Development status of intelligent harvesting technologyfor tea and vegetables in China*
2021-11-11QinLiuLianglongHuYanyanZhengkeTanYemengWangQingChen
Qin Liu,Lianglong Hu,Yanyan Zheng,Lüke Tan,Yemeng Wang,Qing Chen
(Nanjing Institute of Agricultural Mechanization,Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs,Nanjing,210014,China)
Abstract: Based on the patent analysis platform of patents,this article uses the bibliometric analysis method to measure,summarize and visually analyze the patent application amounts,patentees,inventors,technical topics and other classification indicators in the patent literature,so as to find out the development context,main innovation institutions,major innovation teams,core patents,key technologies concerned by the main applicants and others in Chinese tea and vegetables intelligent harvesting technology.The result and the conclusion can provide information support for promoting the innovation and development of tea and vegetables industry.
Keywords: tea;vegetables;intelligent harvesting;patent
0 Introduction
Compared with the developed countries of the United States,Canada,and Germany,the research and application of intelligent agricultural equipment in China started late but developed at a faster rate.A number of common key technologies have been broken through,and a number of intelligent agricultural machinery products with independent intellectual property rights have been innovated and developed.With the continuous development of mechanization of crop planting,harvesting,and picking,middle and high-end agricultural machinery intelligent products will usher in market opportunities.More specifically,the promotion and application of intelligent agricultural machinery will help agricultural machinery enterprises expand new markets and help farmers improve labor productivity faster.
As a major producer and exporter of vegetables,China ranks first in vegetable production and second in the planting area.In 2019,the area planted with vegetables in China had exceeded 20 million hectares,with an output of more than 700 million tons and an output value of 2 trillion yuan.China is an important part of the global vegetable market.In recent years,China’s tea industry has developed rapidly,and the integration of primary,secondary and tertiary industries has shown a good momentum of development.In 2019,China’s tea plantations covered about 3 million hectares,and its annual tea output was about 2.6 million tons,accounting for 60% and 45% of the world,respectively,ranking first in the world.
At present,the vegetable industry and tea industry have become the pillar industries of Rural Revitalization and high-quality agricultural development in China,which play an irreplaceable role in ensuring supply,increasing income,and promoting employment.The development of the vegetable industry and tea industry originates from technological progress,and intelligent harvesting is a key link to promote industrial transformation and upgrading.The evolution and improvement of key core technologies are based on knowledge diffusion.Meyer[1]believes that the output of technological innovation is patent.The patent has technical and market attributes,and it meets the requirements of originality,technical feasibility,and commercial value evaluation[2].As one of the important perspectives for studying knowledge diffusion,patents can reveal the evolutionary context of technological innovation and the innovation profile of patent subjects[3-4].Research on the patent development of intelligent harvesting in vegetable industry and tea industry,analysis of its core technology,innovation institutions,and core patentees can provide credible industrial technical information for the government and industry,and provide references in industrial policy or planning,industrial technology trend prediction,identification of common technologies and key technologies,technological R &D demands,and allocation of technological resources.
As so far,there are few literatures on the development of intelligent harvesting technology in the field of tea and vegetables from the perspective of patents.Based on the Patentics patent analysis platform,this paper analyzes the technological evolution,main innovation institutions,important innovation teams,core patents,and key technologies concerned by main applicants in the field of intelligent tea and vegetables harvesting.Through the multi-angle analysis of intelligent harvesting technology of vegetables and tea,we hope to provide ideas for promoting the innovation and development of the vegetable industry and tea industry.
1 Method and data
1.1 Retrieval platform
The patent search uses Patentics patent intelligent retrieval and analysis platform,which includes patent data of 117 countries,regions,and organizations,as well as data information such as citations,family,legal status,etc.,with a total of more than 190 million items,and continues to expand and update.The platform focuses on intelligent semantic technology,automatic understanding of scientific and technological long texts,and in-depth text mining.Compared with other patent databases,its biggest feature and advantage lies in intelligent semantic retrieval.Any input of “r/a natural language text describing the technology or a patent number”,the Chinese and foreign patent documents related to the input can be obtained and sorted according to the degree of relevance.
