Four FDA-approved drugs exhibited inhibition effect on severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in vitro
2022-02-17WANGTiantianYINZhiyunDENGYaliZHUQiongZHOUMinHUSijingWuQiaoliJINJiayinZHANGDannaLIUXijiaJIANGBoyongSHENShuDENGFeiSHIJunming
WANG Tian-tian, YIN Zhi-yun, DENG Ya-li, ZHU Qiong, ZHOU Min, HU Si-jing,Wu Qiao-li, JIN Jia-yin, ZHANG Dan-na, LIU Xi-jia, JIANG Bo-yong, SHEN Shu, DENG Fei, SHI Jun-ming
1. National Virus Resource Conservation Center, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 430071, China
2. School of Pharmacy, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To screen the anti-SFTSV drugs from 1 430 FDA-approved drugs via mini-genome system, and to investigate which stage of the infection process could be suppressed by the identified drugs. Methods: The SFTSV mini-genome system was used to screen drugs with inhibitory effect on SFTSV replication and transcription, and the 50% inhibitory concentration(IC50) of each drug was calculated by drug concentration gradient inhibition experiment. Drugs were used to pre-incubate with virus and then incubate with cells, to incubate with virus and cells simultaneously, to incubate with cells after virus invading into cells, or to incubate during the whole infection process, and then qRT-PCR was used to measure the viral RNA copies in the culture supernatant. These experiments were performed to quantitatively determine the inhibition effects of drugs on SFTSV indifferent stages of the whole process including virion stability, entry and post-entry stages, so as to clarify the inhibition mechanism of these drugs.Results: Four drugs including Mycophenolate mofetil, Mycophenolic acid, Nitazoxanide, and Vidofludimus were identified having efficient inhibitory effects on SFTSV RNA replication via minigenome system, with the IC50 of 0.014 μmol/L, 0.627 μmol/L, 1.283 μmol/L, and 0.059 μmol/L, respectively. All four drugs showed effective inhibition when adding during the whole
1. Introduction
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) is the causative agent of severe fever with platelet syndrome (SFTS). It belongs to genus Bandavirus of family Phenuiviridae[1, 2]. The main clinical symptoms of SFTSV infection include fever, gastrointestinal symptoms, myalgia, local lymphadenopathy, thrombocytopenia,elevated liver enzyme levels, etc, or even lead to more severe consequence with multiple organ failure or death. The mortality rate of SFTSV infection is 13%-30%, and it is listed as one of the top ten priority infectious diseases by the World Health Organization[1,3]. At present, the clinical treatment of SFTS is mainly rely on symptomatic and supportive treatment, including the immune system enhancement via large dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy (effective in few clinical cases) or injection of hormone combined with immunoglobulin (effective in few clinical cases),pulse steroid therapy (effective in few clinical cases) and plasma exchange (effective in clinical cases)[4-6]. Since there are no effective vaccines and specific drugs for SFTS, the research and development of specific anti-SFTSV drugs has become a scientific problem to be solved urgently.
The genome of SFTSV is composed of three single-stranded negative sense RNA segments, which are termed as large (L),medium (M) and small (S), respectively. The L segment encodes RNA polymerase (RdRp), the M segment encodes glycoproteins Gn and Gc, and the S segment encodes nuclear protein NP and nonstructural proteins NSs[3]. Similar to the transcription and replication mechanism of most negative-strand RNA viruses, conserved motifs are shared within the UTR region of SFTSV genome, forming RNAprotein complex (RNP) with RdRp and NP and are responsible for SFTSV gene replication and transcription[7-9]. RNP is the simplest requirement for SFTSV gene replication and transcription. Based on this theory, we successfully constructed a SFTSV mini-replicon reporter system capable of expressing eGFP fluorescent protein in the early stage[10]. Mini-replicon reporter system can effectively quantify the viral RNA replication and transcription by detecting the report gene expression level, which is an important method for the study of RNA transcription and replication mechanism of RNA viruses as well as an effective means of drug screening for specific target to RNA replication process[11, 12].
