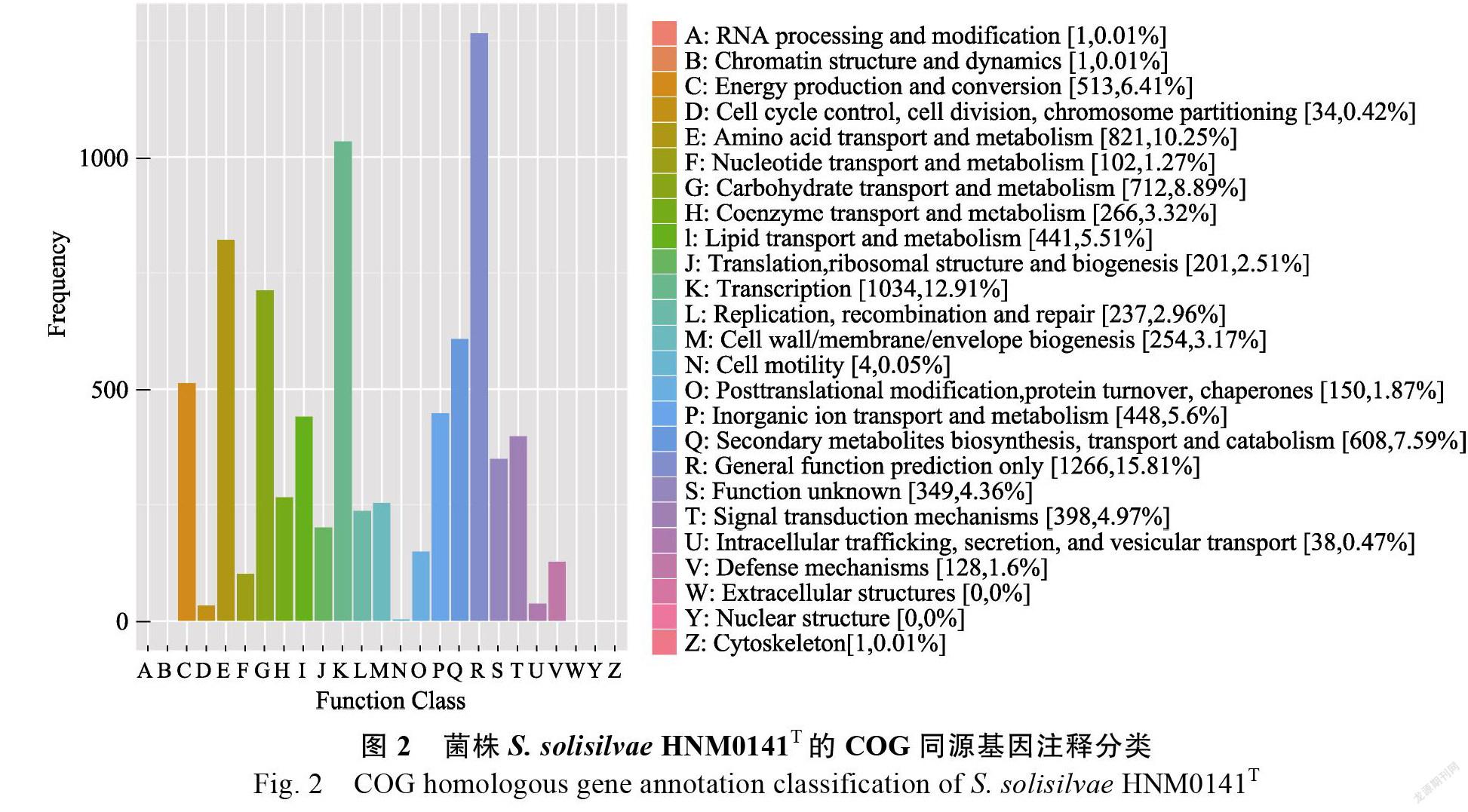
在6376个CDS具有COG功能注释中,共分为25个功能组(图2)。其中,除了一般功能预测(R)之外,有大部分基因参与转录(K)、氨基酸转运和代谢(E)、碳水化合物转运和代谢(G)以及次级代谢生物合成和代谢(Q),基因数占比分别为12.91%、10.25%、8.89%和7.59%。同时在生物代谢大类中,包括能量产生和转化(C)(6.41%)、氨基酸转运和代谢(E)(10.25%)、核苷酸转运和代谢(F)(1.27%)、碳水化合物转运和代谢(G)(8.89%)、同工酶转运和代谢(H)(3.32%)、脂质转运和代谢(I)(5.51%)、无机离子转运和代谢(P)(5.6%)、次级代谢生物合成和代谢(Q)(7.59%)、信号传导与代谢(T)(4.97%)以及防御代谢(V)(1.6%),这些基因占所有功能基因的55.41%。由此可见,菌株HNM0141有相当强的生物代谢能力,特别在次级代谢生物合成方面可能具有强大的合成能力。
功能分类
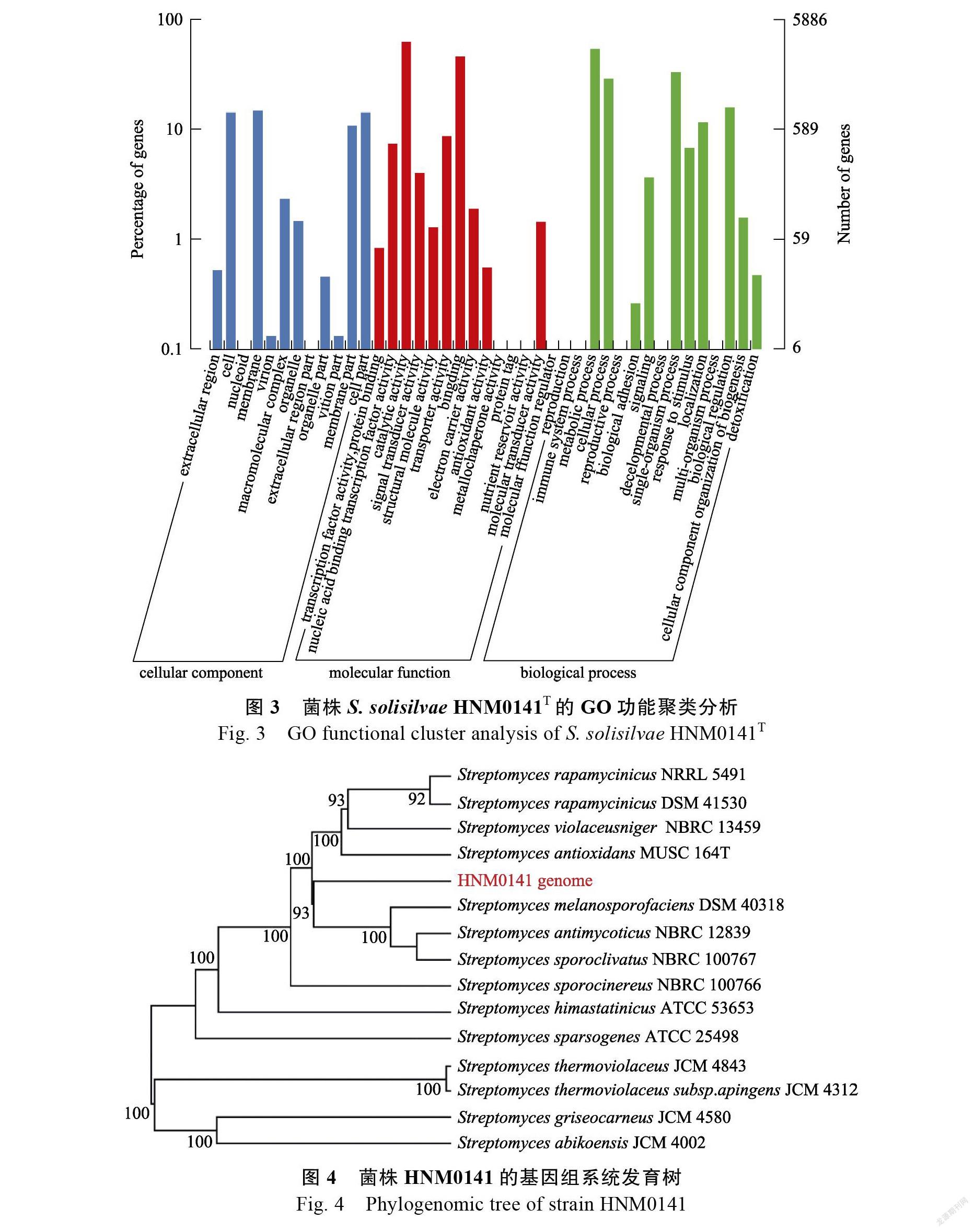
5886个CDS具有GO注释功能,共分为3大类: 细胞组分(cellular component)、分子功能(molecular function)和生物学过程(biological process)(图3)。分子功能中的催化活性和结合,生物学过程中的代谢过程、细胞过程、单生物过程和生物调节等相关基因数量最多。
菌株的基因组系统发育分析
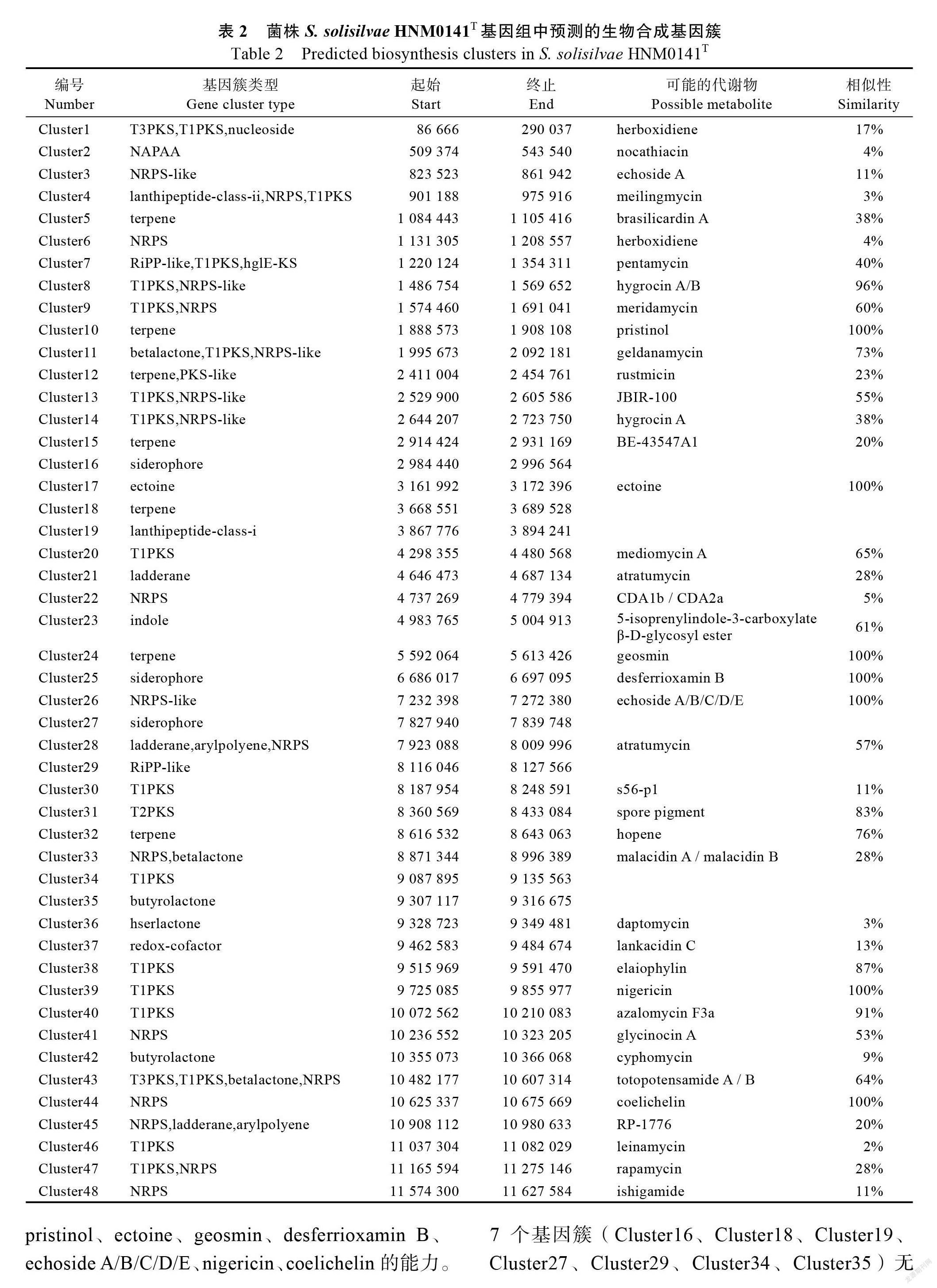
将菌株HNM0141的基因组完成序列,利用Type Strain Genome Server在线软件,构建基因组
