Clinical study on long-snake moxibustion plus Western medicine in treating chronic heart failure due to heart-kidney yang deficiency
2021-08-26XiaMeihua夏梅华LiuJinliang刘金良HaoNa郝娜
Xia Mei-hua (夏梅华), Liu Jin-liang (刘金良), Hao Na (郝娜)
Hengshui Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hebei Province, Hengshui 053000, China
Abstract
Keywords: Moxibustion Therapy; Long-snake Moxibustion; Governor Vessel; Heart Function Tests; Walk Test; Heart Failure; Heart-kidney Yang Deficiency
Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a complex clinical syndrome characterized by ventricular filling or low blood ejection at the end stage of the development of various heart diseases, presenting with dyspnea, edema and fatigue as the primary symptoms[1-2]. The incidence of CHF is increasing year by year, and the mortality rate remains high. The 5-year survival rate is equivalent to that of malignant tumors, which severely hampers the quality of life and threatens life safety of the patients[3].At present, medications such as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker,β-receptor blocker, aldosterone receptor antagonist,diuretic and positive inotropic drugs are the main treatments. But the long-term effect is not ideal, and the mortality and readmission rate cannot be significantly reduced[4]. Recent study has shown that traditional Chinese medicine has certain advantages in the treatment of CHF, as it can improve the efficacy,symptoms and quality of life of patients[5]. Based on this,we observed the efficacy of long-snake moxibustion plus Western medicine in the treatment of CHF due to heart-kidney yang deficiency in this study, and compared it with Western medicine alone. The report is as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria in Western medicine
This study referred the diagnostic criteria of CHF in theHeart Disease[6]. Primary criteria: paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, jugular vein engorgement,pulmonary crackle, heart enlargement, acute pulmonary edema, galloping rhythm of third heart sound, increased venous pressure (>16 cm H2O).Secondary criteria: ankle edema, nocturnal cough,dyspnea after activity, hepatomegaly, pleural effusion,vital capacity decreased to 1/3 of the forced vital capacity, tachycardia (>120 times/min). The primary or secondary criteria included that the body mass reduced by ≥4.5 kg after treatment for 5 d or over. Those who met 2 primary criteria, or 1 primary criterion plus 2 secondary criteria could be diagnosed.
1.2 Criteria for syndrome differentiation of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)
According to theGuiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines[7], the criteria for syndrome differentiation of heart-kidney yang deficiency in TCM were established. Primary manifestations: palpitations,panting and weakness, panting after light activities,feeling cold. Secondary manifestations: oliguria and edema, abdominal distension and loose stool, gray complexion. Tongue and pulse manifestations: a pale fat tongue or teeth-printed tongue, deep and thin pulse or slow pulse.
1.3 Inclusion criteria
Those who met the diagnostic criteria for CHF in Western medicine; met the syndrome of heart-kidney yang deficiency in syndrome differentiation of TCM;New York Heart Association cardiac function classification grade Ⅱ or Ⅲ; aged 20-70 years; agreed to participate in this trial and signed informed consent.
1.4 Exclusion criteria
Patients with severe diseases of lung, liver or kidney;those had heart failure due to liver or kidney failure;with valvular heart disease or pneumocardial disease;women during pregnancy or lactation; those whose life expectancy was shorter than the duration of this trial.
1.5 Elimination and dropout criteria
Those who got worse in the disease condition or presented with adverse reactions during the trial; those dropped out or took other medications without authorization; those with incomplete data or materials that affected the efficacy evaluation.
1.6 Statistical methods
All data were statistically analyzed by the SPSS version 20.0 statistical software. Counting data were processed by Chi-square test. Measurement data were all in normal distribution and expressed as mean ±standard deviation (±s), andt-test was applied.P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
1.7 General data
A total of 80 patients with CHF due to heart-kidney yang deficiency were enrolled from Hengshui Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hebei Province,between January 2017 and October 2018. All patients were randomly divided into a control group and an observation group by the random number table method, with 40 cases in each group. During treatment,there was no case of dropout or elimination in either group. There were no significant differences in the data of gender, average age or average duration of disease between the two groups (allP>0.05), indicating that the two groups were comparable (Table 1).

Table 1. Comparison of general data between the two groups
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Control group
The control group received conventional Western medication. All patients were given oral fosinopril sodium tablets [State Food and Drug Administration(SFDA) Approval No. H20064148, Zhejiang Huahai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China], 10 mg/time, once a day; oral metoprolol tartrate tablets (SFDA Approval No.H32025391, AstraZeneca Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,China), 12.5 mg/time, twice a day; oral spironolactone tablets (SFDA Approval No. H33020070, Hangzhou Minsheng Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China), 20 mg/time,once a day.
