苹果树栽植机幼苗夹持装置改进与试验
2021-12-28林悦香尚书旗连政国王明成张敬国
林悦香,尚书旗,连政国,王明成,张敬国
·农业装备工程与机械化·
苹果树栽植机幼苗夹持装置改进与试验
林悦香1,尚书旗1※,连政国1,王明成2,张敬国3
(1. 青岛农业大学机电工程学院,青岛 266109;2. 东北农业大学工程学院,哈尔滨 150030;3. 潍坊市高密中等专业学校,潍坊 261501)
为了解决现行矮砧密植栽培模式下苹果树幼苗栽植过程所存在的人工栽植效率低、树苗直立度不理想、夹持皮带滑移导致株距变异系数高等问题,该研究以农机农艺融合技术为指导,研制了两点夹持式苹果树幼苗栽植机。该机具在现有连续开沟定距栽植机的基础上,对树苗实施上、下两点夹持,克服了原来一点夹持使得高株苗木相对地面初始角度难以保证的问题,以提高栽植后的直立度;对夹持输送形式进行改进,采用2条同步带代替原来V型带夹持输送苹树苗木以降低滑移率和株距变异系数;对动力匹配进行优化,加装限深轮提高栽植深度稳定性。根据不同品种苹果苗木栽植要求,开沟深度及宽度可调,栽植株距也可按需调节。田间试验表明:栽植后的苹果苗木直立度合格率由原来的90.63%提高至97.14%,平均栽植深度合格率由91.43%提升为93.33%,平均栽植株距变异系数由原来的5.03%降为3.74%,栽植效率由11.89株/min提升到12.26株/min,是人工栽植的37倍。对比现有机具,该研究改进机具的各项性能指标得到改善提升,为后续苹果生产全程机械化打下坚实的基础。
农业机械;试验;苹果苗木;栽植;两点夹持;直立度
0 引 言
作为水果中销量最大的苹果,已成为人们的日常需求产品[1]。苹果中含有丰富的维生素、矿物质等人体所需的微量元素,经常食用可以提高免疫力[2-3]。苹果渣作为饲料,可以缓解国内玉米、豆粕的不足[4-5]。苹果矮砧密植栽培模式有利于全程机械化作业,但苗木栽植需要大量的劳动力[6-8],农村劳动力的短缺与需求形成矛盾,迫切需要实现苹果树栽植环节的机械化[9-10]。
苹果树栽植机研制在国内起步较晚,时间较短[11-14]。山东农业大学研制的原位混肥挖坑回填复式果树栽植机在解决反复耕种的土地上栽植苹果树需要很好的混肥效果上具有突出优势,但机械内部结构复杂,维护难度高,且不具备定距栽植功能,栽植效率较低,应用范围较小[15-16]。河北农业大学研制的苹果苗木栽植机,采用犁铧式开沟器,整机采用三级连接机构,有利于机械的维护和转运[17-19];另研制的苹果苗木夹盘式移栽机,该机采用滚动夹苗装置,栽植机性能稳定,但不能保证栽种后苹果苗木的直立度[20]。山东理工大学研制的2PZ-4000型苹果多功能栽植机能够实现苹果树苗的垄上定距栽植,并且具备同步水肥和镇压功能[21-23]。但该机以起垄栽植的方式作业,在栽植作业前需要对地块进行旋耕松土,才能保证栽植效果,使得苹果苗在长出新根之前会因外力作用出现歪斜,影响后续生长,且定距实施过程需靠人工辅助控制,定距效果不太理想。