Musculoskeletal problems and expressed practices of body mechanics among nursing officers at All lndia lnstitute of Medical Sciences Jodhpur,Rajasthan,lndia
2021-10-12SubhashKumarSAINIVandnaPANDEYAshokKUMARAbhayELHENCE
Subhash Kumar SAINI ,Vandna PANDEY ,Ashok KUMAR ,Abhay ELHENCE
1AIIMS,Jodhpur,2Department of College of Nursing,AIIMS,Jodhpur,3Department of Orthopaedics,AIIMS,Jodhpur,India
ABSTRACT Objective:The objective of the study was to identify musculoskeletal problems (MSPs) among nursing officers.Materials and Methods:A nonexperimental research design was used.Two hundred and seventy nursing officers were selected by purposive sampling technique.The standardized Nordic questionnaire was used to assess the MSPs and self-structured three-point rating scale was used to assess expressed practice of body mechanics of nursing officers.Results:The study findings revealed that 64.4% of nursing officers suffered from MSP such as ache,pain,and discomfort during the past 12 months and 43.7% during the past 7 days.The problem in the low back and the neck were highest 45.1% and 22.2%,respectively.This was followed by MSP of the upper back (14.0%),ankles (13.7%),knees (10.7%),shoulder (10.3%),hip/thighs (5.9%),wrists (4.4%),and elbows (3.3%).Around 49.2% complained that MSPs limit their work.There was significant association of MSP with selected personal variables like body mass index (P=0.001) and family history (P=0.02).There were also significant association of expressed practices of body mechanics with gender (P=0.01),area of current work (P=0.00),professional experience (P=0.03) and physical activity (P=0.00).Conclusion:The study indicates the large number of nursing officers had MSPs with the two most common sites being the lower back and the neck.This creates a need for prompt hospital education programs aimed to create awareness among nursing officers on the prevalence of MSPs.
Keywords:Expressed practice,musculoskeletal problems,nursing officers
INTRODUCTION
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) or problems are the injuries and disorders that affect the muscles,tendons,ligaments,cartilage,supported blood vessels,nerves,discs,or other soft tissues and joints of the body.They are caused or aggravated primarily by work itself and they can affect the upper and lower limb extremities,neck,shoulders,lower and upper back.[1]The most important functions of the musculoskeletal system are to support,protect the body,and foster movement of the extremities.[2]
MSDs cover a broad range of health problems associated with repetitive and strenuous work.These health problems start from discomfort,minor aches,and pains,to more serious medical conditions which can lead to permanent disability.Millions of European workers are affected by MSDs every year.Nowadays,lower limb work-related MSDs are also been recognized as disorders that may be associated with occupational activity.[1]Around the world,the most common and notable problem is chronic low back pain among all health care personnel including nursing personnel.Proper maintenance of body posture is important in decreasing low back pain.[3]According to the department of labor of Bureau of labor statistics,low back pain/injury is the most common work-related musculoskeletal health problem among nursing officers,followed by neck,shoulders,arms,wrist,and knee disorders.[4]
Registered nurses ranked fifth who use manual lifting and moving of the instruments and handling the patient and have musculoskeletal problems (MSPs).Proper body mechanics technique is moving,handling,lifting of patients and instruments or heavy objects in a proper manner.[5]Tinubuet al.[6]described a prevalence of 78% among Nigerian nurses,with work-related MSPs associated with working in the same position for long periods,increased patient load,and transferring/lifting of patients.
Body mechanics is a term used to describe the way of moving in daily lives.It includes how we hold our body when we sit,stand,lift,carry,bend,and sleep.When we do not use body mechanics in the correct way,the spine is subjected to abnormal stresses that over time can lead to degeneration of spinal structures like discs and joints injury and abnormal wear and tear.That’s why it is important to learn about the principle of proper body mechanics and it is vitally important for keeping our spine healthy.[7]Nurses are more prone to work-related physical injuries which results in symptoms like back pain and other MSPs.Therefore,nursing officers require incorporating knowledge and skills into the practice of body mechanics.Many nursing activities require muscle exertion to reduce the risk of musculoskeletal injury to the nursing officers while transferring the patients;the nursing officers must know about the proper body mechanics.The nursing officers should understand how to coordinate body movement which involves integrated functioning of the musculoskeletal system and nervous system.[8]Therefore,the present study aimed to explore MSPs and expressed practices of body mechanics among nursing officers.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A cross-sectional descriptive survey study was conducted at All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS),Jodhpur.The sample of the study was selected from different areas of the hospital.Sample size calculation was based on proportion formula (1 -n/N) × (p×q)/d2and sample size was 270.Nonprobability purposive sampling was adopted to represent 270 Nursing officers.Inclusion criteria for selecting the nursing officers who were willing to participate in the study and those who were present at the time of data collection.Exclusion criteria were nursing officers having chronic MSPs such as osteoarthritis,gout,scoliosis,etc.,who have undergone any musculoskeletal surgery,and nursing officers who were pregnant.Pilot study was conducted on 30 nursing officers and that was found feasible.