1.2 Retrieval strategies and data sources
In the aspect of tea intelligent harvesting technology,the patent retrieval formula is determined as A/(intelligent or robot or vision or automatic or bionic)and B/(tea and not oil tea),and IPC/A01D.A total of 259 patents were retrieved.After the data was merged in the same family to remove noise documents,209 patent documents were obtained.
In the aspect of vegetables intelligent harvesting technology,the patent retrieval formula is determined as A/(machine vision,visual recognition,image recognition,intelligence,bionic,automatic,robot)and B/(leaf vegetables or leafy vegetables or stems and leaves vegetables)and IPC/A01D,a total of 112 patents were retrieved.After the data was merged in the same family to remove noise documents,93 patent documents were obtained.
1.3 Analysis method
This article uses the bibliometric analysis method and Patentics patent intelligent retrieval and analysis platform,combined with Excel data processing software,to measure,summarize and visualize the number of patent applications,patentee,IPC classification number,technical subject,and other classification indicators in patent literature.
1)Technology evolution analysis.The overall development trend of a certain technology can be judged by statistical analysis of the patent applications in a period of time[5].For example,the number of patent applications for intelligent harvesting of vegetables and tea is very small before 2011,which allows analysis of the development trend of related technologies by analyzing the number of patent applications from 2011 to 2019.
2)Analysis of major innovation institutions.The patentee is the patent owner and the master of the technology[6].This article analyzes the number of patents held by patent holders to identify the dominant institutions in the field.
3)Key R &D team analysis.In every technology field,there will be a group of inventors who are active in the front line of R &D.These inventors usually lead their own R &D teams and have different areas of expertise and R &D direction.Their R &D trends will be mapped one by one in the patent application activities[7].Therefore,this article follows the clue of the inventor of the patent application and tries to find the key R &D team in the industry to find the source of innovation.
4)Key technical analysis of the main applicant’s concerns.By analyzing the subject of each mainapplicant’s patent application,we can understand the applicant’s R &D direction,which will help to further explain the development trend of a technology[8].Therefore,this article will focus on analyzing the technologies concerned by the applicants with the highest number of patent applications to understand their R &D focus.
5)Core patent analysis.Core patents have higher quality and represent key technologies in the field[9].Patentics can intelligently evaluates the value spectrum of a patent and judge the innovation and influence of the invention,in whichV1index reflects the market influence of the patent,V2index comprehensively reflects the market influence and technical influence of the patent,andV3index reflects the technical influence of the patent.This article uses theV2value to excavate core patents in the fields of tea intelligent harvesting technology and vegetables intelligent harvesting technology.
6)Analysis of applicant’s cooperation.Co-occurrence analysis is a quantitative analysis method of co-occurrence information in patent applicant’s information carrier[10].Through co-occurrence analysis,the cooperative relationship between applicants can be revealed.This article uses Patentics’co-occurrence analysis to clarify the industry-university-research cooperation in the field of tea intelligent harvesting technology and vegetables intelligent harvesting technology.
2 Analysis of the results
2.1 Tea intelligent harvesting technology
2.1.1 Technology evolution
Figure 1 is drawn according to the number of patent applications for tea intelligent harvesting technology.It can be seen from Figure 1 that the technology development from 2011 to 2013 was in the embryonic stage.In this stage,there are not many patent applications,few applicants participate in the research and market development of intelligent tea harvesting technology,and the development trend and market prospect of the technology are still unclear.The period from 2014 to 2018 is a period of rapid technological development,during which the number of patents granted increased rapidly.Although the number of patents declined slightly in 2015,the number of patents increased rapidly in the following three years,especially reaching a peak in 2018.The number of patents declined again in 2019,and its follow-up development remains to be seen.

Fig.1 Technology evolution
2.1.2 Major innovation institutions
The top 8 applicants for patent applications are Ganzhou Shuangmu Science and Technology,Zhejiang University of Technology,Nanjing Forestry University,Anhui Agricultural University,Nanjing Institute of Agricultural Mechanization,Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs,Sichuan Agricultural University,Hangzhou University of Electronic Science and Technology,and Qingdao University of Science and Technology.These eight applicants are the major innovation institutions in the field.