2017年,在苹果生产机械化项目支持下,青岛农业大学会同合作企业-高密市益丰机械有限公司研发出第一代矮砧密植苹果树连续开沟定距栽植机,极大提高了栽植效率和栽植合格率,但对较大型的高株苗木,栽植后的直立度不太理想,且V型带夹持输送时存在少许滑移,株距变异系数还有改进空间[24]。针对一代机存在的问题,本文对原有设备进行机构改进,研制了第二代两点夹持式苹果树幼苗栽植机。提出树苗上下两点夹持方案,改进夹持输送方案,优化动力配置等。并通过田间试验,对主要性能指标进行验证,以更好地适应现代果园机械化生产需要。
1 整机结构及工作原理
1.1 整机结构
苹果栽植机主要由两点夹持输送装置、定距栽植装置、连续开沟装置、覆土镇压装置以及其他辅助装置组成,具体结构如图1所示。
1.2 工作原理
作业时,配套拖拉机后动力输出轴为V型双圆盘开沟器提供动力,开沟器连续开出梯形栽植沟,挡土板清理栽植沟内的碎土,修整沟形。地轮经各级传动带动两点夹持装置中的同步带轮转动,以相同的线速度运动,保障夹持同步皮带的线速度大小与机组前进速度的大小相等,进而保障夹持输送中的苹果树幼苗与地面保持相对静止。两夹持点上、下平行分布,人工辅助将苹果树幼苗根部放置于挡土底板,并将幼苗树干紧靠在上下两定位栅杆处,随着机具前进,安装在株距定位杆上的光电传感器监测到已栽植的树苗位置后,将信号传递,并通过电磁继电器控制夹持气缸动作,推动夹持前支架转动,同时带动定位栅杆转开,栅杆不再与树干接触,树苗此时被同步皮带夹持住,并随之向与机组前进方向相反的方向输送,在输送过程中,覆土板将土壤回填,树苗脱离同步带夹持后,镇压轮随即镇压树苗两侧附近的土壤。
1.3 主要改进机构
为适应现代果树栽植要求和提高栽植后的苗木直立度,对上一代苹果栽植机的树苗夹持机构及输送装置进行改进。
树苗夹持机构的改进:上一代机夹持点只有一个,在栽植较大的高株树苗时,难以保障在夹持输送过程中树苗相对于地面的初始角度不变,栽植后的苹果树苗直立度不高。本文提出上、下两点夹持方案,在一代机夹持输送装置的上方增加一层夹持输送装置,两者的动力来源相同,且同步带轮型号相同,布置在同一立轴上,保障了同步带的速度相等,可以保障栽植后的树苗有更好的直立度。
树苗输送装置的改进:上一代机在夹持输送树苗时采用普通V型带,这种皮带由于结构缺陷,在传动过程中会有一定的滑移率,并且滑移率不确定,这导致栽植后的树苗株距与定距装置设定好的株距有一定的差距,本文采用滑移率更低的同步带夹持输送苹果树幼苗,可在保证夹持过程中对树苗损失较小的条件下缩小栽植后的树苗株距与设定的株距差异。
1.4 技术参数
整机主要参数如表1所示。
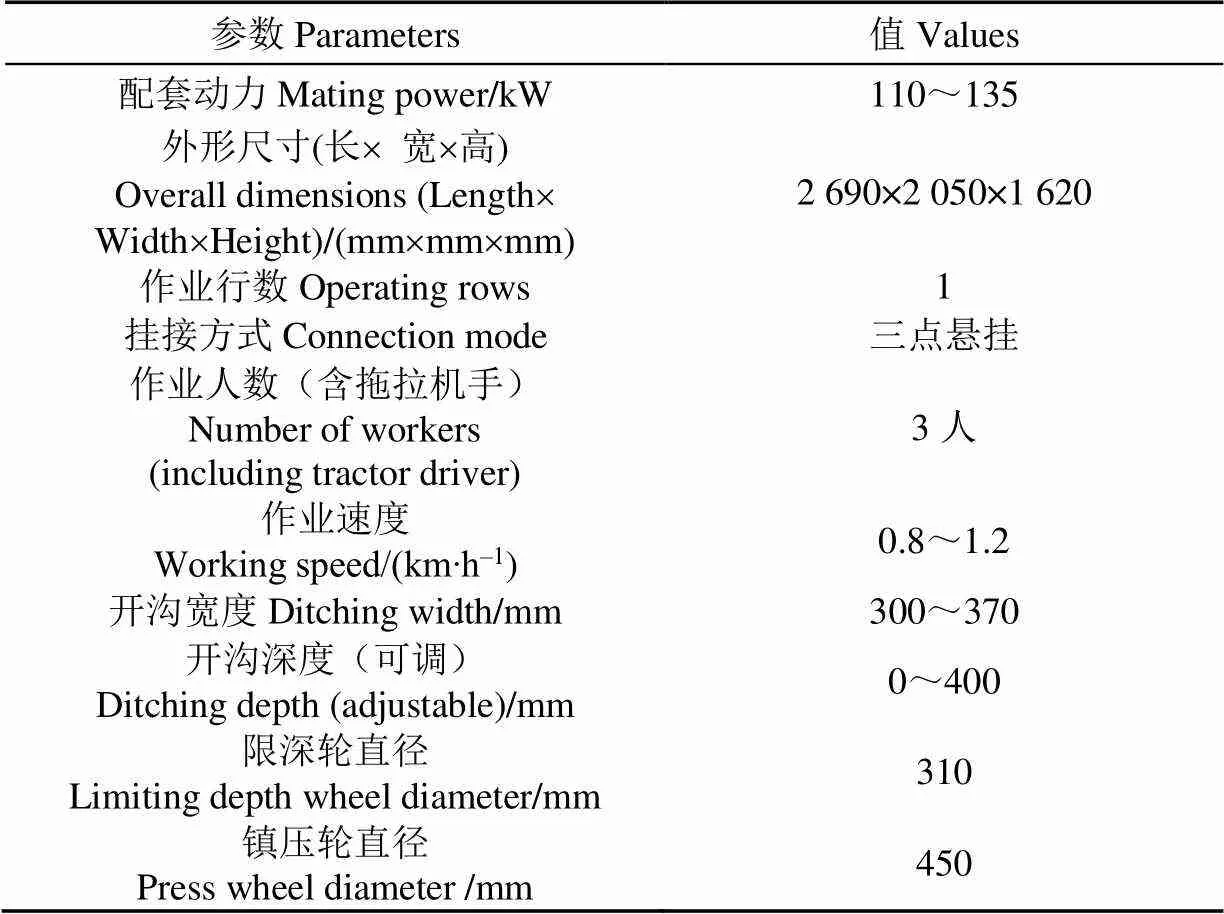
表1 两点夹持式苹果树栽植机主要技术参数
旋耕开沟机机组的前进速度V(m/h)、拖拉机功率(kW)和开沟截面积0(m2)三者之间的关系符合式(1)。
