ALPPS in the treatment of liver cancer with insufficient future liver remnant
2021-09-23JunGuoLiuJunWngWeiSunJinJunZhngYiJunWngGuiMingShuChengLouZhiDu
Jun-Guo Liu ,Jun Wng , ,Wei Sun ,Jin-Jun Zhng , ,Yi-Jun Wng ,,,,,Gui-Ming Shu ,,Cheng Lou ,,Zhi Du ,,,
a Department of Surgery, Third Central Hospital of Tianjin (Third Central Clinical College of Tianjin Medical University), Tianjin 300170, China
b Tianjin Institute of Hepatobiliary Disease, Tianjin 300170, China
c Tianjin Key Laboratory of Extracorporeal Life Support for Critical Diseases, Tianjin 300170, China
d Artificial Cell Engineering Technology Research Center, Tianjin 300170, China
To the Editor:
In 2007,Schlitt firstly reported that the rapid compensatory increase of future liver remnant (FLR) after surgery can be achieved in a very short time which is known as a revolutionary breakthrough of liver surgery for huge or multiple liver cancer therapy [1] .de Santibañes and Clavien later proposed the medical term“ALPPS”[2] .Associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy (ALPPS) was mainly used for treating colorectal liver metastases (CRLM) and consequently was considered an emerging surgical technique for hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC).Up to now,surgical resection is still the most common curative treatment for liver cancer [3] .HCC is the major primary liver cancer in China,and 85%-90% patients with HCC present different degrees of cirrhosis [4],while only about 15%-30% of them are eligible for radical resection [5] .The main reason is that patients are not able to tolerate large-scale hepatectomy or one-stage radical hepatectomy due to the insufficient FLR after tumor resection.In recent years,ALPPS has emerged to win the surgical opportunity for patients with liver cancer who were initially considered unresectable.Also ALPPS prevents postoperative liver failure,especially for the patient who is not willing to receive a liver transplant.
Nevertheless,ALPPS approach requires strict inclusion criteria including:(1) the Child-Pugh grade of liver function is A-B before operation;(2) the FLR/standard liver volume (SLV) (%) of patients without cirrhosis is below 30%;(3) the ICG retention rate at 15 min(ICG15) is between 10% and 20% while the FLR/SLV (%) is not up to 50% in patients with cirrhosis;(4) the ICG15 is less than 10% while the FLR/SLV is not up to 40% in patients with cirrhosis;(5) there is no other organ metastasis,except for the primary lesion or liver lesion;(6) patients are not suitable for radiofrequency ablation (RFA)or microwave ablation (MWA) according to tumor size and quantities;(7) the function of heart,brain,lung,kidney and other organs is normal and the operation can be tolerated.
In our study,patient characteristics are summarized in Tables 1 -5 .The clinical data of 10 patients with liver cancer were collected,including 9 males and 1 female,aged from 42 to 62 years.All patients had Child-Pugh A.The median FLR before operation was 422 cm3(range 240-763 cm3) and the median SLV was 1320.05 cm3(range 1084.61-1658.70 cm3).The diameter of the largest tumor was 15 cm with single tumor,while the smallest one was 5.8 cm with multiple tumors.Seven patients received ICG15.The highest value of ICG15 was 16.8% and the preoperative FLR/SLV was 45.9% for this patient.Preoperative model for endstage disease (MELD) scores are also listed.
ALPPS approach included two steps of operation.Firstly,the liver parenchyma between tumor side and the reserved liver was split and the corresponding portal vein was ligated through anterior approach under the guidance of ultrasound.This process took up a median of 407.5 min (range 325-555 min) and the corresponding median blood loss was 600 mL (range 10 0-2000 mL).Then,CT was performed to examine FLR until achieving the requirement of hepatectomy.The growth rate of liver volume after the first step operation ranged from 9.4% to 218.3%.The postoperative FLR/SLV ranged from 38.2% to 68.2% (Table 2).Median interval between the two steps was 7 days (range 3-12 days).Only one case had an MELD score higher than 15.During the second step of ALPPS,the liver along the tumor side was completely removed.It took a median of 207.5 min (range 60-310 min) and induced corresponding median blood loss 350 mL (range 10-800 mL).The growth rate of liver volume after the second step operation ranged from 1.7% to 59.7%.MELD scores after the second step operation are listed and described (Table 3).