It is found that Ganzhou Shuangmu Science and Technology,Hangzhou University of Electronic Science and Technology,and Qingdao University of Science were involved in the field comparatively late,among which Hangzhou University of Electronic Science and Technology applied for three patents as early as 2017,Qingdao University of Science and Technology applied for two patents in 2019,and the 13 patents applied by Ganzhou Shuangmu Science and Technology were concentrated in 2018.Zhejiang University of Technology and Anhui Agricultural University both started early in this field.They applied for eight patents and three patents,respectively,in 2014.The Nanjing Institute of Agricultural Mechanization,Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs also produced patents earlier,applying for two patents in 2013 and 2014 respectively,but there was no patent application since then,and the attention to this field has been reduced.After applying for two patents in 2013,Sichuan Agricultural University applied for another one in 2018 to 2019,respectively,indicating that the applicant maintained a certain degree of attention to the technological development in this field.Nanjing Forestry University started the research early and produced patents every year during 2017—2019,indicating that the applicant has a strong ability of continuous innovation in this field.
2.1.3 Key R &D teams
By analyzing the inventors of 8 major innovation institutions,the composition of the important R &D teams of these eightinnovation institutions is sorted out.Each team only lists the top 4-5 people.The details are as follows.
The R &D team of Ganzhou Shuangmu Science and Technology:Wu Xiangjiu,Wu Shuiqian,Ouyang Yuping,Xiong Houzhang,Jiang Shuilong.
The R &D team of Zhejiang University of Technology:Zhang Xian,Qiao Xin,Zhang Li,Timing Ming,Zhao Zhangfeng.
The R &D team of Nanjing Forestry University:Chen Yong,Hong Xiaowei,Hao Miao,Pan Zhigang,Xu Linyun.
The R &D team of Anhui Agricultural University:Li Bing,Zhang Zhengzhu,Song Yangyang,Li Weining.
The R &D team of Nanjing Institute of Agricultural Mechanization,Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs:Xiao Hongru,Song Zhiyu,Ding Wenqin,Mei Song,Zhao Ying.
The R &D team of Sichuan Agricultural University:Xu Lijia,Liu Wei,Liu Dewei,Liu Mingdan,Liu Song.
The R &D team of Hangzhou University of Electronic Science and Technology:Li Tianyi,Ji Huawei,Han Shaopeng,Liu Kuan,Wu Liqun.
The R &D team of Qingdao University of Science and Technology:Yang Hualin,Chen Dong,Chen Long,Deng Fang,Ma Zhibin.
2.1.4 Key technology of the main applicant’s concerns
The key technology concerned by the main applicant is closely related to the technological development trend of the industry.With the rise and decline of a certain technology,the patent application activity of the main applicants in a certain technology branch also shows corresponding changes.From Table 1,all main applicants generally pay attention to technology accumulation,and there are common and differences in their concerned technology.Sichuan Agricultural University and Hangzhou University of Electronic Science and Technology focus on key breakthroughs in some fields,while applicants from Zhejiang University of Technology and Nanjing Forestry University pay attention to more technical branches and are good at opening up new technical subdivisions.
