Efficacy of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)plus Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on myocardial infarction by enhancing autophagy in rats
2021-08-09YANGLiangHUANGGuangyaoWANGYuguangHANBaoqiZHENGBinZHUJinmiaoGAOShanGAOYue
YANG Liang,HUANG Guangyao,WANG Yuguang,HAN Baoqi,ZHENG Bin,ZHU Jinmiao,GAO Shan,GAO Yue
YANG Liang,Pharmacology and Toxicology Laboratory,Beijing Institution of Radiation Medicine,Beijing 100850,China;Hefei Normal University,School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Hefei 230601,China
HUANG Guangyao,Department of Pharmacy,Cancer Hospital,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Hefei 230031,China
GAO Shan,School of Basic Medicine,Anhui Medicial University,Hefei 230032,China
WANG Yuguang,GAO Yue,Pharmacology and Toxicology Laboratory,Beijing Institution of Radiation Medicine,Beijing 100850,China
HAN Baoqi,ZHENG Bin,ZHU Jinmiao,Hefei Normal University,School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Hefei 230601,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE:To elucidate the protective effects of Renshen (Radix Ginseng) and Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) on myocardial infarction (MI)through regulating myocardial autophagy.METHODS:Thirty-one male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomized into five groups (n= 6 or 7 for each).After treatment for 3 weeks,electrocardiogram (ECG) and cardiac function were recorded.Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining was used to detect pathological changes in the heart.Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect serum B-type brain natriuretic peptide (BNP),cardiac troponin T (cTnT),tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α),and serum inflammatory cytokines.Metabolomic analysis was used to identify differential biomarkers of MI in rats.Immunohistochemistry and western blotting were used to detect BNP,cTnT,TNF-α,LC3B,Beclin-1,p62,and adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase(AMPK)expression in cardiac tissue.RESULTS:Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)alone or Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) markedly ameliorated cardiac dysfunction and abnormal ECGs,demonstrated by decreases in the heart weight/body weight ratio,BNP,and cTnT.Pro-inflammation cytokine interleukin (IL)-1α significantly decreased and anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 significantly increased in Renshen(Radix Ginseng)single or Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) groups compared with the control group.HE results suggested that co-treatment produced a greater reduction in cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area than Renshen (Radix Ginseng)or Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)alone.Renshen(Radix Ginseng)plus Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) reversed these changes to different degrees in MI rats.Furthermore,Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) down-regulated LC3B,Beclin-1,and AMPK expression in cardiac tissue and upregulated p62 expression.CONCLUSIONS:Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)may have a greater effect on heart injury induced by MI in rats than Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) treatment alone,and the underlying mechanism may be associated with the regulation of myocardial autophagy and anti-inflammation effects.These results provide fresh insight into the mechanism of co-treatment with Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)for MI.
Keywords:myocardial infarction;autophagy;inflammatory;cytokines;Renshen (Radix Ginseng);Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)
INTRODUCTION
Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)1-3has long played a vital role in Chinese health care which has a wide range of biological and pharmacological effects on cardiovascular diseases,such as acute myocardial infarction(MI),4shock,5,6chronic congestive heart failure,7and ischemic cardiomyopathy with cardiac insufficiency,8which is widely used in clinic.9,10While adverse reactions of Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) have been reported either.10The main active components of Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) ralis,aconitum alkaloids,exhibit substantial cardiotoxicity.11-13Renshen(Radix Ginseng) mitigates the cardiotoxicity caused by Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)14and is widely used in a co-treatment formulation with Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) reduce toxicity in acute or chronic cardiovascular disease.15,16However,the mechanism by which Renshen (Radix Ginseng) reduces the toxicity of Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) still unclear.
