Efficacy observation of auricular point sticking in combination with a healthy diet for simple obesity in children
2021-12-17CaoYang曹阳WuXinyi吴心仪ZhaoQingyi赵庆逸MaGuizhi马桂芝ShiYin施茵ZhouJing周竞
Cao Yang (曹阳), Wu Xin-yi (吴心仪), Zhao Qing-yi (赵庆逸), Ma Gui-zhi (马桂芝), Shi Yin (施茵),4, Zhou Jing (周竞)
1 Community Health Service Center of Liangcheng New Village Street in Hongkou District, Shanghai, Shanghai 200434, China
2 Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
3 Shanghai TCM-Integrated Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200082, China
4 Shanghai Research Institute of Acupuncture and Meridian, Shanghai 200030, China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupoint Therapy; Auricular Point Sticking; Diet, Healthy; Obesity; Child
Simple obesity is a chronic disease highly related to lifestyle and featured by excessive nutrition, insufficient physical activities, and abnormal eating behaviors with systemic adipose tissue hyperplasia. As the society and economy constantly thrive in China, the number of obese people also increases rapidly[1], and more and more kids are at risk each year, presenting the low age tendency[2]. Obesity affects the kids’ physical and mental health and brings about threats of various chronic diseases. These influences will possibly extend to adulthood and also lead to higher risks for kinds of metabolic disorders[3]. Therefore, it is necessary and significant to prevent and effectively manage obesity in children.
The available interventions for obesity in Western medicine include dieting, increasing physical activities to assist surgeries such as liposuction, and pharmacological treatments. However, despite the effectiveness of these methods, they are not entirely proper for kids. As an
acupuncture-moxibustion treatment method of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), auricular point sticking works similarly to acupuncture. Furthermore, it is more convenient, safe, controllable, and free of side effects, hence more readily accepted by children and more popularly used to treat simple obesity in children[4].In this trial, we observed the clinical efficacy of auricular point sticking together with a guide on a healthy diet to treat children’s simple obesity. We now report the details as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
We referred to the relevant references to develop the diagnostic criteria for this study[5-7]. Obesity was diagnosed when the body mass index (BMI) was larger or equal to the 95th percentile (P95) of that in the population of the same age and gender, or the body mass (BM) exceeded the standard by over 20%.
The syndrome differentiation of TCM referred to the
Clinical Practice of Pediatrics of Traditional Chinese Medicine[8]and classified obesity in kids as three syndromes: dampness stagnation due to spleen deficiency, stomach heat and dampness stagnation, and deficiency of spleen and kidney. The syndrome of dampness stagnation due to spleen deficiency mainly manifests as a plump figure, bloating, a sticky mouth but not thirsty, lassitude, loose stools, a swollen tongue body with thick greasy coating, and soft and floating pulse beats. The syndrome of stomach heat and dampness stagnation mainly manifests as a plump figure, filthy and dry mouth, weak limbs, constipation, a red tongue body with yellow greasy coating, and slippery and rapid pulse beats. The deficiency of spleen and kidney syndrome mainly manifests as a plump figure, pale complexion,spontaneous sweating and weakness, aversion to physical activities and speech due to weakness, a pale tongue with white liquid coating, and slow or thin sunken pulse beats. The syndrome was confirmed when the main symptoms and the tongue and pulse manifestations were met.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Conformed to the above criteria for diagnosis and TCM syndromes; aged 6-9 years old; not using weightreducing pills or methods during the previous three months; willing to participate in the trial with the written consent from the children’s guardians.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Those with solid muscles and abundant water; those with primary metabolic disorders; those with secondary obesity.
1.4 Dropout criteria
Those who took diet pills during the observation period; those who failed to stick with the treatment as required; those who refused to test the indictors as required, making it impossible to evaluate the efficacy.
1.5 Statistical methods
SPSS version 16.0 statistical software was adopted for statistical analyses. The normally distributed measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s). The independent samplest-test was applied to between-group comparisons, and the paired samplest-test was used for intra-group comparisons.The non-normally distributed measurement data were tested using Wilcoxon signed-rank test. The enumeration data were expressed as rate or percentage and examined by Chi-square test.P<0.05 indicated statistical significance in the difference.