The median levels of preoperative total bilirubin (TBil),that of one week after the first step and that of one week after the second step are 16.2μmol/L,15.4μmol/L and 23.6μmol/L,respectively.The median levels of preoperative alanine aminotransferase (ALT),that of one week after the first step and that of one week after the second step are 39 U/L,95 U/L and 28 U/L,respectively.The median levels of preoperative international normalized ratio (INR),that of one week after the first step and that of one week after the second step are 1.04,1.10 and 1.33,respectively.The median levels of preoperative albumin,that of one week after the first step and that of one week after the second step are 44.5 g/L,36.4 g/L and 36.9 g/L,respectively (Table 4).Five cases experienced postoperative liver dysfunction and abdominal infection.

Table 1 Preoperative clinical data of 10 patients with liver cancer.

Table 2 The first step operation of ALPPS in 10 patients.
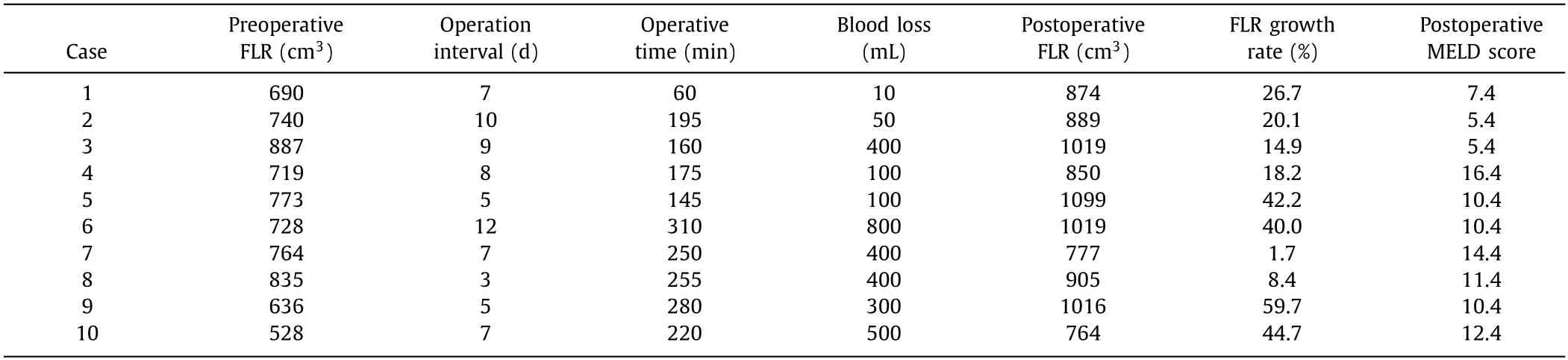
Table 3 The second step operation of ALPPS in 10 patients.

Table 4 Changes of biochemical indexes before and after ALPPS in 10 patients.
In our study,all patients,especially for those with liver cirrhosis and HCC,were treated by ALPPS and achieved R0 resection.None of them showed postoperative death,bile leakage or posthepatectomy liver failure.The median hospital stay was 44 days(range 28-69 days).Pathological examination was performed including 5 cases of HCC,3 cases of metastatic adenocarcinoma,1 case of mixed liver cancer and 1 case of undifferentiated lar ge cell carcinoma.Patients were followed up for at least 90 days after ALPPS.Eight cases were followed up for 10-36 months.Two cases were lost to follow up.Until the date of publication,5 cases survived and 3 died (Table 5).
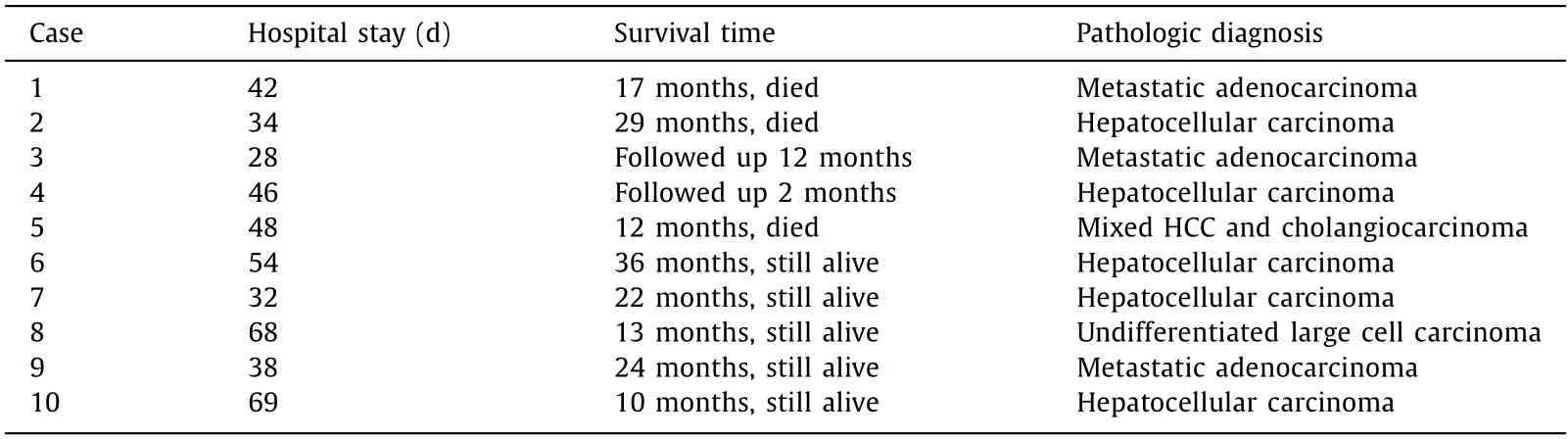
Table 5 The two step operation of ALPPS in 10 patients.
