Therapeutic efficacy observation of Tuina manipulation for pediatric adenoid hypertrophy
2021-12-17LiuKunpeng刘鲲鹏CuiJiawen崔佳文GuFei顾非FangMin房敏WangYichao王怡超WangShuxia王树霞WangCheng王成WangJunliang王峻良ZhouChao周超JiDengjun吉登军LiYazhou李亚洲HuLijun胡丽君
Liu Kun-peng (刘鲲鹏), Cui Jia-wen (崔佳文), Gu Fei (顾非), Fang Min (房敏), Wang Yi-chao (王怡超),Wang Shu-xia (王树霞), Wang Cheng (王成), Wang Jun-liang (王峻良), Zhou Chao (周超), Ji Deng-jun (吉登军),Li Ya-zhou (李亚洲), Hu Li-jun (胡丽君)
1 Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Shanghai 200437, China
2 East Hospital, Tongji University, Shanghai 200120, China
3 School of Acupuncture-moxibustion and Tuina, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
Abstract
Keywords: Tuina; Massage; Pediatric Tuina; Adenoid Hypertrophy; Pharyngeal Tonsil
Adenoid hypertrophy (AH) is a common disease in pediatric otolaryngology, with an incidence rate of 9.9%-29.9% in children. It is more common to affect children under ten years old, especially those four to seven years old. AH can cause obstructive sleep apnea syndrome(OSA). The incidence of OSA in children is about 1.0%-4.0%[1]. Adenoids belong to the pharyngeal lymphatic tissue and play the first immune protection barrier for the human body. When repeatedly stimulated by inflammation, they will develop hyperplasia and hypertrophy[2], thereby blocking the airway and causing symptoms such as mouth breathing and sleep-related apnea. Other complications may include secretory otitis media, upper respiratory tract infection, and chronic sinusitis[3]. Western medicine treatment of AH is mainly surgical resection. Although it can temporarily improve symptoms, it is unclear whether premature resection will affect other body system functions[4]. Western medicine treatment, like nasal hormones, antihistamines, and leukotriene receptor antagonists, mainly focuses on symptomatic relief. Although the medications can improve symptoms in the short term, the long-term effect is not satisfactory[5]. Traditional Chinese medicine believes that the main causes of AH are phlegmdampness, phlegm stasis and heat toxicity. The treatment usually targets phlegm, deficiency and excess,or Zang-Fu organs[6]. Pediatric Tuina (Chinese therapeutic massage) is one of the safe and effective methods to treat pediatric diseases, and is more easily accepted by younger children. In this study, we observed the clinical efficacy of pediatric Tuina for children with AH.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
The diagnostic criteria for AH referred to thePractical Pediatric Respiratory Medicine[7]. Children with mouth breathing, nasal obstruction, snoring, waking up due to suffocation, and occasional typical adenoid face.Rhinoscopy: visible red massive swelling in the nasopharynx with nasal mucosa fully contracted. X-ray examination: the lateral nasopharynx film indicated AH.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Those aged between four and ten years old; met the diagnostic criteria for AH; patients without any previous treatment or after a washout period of one month; the guardians agreed to participate in this trial and signed the informed consent.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Those with a clear history of inhalation allergy;patients with a personal or family history of allergic diseases; those who had severe systemic or infectious diseases; those with congenital dysplasia or choanal space-occupying lesions.
1.4 Elimination, dropout, and discontinuation criteria
Those who were unable to complete the examinations;those who dropped out during the trial; those who did not follow the treatment protocol; those who had severe adverse events or reactions; those presenting with severe complications or got worse in the disease condition during treatment.
According to the above criteria, some cases were suspended or eliminated. The reason for the suspension and elimination and its correlation with this trial were recorded.
1.5 Statistical methods
All data were statistically analyzed by the SPSS version 24.0 statistical software. The measurement data in normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s). Pairedt-test was applied to the comparisons of intra-group data. Independent samplettest was applied to the comparison between the groups.The measurement data in abnormal distribution were expressed as median (lower quartile, upper quartile) [M(QL, QU)], and processed by WilcoxonU-test for intragroup comparisons. Mann-WhitneyU-test was applied to the comparisons between the groups. Counting data were expressed as rate, and analyzed by Chi-square test.All statistical tests were performed by two-sided test.P≤0.05 was considered to indicate a significant difference.
1.6 General data
A total of 60 children who met the diagnostic criteria for AH and aged four to ten years old were enrolled from the Clinic of Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, between October 2017 and January 2019. They were randomly divided into an observation group and a medication group by the random number table generated by computer, with 30 cases in each group. Personal data including name,gender, age, phone number of the guardians, address,and relative disease history were collected. By statistical analysis, there were no significant differences in the data of gender, age, duration, and various test scores before treatment between the two groups (P>0.05), indicating that the two groups were comparable (Table 1).