Data collection tool
The self-structured questionnaire and standardized Nordic questionnaire were tool for data collection.
Personal variable datasheet
The tool includes 13 personal variables that are age,gender,height,weight,body mass index (BMI),marital status,professional qualification,area of current work,professional experience,working hours per week,use of any musculoskeletal relaxation techniques,physical activities and family history of MSPs.
Standardized questionnaire
Standardized Nordic Questionnaire for assessing musculoskeletal symptoms was used.[9]This questionnaire evaluates the MSPs in nine regions of the body,namely neck,shoulders,upper back,elbow,lower back,wrists/hands,hips/thigh/buttocks,knees,and ankle/feet in the last 12 months and within 7 days,respectively.The questionnaire also evaluates the normal activities prevented for an individual due to the occurrence of MSPs in one or more of these regions of the body.The questionnaire also find the existing status of MSPs in terms of pain,trouble,and ache in three specific regions of the body,i.e.neck,lower back,and shoulders.Some section of the Nordic questionnaire identifies the problems faced by the nursing officers that are directly or indirectly associated with MSPs in these specific body regions.These problems may be the number of days pain persisted,leisure and work activity reduced,visit to doctor,swapping of duties,etc.
Self-structured rating scale for expressed practices of body mechanics
Three-point rating scale was used and it consisted of 20 items.The scale consisted of positive items only.The maximum score was 60 and the minimum score was 20.The level of expressed practice was categorized as Good practice (Score 47-60),Average practice (33-46),Poor practice (20-32).The interpretation was mean-based and categories under the best and least used practice of body mechanics.The tool was validated by experts and the reliability of tool was determined by Cronbach’s alpha (0.75).
Ethical considerations
Ethical approval was taken from the ethical committee AIIMS,Jodhpur (Reference Number:AIIMS/IEC/0219-20/770).
Written informed consent was obtained from each study subject.Confidentiality of data was maintained.Permission of standardized Nordic questionnaire was obtained.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed by SPSS 16 version (http://www.winwrap.com).The data were summarized as mean,standard deviation,frequency,and percentage.The Chi-square test was used to test the association.
RESULTS
Description of personal variables of nursing officers
Table 1 depicts that out of 270,168 (62.2%) nursing officers were in the age group below 30 years of age.193 (71.5%) Nursing officers were male.Approximately 52.9% of nursing officers had normal BMI.Most of them (71.1%) were married.Majority of them (60.0%) were bachelor’s degree holders.Approximately 40.4% were working in ICU.Almost 74.4% of nursing officers had 1-5 years of professional experiences.About 64.8% of participants were working <45 h in a week.Only 19.3% of nursing officers were using musculoskeletal relaxation techniques such as gym,yoga,and meditation.Most of them (82.2%) were using physical activity like walking,running,games,and swimming.About 15.9% of nursing officers were reported the family history of MSPs like arthritis,backache,etc.
Finding musculoskeletal problems among nursing officers
Table 2 depicts that out of 270,174 (64.4%) nursing officers were suffering from MSPs such as ache,pain,and discomfort during the last 12 months.Around 133 (49.2%) reported that MSPs obstructed their works.Around 118 (43.7%) of nursing officers had MSPs during the last 7 days.In addition,the problems in the low back and the neck were highest at 45.1% and 22.2%.This was followed by MSPs of the upper back (14.0%),ankles (13.7%),knees (10.7%),shoulder (10.3%),hip/thighs (5.9%),wrists (4.4%),and elbows (3.3%).