Autophagy is a cellular waste disposal process that is important for cell survival,differentiation,development and homeostasis.Autophagy principally serves an adaptive role to protect organisms against diverse pathologies,which including infections,cancer,neurodegeneration,aging,and heart disease.17However,in certain experimental disease settings,the self-cannibalistic,or paradoxically functions of autophagy may be harmful.Autophagy has not been clearly identified as a helpful or detrimental process in cardiovascular medicine.Initially,it was thought that inhibit or overexcite autophagy was maladaptive.18Further evidence indicated that this process can either be protective or maladaptive post-MI.19,20Therefore,it is essential to understand autophagy during the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)have different effects on autophagy.Ginsenosides,including ginsenosides Rb1,21Rg1,22Rb2,23and Rh2,24are the main active components of Renshen(Radix Ginseng),and they inhibit autophagy through regulation of the adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK),Rho/Rho-associated protein kinase,or phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)pathways in a heart failure animal model or myocardial injury model.Meanwhile Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) increases autophagy activity,which protects against starvation-induced cytotoxicity in H9c2 cells,through AMPK/mTOR pathway activation.25However,the effect of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)plus Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) on autophagy in MI in rats has not been reported.
We observed the effects of Renshen (Radix Ginseng)plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) on MI in rats.And also,in the primary work,the fingerprint of both herbs had been built.11,26After the preliminary experiment,the dosage for monotherapy of Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)(0.1g·kg-1·d-1)was selected.
METHODS
Animal and materials
Sixty male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 200-220 g were purchased from Beijing Weitong Lihua Experimental Animal Technology Co.,Ltd.(Beijing,China;Certificate No.SCXK (Jing) 2016-0006).The animals were kept in a controlled environment [(22 ± 2) ℃;12 h dark-light cycle].Approved by the Institution of Animal Care and Use Committee,Academy of Military Medical Science (IACUC of AMMS-2018-009).The animals were kept in the controlled environment for 7 d before the experiments.Renshen (Radix Ginseng)was soaked in 10 times doubly distilled water and then boiled last for 1 h.The filtrate was collected and the extraction steps were repeated.The combined filtrates were concentrated by rotary evaporation to afford crude extracts with concentrations of 0.5 g/mL.The same protocol was used to obtain the Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)extract.
Induction of Myocardial Ischemia
Left coronary artery ligation was carried out based on reported method.27The animals were anesthetized with ketamine(50 mg/kg)and diazepam(5 mg/kg)administeredviaintraperitoneal injection and ventilated with positive pressureviaa tube inserted into the trachea and connected to a small animal respirator.After the chest was shaved,a left thoracotomy was conducted in the intercostal space of the apex beat,and the heart was then quickly exposed.The anterior inter-ventricular branch of the left coronary artery was identified and ligated between the edges of the left auricular appendage and the pulmonary artery with 7-0 prolene sutures(complete within 30 s if possible).
Groups and treatment
Sixty rats underwent the surgical procedure (eight rats in the control group,which underwent the surgical procedure,but without ligation of the left coronary artery;and 52 rats in the model groups,which underwent the same surgical procedure with ligation of the left coronary artery).The surviving rats were divided randomly into the following groups:control,model,Renshen (Radix Ginseng),Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata),Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)groups.0.1 g·kg-1·d-1Renshen (Radix Ginseng) or Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata),Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata).All groups were administered the treatment for 21 d.
Electrocardiogram(ECG)
A multi-channel signal acquisition and processing system(RM6240E,Chengdu Instrument Factory,Chengdu,China) was used to measure the signals.Cardiac function was observed by left common carotid artery intubation after the last gavage.The left ventricular systolic pressure(LVSP),left ventricular end diastolic pressure (LVEDP),and the maximal rate of left ventricular systolic and diastolic pressure (±dp/dtmax) were analyzed according to a recorded computer-based automatic real-time detection system.
Measurement of BNP,cTnT,and inflammatory cytokines in serum
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect the concentration of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α),B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP),cardiac troponin T (cTnT),interleukin (IL)-1α,and IL-10 in rat serum,according to the manufacturers'instructions (Wuhan Service Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.,Wuhan,China).