According to the patient's personal condition, one to three of the following drugs might be added appropriately when necessary. Isosorbide mononitrate tablets (SFDA Approval No. H10940039, Lunan Better Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China), orally, 20 mg/time,twice a day; furosemide tablets (SFDA Approval No.H44023242, Guangdong Sancai Shiqi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China), orally, 20 mg/time, once a day; digoxin tablets (SFDA Approval No. H31020678, Shanghai Sine Pharmaceutical Laboratories Co., Ltd., China), orally,0.25 mg/time, once a day. A total of 3 months of treatments were performed.
2.2 Observation group
On the basis of the same medication in the control group, long-snake moxibustion was added in the observation group.
Moxibustion location: Bilaterally 1.5 cun away from the posterior median line, from Dazhui (GV 14) to Yaoshu (GV 2).
Methods[8]: The patient took a prone position, with his back fully exposed. After fully disinfecting the to-be-treated skin on the back of the patient with alcohol cotton ball, the physician applied ginger juice to the area and spread Du Jiu powder along the midspinal line [Rou Gui(Cortex Cinnamomi),Ding Xiang(Flos Syzygii Aromatici),Fu Zi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata),Chuan Xiong(Rhizoma Ligustici Chuanxiong),etc.]. A layer of ginger mash with narrow top and wide bottom was spread on the powder, covering the moxibustion location. Then the moxa floss was spread on the ginger mash, with sharp top and wide bottom,forming into a long snake-shaped moxa stick with an isosceles triangular cross-section. The head, body and tail of the moxa snake were ignited. And after burnt out,moxa floss was replaced and moxibustion was continued. The moxibustion took 3 moxa ‘snakes’ per time. After treatment, all moxibustion materials were removed, and the skin was cleaned with moist hot gauze. The treatment was performed once a week, for 3 consecutive months.
3 Observation of Curative Efficacy
3.1 Observation items
3.1.1 Echocardiography
Echocardiography was performed before and after treatment. The left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF),stroke volume (SV) and left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDd) were recorded.
3.1.2 Heart function classification
Heart function classification was conducted in both groups before and after treatment. Grade Ⅰ: routine activities do not cause fatigue, palpitations, dyspnea,angina or other symptoms. Grade Ⅱ: activities are slightly restricted and patients have no obvious discomfort at rest. Grade Ⅲ: activities are obviously limited, namely no symptom exists at rest but symptom of heart failure may be caused during activities lower than normal. Grade Ⅳ: the patient cannot do any physical activities, and has symptoms of heart failure at resting state.
3.1.3 Serum brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) level
Before and after treatment, fasting venous blood was taken from the patients, and the serum BNP level was measured by automatic biochemical detector.
3.1.4 Six-minute walk test
The 6 min walking distance of the patients in both groups was recorded before and after treatment, and the exercise endurance was compared.
3.1.5 Quality of life scale
Minnesota living with heart failure questionnaire(MLHFQ) scale was scored in both groups before and after treatment. MLHFQ ranged from 0-105 points. The higher the score, the worse the quality of life of CHF patients[9].
3.1.6 Serum galectin-3 (Gal-3) and soluble growth stimulation expressed gene 2 (sST2) protein levels
Before and after treatment, fasting venous blood was taken from the patients, and serum Gal-3 and sST2 protein levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
3.2 Criteria of curative efficacy
According to the improvement of heart function,curative efficacy was evaluated[10].
Markedly effective: Heart failure was basically controlled, or the heart function improved by 2 grades or more.
Effective: The heart function improved by 1 grade.
Invalid: No improvement or even decline in cardiac function.
3.3 Results
3.3.1 Comparison of basic Western medicine
During the trial, patients in both groups were given conventional Western medicines: fosinopril sodium tablets, metoprolol tartrate tablets and spironolactone tablets. In the control group, 15 cases were given additional isosorbide mononitrate tablets; 34 cases were given additional furosemide tablets, and 21 cases were given additional digoxin tablets. In the observation group, 17 cases were given additional isosorbide mononitrate tablets; 32 cases were given additional furosemide tablets, and 22 cases were given additional digoxin tablets. There was no significant difference in the use of additional Western medicine between the two groups (P>0.05), indicating that the basic Western medication of the two groups were consistent.
3.3.2 Comparison of clinical efficacy
The total effective rate was 92.5% in the observation group and 65.0% in the control group. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant(χ2=9.04,P=0.003), indicating that the observation group had more significant efficacy than the control group (Table 2).
3.3.3 Comparison of echocardiography result
Before treatment, there were no statistical differences in LVEF, SV and LVEDd between the two groups (allP>0.05). After treatment, LVEF and SV in both groups increased (allP<0.05), and LVEDd decreased (allP<0.05). The LVEF, SV and LVEDd in the observation group were statistically different from those in the control group (allP<0.05), indicating that the echocardiography result of the observation group was superior to that of the control group (Table 3).