The data presented in Table 3 shows that out of 122,around 15 (12.2%) respondents were hospitalized due to low back trouble and 18.8% of respondents have changed their job or duties due to the same trouble.The work activity and leisure activity were reduced in 59.2% and 57.5%,respectively.About 47.7% of the nursing officers have visited a doctor,physiotherapist,chiropractor or other such person due to low back trouble in the past 12 months.
The data presented in the Table 4 showed that out of 174,60 (22.2%) nursing officers have complaint of neck trouble.Out of 60,3 (5%) respondents hurt their neck in any accident and 21.6% of them have changed their job or duties due toneck trouble.The work activity and leisure activity were reduced in 70.6% and 56.8%,respectively.About 58.6% of nursing officers have visited a doctor,physiotherapist,chiropractor or other such person in the last 12 months.
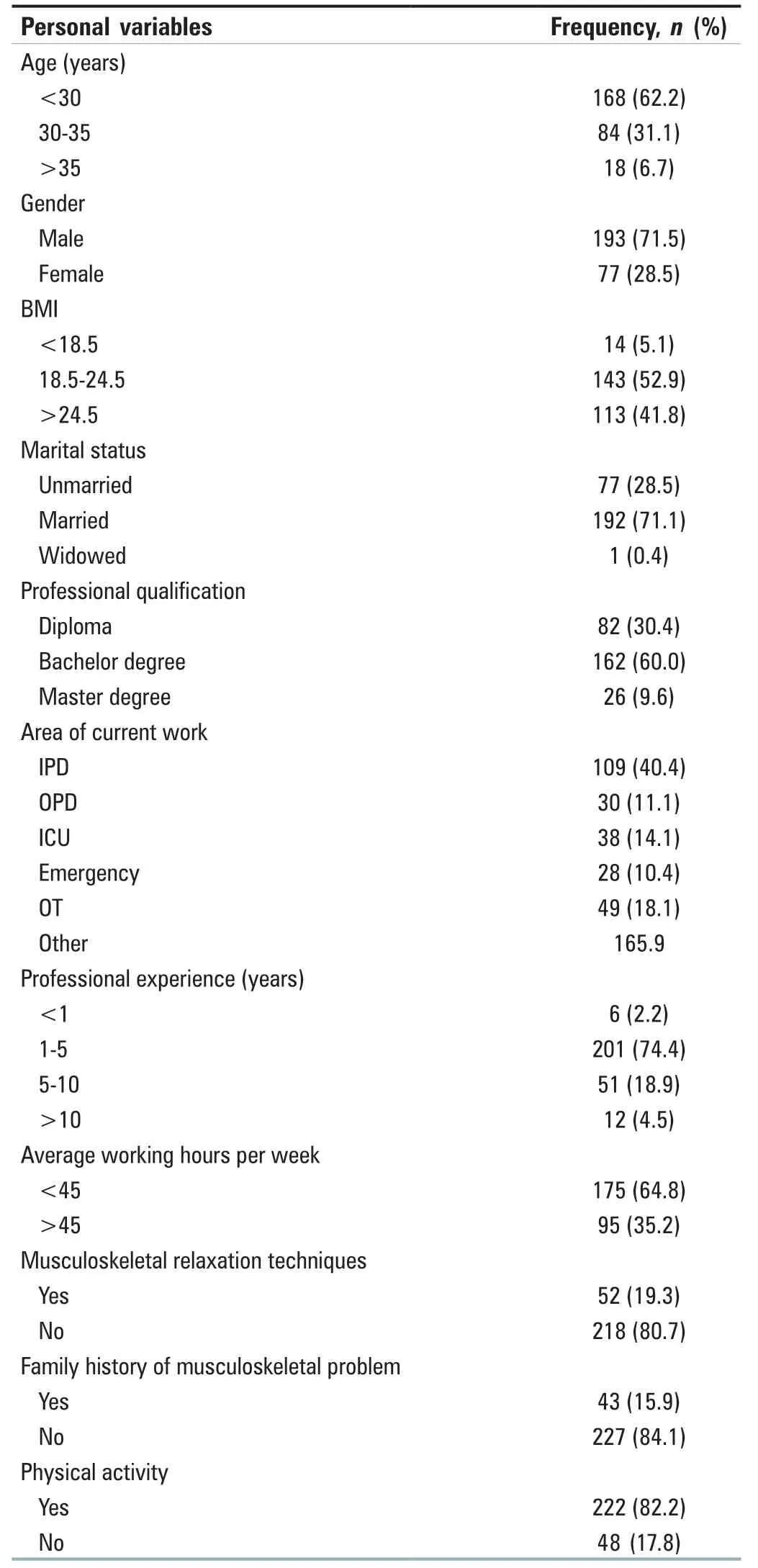
Table 1:Distribution of nursing officers as per personal variable (n=270)
Table 5 depicts that out of 174,28 (10.3%) nursing officers reported shoulder trouble,only 21.4% of respondents hurttheir shoulder in any accident and 32.4% of them have changed their job or duties due to that trouble.The work activity and leisure activity were reduced in 64.8% and 46.4%,respectively.53.5% of nursing officers have visited doctors,physiotherapists,chiropractors,or other such persons in the past 12 months.