式中η为拖拉机动力输出轴的功率输出系数;η为传动效率;k为铣刨单位土方的功能消耗(kW·h/m3)。经计算开沟需不少于110 kW的拖拉机为动力机械,考虑栽植机还要完成土壤回填、镇压等功能,本文选用135 kW的金威盛JWS-1804拖拉机。
1.5 苹果栽植农艺要求
1.5.1 栽植密度
苹果矮化栽培模式下单株苹果产量低于传统乔化栽培模式,但通过合理密植可以提高单位面积的苹果产出率。栽植密度应根据苹果品种和当地的自然环境以及果园管理水平综合考虑,确定适宜的栽植密度[25-28]。矮砧密植模式株、行距一般在(0.8~1.5)m´(3.5~4.0)m之间,据此确定栽植机株距控制机构的株距定位杆位置参数(可以在0.8~1.5 m之间调节,以适应不同苹果品种),并确保整机结构参数适应行距要求。
1.5.2 栽植深度
矮砧苹果树栽植时接穗部分不能埋入土壤中,否则苹果树将失去矮化作用,一般要求接橞与砧木的嫁接口在地表之上5~10 cm处,嫁接口一般位于根部之上35~40 cm处,栽植后浅培土以保护砧段部分[29],由此设计栽植机开沟装置,深度依品种需要可调,调节范围为0~40 cm。
2 两点夹持输送装置设计
两点夹持输送装置是苹果苗栽植后有良好直立度的重要保障。图2为两点夹持输送装置示意图。
所谓两点夹持,指的是上下两层夹持装置,树苗输送过程的任一位置,都由上下两点夹持。两层夹持装置竖直方向上的距离需要根据苹果树幼苗的情况确定。经大量调研,栽植时苹果树幼苗高度在2 m左右,下层的夹持输送装置的位置保持和一代机相同,根据样机试制过程中的栽植效果最终确定上下两层的距离为50 cm。
株距精确度的保障:夹持过程中的苹果苗木相对于地面的速度为0,也就是需要夹持皮带向后运行的速度与栽植机组前进速度大小相等方向相反。采用同步带传送即可避免滑移,确保树苗相对地面速度为0,保证设计株距。
选用镇压轮为两点夹持机构提供动力,镇压轮提供的动力经链传动传递到夹持换向箱,经夹持换向箱实现动力换向并通过换向箱输出链轮带动安装在夹持中间轴上的从动链轮转动,夹持中间轴随着从动链轮转动,带动上下两个同步带轮转动,同步带轮带动同步皮带运动,完成动力传递,并实现夹持皮带与机组等速反方向运动。
栽植机的其他工作部件沿用一代机的结构设计,经使用验证,各结构符合栽植机的作业要求。如覆土装置,覆土量适宜,覆土后土壤均匀分布[30-32]。
3 田间试验
3.1 试验条件与方法
2021年3月18日,在高密市益丰机械有限公司试验场地内进行两点夹持式苹树苗木栽植机的栽植试验。试验样机为青岛农业大学与高密益丰机械有限公司联合研制的2PZ-1B果树开沟栽植机。主要试验目的是检验栽植机栽植直立度情况、株距稳定性等。
试验场地选取长180 m,宽30 m的空地。经测量,地块的土壤坚实度700~950 kPa,土壤含水率小于20%,土壤状况良好,其他条件也满足栽植要求。准备480棵可用于正常栽植的红富士矮化砧木苹果树苗。使用金威盛JWS1804作为试验样机的配套动力。拖拉机行进速度为1.2 km/h,栽植开沟深度为30 cm,栽植株距为1.2 m。