1.6 General data
Based on an epidemiological investigation conducted between January 2015 and January 2016 targeting children aged 6-9 years old in Shanghai Liangcheng Xincun Street, 190 kids were recruited. These included 113 boys and 77 girls, meeting the diagnosis of simple obesity by measurement of their height, BM, BMI, waist circumference (WC), hip circumference (HC), and subcutaneous fat thickness. The 190 obese kids were randomized into an observation group and a control group using the random number table, with 95 cases in each group. Prior to treatment, there were no significant differences in gender, age, height, BM, BMI, WC, HC, or subcutaneous fat thickness between the two groups(P>0.05), indicating the comparability (Table 1).

Table 1. Comparison of the general data
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Observation group
2.1.1 Auricular point sticking Major points: Shenmen (TF4), Endocrine (CO18),Sympathetic (AH6a), Lower Tragus (TG2), Sanjiao (CO17),and Subcortex (AT4).
Adjunct points: Spleen (CO13), Stomach (CO4), Lung(CO14), and Heart (CO15) were added for the syndrome of dampness stagnation due to spleen deficiency. Stomach(CO4), Liver (CO12), Large Intestine (CO7), and Small Intestine (CO6) were added for the syndrome of stomach heat and dampness stagnation. Spleen (CO13), Kidney(CO10), and Bladder (CO9) were added for the syndrome of deficiency of spleen and kidney.
Operation: Location of the points referred to the
Nomenclature and Location of Auricular Points(GB/T 13734-2008), (Figure 1)[9]. We used sterile auricular point plasters for treatment. Each time, the major points were treated together with 1-2 adjunct points selected based on the syndrome. The two ears were treated alternately.The kids were asked to press the plasters four times a day,2-3 min each time, better to produce slight pain. The plasters were replaced every other day. Thus, the efficacy was evaluated three months later.

Figure 1. Illustration of auricular points
2.1.2 Healthy diet
The three-meal healthy diet pattern started simultaneously with the auricular point sticking treatment.
Breakfast: Sugar-free milk or soymilk 250 g, one egg,one bread bun, or one Chinese bread.
Lunch: Chose only one from lean meat, fish, shrimp,beef, and lamb, 100 g, boiled or steamed with less oil and sugar; staple food such as rice and noodles ≤100 g. Side dishes included vegetable salad, quickly-boiled or less-oil stir-fried vegetables, beans or bean products, and soup of white guard/seaweed and pork ribs, but only one kind could be chosen each time.
Dinner: Raw fruits such as cucumbers, tomatoes,apples, and bananas; vegetable salad or stir-fried vegetables. Staple food such as rice and noodles ≤50 g.
We had trained one doctor specifically for quality control over the entire trial, supervising the location of auricular points and guiding the diet pattern.
2.2 Control group
The control group only received the same diet pattern as the observation group.
3 Observation of Therapeutic Efficacy
3.1 Observation items
3.1.1 BM and BMI
The kids’ height and BM were measured every morning after defecation during 7:30-8:30 a.m., and BMI was calculated. BMI = BM ÷ Height2.
3.1.2 WC, HC, and subcutaneous fat thickness
Measurement of the WC: While the kid was standing naturally, exposing the abdomen and keeping natural respiration, the physician used a tape measure to encircle the kid’s waist by the level of the midpoint between the crossing of the mid-axillary line and inferior costal arch and the iliac crest, to measure the WC. The reading was then recorded.
Measurement of HC: While the kid was standing upright with the legs together and arms down, the physician used the tape measure to encircle the lower abdomen by the level of the symphysis pubis and the most prominent part of the gluteus maximus, to measure the HC. The reading was then recorded.
Measurement of the subcutaneous fat thickness:While the kid was standing naturally with the arms down,the physician pinched up the skin and subcutaneous fat tissue 1 cm beside the umbilicus on the right abdomen to measure the subcutaneous fat thickness with calipers.