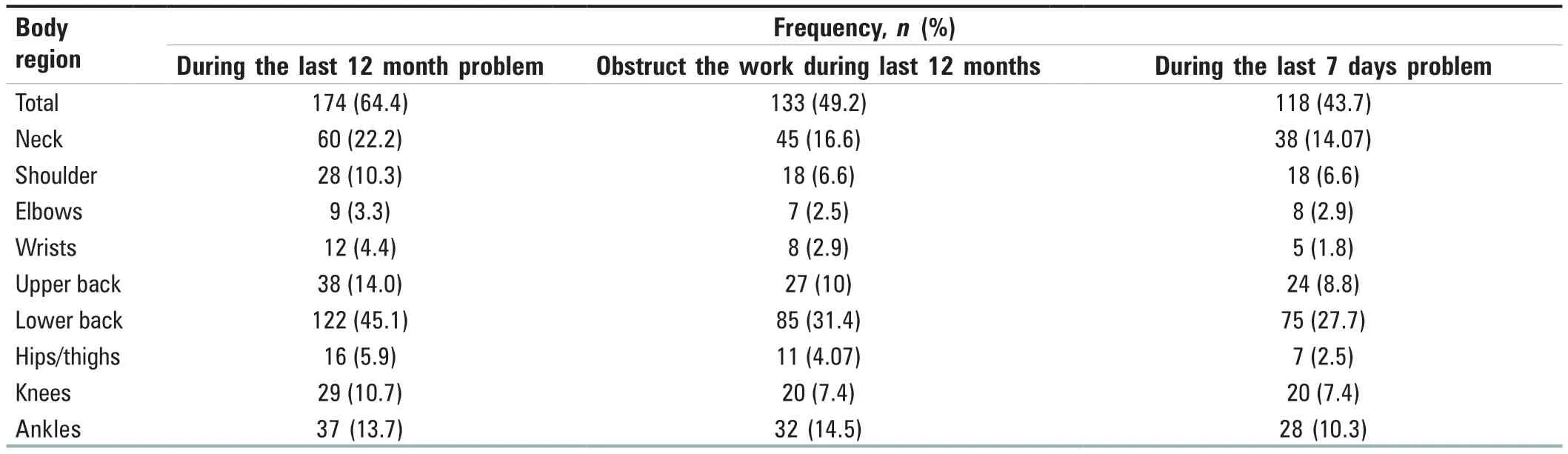
Table 2:Distribution of musculoskeletal problems in terms different body regions (n=270)
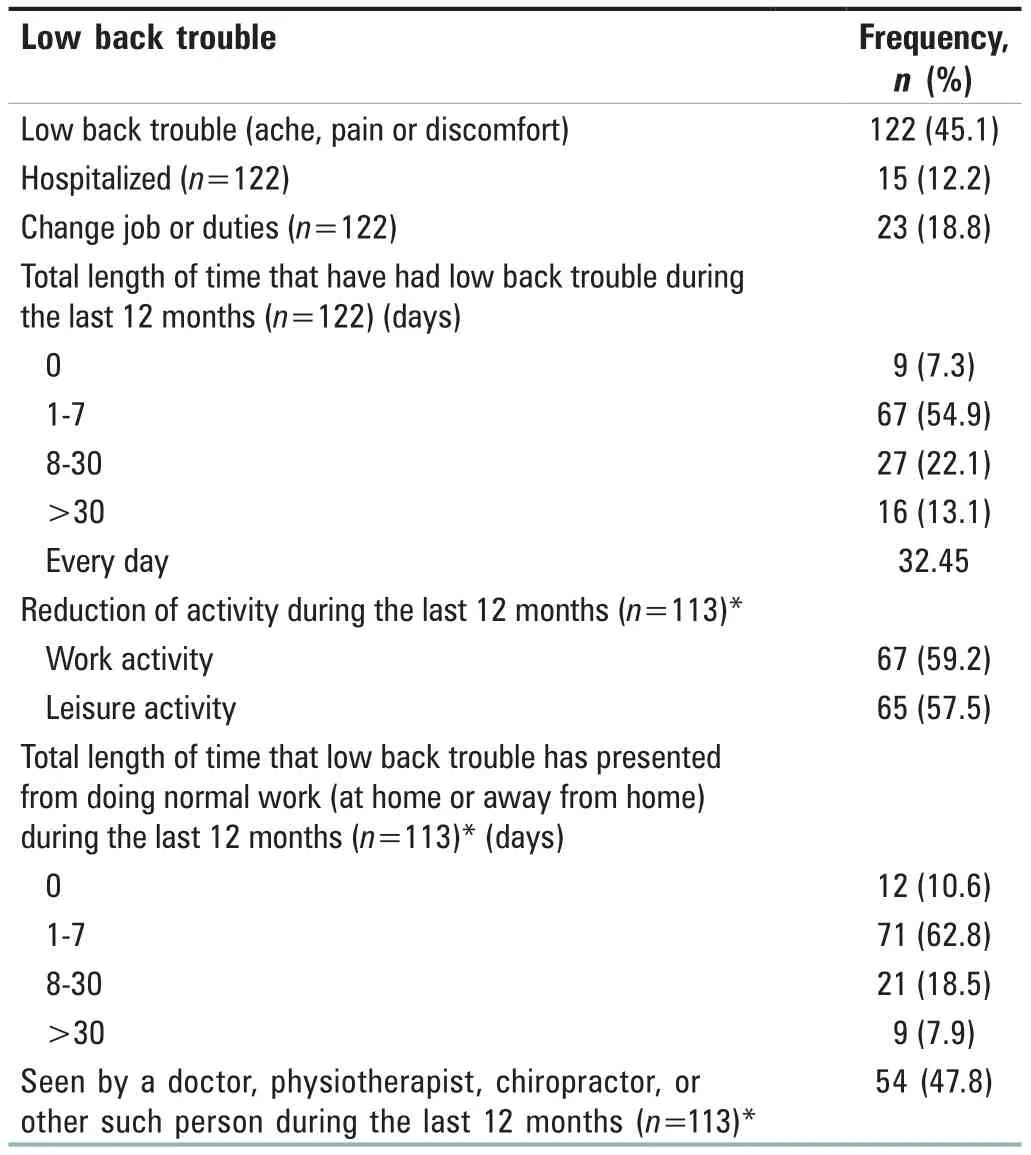
Table 3:Distribution of nursing officers as per trouble with low back
Description the expressed practices of body mechanics among nursing officers
Table 6 depicts that out of 270 nursing officers,190 (70.37%) had good practice whereas 76 (28.14%) had average practice and only 4 (1.5%) had poor practice of body mechanics.

Table 4:Distribution of nursing officers as per trouble with neck
The data presented in Table 7 shows that expressed practices of body mechanics out of 20 items of expressed practices body mechanics the best 4 items were“taking help of a colleague during lifting the heavy patient (2.6 ± 0.55),”“secure and good grip on the object or person during lifting (2.6 ± 0.56),”“explaining the patient for cooperation before transferring from bed (2.6 ± 0.58)”and“maintaining better/suitable height of table and chair while working on the computer (2.6 ± 0.57).”Least 4 items were“little bit of muscular warmup and stretching before attempt lifting or transferring of persons or objects (1.87 ± 0.76),”“using slide boards during moving the patient from one flat surface to another flat surface (2.05 ± 0.80),”“keepinglegs in close proximity while moving the patient on the bed (2.3 ± 0.71)”and“taking the rest/breaks in between the work (2.2 ± 0.69).”