将准备的苹果苗木按3个栽植行程栽植,每个栽植行程栽植150棵。按栽植顺序,将3个行程编为1、2、3号。为减小非客观因素对试验的影响,去除每个行程的前端和后端各5棵苹果苗木,作为栽植试验样本。安排3人进行人工挖坑栽植作为对照。人工栽植与栽植机作业同步。启动拖拉机,一人操作拖拉机前进,两人站立在栽植机上轮流辅助喂苗。测量员手持秒表跟随栽植机行进,记录每个栽植行程所用的时间。3个栽植行程全部栽植完毕,逐棵测量栽植直立度、栽植深度、株距,并记录。图3为田间试验现场。
3.2 评价指标
针对苹果苗木栽植机目前没有专门的评价标准。参考农业机械推广大纲DG37/T010-2016《旱地栽植机械》,LY/T 1518-2012《林业机械开沟式栽植机》,以及课题验收标准,选取栽植直立度合格率,栽植深度合格率,株距变异系数,栽植效率4个指标作为栽植机作业质量和精度的评价指标。
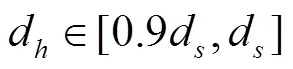
3.3 试验结果与分析
利用上述测定和计算方法,对栽植机栽植效率、栽植株距、栽植直立度和栽植深度指标进行统计分析,结果如表2~表4所示。
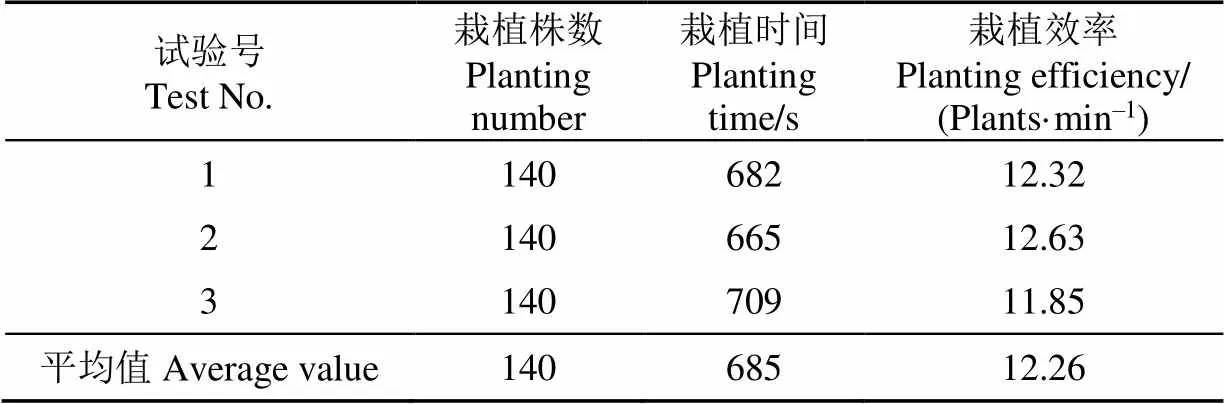
表2 栽植效率试验结果
表2结果表明,在配套拖拉机行进速度为1.2 km/h,栽植株距为1.2 m时。两点夹持式苹果苗木栽植机平均栽植效率约为12棵/min,换算得栽植效率为720棵/h。人工作业栽植效率19棵/h。栽植机栽植效率约是人工的37倍。
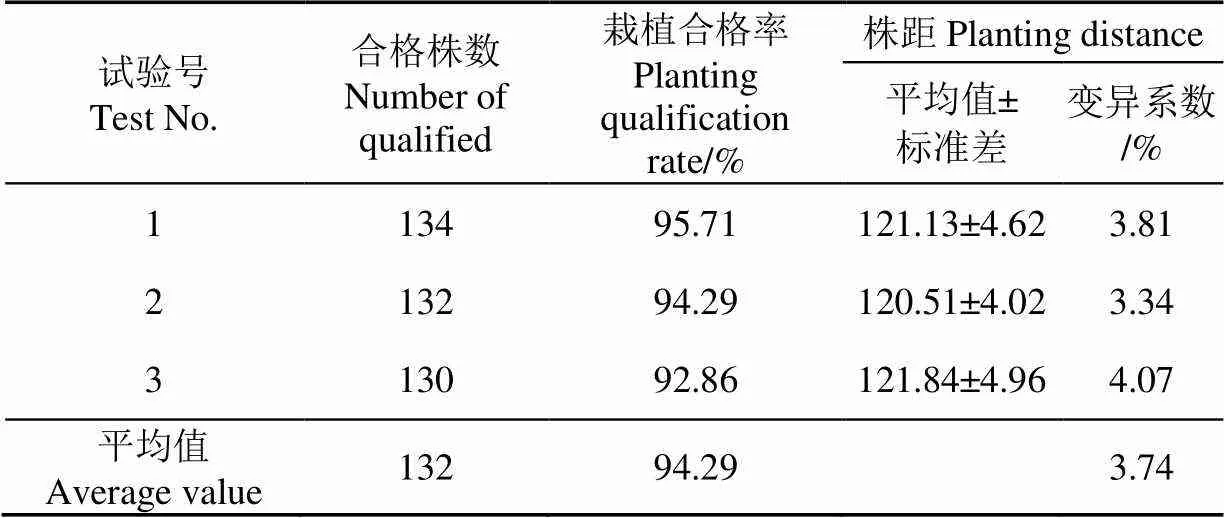
表3 栽植株距试验结果
表3结果表明,栽植株距变异系数平均值为3.74%。
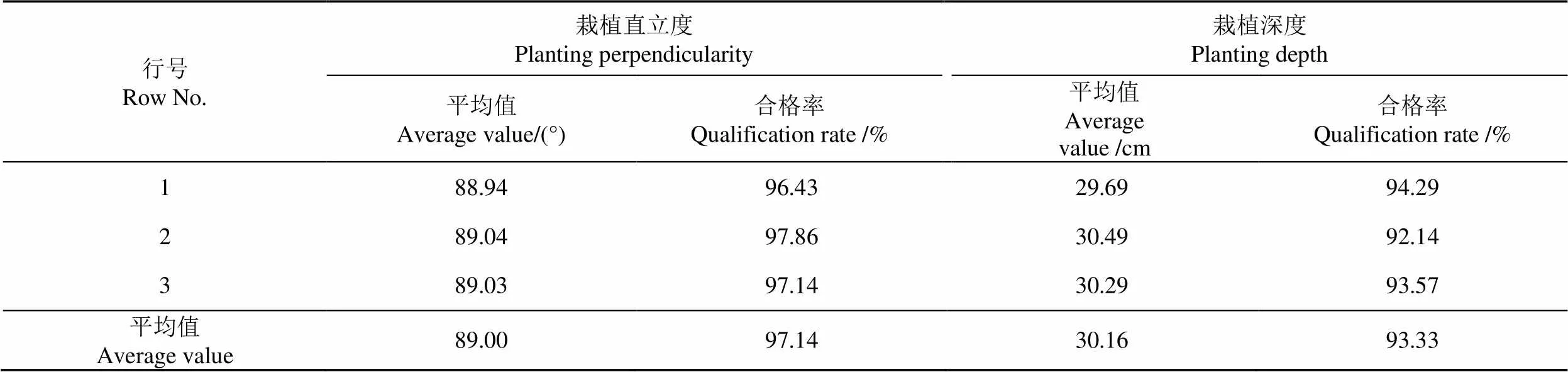
表4 栽植直立度和栽植深度试验结果
表4结果表明,栽植直立度平均合格率为97.14%,高于课题验收标准要求的95%,合格率符合要求。栽植深度平均合格率为93.33%,高于标准要求的75%。
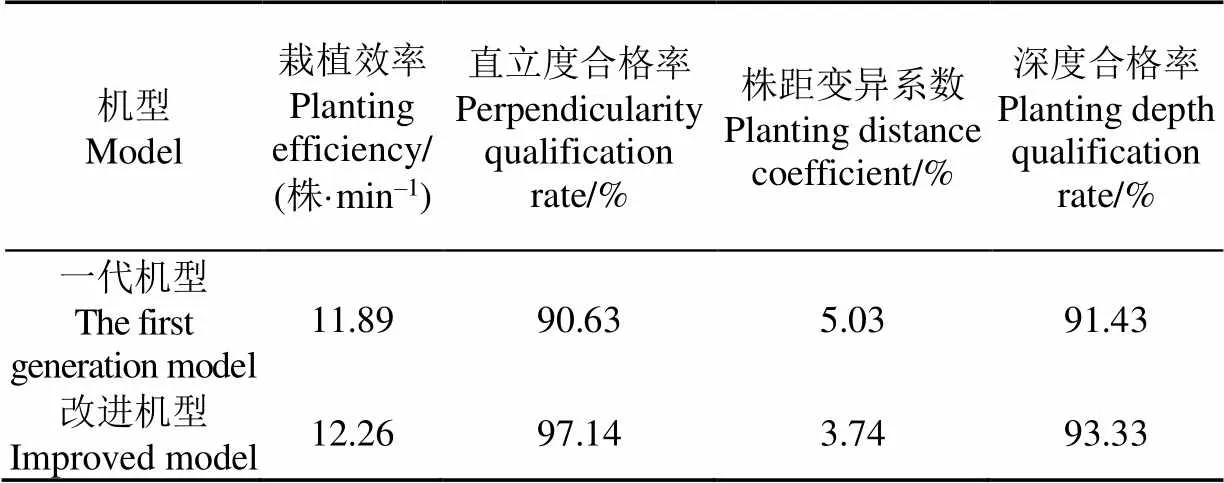
表5 改进机型与一代机型性能对比
对比结果表明:改进机型比一代机型栽植效率提高3.1个百分点、直立度合格率提升6.61个百分点、株距变异系数降低1.29个百分点(株距更加稳定了),深度合格率提升1.9个百分点。
4 结 论
1)对苹果苗木实施两点夹持的方案,提升了树苗栽植后的直立度;采用两条同步带夹持输送苹果苗木,减少滑移,降低株距变异系数。栽植机的性能得到进一步提高,栽植后的苹果树苗更符合农艺要求。
2)田间试验结果表明:苹果栽植机具有良好的栽植效果,苹果苗木直立度合格率平均为97.14%,栽植深度合格率平均为93.33%,栽植株距变异系数平均为3.74%,栽植效率为720棵/h,是人工栽植的37倍。
[1] 常倩,李瑾. 2000年以来中国苹果产业发展趋势分析[J].北方园艺,2021(3):155-160.