So far, several drugs with antiviral effect against SFTSV have been reported, including: (1) antiviral drugs: the broad-spectrum antiviral drug ribavirin (evidence from cell experiments and animal experiments), interferon combined with ribavirin (evidence from cell experiments), plasma exchange combined with ribavirin (evidence from clinical cases), fapilavir evidence from animal experiments);(2) Calcium channel blockers: benidipine hydrochloride and nifedipine (evidence from clinical cases)[4]. The discovery of antiviral effect of these drugs on SFTSV was determined from the perspective of "conventional drug in new use", by evaluating the SFTSV inhibition effect of drugs which are supposed to target other viruses or by reviewing the administration records of clinical SFTS cases. Screening anti-SFTSV drugs from FDA-approved drugs can greatly shorten the development period and reduce cost. In this study,1430 FDA-approved compounds were screened for using the SFTSV mini-replicon reporter system. Further, the anti-SFTSV effect of the screened drugs was evaluated via cell infection with native SFTSV,and the specific effective stage of drug was determined. The findings of this study will provide important theoretical reference for the application of mini-replicon reporter system in the development of SFTSV antiviral drugs, and promote the development of SFTSV specific drugs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1 Cells and viruses
Vero cells (ATCC No. CCL-81) and HEK293T (ATCC No. CRL-3216) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection(ATCC) and stored in our laboratory. Strain of SFTSV (WCH/97/HN/China/2011; S/M/L segment GenBank No. : JQ341190/JQ341189/JQ341188) was obtained from the National Virus Reservation Center of Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
2.1.2 Compounds
A total of 1430 FDA-approved compounds, including Vidofludimus,nitazonide, mycophenolic acid and mycophenolic mofetol, were purchased from Selleck Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The mother liquor of each compounds were prepared with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)and diluted with DEME medium containing 2% FBS to the desired concentration.
2.1.3 Plasmids and detection reagents
The plasmids pRF42-SFTSV-MeGFP, pCAGGS-SFTSV-NP and pCAGGS-SFTSV-RdRp required by SFTSV mini-replicon system were all constructed by our laboratory [13]. Plasmid transfection was performed with Lipofectamine 3000 (ThermoFisher, USA). Mouse anti-SFTSV-NP polyclonal antibody was prepared via immunizing rabbit[13].
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Cell culture
Vero cells and HEK-293T cells were cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% FBS and incubated with 5% CO2at 37℃.
2.2.2 Virus culture
When confluent monolayer Vero cells reached about 80% within T-75 cell culture flask, the old medium was discarded and 6mL of DMEM medium containing 2% FBS was added to cover the cell surface. Then 100 μL seed stock of SFTSV WCH/97/HN/China/2011 strain was added with an MOI at 0.1. Than cells were incubated at 37 ℃ in 5% CO2for 1 h, during which the culture flask was gently shaken every 15min. After incubation, 6 mL fresh DMEM medium containing 2% FBS was added to continue the culture. After 5 days, the supernatant in the culture flask was collected and centrifuged at 3000 g /min for 10 min at 4℃. Then,the supernatant was subpackage 500 uL/per tube and stored at -80℃until use.
2.2.3 Determination of virus titer TCID50 (50% tissue culture infection dose)
Vero cells were diluted to a density of about 105/mL and used for cell seeding in 96-well plates with 100 μL per well. The cells were cultured for 24 h at 37 ℃ in 5% CO2incubator. To measure the titter of seed virus stock, the virus was diluted from 10-1to 10-10at 10-fold gradient with DEME medium containing 2% FBS, and the virus dilution from 10-3to 10-10was used for the following measurement.The old medium in the 96-well plate was discarded, and 100 μL virus dilution was added to each well, and 6 replicated wells were added for each gradient. The wells were incubated at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2for 5 days, and then virus infection cells were detected by immunofluorescence. If there was green fluorescence in the wells,it was recorded as positive, otherwise, it was recorded as negative.Then TCID50was calculated by Reed & Muench method.