水平的系统发育树如图4所示,菌株HNM0141与链霉菌属的菌株聚类在一起,特别跟标准菌株,,,,,和聚合在同一个大的分枝上,而这些标准菌株都为紫黑链霉菌16S rRNA 基因进化枝(16S rRNA gene clade)的主要成员[2]。因此,从基因组水平的系统发育树再次证明了菌株HNM0141为紫黑链霉菌16S rRNA基因进化枝的新种菌株[4]。
次级代谢合成基因簇分析
在菌株HNM0141基因组预测到48个次级代谢产物合成基因簇(表2),其类型包括8个聚酮(PKS)型、7个非核糖体肽(NRPS)型(2个NRPS-like)、14个杂合型、6个terpene、3个siderophore、2个butyrolactone,其余NAPAA、ectoine、lanthipeptide-class-i、ladderane、indole、RiPP-like、hserlactone、redox-cofactor各1个。其中包含PKS型和NRPS型(包括杂合类型)的基因簇占总基因簇的50%以上。从基因簇的相似性来看,有7个基因簇(Cluster10、Cluster17、Cluster24、Cluster25、Cluster26、Cluster39、Cluster44)与已知基因簇的相似性为100%,说明菌株HNM0141具有产生代谢物pristinol、ectoine、geosmin、desferrioxamin B、echoside A/B/C/D/E、nigericin、coelichelin的能力。7个基因簇(Cluster16、Cluster18、Cluster19、Cluster27、Cluster29、Cluster34、Cluster35)无法匹配到已知基因簇,表明这些基因簇为未知基因簇,具有产生新代谢物的潜能。其他34个基因簇的相似性在2%~96%之间,暗示这些基因簇具有产生已知结构代谢物或其结构类似物的潜力。