Chang Qian, Li Jin. Development trend of apple industry in China[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2021(3): 155-160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 吃苹果的六大好处[J]. 中国粮食经济,2015(5):70.
[3] 刘晓丽. 浅析庆阳苹果的营养价值与保健作用[J]. 甘肃科技,2018,34(21):159-160.
[4] 贺克勇,薛泉宏,来航线,等. 苹果渣饲料的营养价值与加工利用[J]. 饲料广角,2004(4):26-28.
[5] 徐椿慧. 苹果渣饲料的加工研究进展[J]. 畜禽业,2009(8):50-52.
[6] 张海进.苹果矮砧密植栽培技术[J]. 乡村科技,2020,11(22):107-108.
[7] 闫俊平. 矮砧苹果优质高效栽培技术[J]. 西北园艺,2020(7):34-35
[8] 董桂海. 矮砧苹果优质高效栽培技术研究[J]. 农业科技与信息,2020(21):93-95.
[9] 王钰莹,许存兴. 基于多元回归的陕西苹果种植成本分析[J]. 陕西师范大学学报:自然科学版,2016,44(4):114-118.
Wang Yuying, Xu Cunxing. An analysis of apple-planting cost in Shaanxi province based on the multiple regression[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2016, 44(4): 114-118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 贾永华,曲亦刚,王永忠,等. 苹果矮砧密植栽培模式与技术要点[J]. 宁夏农林科技,2014,55(9):6-8.
Jia Yonghua, Qu Yigang, Wang Yangzhong, et al. A dwarf rootstock intensive planting and cultivation mode for apple and technological Points[J]. Ningxia Journal of Agri and Fore, Sci & Tech. 2014, 55(9): 6-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 张振国,张学军,曹卫彬,等. 番茄穴盘苗移栽机自动取苗机构的研制[J]. 农机化研究,2014,36(9):177-181,185.
