博弈理论视角下中药产业技术创新战略联盟信任机制的构建
2021-10-29华东史安娜
华东 史安娜
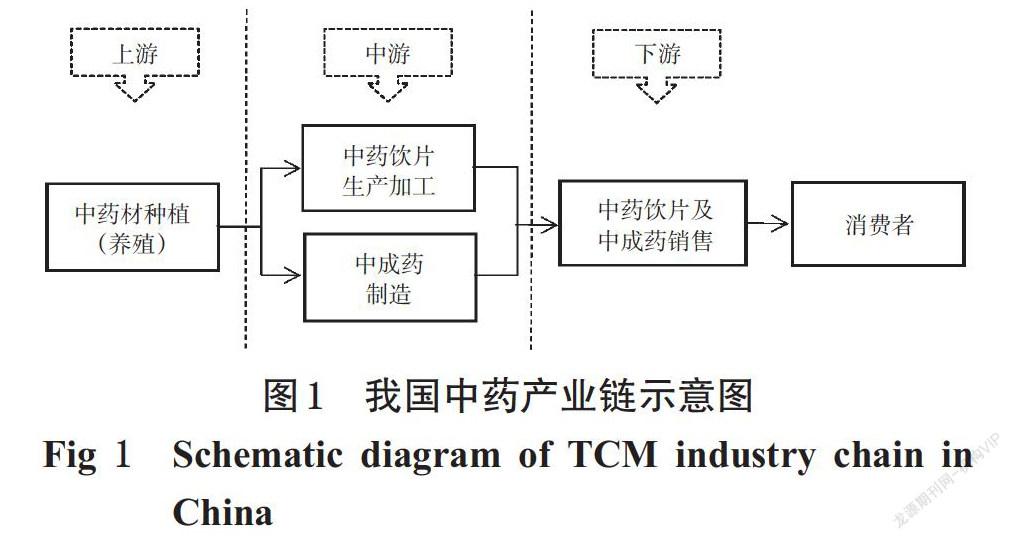
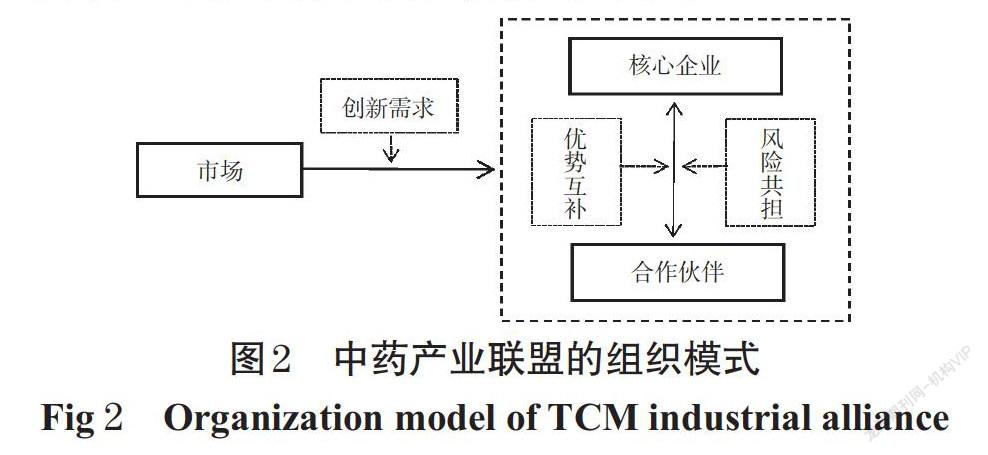
中圖分类号 R288;R95 文献标志码 A 文章编号 1001-0408(2021)20-2438-07
DOI 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2021.20.02
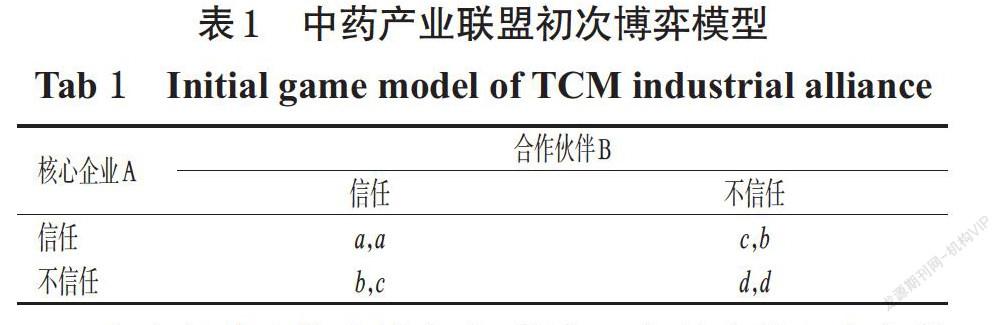
摘 要 目的:为促进我国中药产业技术创新战略联盟(以下简称“中药产业联盟”)的稳定运行和中药产业的转型升级提供参考。方法:运用博弈理论,构建道德自律下中药产业联盟成员合作信任的初次博弈、重复博弈模型以及外部约束力量下的混合策略博弈模型,分析中药产业联盟信任机制构建的主要影响因素,并为我国中药产业联盟信任机制的构建提出对策与建议。结果与结论:初次博弈模型和有限次重复博弈模型均显示,(不信任,不信任)的策略组合为唯一纳什均衡,此时联盟整体得益最小,联盟创新效率和稳定性十分低下。无限次重复博弈模型显示,(信任,信任)的策略组合为该重复博弈的均衡路径,博弈双方因守信而收获的长期得益大于失信所带来的得益,此时联盟总得益最大,但需要博弈双方有充分的耐心和足够多的博弈次数。混合策略博弈模型显示,在背信损失足够大且上不封顶的情况下,联盟成员均选择彼此信任,(信任,信任)的策略为唯一纳什均衡;在背信损失比较小且越接近上限时,联盟成员越不愿意选择守信,此时外部约束力量较弱。博弈次数的多少、博弈信息的完全性和外部约束力量的强弱是影响中药产业联盟信任机制构建的关键因素。建议中药产业联盟内部应建立高效的沟通体系、透明的信息公开制度和完善的奖惩制度,并充分发挥政府及非政府第三方的作用,以促进我国中药产业联盟的稳定运行。
关键词 博弈理论;中药产业;产业技术创新战略联盟;信任机制
Construction of Trust Mechanism about TCM Industrial Technology Innovation Strategic Alliance from the Perspective of Game Theory
HUA Dong1,2,SHI Anna1(1. Business School, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China;2. School of Health Economic and Management, Nanjing University of TCM, Nanjing 210023, China)
ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To provide reference for the stable operation of TCM industrial technology innovation strategic alliance (called “TCM industrial alliance” for short) as well as the transformation and upgrading of TCM industry. METHODS: The game theory was adopted to construct the initial game model and repeated game model of cooperative trust among the members of TCM industrial alliance under moral self-discipline, and mixed strategy game model under external constraints. The main influential factors of trust mechanism construction for TCM industrial alliance