Hematoxylin and eosin(HE)staining and Immunohistochemistry
Heart specimens were fixed in 4% buffered formalin and embedded in paraffin (Sakura,Tokyo,Japan).Tissue sections (4 µm) were prepared and stained with HE.Necrotic areas were quantified by area fraction analysis (Image J).Immunohistochemical analysis was used to detect BNP,cTnT,LC3-B,and Beclin-1 expression in heart tissue.The primary antibodies for BNP(ab19654),p62 (ab56416),and LC3-B (ab48394)were obtained from Abcam (Cambridge,UK),and that for cTnT,(15513-1-AP) was obtained from Proteintech(Chicago,IL,USA).Beclin-1(3495S)was obtained from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers,MA,USA).
Western blotting
Proteins were extracted from frozen heart tissue,and the protein concentration was determined with a BCA Protein Assay Kit(CW Biotech,Beijing,China).Equal amounts of proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE.The membranes were reacted with antibodies for IL-1α (1∶1000,Abcam,Cambridge,UK),IL-10 (1∶2000,Abcam,Cambridge,UK),TNF-α (1∶1000,Abcam,Cambridge,UK),cTnT,(1∶1000,Proteintech,Chicago,USA),BNP (1∶1000,Abcam,Cambridge,UK),Beclin-1 (1∶1000,Cell Signaling Technology,Boston,USA),LC-3B (1∶3000,Abcam,Cambridge,UK),AMPK (1∶1000,Abcam,Cambridge,UK),p62(1∶1000,Abcam,Cambridge,UK),and GAPDH (1∶3000,Abcam,Cambridge,UK).
UHPLC-MS analysis
Serum(100µL)was placed in a labeled 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube and acetonitrile (300 µL) was added.The sample was thoroughly mixed on a vortex mixer for 15 s and the protein precipitate was pelleted in a centrifuge at 4 ℃and 12 000 ×gfor 10 min.The supernatant(100µL)was transferred to a 200µL vial insert for analysis.UHPLC was performed on a rapid separation liquid chromatography system with a reversed-phase C18 column or hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) column.For the C18 separation,mobile phase A was acetonitrile/water (60/40) and mobile phase B was isopropanol/acetonitrile(90/10),and mobile phases A and B contained 0.1%formic acid and 10 mmol/L ammonium acetate.
Statistical analysis
SAS (Version 9.4,SAS Institute,Cary,NC,USA) statistical software was used to determine the differences between the groups.All data was presented as mean ±standard deviation (±s),andP <0.05 was considered statistically significant.The figures were processed and displayed with Graphpad(Version 5.01,GraphPad Software Inc.,San Diego,CA,USA).The pictures were processed with Corel DRAW X3 (Corel,Toronto,Canada).
RESULTS
Survival rate of rats after surgery
After 1 week,31 rats survived(six in the control group and 25 in the model groups),giving a survival rate of 51.6%.
Effects of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on ECG in MI rats
During the surgical procedures,the ECG was monitored.The elevation of the ECG after coronary artery ligation was observed in the MI rat groups compared with the control group.However,Renshen(Radix Ginseng) and Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) treatment significantly diminished the S and T wave abnormalities compared with the model group.
Organ coefficient and pathological changes in cardiac tissue
Photographs of cardiac tissue are shown in Figure 1A.Compared with the control group,cardiac hypertrophy was observed in the model group.Treatment with Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)or Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)plus Renshen(Radix Ginseng)significantly reduced the heart organ coefficient (HW/BW) compared with the model group (Figure 1D).Morphological hypertrophy of the heart was indicated by the increased HW/BW ratio in the model group(P <0.01).The HE staining of cardiac tissue (Figure 1B,1C,1E) from the model group showed that the longitudinal diameter and myocyte cross-sectional area increased markedly compared with those of the control group(P<0.01).Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)and Renshen(Radix Ginseng)plus Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) treatment in MI rats for three weeks reversed these pathological changes.