3.3.4 Comparison of heart function classification
Before treatment, there was no statistical difference in heart function classification between the two groups(Z=-0.224,P=0.823). After treatment, heart function classification in both groups improved (control group:Z=-2.852,P=0.004; observation group:Z=-5.727,P=0.000), and the heart function classification of the observation group was superior to that of the control group (Z=-2.788,P=0.005), (Table 4).

Table 2. Comparison of clinical efficacy between the two groups (case)

Table 3. Comparison of echocardiography result between the two groups ( x ±s)
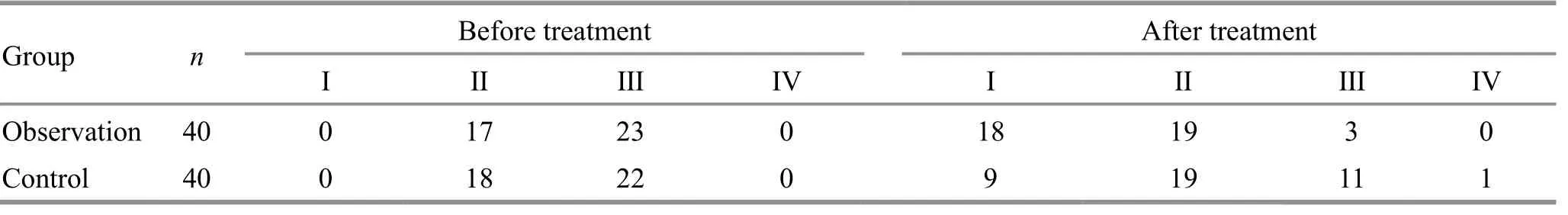
Table 4. Comparison of heart function classification between the two groups (case)
3.3.5 Comparison of the serum BNP level
Before treatment, there was no statistical difference in the serum BNP level between the two groups(P>0.05). After treatment, the serum BNP level in both groups decreased (bothP<0.05), and the serum BNP level in the observation group was lower than that in the control group (P<0.05), (Table 5).
3.3.6 Comparisons of 6 min walking distance and MLHFQ score
Before treatment, there was no statistical difference in the 6 min walking distance or MLHFQ score between the two groups (bothP>0.05). After treatment, the 6 min walking distance and MLHFQ score in both groups improved (allP<0.05), and the 6 min walking distance and MLHFQ score in the observation group were superior to those in the control group (bothP<0.05),(Table 6).
3.3.7 Comparisons of the serum Gal-3 and sST2 levels
Before treatment, there was no statistical difference in the serum Gal-3 and sST2 levels between the two groups (bothP>0.05). After treatment, the serum Gal-3 and sST2 levels in the observation group decreased significantly (bothP<0.05), and were lower than those in the control group (bothP<0.05). In the control group,only serum sST2 level was lower than that before treatment (P<0.05), (Table 7).
Table 5. Comparison of the serum BNP level between the two groups (±s, pg/mL)

Table 5. Comparison of the serum BNP level between the two groups (±s, pg/mL)
Note: Compared with the same group before treatment, 1) P<0.05;compared with the control group after treatment, 2) P<0.05
Group n Before treatment After treatment Observation 40 475.53±43.14 251.33±26.921)2)Control 40 480.31±45.03 356.09±32.641)

Table 6. Comparisons of the 6 min walking distance and MLHFQ score between the two groups ( x ±s)
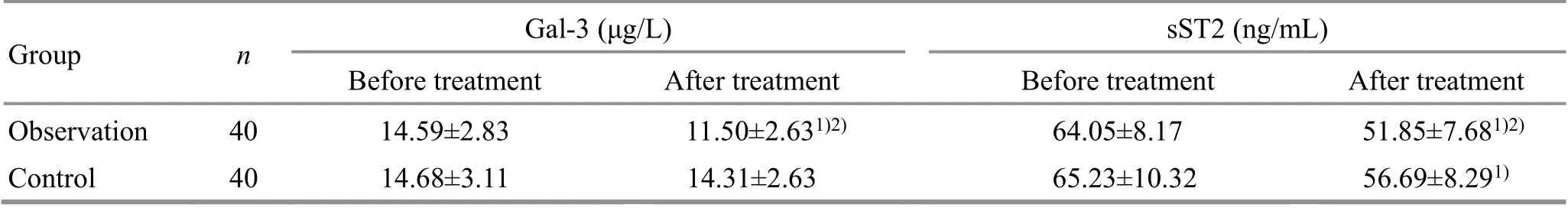
Table 7. Comparisons of the serum Gal-3 and sST2 levels between the two groups ( x ±s)
4 Discussion
CHF belongs to heart Bi-impediment syndrome, heart edema or edema in TCM. The location of CHF is in the heart, and related to the lung, spleen and kidney.Deficiency of heart-qi and heart-yang is an important pathological basis of this disease. Heart-qi and heart-yang deficiency causes excessive water pathogen,and the water pathogen attacks heart, resulting in dyspnea, palpitations and inability to lie down. The deficiency causes it unable to promote blood circulation,resulting in blood stasis blocking the vessels, and blood failing to transport around the body[11]. Long-time heart-yang deficiency causes it unable to warm the kidney yang, resulting in kidney-yang deficiency and qi transformation disorder, leading to oliguria and edema.Moreover, kidney-yang deficiency also in turn aggravates the weakness of heart-qi and heart-yang,forming a vicious circle[12]. Therefore, heart-kidney yang deficiency is the key pathogenesis of CHF, and the treatment should be based on the principles of warming yang for invigorating qi, benefiting the kidney and strengthening the heart.