Table 1. Comparison of the baseline data between the two groups
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Observation group
Children in the observation group were treated with pediatric Tuina.
The child took a supine position. The physician performed Kai-Opening Tianmen 50 times (Figure 1), Tui-Pushing Kangong 50 times (Figure 2), Nian-Twisting the neck with four fingers 250-300 times (Figure 3), An-Pressing and Rou-Kneading Yingxiang (LI 20), Danzhong(CV 17), Hegu (LI 4) and Zusanli (ST 36) 300 times respectively, Bu-Reinforcing Feijing (Figure 4), Pijing(Figure 5), and Shenjing (Figure 6) 300 times respectively.
Then the child took a prone position. The physician performed one-thumb Tui-Pushing Dingchuan (EX-B 1)and Fengmen (BL 12), Rou-Kneading Feishu (BL 13)(Figure 7), Pishu (BL 20), and Shenshu (BL 23) (Figure 8)for 30 s respectively, and Nie-Pinching the spine 3-5 times. The treatment was performed for 15-20 min each time, three times a week, once every other day,four weeks as a course of treatment, and the efficacy was evaluated after one treatment course.

Figure 1. Kai-Opening Tianmen

Figure 2. Tui-Pushing Kangong

Figure 3. Nian-Twisting the neck
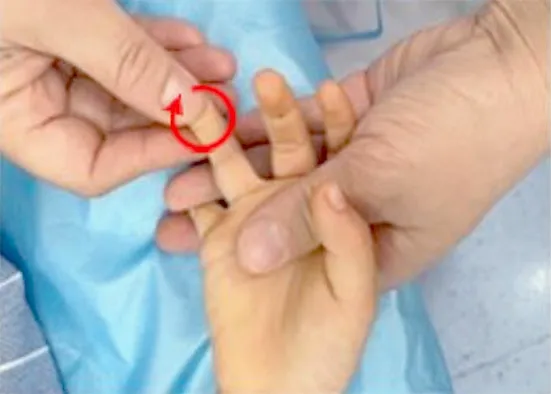
Figure 4. Bu-Reinforcing Feijing

Figure 5. Bu-Reinforcing Pijing

Figure 6. Bu-Reinforcing Shenjing

Figure 7. Rou-Kneading Feishu (BL 13)