3.2 Criteria for therapeutic efficacy[10]
Markedly effective: The BMI decreased by ≥4 kg/m2.
Effective: The BMI decreased by ≥2 kg/m2but<4 kg/m2.
Invalid: The BMI decreased by <2 kg/m2.
3.3 Treatment results
3.3.1 Comparison of the clinical efficacy
The total effective rate was 91.6% in the observation group versus 74.7% in the control group, and the between-group difference was statistically significant(P<0.01). Thus, it is suggested that auricular point sticking combined with a healthy diet can produce more significant efficacy than a healthy diet alone (Table 2).
3.3.2 Comparison of the BM
Prior to treatment, there was no significant difference in BM between the two groups (P>0.05). After treatment,BM significantly dropped in the observation group(P<0.01) and the control group (P<0.05). It is suggested that auricular point sticking plus a healthy diet can produce a more notable effect in improving the BM in obese children than a healthy diet alone (Table 3).
3.3.3 Comparison of the BMI
Before treatment, there was no significant difference in BMI between the two groups (P>0.05). After treatment, BMI dropped in both groups (P<0.05) and was lower in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05). It is indicated that auricular point sticking plus a healthy diet can better improve the BMI in obese children than a healthy diet alone (Table 4).
3.3.4 Comparison of the WC
Before treatment, there was no significant difference in WC between the two groups (P>0.05). However, after treatment, the WC decreased in both groups (P<0.05)and was smaller in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05). Thus, it is demonstrated that auricular point sticking plus a healthy diet can more significantly improve the WC in obese children than a healthy diet alone (Table 5).
3.3.5 Comparison of the HC