ALPPS provides a new curative option for patients with liver cancer,increases the proportion of patients who can be operated and reduces the withdrawal rate of classic two stage hepatectomy.ALPPS is performed through the first step of“insitusplitting”and portal vein ligation (PVL) to separate FLR from the diseasedhalf liver.It can adjust and change the blood flow into the liver,and increase the blood supply of the remaining portal vein to the liver,therefore promote the regeneration of the remaining liver tissue and reserve the blood supply of the hepatic artery.Thus it avoids the occurrence of acute liver failure by preserving function of the liver tissue [6] .ALPPS brings the opportunity of radical operation for patients with unresectable liver cancer,which has been recognized,respected and applied by surgical colleagues worldwide [7,8].Michal et al.[9] reviewed 1088 cases from openended ALPPS and 46 cases from minimally invasive ALPPS that had been completed worldwide.Most of them were adults with right lobe giant tumors without cirrhosis or multiple liver metastases.
With the emergence of intensive care equipment and technology,the mortality related to hepatectomy has been reduced to less than 5%,a large part of which is still caused by liver failure after hepatectomy [10] .Shen et al.[11] reported a meta-analysis including 7 retrospective observation studies that involved 561 patients.The completion rate of two-step hepatectomy in ALPPS group was higher.And there was no significant difference in the incidence of complications,liver failure and 90-day mortality between the first step operation and the second step operation.Cao et al.[12] conducted a meta-analysis,including 620 patients in 10 publications,and analyzed ALPPS in comparison with portal vein embolization (PVE).Compared with PVE,ALPPS achieved significant higher two-step operation completion rate,FLR growth rate,R0 resection rate and shorter two-step operation interval time (P<0.05).But there were no significant differences in the total length of hospital stay,mortality,total complication,and postoperative liver failure(P>0.05).
In conclusion,the success rate of ALPPS can be improved by both strictly screening of patients before surgery and comprehensive assessment of liver function.ALPPS reduces the incidence of postoperative complications and brings the opportunity of radical surgery to patients with insufficient FLR.However,large sample prospective randomized controlled study is urgently needed.At the same time,we need to understand that ALPPS is now a general term,and that the necessary conditions for the rapid proliferation of FLR are PVL and liver partition.
Acknowledgments
None.
CRediTauthorshipcontributionstatement
Jun-GuoLiu:Data curation,Investigation,Writing -original draft.JunWang:Data curation,Investigation,Writing -review &editing.WeiSun:Data curation,Investigation,Writing -review&editing.Jin-JuanZhang:Conceptualization,Funding acquisition,Investigation,Writing -review &editing.Yi-JunWang:Conceptualization,Funding acquisition,Investigation,Writing -review &editing.Gui-MingShu:Writing -review &editing.ChengLou:Writing -review &editing.ZhiDu:Writing -review &editing.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Key Projects of Tianjin Health Industry (15KG114) and Tianjin Science and Technology Plan Project (17YFZCSY01070,17ZXMFSY00050 and 16PTSYJC00210).
Ethicalapproval
The consent for publication was obtained from the reported patients.
CompetinginterestNo benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
杂志排行
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International的其它文章
- Recurrence and survival following microwave,radiofrequency ablation,and hepatic resection of colorectal liver metastases:A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- Mitochondria:A critical hub for hepatic stellate cells activation during chronic liver diseases
- Symptomatic Val122del mutated hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis:Need for early diagnosis and prioritization for heart and liver transplantation
- The growth rate of hepatocellular carcinoma is different with different TNM stages at diagnosis
- Overexpression of anillin is related to poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- Micro-positron emission tomography imaging of angiogenesis based on 18 F-RGD for assessing liver metastasis of colorectal cancer