讨论
紫黑链霉菌16S rRNA基因进化枝放线菌以产生丰富的活性物质而著称。例如: 产生著名的免疫抑制剂雷帕霉素(apamycin)[;产生格尔德霉素(geldanamycin)[1]以及產生阿扎霉素(azalomycin)[;而吸水链霉菌则是产生抗生素最多的放线菌,该类菌株能产生包括井冈霉素(validamycin)、米尔贝霉素(milbemycin)、双丙氨膦(bialaphos)、除莠霉素(herbimycin)等在内的650多种活性物质[。近年来,从一些特殊生境分离的紫黑链霉菌16S rRNA基因进化分枝菌株中发现了多种新颖的活性化合物。洪葵课题组从红树林来源的该分枝菌株211726中发现了7个具有强抗真菌和肿瘤活性的新型阿扎霉素F类大环内酯化合物[;甘茂罗课题组从大连海洋沉积物来源的该分枝菌株7-145中挖掘到2个新型洋橄榄叶素(elaiophylin)和4个新型尼菲霉素(niphimycin)类化合物,对耐药菌MRSA和VRE呈现出较强的抗菌活性[。本实验室从HNM30702中分离到阿扎霉素Azalomycin F4a和F5a,以及具抗病毒活性的新颖环六肽Soliseptide A。基因组测序显示该分枝放线菌菌株的基因组普遍大于一般的链霉菌,如. 5008基因组长度为10.3 Mb[, NRRL 5491的基因组长度为12.7 Mb,subspNBRC 16556基因组长度为10.1 Mb[。基因组学分析表明该分枝的菌株基因组中含有丰富的次级代谢产物合成基因簇,特别是聚酮类(PKS)和非核糖体肽(NRPS)类基因簇。因此,对该类菌株进行全基因组测序分析将有助于从分子水平上了解其生物学功能和次级代谢产物的生物合成潜力,为深入开发与利用此类菌株提供理论依据。