Before treatment, there was no significant difference in HC between the two groups (P>0.05). After treatment,the HC decreased in both groups (P<0.05) and was smaller in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05). It is suggested that auricular point sticking plus a healthy diet can produce a more notable effect in improving the HC in obese children than a healthy diet alone (Table 6).
3.3.6 Comparison of the subcutaneous fat thickness
Before treatment, there was no significant difference in the subcutaneous fat thickness between the two groups (P>0.05). After treatment, the subcutaneous fat thickness decreased in both groups (P<0.05) and was smaller in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05). It is indicated that auricular point sticking plus a healthy diet can produce a more notable effect in improving the subcutaneous fat thickness than a healthy diet alone (Table 7).
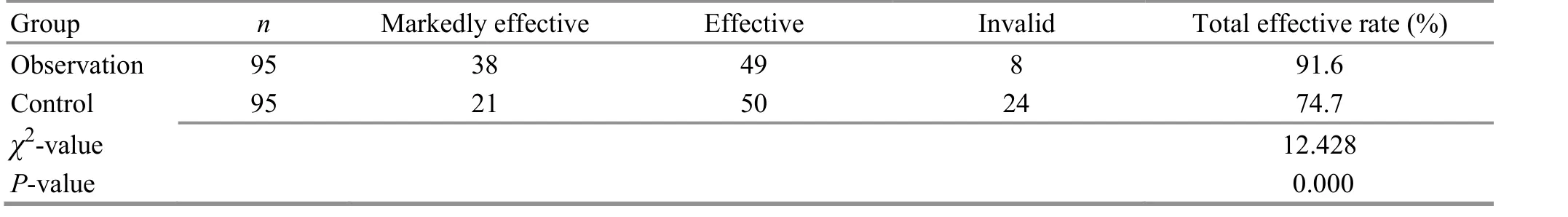
Table 2. Comparison of the clinical efficacy (case)
Table 3. Comparison of the BM before and after treatment ( ±s, kg)
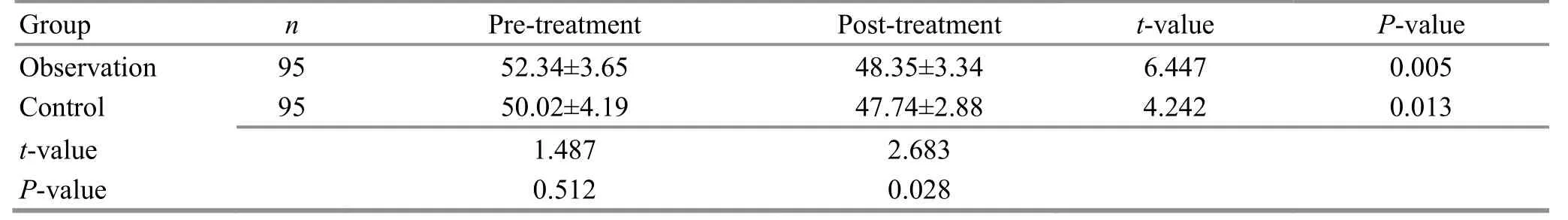
Table 3. Comparison of the BM before and after treatment ( ±s, kg)
t-value P-value 6.447 0.005 4.242 0.013
Table 4. Comparison of the BMI before and after treatment ( ±s, kg/m2)
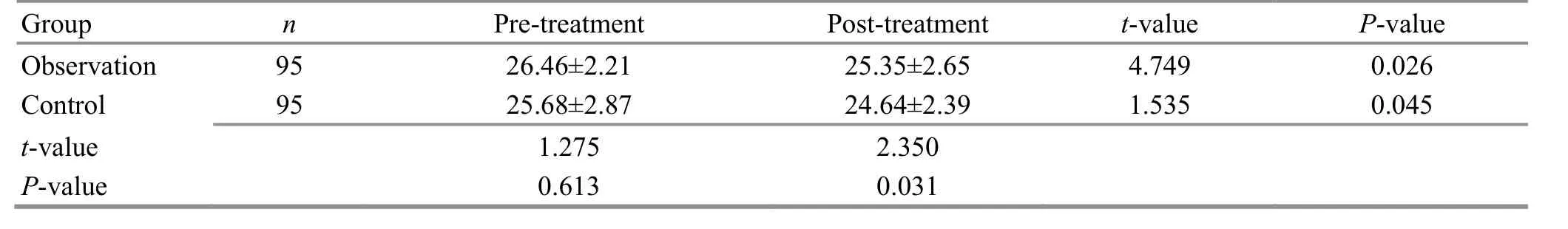
Table 4. Comparison of the BMI before and after treatment ( ±s, kg/m2)
t-value P-value 4.749 0.026 1.535 0.045
Table 5. Comparison of the WC before and after treatment ( ±s, cm)
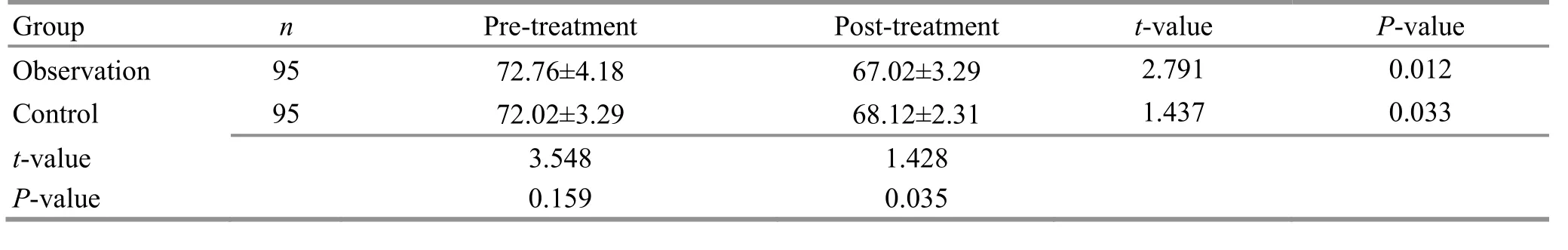
Table 5. Comparison of the WC before and after treatment ( ±s, cm)
t-value P-value 2.791 0.012 1.437 0.033
Table 6. Comparison of the HC before and after treatment ( ±s, cm)
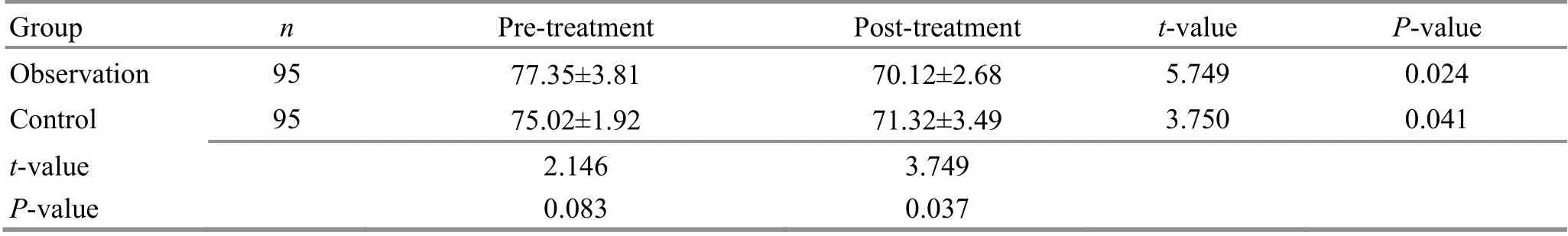
Table 6. Comparison of the HC before and after treatment ( ±s, cm)
Group n Pre-treatment Post-treatment t-value P-value Observation 95 77.35±3.81 70.12±2.68 5.749 0.024 Control 95 75.02±1.92 71.32±3.49 3.750 0.041 t-value 2.146 3.749 P-value 0.083 0.037