Figure 8. Rou-Kneading Shenshu (BL 23)
2.2 Medication group
Children in the mediation group were treated with 0.05% mometasone furoate nasal spray, one spray per nostril each time, once a day, four weeks as a course of treatment, and the efficacy was evaluated after one treatment course.
3 Observation of the Curative Efficacy
3.1 Observation items
3.1.1 Main clinical symptom score
The main clinical symptom score scale scored the degree of nasal obstruction, snoring, and mouth breathing. Each item was divided into five levels according to the severity, namely, normal, mild,moderate, severe, and extremely severe, with 0, 2, 4, 6,and 8 points, respectively.
3.1.2 Quality of life (QOL) score
According to thePractical Pediatric Respiratory Medicine[8], and referring to the QOL for children with obstructive sleep apnea 18 items survey (OSA-18), the QOL score was divided into 5 dimensions for scoring, and was divided into 7 levels according to the frequency of symptoms, which were 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 points in turn.The higher the score, the higher the frequency of symptoms.
3.1.3 X-ray nasopharynx lateral film
Nasopharynx lateral film in the inspiratory phase of the children was taken before and after treatment.According to adenoid thickness (A) and nasopharyngeal cavity width (N), the A/N value was calculated. In this study, the A/N value was divided into three levels: A/N<0.60, normal adenoids; A/N ≥0.60 but ≤0.70, moderate adenoid hypertrophy; A/N >0.70, pathological adenoid hypertrophy.
3.2 Criteria for curative efficacy
This study referred to theGuiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines[9], and according to the QOL score, the efficacy index was calculated by Nimodipine method. Efficacy index = (QOL score before treatment - QOL score after treatment) ÷ QOL score before treatment × 100%. According to the efficacy index,the criteria for curative efficacy in this study were established.
Cured: Symptoms and signs disappeared or basically disappeared, and the efficacy index was ≥95.0%.
Markedly effective: Symptoms and signs were significantly improved, and the efficacy index was≥70.0%, but <95.0%.
Effective: Symptoms and signs were improved, and the efficacy index was ≥30.0%, but <70.0%.
Invalid: No significant improvement was found in symptoms or signs, or even worsening, with the efficacy index <30.0%.
3.3 Results