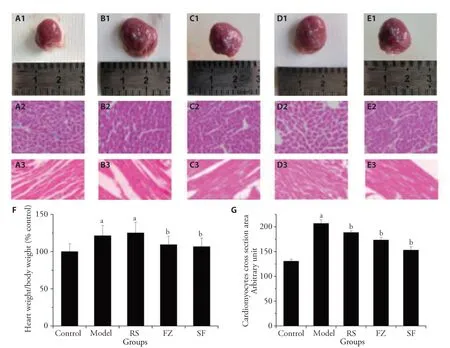
Figure 1 Effects of Renshen (Radix Ginseng) and Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) on organ coefficient and pathological changes in cardiac tissue in MI rats
Effects of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on cardiac function of MI rats
LVSP,LVEDP,heart rate,+dp/dtmax and-dp/dtmax were measured 28 d after surgery (Table 1).Compared with the control group,the heart rate,systolic cardiac parameters,such as LVSP and +dp/dtmax,and diastolic cardiac parameter-dp/dtmax,all decreased markedly in MI-treated rats,whereas LVEDP was increased.These changes were prevented by treatment with Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)for 21 d,giving+dp/dtmax and-dp/dtmax higher than the control group(P <0.05) and LVEDP lower than the control group(P <0.05).However,+dp/dtmax,-dp/dtmax and LVEDP of the Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)group showed no significant difference compared with the control group.
Table 1 Effects of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on cardiac function in MI rats(±s)
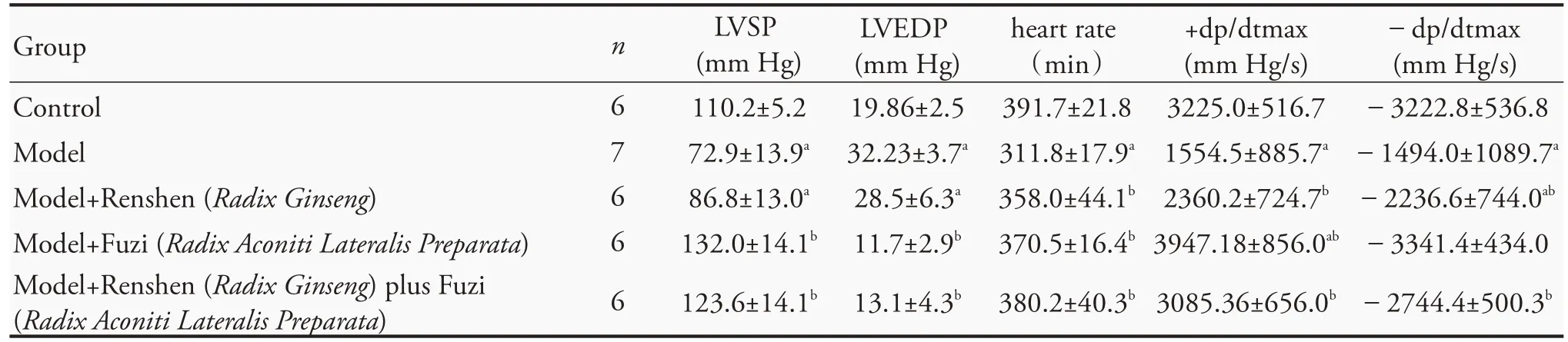
Table 1 Effects of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on cardiac function in MI rats(±s)
Notes:groups:control,model,RS:Model+0.1 g/kg Renshen(Radix Ginseng);FZ:model+0.1 g/kg Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata);SF:model+0.1 g/kg Renshen(Radix Ginseng)+0.1 g/kg Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata).LVSP:left ventricular systolic pressure;LVEDP:left ventricular end diastolic pressure;dp/dtmax:the maximal rate of left ventricular systolic and diastolic pressure.aP <0.05,compared with the control group;bP<0.05,compared with the model group.
Effects of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on inflammation markers in serum and cardiac tissue
Inflammation is an important characteristic of the MI model.IL-1α was elevated in the serum and cardiac tissue of MI model rats,and Renshen (Radix Ginseng)down regulated the concentration of IL-1α in both cardiac tissue (Figure 2) and serum.The anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was down regulated in the model group,whereas it was increased significantly in rats administered Renshen (Radix Ginseng) (P <0.01),compared with the model group.Moreover,TNF-α was markedly elevated in the serum of MI rats,but significantly decreased after treatment with Renshen (Radix Ginseng) (P <0.05) and Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)(P<0.05).