were analyzed, and countermeasures and suggestions were put forward for the trust mechanism construction of TCM industrial alliance in China. RESULTS & CONCLUTIONS: Both the initial game model and the finite repeated game model showed that the strategy combination of (distrust, distrust) was the only Nash equilibrium. At this time, the overall benefit of the alliance was the smallest, and the innovation efficiency and stability of the alliance were very low. The infinite repeated game model showed that the strategy combination of (trust, trust) was the equilibrium path of the repeated game. The long-term benefits of both sides of the game due to trustworthiness were greater than those obtained by dishonesty. At this time, the total benefits of the alliance were the largest, but both sides of the game needed to have sufficient patience and enough game times. The mixed strategy game model showed that when the loss of breach of trust was large enough and there was no upper limit, the alliance members chose to trust each other, and the strategy of (trust, trust) was the only Nash equilibrium; when the loss of breach of trust was relatively small and closer to the upper limit, the more reluctant the alliance members were to choose to keep faith, and the external constraint force was weak. The number of games, the completeness of game information and the strength of external constraints were the key factors to establish alliance trust mechanism. It is suggested that an efficient communication system, transparent information disclosure system and perfect reward and punishment system should be established within TCM industrial alliance, and the role of government and non-governmental third parties should be fully played to promote the stable operation of TCM industrial alliance in China.