2.2.4 Immunofluorescence detection
The old medium in the 96-well cell culture plate was discarded,and 100 μL of 4% paraformaldehyde was added to each well and fixed for 30 min in dark. Rinse with double-distilled H2O 3 times;Then 100 μL 0.2% Triton X-100 was added to each well for 15 min to permeate the cells. Rinse with double-distilled H2O 3 times; then blocked with block solution which containing 5% Bovine serum albumin (BSA) diluted with PBS at 37 ℃ for 1 h or 4 ℃ overnight.The blocking solution was discarded, and 100 μL of diluted primary antibody incubation solution (antibody 1:2000 dilution) was added to each well and incubated at 37 ℃ for two hours or 4 ℃ overnight.Discard of primary antibody and rinse 3 times with double-distilled H2O; FITC-labeled goat anti-rabbit serum was diluted 1:2000 in PBS containing 1% BSA, and 100 μL of secondary antibody dilution was added to each well and incubated at 37 ℃ for 1 h. After discarding the diluent of the secondary antibody and rinsing with double-distilled H2O for 3 times, the fluorescence microscope was used to observe and record.
2.2.5 Determination of the 50% cytotoxic concentration(CC50) of drug
Vero cells were spread into 96-well plates with a cell density of about 1.0×104cells/well, and the volume of each well was 100 μL.The cells were placed in 37 ℃ incubator for 24 h, and the confluence of the cells reached about 90%. The old medium was discarded, and the gradient diluted drugs (100 μm, 50 μm, 25 μm, 12.5 μm, 6.25 μm and 3.125 μm) were added into the cell wells. Three replicated experimental per wells were made for each drug gradient, and the cells were incubated at 37 ℃ for 24 h. The 96-well plates were removed from the incubator, and 10 μL CCK-8 reagent was added to each well, and the plates were incubated for 1 h at 37 ℃. Finally,the percentage of cell activity of experimental group and negative control group was detected by microplate reader at 450 nm. With drug concentration as abscissa and percentage of cell activity as ordinate, GraphPad Prism 8.0 was used for drawing dose-dependent curves of cell activity and regression was performed to calculate the median cytotoxic concentration.
2.2.6 Screening of antiviral drugs via mini-replicon system
HEK-293T cells were spread into a 24-well plate at a rate of 2×105/well, with 500 μL in each well, and incubated at 37 ℃for 24 h in a 5% CO2incubator for the next experiment. The plasmids pCAGGSSFTSV-RdRp, pRF42-SFTSV-MeGFP and pCAGGS-SFTSV-NP were mixed at a mass ratio of 2:1:1, transfected at 2 μg per well according to the instructions of Lipofectamine 3000 transfection reagent, and cultured at 37 ℃.The mother liquor of the drug was diluted with DMEM medium containing 2% FBS by two-fold gradient dilution, and the old medium in the cell culture plate 6 h after transfection was discarded. Then 200 μL of the corresponding concentration of drug dilution was added to each well, and the control well was treated with the drug dilution containing only DMSO(the amount added at the highest concentration of drug),and the culture was continued for 42 h. eGFP was counted by highcontent analyzer, and the median inhibitory concentration of the drug was calculated by nonlinear regression method of GraphPad Prism 8.0.1 software.
2.2.7 Drug effective stage determined via SFTSV infection on live virus system
Vero cells were spread into 24-well plates at a volume of 500 μL per well at 5 104 per well, and cultured at 37 ℃ for 24 h in 5% CO2until use. DMEM medium containing 2% FBS was used to dilute the drug to the required concentration, and DMEM medium containing 2% FBS was used to dilute the virus to a titer of 1×105PFU /mL.And 500 L of virus dilution solution was added to each well, and drug inhibition experiments were carried out as follows (Fig 1).Specifically, (1) the drug acted on the entire stage of virus infection:diluted drugs were added to the cell culture wells one hour before infection, and then diluted SFTSV liquid was added and incubated for 1 h. After that, the old medium was discarded, and a new medium containing drugs was changed to continue the culture; (2) drug was added before the infection the: the diluted drug was incubated with the virus for 1 h, and the virus was incubated with the virus for 1 hour and then the culture medium without the drug was changed to continue the culture; (3) drug was added at the entry stage of SFTSV infection: virus and drug were added to the cell culture wells at the same time and incubated for one hour. Then the old medium was discarded and replaced with a new drug-free medium to continue the culture; (4) drug was added after the virus infection: the old culture medium is discarded one hour after the virus infects the cells, and then the medium containing the drug is replaced to continue the culture.After 23 h of cell culture, the old medium in the well was discarded and washed with sterile PBS for 3 times. And 400 μL Trizol was added to each well for 5min. After that, the cells were blown and mixed with a pipette and absorbed into a 1.5 mL EP tube for subsequent RNA extraction and absolute quantitative analysis.