本研究利用第三代全基因组测序技术,首次获得了模式菌株HNM0141的基因组完成图,其线状基因组长度大于11.6 Mb,符合该类菌株的基因组较大的基本特征。利用antiSMASH软件,预测得到48个次级代谢产物合成基因簇,且含有丰富的聚酮类(PKS)和非核糖体肽(NRPS)类(包括杂合类型)的基因簇,无疑证明了该菌株具有强大次级代谢产物合成的能力。同时发现该菌株基因组中含有与梅岭霉素(meilingmycin)、格尔德霉素(geldanamycin)、达托霉素(daptomycin)、阿扎霉素(azalomycin)、雷帕霉素(rapamycin)等知名抗生素合成基因簇相似性较低的基因簇(如:Cluster4、Cluster11、Cluster36、Cluster40、Cluster47)以及7个未知类型的基因簇,预示该菌株在新颖抗生素的挖掘上具有良好的开发潜能。
参考文献
- GOODFELLOW M, KUMAR Y, LABEDA D P, SEMBIRING L. The clade: a home for with rugose ornamented spores[J]. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2007, 92: 173-199.
- SEMBIRING L, WARD A C, GOODFELLOW M. Selective isolation and characterisation of members of theclade associated with the roots of [J]. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2000, 78: 353-366.