3.3.1 Comparison of the therapeutic efficacy
The total effective rate of the observation group was 90.0%, which was significantly higher than 66.7% of the medication group, and the difference between the groups was statistically significant (P<0.05), indicating that pediatric Tuina had more significant efficacy than mometasone furoate nasal spray in treating pediatric AH(Table 2).
3.3.2 X-ray nasopharynx lateral film
After treatment, the A/N value had no statistical change in either group (P>0.05), and the difference between the two groups was statistically insignificant(P>0.05), (Table 3).equivalent in improving the clinical symptoms (Table 4).

Table 2. Comparison of the therapeutic efficacy between the two groups (case)
Table 3. Comparison of the A/N value between the two groups before and after treatment ( ±s)
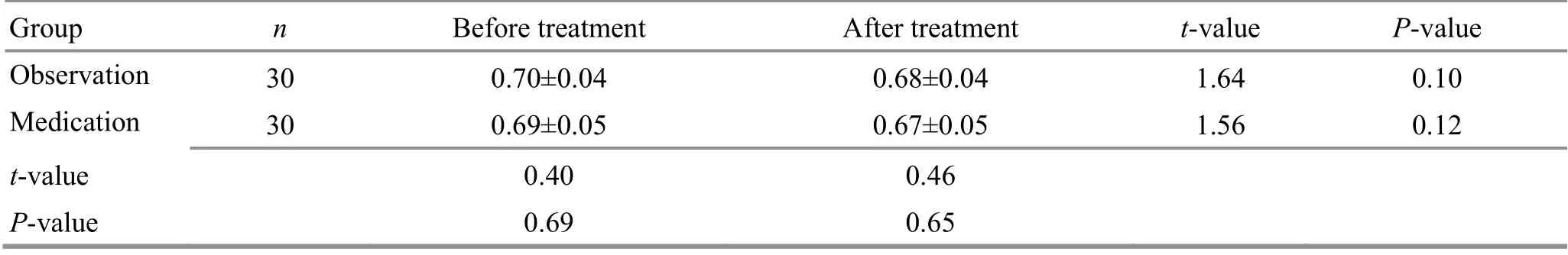
Table 3. Comparison of the A/N value between the two groups before and after treatment ( ±s)
Group n Before treatment After treatment t-value P-value Observation 30 0.70±0.04 0.68±0.04 1.64 0.10 Medication 30 0.69±0.05 0.67±0.05 1.56 0.12 t-value 0.40 0.46 P-value 0.69 0.65
3.3.4 Comparison of the QOL score
After treatment, the Mann-WhitneyU-test showed that the QOL scores in both groups were statistically different from those before treatment (P<0.001),indicating that both treatment methods could improve the QOL in children with AH. After treatment, there was a statistical difference in the QOL score between the two groups (P<0.001), indicating that pediatric Tuina had a better effect in improving QOL in children with AH than mometasone furoate nasal spray (Table 5).
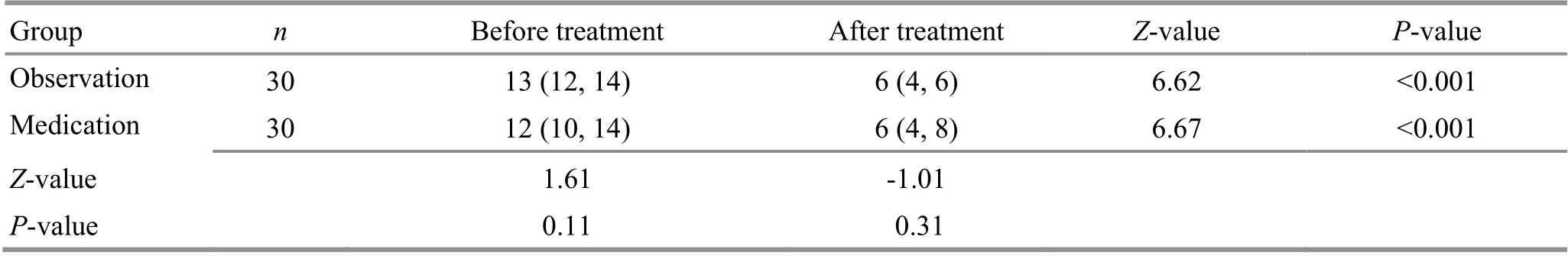
Table 4. Comparison of the main clinical symptom score between the two groups before and after treatment [M (QL, QU), point]
3.3.3 Comparison of the main clinical symptom score
After treatment, the Mann-WhitneyU-test showed that the main clinical symptom scores in both groups were statistically different from those before treatment(P<0.001), which was, the main clinical symptom scores in both groups were lower than those before treatment,indicating that both treatment methods could improve the clinical symptoms in children with AH. After treatment, there was no statistical difference in the main clinical symptom score between the two groups (P>0.05),indicating that the two treatment methods were