Effects of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on acute coronary syndrome in MI rats
Compared with the control group,the levels of BNP,which is a molecular marker for cardiac hypertrophy,were increased significantly (P <0.05) in the serum and cardiac tissue (Figure 3) of the model group.The levels of cTnT,which is used in the early diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome,were increased significantly(P <0.05) in serum and cardiac tissue in the model group,compared with those in the control group.Renshen (Radix Ginseng),Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata),and Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)reversed these changes.
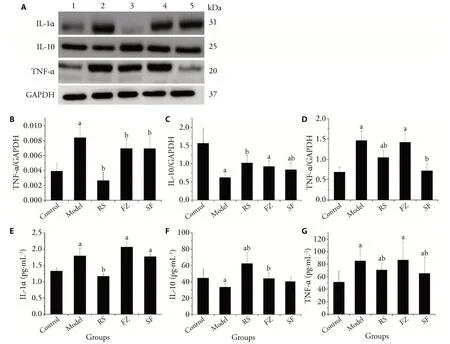
Figure 2 Western blotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results showing the effects of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on IL-10,IL-1α,and TNF-α in cardiac tissue and serum of MI rats
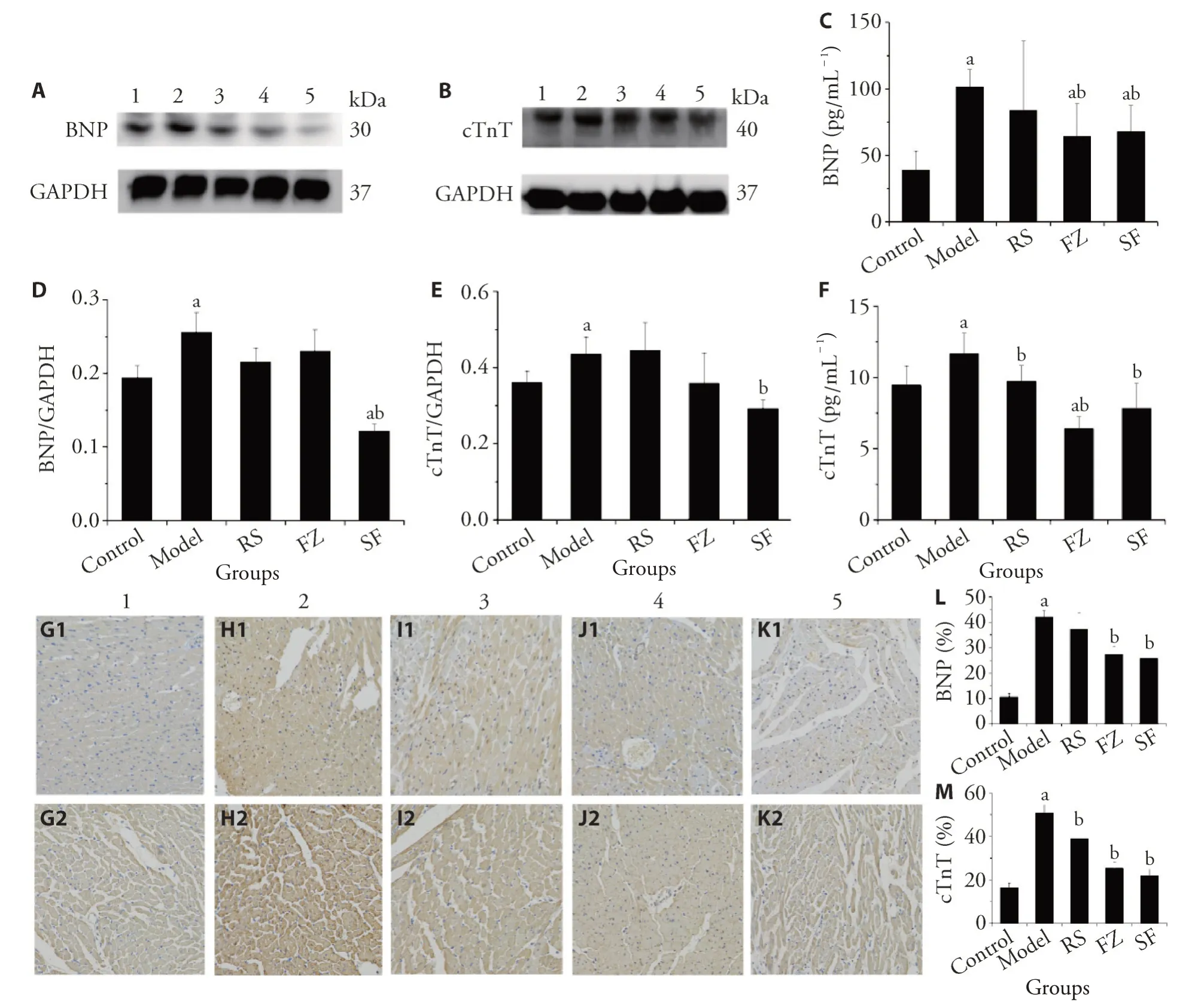
Figure 3 Effects of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on BNP and cTnT levels in MI rats
Metabolomic analysis of effects of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)in MI rats
Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to analyze the results to investigate the global lipidomics and amino acid metabolism variations.The lipid metabolic phenotypes and amino acid metabolism variations based on all imported samples were classified by PCA.The data showed a clear grouping trend for the control group,model group,MI+Renshen (Radix