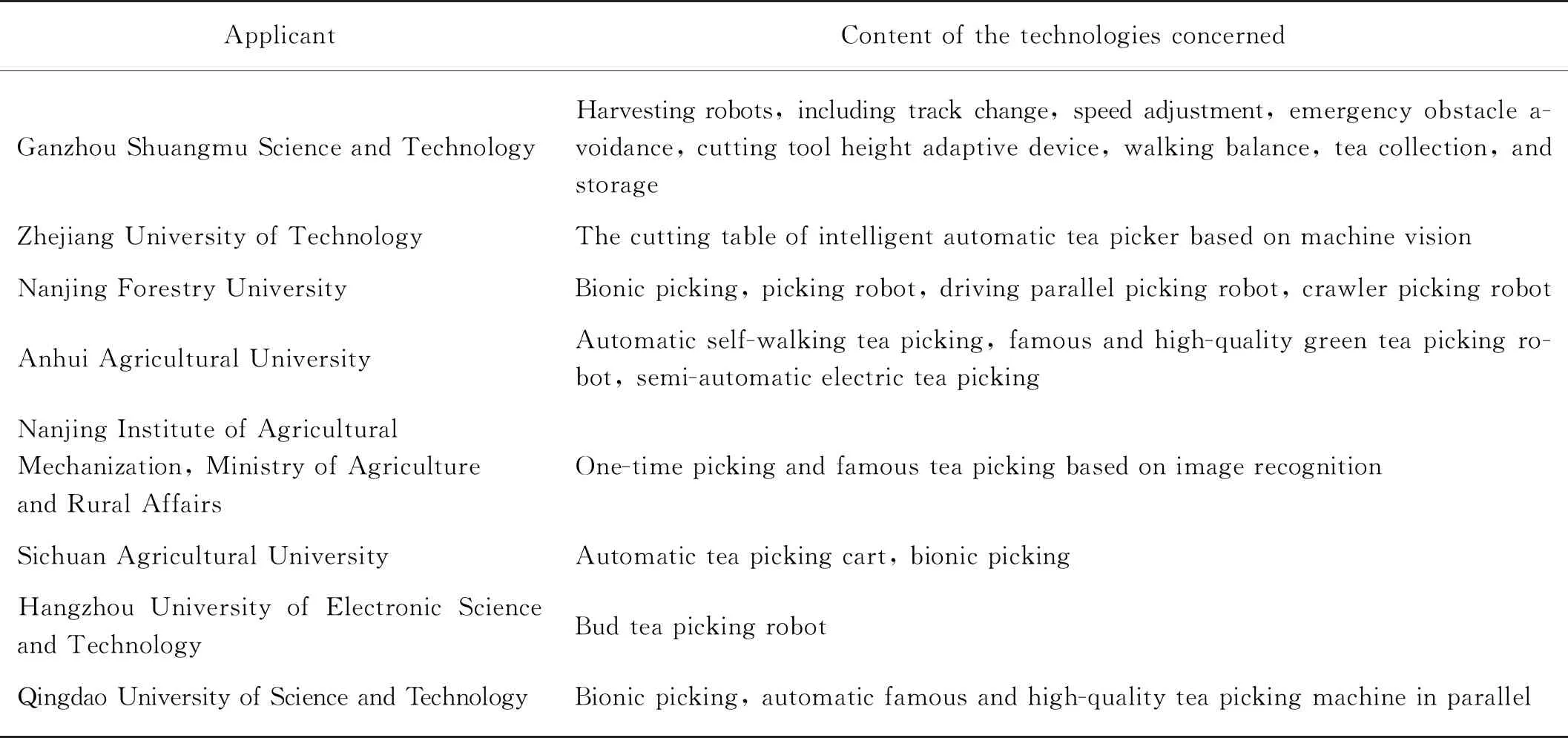
Tab.1 Technologies concerned by the main applicant
2.1.5 Core patents
According to the value of theV2index,four core patents ranked top are listed in Table 2,which play an important leading role in technological innovation in this field.

Tab.2 Core patents
2.1.6 Applicant’s cooperation
Among the top 20 patent applicants,except for the cooperation applications made by Shaoxing College of Arts and Sciences with two natural persons,the number of cooperative patents applied for by the other 19 applicants is all 0.It can be seen thata general situation of industry-university-research cooperation has not yet been formed in the field of intelligent tea harvesting.
2.2 Vegetables intelligent harvesting technology
2.2.1 Technology evolution
Figure 2 is drawn according to the number of patent applications in the field of intelligent vegetables technology.It can be seen from Figure 2 that the technology is in the embryonic stage from 2013 to 2014.In this stage,the number of patent applications is less,and there are not many applicants who pay attention to the development of technology in this field.The number of patent applications in this field increased significantly in 2015 and reached a peak.Although the number of patents decreased significantly in 2016,it soon turned upward again.In 2018,the number of patent applications reached the second highest,but the number of patent applications turned downward again in 2019,and the follow-up development trend is still unclear.Overall,technological development from 2015 to 2019 is in a period of fluctuating development.
