A case of resection of giant decidual polyp in first trimester
2021-10-20YiLeiLiYuanYuanZhangYongZhongGu
Yi-Lei Li ,Yuan-Yuan Zhang ,Yong-Zhong Gu
1Department of Obstetrics,Shandong Provincial Hospital,Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University,Jinan,250021,China.
Abstract A 29-years-old primiparous woman,presented at 9 weeks 2 days pregnant due to moderate vaginal bleeding with neoplasm prolapsed from vagina for two days.She have suffered from recurrent vaginal spotting for about 4 weeks,and took dydrogesterone more than 3 weeks following the doctor's instructions at the local hospital.She had diagnosed as an endometrial polyp of about 1.3×0.6 cm in size by ultrasound scan before pregnancy.At present,the color doppler ultrasound revealed that a giant decidual polyp occupied the whole cervix canal,with wide pedicle base arised from the middle and lower part of the uterine cavity,and the lower part prolapsed the outside of cervix.After hospital admission,the speculum examination showed that a dark purple neoplasm with a size of about 5×3×3cm in the vagina protruding out of the cervical canal,on which surface there was a spontaneous bleeding point.The blood test findings included a WBC count of 8.59×910/L and C-reactive protein level of 3.02ng/L.Her temperature was 36.2℃.Cefuroxime was given to prevent infection after admission.Compression was given to stop bleeding,but there was still active bleeding on the surface of the polyp the next day.Therefore,a ultrasound-guided torsion polypectomy was performed in emergency.In the therter,we twisted the neoplastic tissues by oval forceps taking a step-by-step approach,until 1cm above the outsise of cervix.At this point,ultrasound scan showed that the pregnant sac was obviously pulled by external forces.So,we stop the polypectomy,leaving a small portion of the giant polyp.Ceftrixone sodium and dydrogesterone were given after the operation and a small amount of vaginal bleeding lasted for 6 days without obvious abdominal pain.A medium to strong echo of about 1.7×0.6×0.9cm in the cervical canal was showed by color doppler ultrasound,which continued upward to the upper part of the cervical os.Histopathological examination revealed a decidual polyp.The patient had no abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding during pregnancy.She had a premature rupture of membranes and gave birth to a baby with the weight of 3300g through vaginal at 37 weeks and 1 day of gestation.
Keywords:decidual polyp
A 29-years-old primiparous woman,presented at 9 weeks 2 days pregnant due to moderate vaginal bleeding with neoplasm prolapsed from vagina for two days.She have suffered from recurrent vaginal spotting for about 4 weeks,and took dydrogesterone more than 3 weeks following the doctor's instructions at the local hospital.She had diagnosed as an endometrial polyp of about 1.3×0.6 cm in size by ultrasound scan before pregnancy.At present,the color doppler ultrasound revealed that a giant decidual polyp occupied the whole cervix canal,with wide pedicle base arised from the middle and lower part of the uterine cavity,and the lower part prolapsed the outside of cervix (Fig.1a).
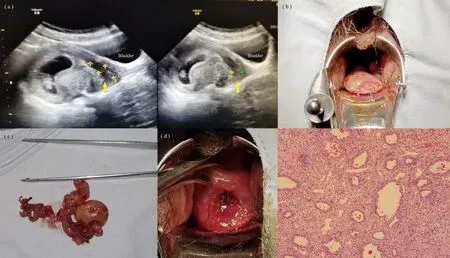

Figure 1.(a).Doppler image shows the decidual polyp (b).The decidual polyp protruding out of the cervical noted on speculum examination (c).The decidual polyp resected from uterine (d).After polypectomy,the outside of the cervix was clearly visible.(e).Histopathological examination confirmed decidual polyp.