The primers used for quantitative detection of SFTSV by RT-qPCR were HEX dye-labeled sequences: HEX-ttctgtcttgctggctccgcgc-BHQ-2, the detection Kit was HiScript II One Step QRT-PCR Probe Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China).

Fig 1 Flowchart of drug administration in different stages of SFTSV infection
3. Results
3.1 Median cytotoxic concentration of drug cells (CC50)
CCK-8 reagent was used to detect the effects of the four candidate drugs on cell activity, and the results showed that the cell activity was still greater than 80% at each concentration, and regression analysis showed that the CC50of each drug was greater than 100 μM(Tab 1). Therefore, the inhibitory effect of the drug on virus infection was further studied in the concentration range of less than 100 M and the IC50of the drug was determined.

Tab 1 Median cytotoxic concentration(CC50)of four drug candidates
3.2 Screening of antiviral drugs on the mini-replicon system
The effects of 1430 FDA-approved drugs on SFTSV mini-replicon were analyzed by high-content scanning. Four drugs with significant inhibitory effects were screened out, which were mycophenolate mofetol, mycophenolic acid, nitazonide and Vidofludimus. Drug gradient inhibition experiments showed that with the increase of drug concentration, the inhibitory effect of drugs on SFTSV gradually increased, showing a strong dose correlation (FIG. 2).The median inhibitory concentrations of mycophenolate mofel, mycophenolic acid, nitazonide and Vidofludimus on the microreplication subsystem were 0.014 μm, 0.627 μm, 1.283 μm and 0.059 μm, respectively.Combined with the CC50of the drugs, the therapeutic index (TI) of each drug was greater than 10, indicating the high safety of these drugs (Tab 2).
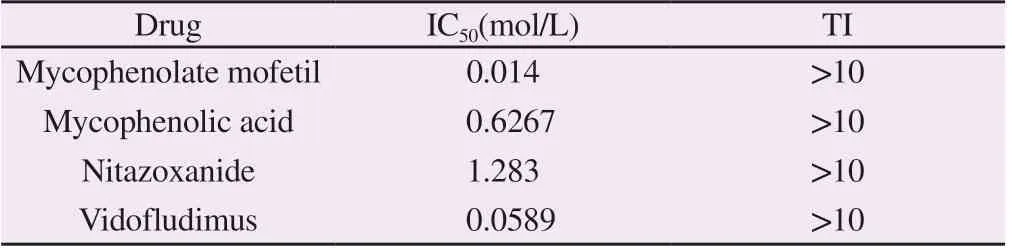
Tab 2Inhibitory effect and safety of the four drugs at different concentrations to SFTSV infection.
3.3 Quantitative analysis of four drugs on live virus system to inhibit SFTSV infection in different stages
To further determine the stage of drug action on viral infection, four different drug delivery methods were carried out at the cellular level:drug action on SFTSV (Entire stage), drug action before SFTSV infection (Virion stability), drug action during SFTSV infection invasion (Entry stage), and drug action after SFTSV invasion (postentry).The results were shown as in FIG. 3 and Table 2. When the drugs acted on SFTSV throughout, the four drugs had significant inhibitory effects on SFTSV at three concentrations. When SFTSV was pretreated with drugs, the four drugs had no inhibitory effect on the increment of SFTSV. When SFTSV invaded cells were treated with drugs, only mycophenolate mofetil had a positive inhibitory effect on SFTSV at a high concentration, while the other three drugs had no inhibitory effect on SFTSV (Figure 3A).When the drugs were used in the post-invasion stage of SFTSV cells, the proliferation inhibition effect of the four drugs on SFTSV was significant. It is worth noting that the inhibition effect of Vidofludimus on SFTSV reached more than 99% at the three concentrations.The combined results showed that the inhibitory effect of the four drugs on SFTSV mainly occurred after SFTSV invaded cells.