Table 7. Comparison of the subcutaneous fat thickness before and after treatment ( ±s, cm)

Table 7. Comparison of the subcutaneous fat thickness before and after treatment ( ±s, cm)
Group n Pre-treatment Post-treatment t-value P-value Observation 95 5.34±0.58 4.37±0.41 2.358 0.019 Control 95 4.98±0.37 4.12±0.88 0.478 0.037 t-value 0.159 3.745 P-value 0.273 0.041
4 Discussion
TCM holds that obesity is caused by excessive fat and dampness resulting from various factors such as natural endowment, improper diet, contraction of the external dampness pathogen, and daily living habits. TCM also summarizes its pathogenesis as Qi deficiency and too much dampness. Obese people usually prefer sitting to moving around. Nevertheless, a sedentary lifestyle may damage the spleen and sticking to bed may consume Qi,where the fluid transportation and transformation will be hampered, encouraging dampness accumulation, and causing obesity.
Western medicine believes that obesity in children results from the joint effect of genetic factors, eating habits, behaviors, family environment, and psychological factors. Unlike adults, kids’ bodies are still developing,with tender organs and an immature Qi system.Therefore, popular weight-reducing methods such as dieting, surgery, and drugs are unsuitable for kids.Changing diet patterns and exercises play a critical role in managing simple obesity in kids but are limited by the long course, insignificant short-term efficacy, and relapses. In addition, it is indeed a challenge for kids to stick to diet control and exercises, which also causes the diversity of efficacy[11].
We adopted low-calorie, low-carbohydrate, and highprotein diets to maintain the body in a negative energy balance and consume fat in the body. Besides, the observation group was offered additional auricular point sticking therapy, which kids can easily accept[12].