After hospital admission,the speculum examination showed that a dark purple neoplasm with a size of about 5×3×3cm in the vagina protruding out of the cervical canal,on which surface there was a spontaneous bleeding point (Fig.1b).The blood test findings included a WBC count of 8.59×910/L and C-reactive protein level of 3.02ng/L.Her temperature was 36.2℃.Cefuroxime was given to prevent infection after admission.Compression was given to stop bleeding,but there was still active bleeding on the surface of the polyp the next day.Therefore,a ultrasound-guided torsion polypectomy was performed in emergency.In the therter,we twisted the neoplastic tissues by oval forceps taking a step-by-step approach,until 1cm above the outsise of cervix.At this point,ultrasound scan showed that the pregnant sac was obviously pulled by external forces.So,we stop the polypectomy,leaving a small portion of the giant polyp (Fig.1c,d).Ceftrixone sodium and dydrogesterone were given after the operation and a small amount of vaginal bleeding lasted for 6 days without obvious abdominal pain.A medium to strong echo of about 1.7×0.6×0.9cm in the cervical canal was showed by color doppler ultrasound,which continued upward to the upper part of the cervical os.Histopathological examination revealed a decidual polyp (Fig.1e).
The patient had no abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding during pregnancy.She had a premature rupture of membranes and gave birth to a baby with the weight of 3300g through vaginal at 37 weeks and 1 day of gestation.
Discussion
Decidual polyps include extruded fragments of the decidua,the cevical polyps and endometrial polyps which occur decidual reaction.Their clinical manifestations are similar to cervical polyps.There are no guidelines and consensus on the treatment of cervical polyps in pregnancy.Some authors hold that polyps should be removed during pregnancy.On one hand polyps are caused by local inflammation and removal of polyps can reduce the incidence of chorioamnionitis [1].On the other hand cervical polyps in early pregnancy are risk factors for late abortion and spontaneous preterm birth [2].Furthermore polyps increase the occurrence of cervical insufficiency [2].However some authors believes that it's the resection of polyps,especially decidual polyps [3],may increase the risk of miscarriage [4],infection,premature rupture of membranes and preterm delivery.Sameer Hamadeh et al.[5] reported a case of huge endocervical polyp managed conservatively from 32 to 38 weeks gestation.Therefore conservative treatment is recommended in pregnancy except in cases in which the polyps are suspected to be malignant [6].
Resection of large and bleeding cervical polyps is generally recommended for pregnancy patients in our hospital.The decidual polyp was formed by decidual reaction of the endometrial polyp found before pregnancy in this case.It grew rapidly and protruded from the cervix,and bleed for about 4 weeks.Compression to stop bleeding was ineffective.Miscarriage would have happened without resection the polyp.
Fukuta et al.[4] reported that bleeding before polypectomy is one of the clinically relevant predictors of premature birth.Therefore,bleeding after polypectomy may lead to poor outcomes.Polypectomy is not necessary if the decidual polyps are not accompanied by bleeding.If the polyps need to be surgically removed,stopping bleeding thoroughly during poylpectomy may reduce the risk of premature delivery and miscarriage.The methods of polypectomy include traditional torsion polypectomy,suture ligation polypectomy and electrocoagulation polypectomy.Aoki et al.[7] reported a case of premature rupture of membrane at 22 weeks of gestation who had undergone ligation polypectomy using an Endoloop polydioxanone suture IITM.They found decidual polyps moved upwards with the progression of pregnancy and the suture could have been responsible for miscarriage and preterm delivery.In our case,as the ultrasound revealed that upper part of the poly connected to the middle and lower part of the uterine cavity,the risk of bleeding was high.We planned to remove the polyp by torsion.If the wound was bleeding,we could try bipolar electrocoagulation hemostasis with the help of endoscopy.
杂志排行
Clinical Research Communications的其它文章
- Effect of feedback health education on postoperative rehabilitation of patients with lumbar disc herniation:a cluster randomised trials
- Clinical observation of Guipi Decoction Combined with non steroidal drugs on sleep in elderly patients with acute traumatic pain and Qi deficiency constitution
- Effects of crude thymus gland extract on some physiological and biochemical parameters in local rabbits
- A clinical protocol:A double-blinded,randomized controlled trial on the effect of traditional Chinese medicine formula Shoutai Pill in the treatment of threatened abortion