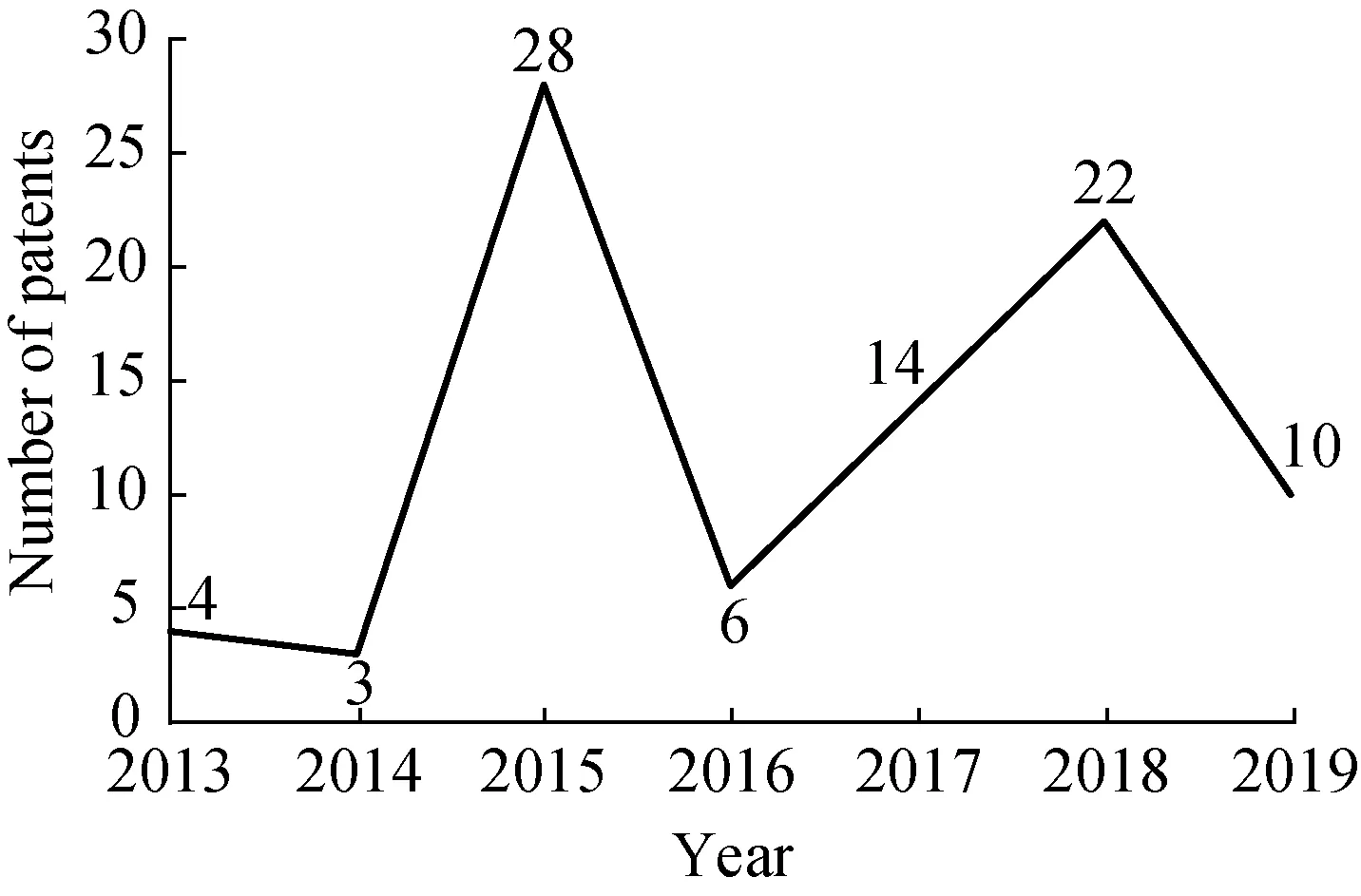
Fig.2 Technology evolution
2.2.2 Major innovation institutions
The top 8 applicants for patent applications are Shandong Agricultural University,Jiangsu University,Shanghai Jiaotong University,Jiangsu Vocational College of Agriculture and Forestry,Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Chongqing Academy of Agricultural Sciences,and Qingdao Agricultural University.These eightapplicants are the major innovative institutions in the field of intelligent vegetables harvesting.