Table 5. Comparison of the quality of life score between the two groups before and after treatment [M (QL, QU), point]
4 Discussion
AH is a common disease in otolaryngology. It usually occurs in children under ten years old, and the peak age of onset is 6-7 years old. This disease may cause sinusitis,bronchitis, sleep-related breathing disorders, and even severe conditions such as adenoid face, bringing about severe physiological and psychological damages to children[10]. Modern medicine believes that once AH is diagnosed, surgery should be performed immediately.Otherwise, the growth of the child will be affected[11].However, surgery may damage the nasopharynx of the child, and may cause nasal bleeding and infection[12]. In addition, adenoids are a major component of the pharyngeal endolymphatic ring and an important immune organ of the human body[13]. Premature resection may increase the chance of upper respiratory tract infection in children[14].
Study has shown that mometasone furoate has an antagonistic effect on inflammatory factors such as prostaglandins and histamine. In children with AH, the drug can control inflammation in the nasal cavity,thereby improving symptoms such as runny nose and nasal obstruction[15]. There are abundant glucocorticoid receptors in the tissues in AH. As one of the glucocorticoids, mometasone furoate can inhibit the activity of lymphocytes in the adenoids and reduce inflammatory responses of nasopharynx[16]. In addition,mometasone furoate nasal spray is suitable for various age groups, including adults, adolescents and children aged 3-11 years old. Therefore, mometasone furoate nasal spray was applied for the medication group in this study.
Although AH has no records in the ancient literature,based on modern medical anatomy and basic theories of traditional Chinese medicine, it can be classified into categories of Han (snoring) symptom, Han Mian (sleep apnea), and phlegm nodule. Chinese medicine believes that the disease location of AH is the nasopharynx, and it is closely related to the lung, spleen, and liver. If the disease is not cured, it will involve the heart and kidney over time, resulting in the deficiency of five Zang organs.
Tuina is mainly based on manual manipulation.Compared with surgery and drug treatment, it is more easily accepted by children. Tuina has the effects of activating Qi flow for promoting blood circulation,unblocking the meridians and collaterals, and regulating Zang-Fu organs, and thus it can promote blood flow,improve microcirculation, reduce peripheral resistance,and promote inflammation absorption[17].
In this study, based on summarizing the experience of ancient physicians in combination with Professor Cao Ren-fa's clinical experience, we developed a set of Tuina manipulations to treat both symptoms and root causes of AH. First, An-Pressing and Rou-Kneading Hegu (LI 4)and Zusanli (ST 36), and Rou-Kneading Feishu (BL 13),Pishu (BL 20), and Shenshu (BL 23) were applied to reinforce the lung, spleen, and kidney. Hence, the lung regained the dispersing and descending function, the spleen could transport and transform water-dampness properly, and the kidney regained Qi transformation function. Consequently, the water-dampness would not generate, and adenoid function was normal. Meanwhile,Rou-Kneading Danzhong (CV 17) and Kai-Opening Tianmen have certain effects of activating Qi flow and promoting blood circulation, which makes the whole set of manipulations more effective with reinforcing but no stagnation, and reinforcing bearing reducing. Secondly,Nian-Twisting the neck with four figures used in this study has a good effect of promoting blood circulation to remove blood stasis, reducing swelling, and dispersing nodules. Thus, it can improve the circulation of Qi and blood in the throat, promote the elimination of inflammatory factors, and exert a good effect on AH.Thirdly, Nie-Pinching the spine is helpful to improve children’s resistance to disease. Meanwhile, An-Pressing and Rou-Kneading Yingxiang (LI 20) can clear the nasal passage and promote the discharge of purulent snivel,thereby breaking the vicious circle of "adenoid-purulent snivel-adenoid". The combination of these manipulations finally produces a satisfactory effect in treating AH.
The results of this study showed that the QOL score in the observation group after treatment was statistically different from that in the medication group (P<0.001),while the differences in the A/N value of X-ray examination and clinical symptom scores between the two groups were statistically insignificant (P>0.05). The reason may be that the focus of QOL score observation is not only the physiological symptoms, but also the mental health of the children and the psychological situation of their parents. Before and after the Tuina treatment, the physician can communicate with the child and his parents to relieve their tension. Just as Professor Cao Ren-fa once said, Tuina had four adjustments, which were body adjustment, heart adjustment, mind adjustment, and breathing adjustment. During the entire Tuina treatment process, due to the requirement of according cooperation of the children, most parents would encourage them with encouraging words.According to our experience, many children often resist Tuina the first time. However, after one to two weeks of treatment, children would be more interested in Tuina,which might also be related to the endorphin substances produced by Tuina therapy[18], so that children can develop a sense of pleasure in the treatment process.However, medication treatment lacks these auxiliary effects, so that its improvement in QOL score is inferior to that of Tuina treatment.
There are two possible reasons why there was no significant change in the A/N value in either group after treatment. One is that the treatment cycle was too short.This study referred to relevant literature and clinical experiences, and established the treatment cycle as one month. The treatment cycle was relatively short that either Tuina or mometasone furoate nasal spray was unable to reduce the size of adenoids. The second reason is the children's age. As mentioned above, AH is more common in children aged 4-7 years old, during which the adenoids of children grow rapidly. The children enrolled in this study were mainly 4-5 years old, which is in this age stage. Therefore, the therapeutic interventions were insufficient to significantly reduce the adenoid size. The clinical symptom scores of both groups decreased after treatment, but there was no significant difference between the two groups. It may be because that the three symptoms that the scale mainly targets are closely related to nasal ventilation, and both Tuina group and medication group could improve nasal ventilation.
Results in this study suggested that Tuina treatment had a certain effect on AH. It can improve the clinical symptoms in children with AH and improve their QOL,thereby reducing the rate of surgery, the suffering of the children, and the financial burden of the family.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (上海市科学技术委员会, No.17401935600); Academic Experience Inheritance Studio of Shanghai Famous Chinese Medicine Practitioners Cao Renfa (曹仁发上海市名老中医学术经验研究工作室, No.ZYSNXD-CC-MZY004).
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the guardians of the recruited children in this study.
Received: 14 September 2020/Accepted: 28 December 2020
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Evaluation of the effect of acupuncture on pain of patients with refractory trigeminal neuralgia
- Mild moxibustion plus loratadine tablets for children with allergic rhinitis: a randomized controlled trial
- Effect of acupuncture on serum PYY and nesfatin-1 in obese patients with insulin resistance
- Clinical study on Tuina plus umbilical therapy for senile functional constipation
- Evaluation of the clinical efficacy of muscle regions of meridians needling method for refractory facial paralysis based on infrared thermal imaging technology
- Therapeutic efficacy observation of warm needling moxibustion plus spine subtle adjusting manipulation for cervical radiculopathy