Zhang Zhenguo, Zhang Xunjun, Cao Weibin, et al. The research and manufacturing of plug transplanter’s tomato seeding picking machanism[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2014, 36(9): 177-181, 185. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 韩长杰,徐阳,张静,等. 半自动压缩基质型西瓜钵苗移栽机设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(13):54-61.
Han Changjie, Xu Yang, Zhang Jing, et al. Design and experiment of semi-automatic transplater for watermelon seedings raised on compression substrate[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(13): 54-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 刘洋,李亚雄,赵华伟,等. 吊篮式移栽机喂苗机构的设计[J]. 农机化研究,2010,32(9):73-75.
Liu Yang, Li Yaxiong, Zhao Huawei, et al. The design of picking seedling machanism of the bastkate-type transplanterc[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2010, 32(9): 73-75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 朱兴亮,郭彦克,韩长杰,等. 茄果类钵苗自动移栽机设计与试验[J]. 中国农机化学报,2021,42(5):19-26.
Zhu Xingliang, Guo Yanke, Han Changjie, et al. Design and experiment of automatic transplater for Solanaceae vegetables pot seedings[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechunization, 2021, 42(5): 19-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 苑进,尹然光,刘功,等. 原位混肥挖坑回填复式果树栽植机设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2021,52(2):110-121.