Fig 2 Inhibition of SFTSV by the four drugs at different concentrations on the mini-replicon system
Tab 3 Statistical analysis of the inhibitory effects of the four drugs in different stages of SFTSV infected cells(±s)

Tab 3 Statistical analysis of the inhibitory effects of the four drugs in different stages of SFTSV infected cells(±s)
Drug Stage of incubation Control group Treated group(Mean ±STD) T value/P value 5 μmol/L 10 μmol/L 20 μmol/L 5 μmol/L VS.Vehicle 20 μmol/L VS.Vehicle Mycophenolate mofetil Entire Stage 8.467 ± 0.123 6.042 ± 0.125 6.454 ± 0.38 6.535 ± 0.08 6.425/0.003 13.83/0.000 2 5.034/0.007 Virion stability 8.43 ± 0.058 8.565 ± 0.176 8.539 ± 0.068 8.9 ± 0.05 0.7265/0.50 1.21 /0.292 5.984/0.003 9 Entry stage 7.63 ± 0.055 7.357 ± 0.134 7.61 ± 0.013 7.19 ± 0.10 1.876/0.133 0.350 3/0.743 3.837/0.018 5 Post-entry 7.367 ± 0.194 6.59 ± 0.015 6.471 ± 0.048 5.87 ± 0.229 3.972/0.057 4.463/0.046 7 4.971/0.038 Mycophenolic acid Entire Stage 8.467 ± 0.123 6.535 ± 0.081 7.113 ± 0.142 6.663 ± 0.276 13.1/0.000 2 7.19/0.002 0 5.953/0.004 0 Virion stability 8.43 ± 0.058 8.58 ± 0.084 8.573 ± 0.038 8.664 ± 0.130 1.463/0.217 4 2.046/0.110 2 1.632/0.178 0 Entry stage 7.63 ± 0.055 7.56 ± 0.077 7.563 ± 0.076 7.326 ± 0.096 0.734 8/0.503 2 0.707 9/0.518 1 2.739/0.052 0 Post-entry 7.122 ± 0.269 5.728 ± 0.191 5.743 ± 0.358 5.623 ± 0.136 4.222/0.013 5 3.076/0.037 1 4.965/0.007 7 Nitazoxanide Entire Stage 8.707 ± 0.098 8.629 ± 0.086 8.47 ± 0.011 7.341 ± 0.054 0.597 8/0.582 2 2.397/0.074 6 12.16/0.000 3 Virion stability 6.736 ± 0.08026,n=3 10 μmol/L VS.Vehicle 6.14 ± 0.01137,n=3 6.742 ± 0.1643,n=3 6.686 ± 0.1273,n=3 7.352/0.001 8 0.0322 9/0.975 8 0.3324/0.756 3 Entry stage 6.814 ± 0.149 6.191 ± 0.292 7.008 ± 0.120 6.951 ± 0.228 1.898/0.130 6 1.011/0.3690 0.4996/0.643 6 Post-entry 6.874 ± 0.182 7.227 ± 0.046 6.8 ± 0.172 6.261 ± 0.062, 1.878/0.122 6 0.292 8/0.784 2 3.185/0.033 4 Vidofludiums Entire Stage 8.568 ± 0.091 6.294 ± 0.08 5.671 ± 0.133 5.742 ± 0.250 18.61/<0.000 1 17.91/<0.000 1 10.58/0.0005 Virion stability 7.141 ± 0.297 7.254 ± 0.086 7.126 ± 0.115 7.017 ± 0.185 0.362 6/0.735 3 0.049/0.9631 0.3552/0.740 4 Entry stage 7.216 ± 0.175 7.595 ± 0.088 7.433 ± 0.025 7.647 ± 0.042 1.926/0.1265 1.22/0.2895 2.381/0.075 9 Post-entry 7.464 ± 0.136 4.98 ± 0.149 4.563 ± 0.096 4.774 ± 0.013 12.28/0.000 3 17.37/<0.000 1 19.67/<0.000 1

Fig 3 Inhibitory effects of the four drugs on SFTSV infected cells at different stages
4. Discussion
The prevalence of SFTSV continues to expand. In addition to at least 15 provinces in China, the disease has also been reported in South Korea, Japan, Vietnam and other Asian countries. SFTSV has become a serious threat to human public health [14].The research and development of effective anti-SFTSV drugs has become an urgent scientific problem. In this study, 1 430 compounds approved by FDA were screened for anti-SFTSV drugs through the minireplicon system. The results showed that mycophenolate mofetol,mycophenolic acid, nitazonide and Vidofludimus had inhibitory effects on SFTSV. At the same time, nitzonide and Vidofludimus had a good dose dependence, and the inhibitory effect on SFTSV was enhanced with the increase of concentration. The results of cell model of live virus infection showed that all the four drugs could significantly reduce the copy number of SFTSV and effectively inhibit live virus infection. By administering the drugs at different stages during SFTSV infection, it was further determined that the four drugs mainly acted at the stage after SFTSV invaded cells,which was consistent with the results of mini-replicon system detection. The mini-replicon system can effectively reflect the transcription and replication efficiency of the viral genome, and drug screening through this system can more effectively and accurately target the transcription and replication process of the virus.Therefore, the use of mini-replicon systemis an important and safe method for screening anti-RNA viral drugs without involving live virus manipulation.
