基于NF-κB信号通路探讨氯化镧抑制高磷致血管平滑肌细胞钙化的机制
2021-10-29谷超赵璐璐李刚高原王胜男李晓佳元晓荣王琪雯包勒朝鲁韩瑞兰
谷超 赵璐璐 李刚 高原 王胜男 李晓佳 元晓荣 王琪雯 包勒朝鲁 韩瑞兰


中图分类号 R692.5;R589.5;R965 文献标志码 A 文章编号 1001-0408(2021)20-2458-09
DOI 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2021.20.05
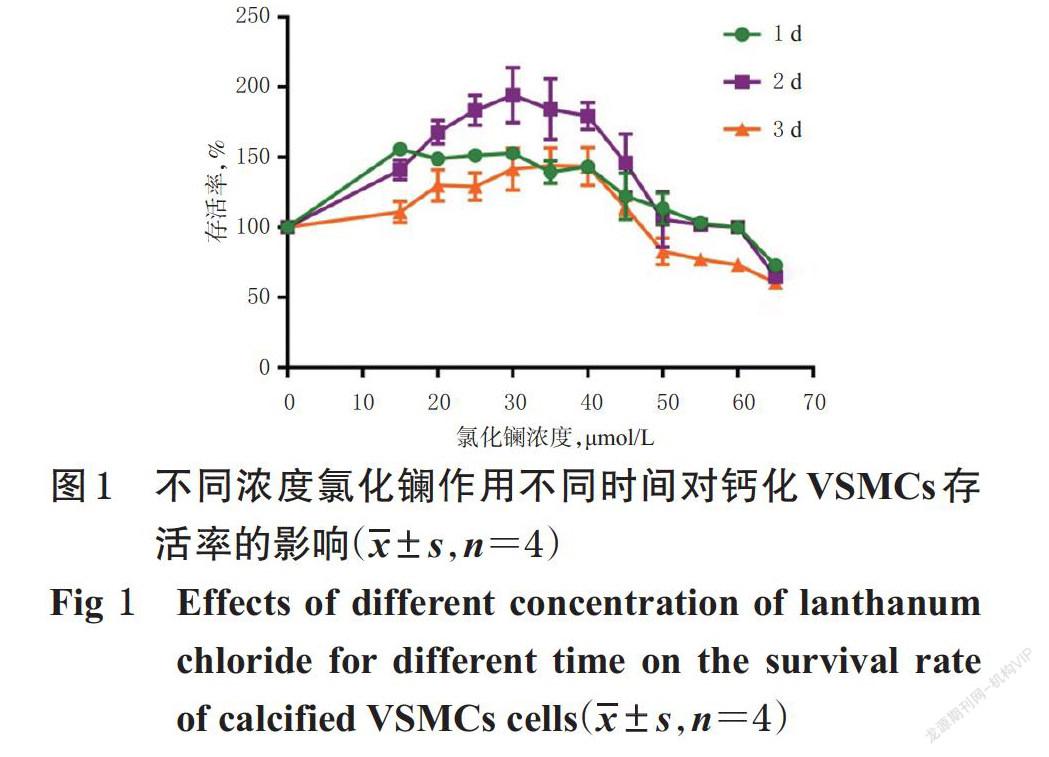
摘 要 目的:探讨氯化镧对高磷致血管平滑肌细胞(VSMCs)钙化的抑制作用及其机制。方法:在MTT法筛选氯化镧作用浓度及时间的基础上,将人VSMCs分为对照组(1 mmol/L磷溶液)、氯化镧高浓度对照组(1 mmol/L磷溶液+60 μmol/L氯化镧)、模型组(3 mmol/L磷溶液)、氯化钠组(3 mmol/L磷溶液+180 μmol/L氯化钠)、核因子κB(NF-κB)信号通路激动剂+氯化镧组(3 mmol/L磷溶液+1 μg/mL脂多糖+60 μmol/L氯化镧)、阳性对照组(3 mmol/L磷溶液+100 μmol/L焦磷酸钠)和氯化镧低、中、高浓度组(3 mmol/L磷溶液+15、30、60 μmol/L氯化镧),采用茜素红S染色法和Von Kossa染色法检测经磷溶液作用6 d、相应药物作用2 d后各组细胞的钙化情况,采用Western blot法检测细胞中肿瘤坏死因子受体相关蛋白6(TRAF6)、核因子κB抑制蛋白α(IκBα)、NF-κB p65、骨形态发生蛋白2(BMP-2)、平滑肌22α(SM22α)、Runt相关转录因子2(Runx2)蛋白的表达水平,采用实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应法检测细胞中TRAF6、IκBα、BMP-2、SM22α、Runx2 mRNA的表达水平。结果:与对照组比较,氯化镧高浓度对照组细胞没有出现钙化,模型组和氯化钠组细胞均出现明显钙化且光密度(OD)值均显著升高(P<0.01),细胞质中TRAF6、BMP-2蛋白及其mRNA的表達水平和Runx2 mRNA的表达水平以及细胞核中NF-κB p65、Runx2蛋白的表达水平均显著升高(P<0.01),细胞质中IκBα、SM22α蛋白及其mRNA的表达水平和NF-κB p65蛋白的表达水平均显著降低(P<0.01)。与模型组比较,氯化镧各浓度组和阳性对照组细胞的钙化均明显改善,OD值均显著降低,上述蛋白及mRNA的表达水平均不同程度逆转(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与氯化镧高浓度组比较,NF-κB信号通路激动剂+氯化镧组细胞出现明显钙化,OD值显著升高,细胞质以及细胞核中上述指标均显著逆转(P<0.05或P<0.01)。结论:氯化镧可抑制高磷诱导的VSMCs钙化,其机制可能与抑制NF-κB信号通路活化有关。
关键词 氯化镧;高磷;血管钙化;核因子κB信号通路;人血管平滑肌细胞
Discussion on the Inhibitory Mechanism of Lanthanum Chloride on Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Calcification Induced by High Phosphorus Based on NF-κB Signaling Pathway
GU Chao1,ZHAO Lulu1,LI Gang1,GAO Yuan1,WANG Shengnan1,LI Xiaojia1,YUAN Xiaorong1,WANG Qiwen1,Baolechaolu2,HAN Ruilan1(1. School of Pharmacy, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, China; 2. Collaborative Innovation Center of Mongolian Medicine,Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010110, China)
ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To discuss the inhibitory effect of lanthanum chloride on the calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) induced by high phosphorus and its mechanism. METHODS: On the basis of screening the action concentration and time of lanthanum chloride by MTT method, human VSMCs were divided into control group (1 mmol/L phosphorus solution), lanthanum chloride high concentration control group (1 mmol/L phosphorus solution+60 μmol/L lanthanum chloride), model group (3 mmol/L phosphorus solution), sodium chloride group (3 mmol/L