Ginseng)group,MI+Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)group,and MI+Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) group.The model group vs the control group exhibited an improved separation,indicating that MI may disturb lipid metabolism.Renshen (Radix Ginseng) and Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) showed effects in the MI rats.To confirm the lipids and amino acid used as selective and sensitive biomarkers,the orthogonal projections to latent structures-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) approach was used to compare the changes in lipid and amino acid metabolites between the MI and the control rats.There was a clear separation of the control rats and the MI rats in the OPLS-DA scores scatter plot.Lysophosphatidylcholine (LysoPC) (22∶0),phosphatidylcholine (PC) [16∶0/16∶1 (9Z)],PC [20∶4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:∶0],PC [20∶4 (8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18∶1 (11Z)],PC [18∶0/18∶1 (11Z)],LysoPC [16∶1 (9Z)],and LysoPC [18∶4 (6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)]were decreased in the model rats.Compared with the control group,cytosine,N-acetylornithine,L-asparagine,symmetric dimethylarginine,and creatinine were decreased,whereas linoleyl carnitine and vaccenyl carnitine were increased significantly in the MI group.Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) reversed these changes to different degrees.The significantly changed lipid metabolites in the MI group compared with the normal group were filtered out based on variable importance in the projection (VIP) values (VIP >1) and Student'st-test(P <0.05).Six pathways involving the differential metabolites between the groups were identified.