- KUMAR Y, AIEMSUM-ANG P, WARD A C, GOODFELLOW M. Diversity and geographical distribution of members of the 16S rRNA gene clade detected by clade-specific PCR primers[J]. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 2007, 62: 54-63.
- ZHOU S, YANG X, HUANG D, HUANG X. sp. nov., isolated from tropical forest soil[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2017, 67(9): 3553-3558.
- KUSUMA A B, NOUIOUI I, GOODFELLOW M. Genome-based classification of the clade and description sp. nov. from an Indonesian sand dune[J]. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 2021, 114: 859-873.
- XU T, CAO L, ZENG J, FRANCO C M M, ZHU Y. The antifungal action mode of the rice endophyte OsiSh-2 as a potential biocontrol agent against the rice blast pathogen[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 2019, 160: 58-69.
- 黄小龙, 陈吉良, 李建平, 林海鹏, 庄 令, 李 佳, 洪 葵. 热带药用植物根际放线菌的分离、鉴定及生物活性分析[J]. 生物技术通报, 2012, 2: 121-127.HUANG X L, CHEN J L, LI J P, LIN H P, ZHUANG L, LI J, HONG K. Isolation, identification and bioactivity analysis of from tropical medicinal plants[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2012, 2: 121-127. (in Chinese)
- 丛子文, 焦敬华, 周双清, 黄东益, 吴文嫱, 许 云, 夏 薇, 张荣萍, 黄小龙. 链霉菌30702的鉴定及其生防特性[J]. 生物技术通报, 2018, 34(8): 1-6.CONG Z W, JIAO J H, ZHOU S Q, HUANG D Y, WU W Q, XU Y, XIA W, ZHANG R P, HUANG X L. Identification and biocontrol characteristics of 30702[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2018, 34 (8): 1-6. (in Chinese)
- BARANASIC D, GACESA R, STARCEVIC A, ZUCKO J, BLAŽIC M, HORVAT M, GJURACIC K, FUJS Š, HRANUELI D, KOSEC G, CULLUM J, PETKOVIC´ H. Draft genome sequence of strain NRRL 5491, the producer of the immunosuppressant rapamycin[J]. Genome Announc, 2013, 1(4): e00581-13.
- PALANIYANDI S A, YANG S H, SUH J W. Foliar application of extract from an azalomycin-producing strain MJM1968 suppresses yam anthracnose caused by[J]. Journal Microbiol Biotechnol, 2016, 26: 1103-1108.
- KOMAKI H, ICHIKAWA N, OGUCHI A, HAMADA M, SUZUKI K I. Genome analysis-based reclassification of and as later heterotypic synonyms of subsp. [J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 2017, 67(2): 343-345.
- JIANG J, SUN Y F, TANG X, HE C N, ZHOU W W. Alkaline pH shock enhanced production of validamycin A in fermentation of [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 249: 234-240.
- YUAN G, HONG K, LIN H, SHE Z, LI J. New azalomycin F analogs from mangrove sp. 211726 with activity against microbes and cancer cells[J]. Marine Drugs, 2013, 11(3): 817-829.
- WU C, TAN Y, GAN M, WANG Y, GUAN Y, HU X, ZHOU H, SHANG X, YOU X, YANG Z. Identification of elaiophylin derivatives from the marine-derived actinomycete sp. 7-145 using PCR-based screening[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2013, 76(11): 2153-2157.
- HU Y, WANG M, WU C, TAN Y, LI J, HAO X, DUAN Y, GUAN Y, SHANG X, WANG Y, XIAO C, GAN M. Identification and proposed relative and absolute configurations of niphimycins C-E from the marine-derived sp. IMB7-145 by genomic analysis[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 2018, 81(1): 178-187.
- WANG J, CONG Z, HUANG X, HOU C, CHEN W, TU Z, HUANG D, LIU Y. Soliseptide A, a cyclic hexapeptide possessing piperazic acid groups from HNM30702[J]. Organic Letters, 2018, 20(5): 1371-1374.
- WU H, QU S, LU C, ZHENG H, ZHOU X, BAI L, DENG Z. Genomic and transcriptomic insights into the thermo- regulated biosynthesis of validamycin in 5008[J]. BMC Genomics, 2012, 13(1): 337.
- KOMAKI H, ICHIKAWA N, OGUCHI A, HAMADA M, FUJITA N. Draft genome sequence of subsp. NBRC 16556[J]. Genome Announc, 2016, 4(3): e00139-16.