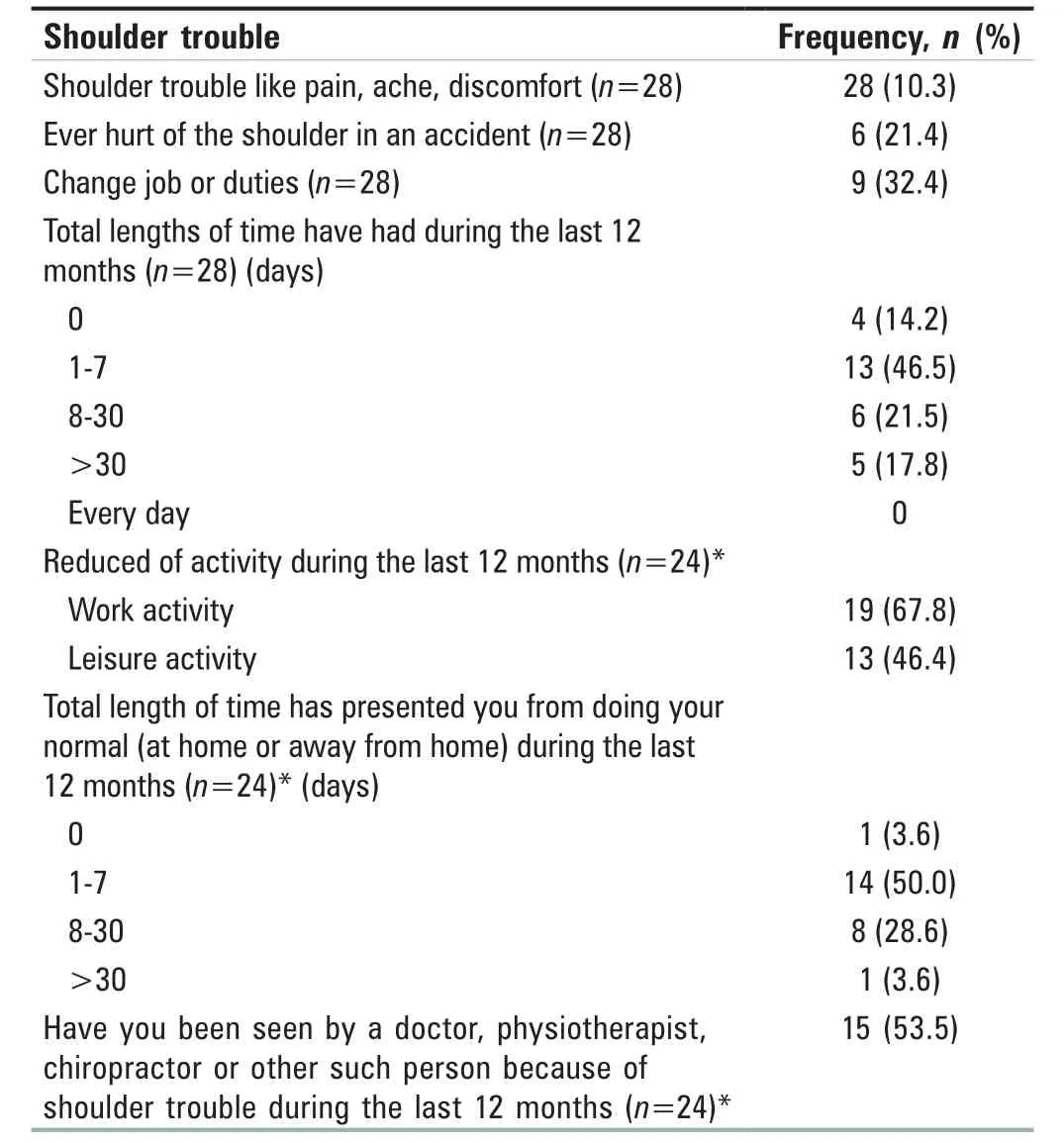
Table 5:Frequency and percentage distribution of nursing officers as per trouble with shoulder

Table 7:Expressed practices of body mechanics among nursing officers
Association between musculoskeletal problems with selected personal variables
The significance was tested at the level of 0.05.There was a significant association between MSPs and BMI (P=0.001),family history of MSP (P=0.02).There was no significant association of MSP with other personal variables.
Association of expressed practices of body mechanics with selected personal variables
The significance was tested at the level of 0.05.There was significant association between expressed practices of body mechanics and gender (P=0.01),area of current work (P=0.000),professional experience (P=0.03) and physical activity (P=0.000).There was no significant association of expressed practices of body mechanics with other personal variables.
DISCUSSION
The study was conducted to assess the MSPs and expressed practices of body mechanics among nursing officers.The study included a total of 270 nursing officers currently working in different areas of the hospital.