Yuan Jin, Yin Ranguang, Liu Gong, et al. Design and experiment of in-situ fertilizer mixing integrated digging and backfilling planter for fruit tree[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52(2): 110-121. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 尹然光. 自走式挖坑混肥回填果树栽植智能作业机的研制[D]. 泰安,山东农业大学,2020.
Yin Ranguang. Development of an Intelligent Machine for Planting Fruit Trees with Self-propelled Pit Digging Mixed Fertilizer Backfill[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 宋帅帅,杨欣,殷梦杰,等. 果树苗木移栽机开沟装置模型建立与参数设计[J]. 农机化研究,2018,40(5):36-40,45.
Song Shuaishuai, Yang Xin, Yin Mengjie, et al. Model establishment and parameter design of ditching device for fruit tree seedling transplanting machine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2018, 40(5): 36-40, 45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 王鹏飞,何建华,刘俊峰,等. 苹树苗木栽植机的设计与试验研究[J]. 农机化研究,2017,39(1):122-126.
Wang Pengfei, He Jianhua, Liu Junfen, et al. Design and experimental research of apple seedling planting machine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2017, 39(1): 122-126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 宋帅帅,殷梦杰,杨欣,等. 果树苗木栽植机覆土镇压轮系单体功能结构设计[J]. 农机化研究,2018,40(8):58-62,69.
Song Shuaishuai, Yin Mengjie, Yang Xin, et al. Functional structure design of tailor crushing system for fruit trees[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2018, 40(8): 58-62, 69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 裴晓康,刘洪杰,杨欣,等. 苹树苗木夹盘式移栽机的设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2020,42(4):109-112,179.
Pei Xiaokang, Liu Hongjie, Yang Xin, et al. Design and test of apple seedling clamp transplante[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2020, 42(4): 109-112, 179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 高光明,宫玉敏,张义胜,等. 2PZ-4000型苹果多功能栽植机设计与试验[J]. 山东理工大学学报:自然科学版,2019,33(2):31-37,42.
Gao Guangming, Gong Yumin, Zhang Yisheng, et al. Design and experiment of 2PZ-4000 multifunctional apple planting machine[J]. Journal of Shandong Unive-rsity of Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2019, 33(2): 31-37, 42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 刘琦,宫玉敏,高光明,等. 2PZ-4000型苹果多功能栽植机栽植株距试验分析[J]. 农业装备与车辆工程,2020,58(9):46-49.
Liu Qi, Gong Yumin, Gao Guangming, et al. Test and analysis of planting spacing of 2PZ-4000 apple multifunctional planter[J]. Agricultural Equipment & Vehicle Engineering,2020,58(9):46-49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 张义胜,宫玉敏,高光明. 2PZ-4000型苹果多功能栽植施水机构的设计[J]. 林业机械与木工设备,2018,46(5):21-23,28.
Zhang Yisheng, Gong Yumin, Gao Guangming. Design of the watering mechanism of 2PZ-4000 Multi-functional apple planters[J]. Forestry Machinery & Woodworking Equipment, 2018, 46(5): 21-23, 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 林悦香,尚书旗,王东伟,等. 矮砧密植苹果树连续开沟定距栽植机研制[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(1):23-30.
Lin Yuexiang, Shang Shuqi, Wang Dongwei, et al.Design of apple planting machinefor high density dwarfing orchard[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(1): 23-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 苏金花,何凤萍. 苹果矮化密植栽培技术[J]. 河南农业,2018(5):22,24.
[26] 韩明玉. 苹果矮砧集约高效栽培模式[J]. 果农之友,2009(9):12.
[27] 李丙智. 矮砧苹果园建立与栽培[J]. 新农业,2010(2):22-23.
[28] 王忠和. 苹果矮砧密植栽培中存在的关键问题及其对策[J]. 科学种养,2014(10):21-22,23.
[29] 马宝焜,徐继忠,孙建设. 关于我国苹果矮砧密植栽培的思考[J]. 果树学报,2010,27(1):105-109.
Ma Baokun, Xu Jizhong, Sun Jianshe. Consideration for high density planting with dwarf rootstocks in apple in China[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2010, 27(1): 105-109. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 郭慧,陈志,贾洪雷,等. 锥形轮体结构的覆土镇压器设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(12):56-65.
Guo Hui, Chen Zhi, Jia Honglei, et al. Design and experiment of soil-covering and soil-compacting device with cone-shaped structure of wheel[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(12): 56-65. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 李宝筏. 农业机械学[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社,2003.