phosphorus solution+180 μmol/L sodium chloride), nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway agonist+lanthanum chloride group (3 mmol/L phosphorus solution+1 μg/mL lipopolysaccharide+60 μmol/L lanthanum chloride), positive control group (3 mmol/L phosphorus solution+100 μmol/L sodium pyrophosphate), and lanthanum chloride low, medium, and high concentration groups (3 mmol/L phosphorus solution+15, 30, 60 μmol/L lanthanum chloride). Alizarin red S staining and Von Kossa staining were used to detect cell calcification in each group after treated with phosphorus solution for 6 d and relevant medicine for 2 d. Western blot assay was used to detect the protein expression of TNF-α receptor associated protein 6 (TRAF6), nuclear factor κB inhibitor protein α (IκBα), NF-κB p65, bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2), smooth muscle 22 α (SM22α) and Runt related transcription factor 2 (Runx2). Real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to detect mRNA expression of TRAF6, IκBα, BMP-2, SM22α and Runx2. RESULTS: Compared with control group, no cell calcification was observed in the lanthanum chloride high concentration control group, while obvious cell calcification and significant increase of OD value were observed in model group and sodium chloride group (P<0.01); protein and mRNA expression of TRAF6 and BMP-2 in cytoplasm as well as mRNA expression of Runx2, protein expression of NF-κB p65 and Runx2 in nucleus were significantly increased (P<0.01); protein and mRNA expression of IκBα and SM22α as well as protein expression of NF-κB p65 in cytoplasm were significantly decreased (P<0.01). Compared with model group, cell calcification was significantly improved in lanthanum chloride groups and positive control group, while OD values were significantly reduced; the expression levels of the above-mentioned protein and mRNA were reversed to varying degrees (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Compared with lanthanum chloride high concentration group, obvious cell calcification was observed in NF-κB signaling pathway agonist+lanthanum chloride group, and OD value was significantly increased; the above indexes were significantly reversed in cytoplasm and nucleus (P<0.05 or P<0.01). CONCLUSIONS: Lanthanum chloride can inhibit the calcification of VSMCs induced by high phosphorus, and its mechanism may be related to the inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway activation.