According to modern medicine, auricular point therapy is a comprehensive system that works through multiple means. Bioholographic theory holds that the distribution of auricular points follows an inverted fetus.We can find reaction points on the ear, presenting as spots, tender points, prominence, red, and swelling for different diseases. Therefore, we can treat diseases by stimulating the corresponding reaction points[13-14].Electrobiologists have found abnormal bioelectrical impedance at the auricular points corresponding to the diseased organs. Stimulating these auricular points can produce potential differences and current transmitting to tissues or organs via the meridian system[15]. Another study found high concentrations of zinc, iron, and calcium ions in the corresponding auricular points of the diseased organs, accompanied by reduced magnesium and potassium ions[16]. Moreover, from the perspective of nerve conduction, the mechanical stimulation to auricular nerves can produce nerve impulses that hinder the gastrointestinal tract’s dieting signals, thus reducing the patient’s sense of hunger and craving for food[17]. In addition, the auricular concha and triangular fossa distribute the richest nerves and vessels in the auricle.Stimulation to the auricular points located in these areas can transmit to the central nervous system via the vagus nerve, impacting the secretion of insulin and finally achieving the weight-loss effect[18]. As for this, it is found that children’s simple obesity is closely related to insulin resistance and hyperinsulinism[19]. Also, psychological research has discovered that stimulating auricular points can repress people’s desire for food and break eating signals, thus reducing the food intake[20].
According to TCM, the ear is more than an auditory organ but also a miniature of the human body, and it has connections to every meridian. The meridian system bridges the organs and auricle. When a pathological reaction occurs to a specific organ, corresponding reaction points will show on the auricle via the work of meridians; pressing these reaction points can regulate the corresponding organs and meridian function.
Based on the above theory and physiopathological features of the obese children, we selected Shenmen(TF4), Endocrine (CO18), Sympathetic (AH6a), Lower Tragus (TG2), Sanjiao (CO17), and Subcortex (AT4) as the major points. Of which, Endocrine (CO18), Sympathetic(AH6a), and Subcortex (AT4) are named according to modern medical concepts. Endocrine (CO18) was chosen to modulate the endocrine function, improve the fluids flow and reduce swelling. Sympathetic (AH6a) was used to improve autonomic nervous dysfunction. Subcortex(AT4) can smooth the intestines, harmony the stomach,and simultaneously influence the ingestion-related nerves in the hypothalamus. Lower Tragus (TG2), also named Hunger Point, just as its name implies that it can modulate the craving for food. In the meantime, this point can also clear heat and soothe the stomach. Hence it has become a point commonly used to treat obesity[21].Shenmen (TF4) and Sympathetic (AH6a) can inhibit appetite and regulate the gastrointestinal nerve functions to reduce the sense of hunger. According to the TCM theory, obesity is usually associated with phlegm and dampness, which combine with deficient Yang Qi,resulting in a poor distribution of fluids and excessive accumulation of fat and fluids. For this reason, we adopted Sanjiao (CO17) to boost the metabolism and elimination of fluids and fat[22]. Meanwhile, adjunct points were selected based on different syndromes.These auricular points worked in one to finally achieve the goal of treating obesity[23].
The results showed that with the 3-month treatment of auricular point sticking and a healthy diet, 91.6% of the 95 kids with simple obesity had a reduction of BMI≥2 kg/m2, along with a more significant reduction of WC,HC, and subcutaneous fat thickness compared with those intervened by a healthy diet alone. Hence, it is suggested that auricular point sticking plus a healthy diet can work synergistically to improve the symptoms and signs of obese children, and thus is worthy of promotion.
Conflict of Interest
There is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Shanghai Sailing Program(上海市青年科技英才扬帆计划项目, No. 20YF1445800);Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (上海市自然科学基金, No. 19ZR1451700); Shanghai Municipal Health Commission Research Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine (上海市卫生健康委员会中医药科研项目, No.2020JQ004).
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the guardians of the recruited children in this study.
Received: 1 November 2020/Accepted: 18 February 2021
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effects of sinew-regulating bone-setting manipulations on chondrocytes, IL-1β and NO in rabbits with knee osteoarthritis
- Clinical efficacy of sticking-needle acupuncture plus tendon-regulating manipulation in the treatment of acute ankle sprain
- Therapeutic efficacy observation of warm needling moxibustion plus spine subtle adjusting manipulation for cervical radiculopathy
- Evaluation of the clinical efficacy of muscle regions of meridians needling method for refractory facial paralysis based on infrared thermal imaging technology
- Clinical study on Tuina plus umbilical therapy for senile functional constipation
- Effect of acupuncture on serum PYY and nesfatin-1 in obese patients with insulin resistance