The clinical application of the four SFTSV inhibitors screened and identified in this study is not related to antiviral. Mycophenolate mofetil[15] and mycophenolate acid[16] are non-competitive and reversible inhibitors of hypoxanthine nucleoside phosphate dehydrogenase, which have a powerful effect on inhibiting lymphocyte proliferation and are mainly used for immunorejection therapy during transplantation. The results based on the SFTSV microreplication subsystem showed that mycophenolate mofetil had the lowest IC50value and had a good inhibitory effect on SFTSV at a low concentration, suggesting that mycophenolate mofetil was a potential effective anti-SFTSV drug. Whether such hypoxanthine nucleoside phosphate dehydrogenase inhibitors have a broad spectrum of anti-RNA viruses is worth further investigation.Nitazonide is a synthetic derivative of nittathiacylamide, which is mainly used for antigenic worms and anti-intestinal parasites[17].Some studies have reported that this drug has good antiviral effect,such as anti-canine influenza virus (IC50of 0.17 to 0.21 μm), and it also shows effective inhibition of HBV and HCV replication[18].The results of this study further suggest that the antiviral effect of nitazonide may be broad spectrum.Vidofludimus is an oral dihydrolorate dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibitor, which is an immunosuppressive agent.Although almost no antiviral studies have been reported, a next-generation derivative of the compound,Vidofludimus calcium (also known as IMU-838), is used to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, an autoimmune disease, and has entered phase II clinical trials. The novel coronavirus SARS-COV-2,human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), hepatitis C virus,HCV and human immunodeficiency type 1 (HIV-1) have inhibitory effects[15, 19-21],suggesting that the drug may have broad spectrum antiviral effect and potential application value.
The analysis of the complex relationship and mechanism among drugs, host and virus is an important theoretical basis for the discovery of new targets of antiviral action and the screening of antiviral drugs. In this study, from the perspective of "conventional drug in new use", four drugs with good anti-SFTSV effect were screened based on mini-replicon system and virus-infected cell model, suggesting that "conventional drug in new use" is an important means to obtain effective antiviral drugs quickly.Contribution of author
The experimental design was Wang Tiantian, Shen Shu, Deng Fei and Shi Junming; the experiments were carried out by Wang Tiantian, Yin Zhiyun, Zhu Qiong, Deng Yali; Zhou Min, Jin Jiayin,Hu Sijing, Zhang Danna were responsible for the experimental research involving cells, reagents and consumables. Antibodies were prepared by Xijia Liu, Baiyong Jiang, Qiaoli Wu; the article was written by Wang Tiantian; the article reviewed and revised by Shen Shu, Deng Fei, Shi Junming
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest are involved.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress on pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis
- Advances in the application of optical coherence tomography in the assessment of ischemic stroke
- Meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy of Chinese herbal decoction combined with arthroscopy in the treatment of gouty arthritis
- Study on syndrome distribution and medication characteristics of patients with rectal cancer in the real world
- Experimental study of TGF-β1/Smads pathway inhibition of macrophage polarization based on miR145-5P negative feedback regulation
- Exploring the key pathways of tetrandrine in the treatment of early silicosis based on bioinformatics and in vitro experiments