Shandong Agricultural University and Jiangsu University,which ranked first and second,both started early inthefield.Shandong Agricultural University’s patent output peaked in 2015 when the applicant applied for 12 patents related to leafy vegetables harvesting robots.But after 2016,the applicant no longer pays attention to the field.Jiangsu University has sustained patent output from 2013 to 2019,indicating that the applicant has a strong ability of continuous innovation in this field.Shanghai Jiaotong University and Jiangsu Vocational and Technical College of Agriculture and Forestry also started early,both of which applied for two patents in 2013 and 2015,but the applicant stopped paying attention to technological development in this field after 2015.Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Chongqing Academy of Agricultural Sciences,and Beijing University of Technology all paid attention to this field relatively late,and the patent output time was concentrated in 2018 and 2019.
2.2.3 Key R &D teams
Through the analysis of inventors,the composition of the core innovation teams of 8 major innovation institutions is sorted out,as follows:
The R &D team of Shandong Agricultural University:Liu Xuemei,Yuan Jin,Liu Chengliang,Li Ming,Li Yang
The R &D team of Jiangsu University:Liu Jizhan,Ding Xinming,Liu Chengyang,Bian Lina,Wu Mingcong
The R &D team of Shanghai Jiaotong University:Liu Chengliang,Liu Xiaosong,Lu Tiansheng,Tang Dongmei,You Jiaxin
The R &D team of Beijing University of Technology:Zhang Shuo,Liang Yongzhi,Gao Guohua,Liu Jingfang
The R &D team of Jiangsu Vocational and Technical College of Agriculture and Forestry:Liu Yonghua,Wu Yujuan,Ding Longbao,Wu Dan,Yin Hua
The R &D team of Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences:Hou Xilin,Lu Xiaolan,Tang Yuxin,Bai Zongchun,Wang Min
The R &D team of Chongqing Academy of Agricultural Sciences:Shi Jin,Wang Yumei,Zheng Jishu,Gao Lihong,Zeng Baigong
The R &D team of Qingdao Agricultural University:Li Xincheng,Wang Jiasheng,Yuan Yuliang,Zhang Jian,Li Yefeng
2.2.4 Key technology of the main applicant’s concerns
The key technologies of the eight main applicants’concerns are as follows (Table 3).
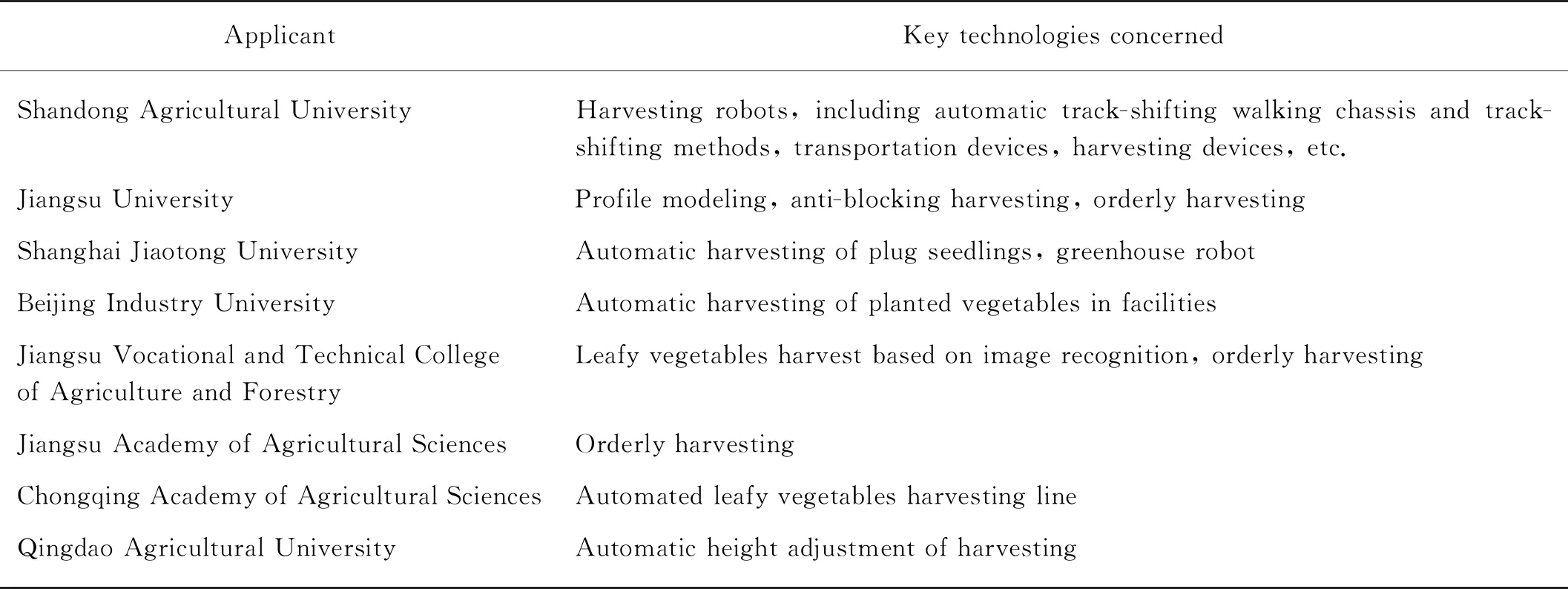
Tab.3 Technologies concerned by the main applicant
2.2.5 Core patents
According to the value of theV2index,fourcore patents in the field of intelligent vegetables harvesting technology are sorted out (Table 4).

Tab.4 Core patents
2.2.6 Applicant’s cooperation
According to the co-occurrence analysis of the applicants in this field,it is found that among the top 20 applicants,except for the patents jointly applied by Nanjing Institute of Agricultural Mechanization,Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and Yuantian Agricultural Machinery Research Institute of Lianyungang City,none of the other applicants have ever cooperated with other applicants,which shows that the overall intensity of industry-university-research cooperation in this field is on the low side.
3 Conclusions and suggestions
Through the analysis of patents on tea and vegetables intelligent harvesting technology,the following conclusions are drawn:
From the perspective of the development trend of patented technology,the tea intelligent harvesting technology was in the embryonic stage from 2011 to 2013 and was in rapid development stage from 2014 to 2018.The vegetables intelligent harvesting technology was in the embryonic stage from 2013 to 2014 and was in a period of fluctuating development from 2015 to 2019.From the perspective of major innovation institutions,applicants such as Zhejiang University of Technology and Nanjing Forestry University lead the innovation of tea intelligent harvesting technology in China,and Shandong Agricultural University and Jiangsu University are at the forefront of technology innovation for intelligent vegetables harvesting.These major innovation institutions have different technical concerns,but they all have certain technical deep ploughing capabilities in the field and have produced a number of core patents that played an important role in promoting industrial technological innovation.From the perspective of applicant cooperation,the intensity of industry-university-research cooperation in the field of tea and vegetables intelligent harvesting is low,and a good situation of industry-university-research cooperation has not yet been formed.From the perspective of important R &D teams,a group of core inventors hasmade positive contributions to the innovation of tea and vegetables intelligent harvesting technology.
Based on this,suggestions are made for the development of tea and vegetables intelligent harvesting technology:first,adhere to policy support and strategic guidance to improve the innovative quality of tea and intelligent vegetables harvesting technology;second,increase efforts to support a number of superior innovation institutions,create a batch of high-value patents and patent portfolios,demonstrate and lead the improvement of innovation capabilities;third,make good use of the scientific and technological innovation resources of major innovation institutions and key innovation teams,strengthen collaborative innovation,and strive to achieve major breakthroughs in key core technologies and promote the organic connection between innovation factors and production factors at the industrial level;the fourth is to promote the patent application,implementation and protection of tea and vegetables intelligent harvesting technology in multiple ways,focusing on the improvement of patent quality and patent overseas layout,and striving to seize the commanding heights of technology;the fifth is to improve technical services system,strengthen the demonstration,popularization and application of new technologies for intelligent harvesting of vegetables and tea,and promote the transformation of scientific and technological achievements.Sixth,increase the utilization of core patents in the field of vegetables and tea intelligent harvesting,improve the starting point of research and development,shorten research and development time,and build a number of peripheral patents around the core patents to form an overall competitive advantage.