Effects of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on the expression of heart autophagy-related proteins in MI rats
Autophagy-related proteins LC3-II/LC3-I and p62 were detected by western blotting.Compared with the control group,LC3-II/LC3-I were significantly increased (Figure 4),whereas p62 was downregulated in MI rats,which indicated that myocardial autophagy pathways were unimpeded in model rats.However,the changes were reversed in the Renshen (Radix Ginseng)and Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) groups.To identify the mechanism of the effects on myocardial autophagy,Beclin-1 and AMPK protein expression in cardiac tissue was measured
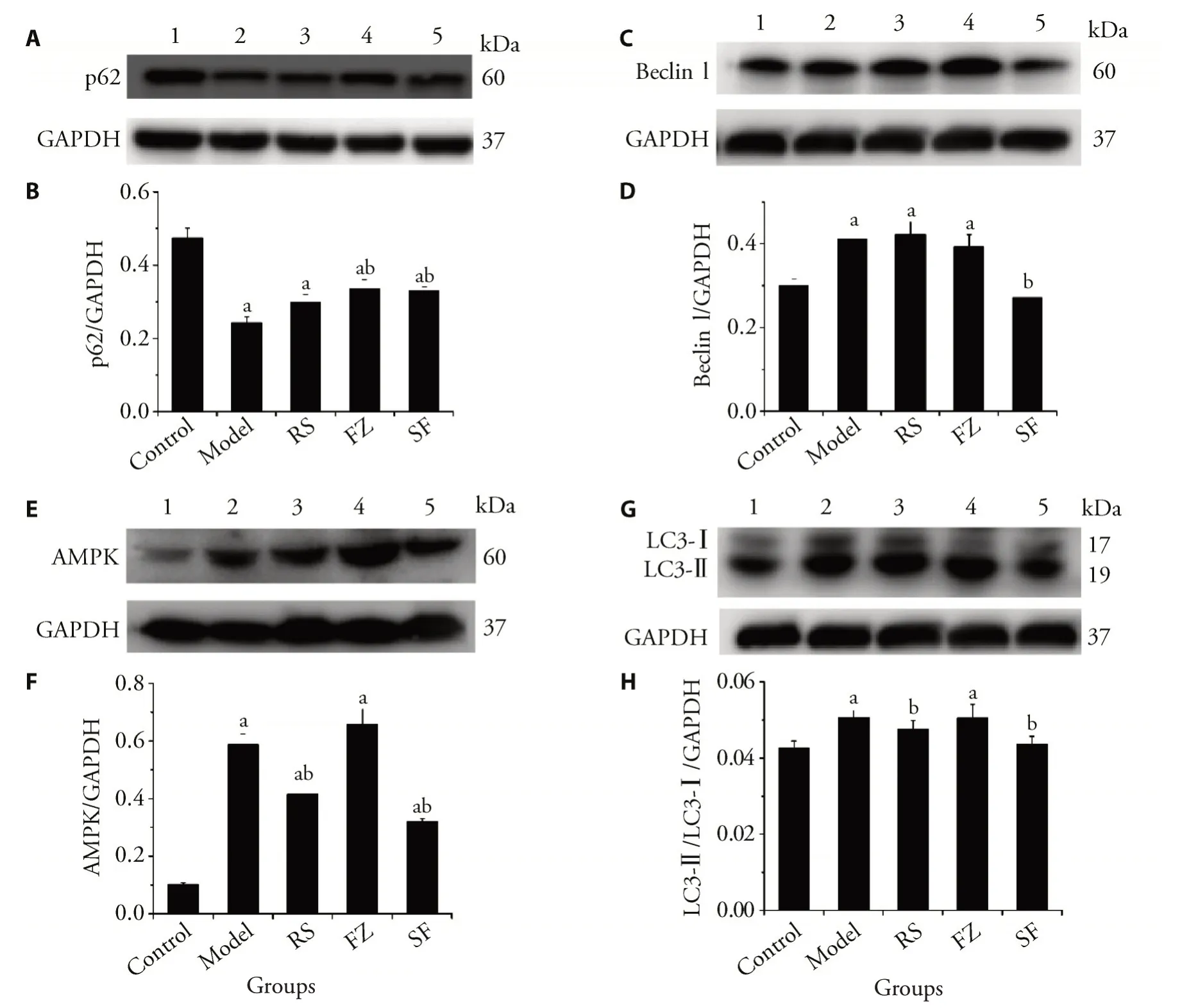
Figure 4 Western blots showing effects of Renshen(Radix Ginseng)and Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)on protein expression in MI rats
DISSCUSION
Because of the Cardiotoxicity of Aconitum alkaloids,which are the main active components of Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) ralis,the clinical applications of Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) are restricted.However,Renshen (Radix Ginseng) attenuates the cardiotoxicity caused by Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata).28Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) significantly improved the quality of life and hepatic injury in chronic heart failure patients,29-31although the combinative mechanism is still unclear.