[32] 贾洪雷,陈忠亮,马成林,等. 北方旱作农业区耕作体系关键技术[J]. 农业机械学报,2008,39(11):59-63.
Jia Honglei, Chen Zhongliang, Ma Chenglin, et al. Key technologies for the tillage system in area of dry farming of northern China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2008, 39(11): 59-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Improvement and experiment of the seedling clamping device of apple tree planting machines
Lin Yuexiang1, Shang Shuqi1※, Lian Zhengguo1, Wang Mingcheng2, Zhang Jingguo3
(1.,266109,;2.,150030,;3,261501,)
At this stage, the domestic development of apple tree seedling planting machines is still in its infancy, and few planting machines had been developed for apple trees. Planting apple trees requires a large amount of labor, but the current shortage of labor is a prominent contradiction. The problem of non-mechanized planting of apple tree seedlings urgently needs to be solved. In order to solve the problems in the apple planting process under the current high density dwarfing orchard cultivation mode: low manual planting efficiency, unsatisfactory erection of fruit seedlings with the developed machines, and slightly higher coefficient of variation of plant spacing caused by the slippage of the clamping belt. Under the guidance of agricultural machinery and agronomic integration technology, a two-point clamping apple seedling planting machine was developed by a combination of extensive research, virtual design, prototype manufacturing, and field trials. This machine is based on the existing continuous ditching fixed-distance planting machine previously developed by the same team, and implements structural improvements and performance optimization. Firstly, the fruit seedling clamping device is improved, and the fruit seedlings are clamped at the upper and lower points. On top of the previous generation planting machine, a layer of clamping and conveying device is installed above the lower clamping and conveying device, and the upper and lower layers are perpendicular to each other. The distance is set to be 50 cm, which is based on the comprehensive consideration of the height and status of the apple tree seedlings and the comparison of the planting effectiveness at different distances. The upper and lower clamping points work with each other during the transportation of apple tree seedlings to clamp the apple tree seedlings together. The apple tree seedlings will not rotate during operation and maintain a good initial status. It overcomes the problem that it is difficult to guarantee the initial angle of the tall seedlings relative to the ground because of the original one-point clamping, and significantly improves the perpendicularity after planting; Secondly, the transportation method is improved and the coefficient of variation of plant spacing is reduced. Considering that the trunk and bark of apple tree seedlings should not be damaged during the clamping and conveying process of the transplanter, the solution was still sought in the belt category. The initial idea was to add more tension wheels to change the belt slippage. However, the experimental results observed showed that this method makes almost no effect on reducing the belt slip rate. The timing belt can ensure that the apple tree seedlings are protected from damage during the clamping and conveying process, and it has a good transmission effect with little sliding. In order to improve clamping, the conveying mode adopts two synchronous belts to clamp and convey apple seedlings, which has a lower slip rate than the original V-belt clamping and conveying, and significantly reduces the coefficient of variation of the plant spacing; in addition, the power matching is optimized by the corresponding calculation formula. The depth-limiting wheel is installed to improve the stability of the planting depth, and the ditching machine, plant spacing control and other parts follow the first-generation machine plan. According to the planting requirements of different varieties of seedlings, the depth and width of the ditch can be adjusted, and the planting distance can also be adjusted as needed, and the adjustment is simple and convenient. Field tests showed that the qualified rate of apple seedlings planted by the machine is increased from 90.63% to 97.14%, the average planting depth qualified rate is increased from 91.43% to 93.33%, and the average plant spacing coefficient of variation is reduced from 5.03% to 3.74%, and the planting efficiency is increased from 11.89 plants/min to 12.26 plants/min, which was 37 times faster than that of manual planting. Compared with the existing machines, all performances have been improved, laying a solid foundation for the subsequent mechanization of apple's production.
agricultural machinery;experiment; apple seedlings; planting; two-point clamping; perpendicularity
林悦香,尚书旗,连政国,等. 苹果树栽植机幼苗夹持装置改进与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(19):1-6.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.19.001 http://www.tcsae.org
Lin Yuexiang, Shang Shuqi, Lian Zhengguo, et al. Improvement and experiment of the seedling clamping device of apple tree planting machines[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2021, 37(19): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.19.001 http://www.tcsae.org
2021-08-06
2021-09-28
山东省农机装备研发创新计划项目“苹果生产全程机械化技术与装备研发(2017YF006)”;苹果开沟栽植关键技术与装备优化提升(SD2019NJ001-1)
林悦香,副教授,研究方向为现代农业机械装备工程。Email:yxlin@qau.edu.cn
尚书旗,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为农业机械化工程。Email:sqingnong@126.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.19.001
S233.2
A
1002-6819(2021)-19-0001-06
