果绿染色试验在评价脑卒中后气管切开并吞咽障碍患者渗漏和误吸的临床应用价值
2021-11-13樊留博韩文胜张露丁罗咪咪刘宝华
樊留博 韩文胜 张露丁 罗咪咪 刘宝华
[关键词] 气管切开;吞咽障碍;脑卒中;果绿染色;渗漏;误吸
[中图分类号] R74 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)25-0098-04
The clinical application value of fruit green staining test in the evaluation of leakage and aspiration in the patients undergoing tracheotomy and dysphagia after stroke
FAN Liubo1 HAN Wensheng1 ZHANG Luding1 LUO Mimi1 LIU Baohua2
1.Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province, Shaoxing University, Taizhou 317000, China; 2.The Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325035, China
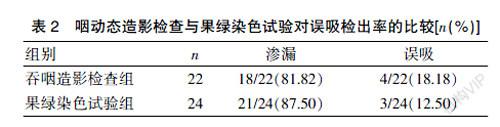
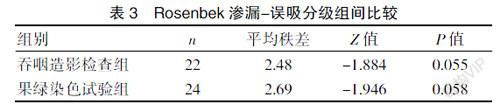
[Abstract] Objective To explore the clinical application value of fruit green staining test in the evaluation of leakage and aspiration in the patients undergoing tracheotomy and dysphagia after stroke. Methods From January 2018 to June 2019, 46 patients with stroke who underwent difficulty in being unable to pull out the cannula and dysphagia after tracheotomy were selected. They were hospitalized in Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province and the Second Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University. Fruit green staining test and pharyngeal dynamic contrast test were carried out respectively. The difference in aspiration detection rate was compared between the two tests. At the same time, the occurrence of aspiration after eating different doses and shapes of food was observed. Results There was no statistically significant difference between the fruit green staining test and the pharyngeal dynamic contrast test in the incidence of mild leakage, severe leakage and aspiration (P>0.05). In the patients with leakage and aspiration, the incidence of aspiration increases as the viscosity of food increases. The aspiration rate of swallowing 10 mL of food was higher than that of 3 mL, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion The fruit green staining test can detect occult aspiration in the patients undergoing tracheotomy and dysphagia after stroke, and effectively improve the detection rate of aspiration. The method is objective, simple, and effective. The batter-like diet and the reduction of a mouthful amount can help patients reduce the occurrence of aspiration.
[Key words] Tracheotomy; Dysphagia; Stroke; Fruit green staining; Leakage; Aspiration
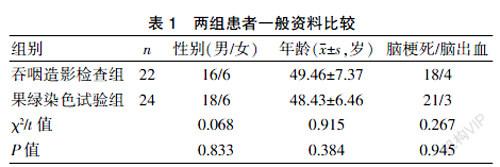
急性腦卒中患者并发吞咽障碍的发生率为22%~65%,由于脑卒中患者的机体防御能力下降,咳嗽反射减弱,呼吸道清除机制异常,支气管管壁弹性降低等原因常会导致误吸,发展至吸入性肺炎,甚至出现气道阻塞等严重威胁生命安全的情况,病情严重患者给予留置胃管更易出现,脑卒中后吞咽困难患者误吸发生率是52%~74%,期间安静时误吸大约占误吸患者的44%~72%;同时吞咽障碍又会导致一系列并发症,水、电解质、营养摄入不足,身体脱水、内环境紊乱,严重可导致死亡;同时患者在进食训练时会出现不同程度的心理障碍,主要表现为焦虑、抑郁、甚至会出现自杀倾向,由于吞咽障碍引起的这些种种因素进而严重影响患者康复进度及生活质量[1]。脑卒中由于呼吸中枢受损、呼吸下行传导通路被破坏后会继发肺部疾病,病情逐渐加重常常出现呼吸功能衰竭的危险,此刻需要立即进行气管切开术以尽快开放气道采取呼吸机支持治疗,随着患者呼吸功能逐渐好转,患者气道压力也逐渐发生改变,以至于患者在经口进食会出现不同程度的吞咽困难,待患者好转后患者会出现气道反射及咽反射减退或消失等情况,严重影响后期整体康复,对患者早期评价及干预,及时采取有计划的康复训练,在预防误吸的发生及加快康复等方面有着非常重要的临床意义,况且这方面目前在国内未见相关报道[2-3]。本研究在临床应用果绿染色实验能够快速、准确地判定患者是否存在误吸,受到患者及家属的一直好评,对于加快患者康复时间有明显的效果。临床通常采用吞咽荧光透视造影检查来评估患者在进食过程中的吞咽功能状态,由于气管切开患者病情较重,不能采取坐位等特定体位,同时搬动也不方便,因此在性吞咽造影检查存在一定的困难。经过我们在临床多年的摸索实验,发现采用果绿染色试验对重症脑卒中后气管切开并吞咽障碍患者渗漏和误吸评估观察取得较好的效果,现报道如下。