Morphological hypertrophy of the heart was reflected in the increased HW/BW ratio in the model group.HE staining suggested that both Renshen (Radix Ginseng) and Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) prevented heart hypertrophy.Cardiac remodeling was also indicated by the elevated HW/BW ratio,increased LVEDP,and impairments in LVSP and ± dp/dtmax.Progressive left ventricular (LV) dysfunction was prevented and the progressive cardiac remodeling was attenuated in the MI model of rats after Renshen (Radix Ginseng) and Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)treatment for three weeks.Renshen(Radix Ginseng)exerted anti-inflammation effects that were more significantviaregulating IL-10,IL-1α,and TNF-α expression.BNP is a hormone secreted by the heart in response to volume expansion and pressure overload.BNP production increases proportionally to the severity of LV dysfunction and is associated with predominantly LV concentric remodeling and hypertrophy,which are clinical markers for the diagnosis,severity,and prognosis of heart failure.32,33cTnT is another important indicator of myocardial injury and originates from myocardial fibers degraded during myocardial cell injury.34,35The elevation of cTnT in serum reflects damage to myocardial cells.Our results showed that Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) decreased BNP and cTnT levels in both serum and cardiac tissue from MI rats.Treatment with Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) prevented heart hypertrophy,generated anti-inflammation effects,and relieved the excessive correction of MI compared with Fuzi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)treatment alone.Metabolomics has been used to explore potential biomarkers in urine or serum samples to understand MI rats,and assess the integral efficacy of medication.8,36Several differential endogenous compounds are involved in several lipid metabolism pathways,which were strongly associated with autophagy.37Autophagy serves an adaptive purpose of protecting organisms against diverse pathologies,which have important roles in myocardial remodeling.38,39Autophagy is necessary to maintain the normal function of living organisms,although excessive autophagy damages organs.Various components from Renshen (Radix Ginseng)40-43and Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) have different effects on myocardial autophagy.The present study is the first to explore the effects of Renshen (Radix Ginseng) and Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) on MI-induced autophagyin vivo.LC3B is related to phagocytosis in early autophagy,and LC3B expression is used as a marker for autophagic membranes and can be used to monitor the development of autophagic membranes.44Overexpression of Beclin-145promotes autophagy,suppresses mTOR signaling,improves cardiac function,and alleviates inflammation and fibrosis after a lipopolysaccharide challenge.In contrast,haplosufficiency for Beclin-1 produces the opposite effects.Beclin-1 also protects mitochondria,reduces the release of mitochondrial DAMPs,and promotes mitophagyviaPINK1-Parkin.Adaptor p62 has an important role in myocardial remodeling,which plays a key autophagy-independent role in signaling functions to tumor initiation in the epithelium.46Our results suggested that levels of LC3-II/LC3-I,Beclin-1,and AMPK were upregulated in the model group,Renshen (Radix Ginseng) treatment downregulated autophagy expression,and excessive autophagy was observed in the Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) group,in which excessive upregulation of Beclin-1 and AMPK protein expression occurred.Compared with Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) treatment,Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) treatment alleviated excessive autophagy.The study has its drawbacks.Because of the difficulty of operation,it is difficult to repeat the model animals with large sample size in a short time.The purpose of this article was explored the Renshen plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata)of Myocardial Ischemia,Single drug or combination is the attention we focus.At the same time,it is really difficult to find a positive drug consistent with the purpose of this experiment,thus we did not add the positive control in the experiment design.In the following further studies,nifedipine will be selected as the positive control drug.
In conclusion,our results indicated that Renshen (Radix Ginseng) plus Fuzi (Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) may exert beneficial effects on heart injury induced by MI in rats,and the underlying mechanism may be associated with the regulation of anti-inflammatory effects and myocardial autophagy through the AMPKBeclin-1-LC3B signaling pathway.
杂志排行
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- In vivo anti-diarrheal activity of jujube honey on castor oil-induced diarrhea in mice
- Ethanolic extract of Puhuang (Pollen Typhae) modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response through inducible nitric oxide synthase/cyclooxygenase-2 signaling in RAW 264.7 macrophages
- Target prediction and activity verification for the antidepressant action of Huangqin(Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis)
- Pingchuan formula (平喘方) improves allergic asthma in mice through inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
- Can Fig and Olive Ameliorate the toxicity Induced by 2-nitropropane in some organs of mice? role of inflammatory versus anti-inflammatory genes
- Anti-hypertensive and endothelia protective effects of Fufang Qima capsule (复方芪麻胶囊) on primary hypertension via adiponectin/adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase pathway