The study reveals that low back pain was the most commonly reported MSP,affected 45.1% of all nursing officers followed by MSP of the neck (22.2%).The study results were supported by a study conducted by Luanet al.[10]in which the prevalence of MSDs with the two most common sites being the low back (44.4%) and neck (44.1%) was found.Similarly,the result of the study by Mehrdadet al.[11]showed that the prevalence of low back pain,knee pain,shoulder pain,and neck pain were 73.2%,68.7%,48.6%,and 46.3%,respectively.
The present study found that 122 nursing officers out of 270 reported low back trouble,fifteen out of 122 nursing officers were hospitalized and 23 respondents reported change of job or duties due to low back trouble.47.7% of the nursing officers have visited a doctor,physiotherapist,chiropractor,or other such person due to low back trouble in the past 12 months.Similar result was found in the study of Smithet al.[12]where MSDs were important occupational issues for professional nurses.
The study reveals that the MSPs in last 12 month were observed in 64.4% of nursing officers and in the last 7 days were in 43.7%.These findings are consistent with the study conducted by Tinubuet al.[6]reported the 12-month period prevalence of self-reported MSDs at any body site 78%.[6]Furthermore,the study results resemble with study conducted by Smithet al.[13]where the 12-month prevalence of MSDs at any body site was 85.5%.
In the present study,low back pain was the most commonly reported MSP,affected 45.1% of all nursing officers.Similar results seen in study conducted by Hignett[14]where low back pain is one of the most common work-related MSDs (WMSDs) among nurses,study results shown that point prevalence of approximately 17%,an annual (period) prevalence of 40%-50% and lifetime prevalence of 35%-80%.[15]
The present study shows that 28 nursing officers reported shoulder trouble out of 270 respondents,around 6 respondents were hurt their shoulder in any accident and 9 of them have changed their job or duties due to that trouble.53.5% of nursing officers have to visited Doctors,Physiotherapist,Chiropractor,or other such person in the last 12 months.Results in this study are similar to the studyconducted by Abdulla[16]where the previous 12-month prevalence of work related MSDs among nurses was 67%,and lower back disorders (75%) was the most prevalent disorders compared to other body regions.
The present study found that out of 270 nursing officers,70.37% had good practice whereas 28.14% had average practice and only 1.5% had poor practice of body mechanics.Finding is supported by a study conducted by Vidya and Vinita[17]where mostly (88%) of the participants had the average practice of body mechanics,followed by 12% had good practice of body mechanics,and the mean percentage of the overall level of practice was 73.33%.
Limitation of the study
The study was purposively conducted at AIIMS Hospital in Jodhpur.This affects the generalizability of the results to nursing officers outside the AIIMS,Jodhpur.
Recommendations
On the basis of findings of the study,it is recommended that:(1) A similar study can be conducted on the large number of nursing officers for generalization;(2) The study can be conducted in a hospital organization like government,private,nursing homes,non-medical teaching hospitals,etc.;(3) The same study can be conducted with an experimental research approach;(4) The study can be conducted to evaluate the long-term effect of the teaching program on body mechanics to assess the skill and practice.(5) Different teaching strategies can be used to educate the staff nurses regarding body mechanics;(6) More research can be conducted in the future regarding preventive measures to reduce the MSPs in the nursing profession.
CONCLUSION
The present study aimed to identify the frequency and percentage of MSPs occurring in nursing officers as related to age,gender,marital status,and problem in different body regions.The study indicates the large numbers of nursing officers were having the MSP with the two most common sites being the lower back and the neck.Taking help of a colleague during lifting the heavy patient,secure and good grip on the object or person during lifting,explaining the patient for cooperation before transferring from bed and maintaining better/suitable height of table and chair while working on the computer are the top four items of expressed practice of body mechanics.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There were no conflicts of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- Effect of a traditional Chinese medicine theory-based mobile app on improving symptoms in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus:A randomized controlled trial
- Comparison of in-vial exhaust method versus conventional exhaust method in the injection of COVlD-19 vaccine
- Analysis of licensure examination anxiety and its influencing factors among undergraduate nursing students
- Correlation between psychological resilience and burnout among female employees in a shopping mall in Xi Xian New Area,China:A cross-sectional survey
- Status quo and influencing factors of comfort with touch among nursing staff in rehabilitation department:A cross-sectional study
- Evidence summaries for nutritional screening of head-and-neck cancer patients