Long-snake moxibustion, also known as spreading moxibustion and Governor Vessel (GV) moxibustion,combines the effects of meridians, acupoints and moxibustion, and has the characteristics of wide range of moxibustion, long duration, abundant heat and strong effect of warming yang[13]. GV is located in the middle of the back. It can governor yang qi of the whole body, and is the sea of yang meridians. Moreover, there are many acupoints on GV that cross with the six yang meridians of hand and foot. Meanwhile, the route of GV is closely related to heart and kidney. Therefore,moxibustion to GV can achieve the effects of warming and tonifying yang qi, benefiting kidney and strengthening heart[14].
Gal-3 is a kind of inflammatory mediators involved in immune response, mainly produced by macrophages. It can induce and promote macrophages to infiltrate the myocardium, activate and form fibroblasts, resulting in myocardial fibrosis[15]. Gal-3 not only reflects the inflammatory response, but also indicates the degree of myocardial fibrosis. It plays an important role in mediating ventricular remodeling and the development of heart failure. The level of Gal-3 is closely related to the severity of heart failure and ventricular remodeling,and is a predictive indicator for the assessment of acute and chronic heart failure[16-17]. sST2 is a secreted protein that can penetrate the vascular wall. By competing with transmembrane growth stimulation expressed gene 2(ST2), it binds with interleukin-33. And it antagonizes the cardio-protection effect mediated by transmembrane ST2, promoting the occurrence and development of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis, myocardial fibrosis and ventricular dysfunction, and accelerates the deterioration of heart function[18-19].
Results in this study showed that the total effective rate of the observation group was higher than that of the control group (P<0.05). After treatment, LVEF, SV and LVEDd in both groups improved (allP<0.05), and the improvements in the observation group were superior to those in the control group (allP<0.05). After treatment, the heart function classification in both groups improved (bothP<0.05), and the grading in the observation group was better than that in the control group (P<0.05). The serum BNP level in both groups decreased (bothP<0.05), and the serum BNP level in the observation group was lower than that in the control group (P<0.05). After treatment, 6 min walking distance in both groups increased, and MLHFQ score decreased (allP<0.05), and the improvements in the observation group were superior to those in the control group (bothP<0.05). After treatment, the serum Gal-3 and sST2 levels in the observation group significantly decreased (bothP<0.05), and were lower than those in the control group (bothP<0.05). All the above results suggested that long-snake moxibustion plus Western medicine produced a certain efficacy in treating CHF due to heart-kidney yang deficiency. It could improve the heart function, reduce the serum BNP level, and improve exercise endurance and quality of life of the patients[20], which might be related to the downregulation of the serum Gal-3 and sST2 levels.
In this study, objective echocardiography and serological indicators were used, and the results were quite convincing. However, there were shortcomings such as small sample size and single source of samples,and data such as readmission rate and mortality rate were not followed up and collected. Therefore, the next step is to carry out high-quality clinical trial with multi-centers and large sample size, and follow-up and collection of the readmission rate and mortality rate of patients within a certain period of time, so as to provide more reliable evidence for the treatment of CHF with long-snake moxibustion.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
There was no project-fund supporting for this study.
Author’s contribution
Xia Mei-hua designed the study and wrote this article;Liu Jin-liang collected the patients and analyzed the data;Hao Na collected the patients.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Received: 16 May 2020/Accepted: 25 September 2020
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Modern literature study of auricular point therapy for primary insomnia
- Effects of acupuncture plus MOTOmed intelligent motor training in treating children with spastic cerebral palsy
- Efficacy and effect on serum VEGF-C of mild moxibustion plus functional exercise for upper-limb lymphedema after breast cancer surgery
- Adjunctive effects of acupressure therapy on pain and quality of life in patients with knee osteoarthritis: an interventional study
- Muscle regions of meridians warm needling method plus pricking Jing-Well points for blood-letting in the treatment of shoulder-hand syndrome after stroke
- Effect of moxibustion at Shenque (CV 8) on myocardial remodeling and function in exercise-induced fatigue rats
