Digital Economy Empowers China’s Rural Revitalization: Current Situations, Problems and Recommendations
2021-06-30RunzheHU
Runzhe HU
School of Economics and Management, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, China
Abstract With the development of information technology, especially information and communications technology (ICT) technology, in the new era, the digital economy has penetrated into all walks of life in society and has gradually become the main economic form of contemporary social and economic development. In this context, the digital economy has become a powerful tool for promoting China’s rural revitalization and innovation development, bringing new opportunities for the implementation of China’s rural revitalization strategy. However, its development also has problems such as gaps in infrastructure construction, insufficient supply of talents, and lack of in-depth integration. Therefore, giving full play to the empowering role of the digital economy requires the government to accelerate infrastructure construction, increase talent training, and strengthen top-level design.
Key words Digital economy, Digital village, Rural revitalization
1 Introduction
The current rapid development of digital economy has become an important driving force for high-quality economic development and economic transformation and upgrading in China. The Central Economic Work Conference of China held in Beijing in 2019 clearly stated that the digital economy must be vigorously developed, digital rural construction will inevitably become a new strategic development direction for rural revitalization, which means that the digital economy will be the new direction, new driving force and a powerful tool for the revitalization and development in China’s rural areas. How to implement the digital economy to boost the implementation of China’s rural revitalization strategy has become a new subject research direction that domestic scholars have focused on in recent years.
Zhao Yuezhiet
al.
took the development path of the digital village in Jinyun County, Zhejiang Province as an example, analyzed the role played by the Chinese government and rural youth in promoting the digitalization of the rural economy in the development process, put forward some understanding of the existing opportunities and challenges faced by the digital economy in promoting rural revitalization, and pointed out some limitations of the concepts of "digital labor" and "local culture" in digital economy promoting the construction of digital villages. Liu Yuanshengbelieved that the development of the digital economy has promoted the digital transformation of China’s agricultural development. After analyzing the background and effectiveness of agricultural digital transformation, he pointed out that the digital transformation of agriculture in China still has problems such as lack of system, shortcomings in infrastructure, and lack of deep integration of digital technology and agriculture. Simultaneously, he also proposed that promoting the high-quality development of China’s agriculture to boost the rural economy requires starting from the top-level design and ecological system, continuously improving the digital literacy of agricultural entities, and promoting the in-depth integration of digital economy and agricultural development. Zhang Honget
al.
applied the AHP-entropy method to construct a comprehensive evaluation model for digital rural development in China, found that the digital rural development of various provinces and cities in China is unbalanced, and most provinces and cities are currently only in the growth or initial stage of development. They proposed that the development of digital villages needs to strengthen the construction of rural digital infrastructure and strengthen the supply of science and technology. Under such circumstance, it is very necessary to further analyze the problems and deficiencies in the current digital economy empowering rural revitalization, and propose corresponding countermeasures to promote the deep integration of digital economy and rural economic development.2 Development status of digital economy empowering rural revitalization
2.1 Development of agricultural digital economy
In recent years, the scale of China’s digital economy has been expanding, and its contribution to the growth of the national economy has increased continuously. According to data from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, the scale of added value of China’s digital economy has expanded from 2.6 trillion yuan in 2005 to 35.8 trillion yuan in 2019, its share of GDP has increased from 14.2% in 2005 to 36.2% in 2019, Simultaneously, its share in 2019 has increased by 1.4 percentage points year-on-year, and the digital economy has continued to penetrate into the development of social and economic industries.As shown in Fig.1, it can be found that the development of agricultural digital economy is significantly lower than the development of industry and service industry. This may be due to the natural attributes of agricultural production that have led to relatively weak demand for digital transformation of the agricultural economy. But on the other hand, the proportion of the added value of China’s agricultural digital economy in the added value of the industry has risen from 6.2% in 2016 to 8.2% in 2019, and its growth has shown a slow accelerating trend, which shows the digital development potential of China’s agricultural economy is still great.

Data source: White Paper on China’s Digital Economy Development (2020) by China Academy of Information and Communications Technology.
2.2 Development of rural e-commerce
At present, the development of digital economy in China’s rural areas is mainly focused on the construction of Taobao villages and Taobao towns, in order to play the leading role of rural e-commerce in boosting the rural economy and promoting rural revitalization in the digital economy era, and promote rural primary, secondary and tertiary industries to realize "Digital industrialization, industrial digitization". Therefore, the development status of Taobao villages and towns in China cannot be ignored when analyzing the development status of digital economy empowering rural revitalization.Since China’s Taobao Village was first discovered in 2009, the number has been increasing in the past ten years. From Fig. 2, it can be seen that the number of Taobao villages in China has increased from 3 in 2009 to 4 310 in 2019, showing a vigorous development. In addition, the wealth effect brought by the continuous development of Taobao Village in China has caused it to continuously spread to the surrounding areas, resulting in a cluster effect, and gradually formed Taobao village clusters and Taobao towns, and further play the role of Taobao villages and Taobao towns in promoting the implementation of China’s rural revitalization strategy in the construction of agricultural digital economy. According to the data from the Ministry of Commerce of China, the annual sales of e-commerce in Taobao villages and towns exceeded 700 billion yuan in 2018, accounting for nearly 50% of China’s rural e-commerce retail sales, and at the same time it brought more than 6.83 million job opportunities. In this way, Taobao Village and Taobao Town have highlighted important economic and social values in boosting the agricultural digital economy, promoting the development of the rural e-commerce industry, driving rural residents to return to their hometowns for entrepreneurship and employment and increasing rural residents’ income.
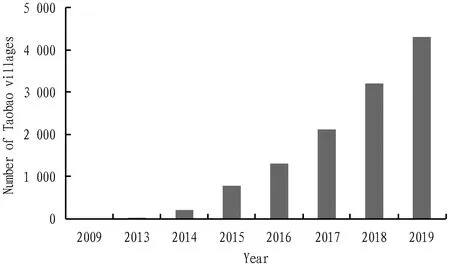
Data source: China Taobao Village Research Report (2009-2019) by Alibaba Research Institute.
3 Deficiencies of the digital economy empowering rural revitalization
3.1 Infrastructure for supporting the development of the agricultural digital economy still needing to be improved
The development of rural economy in the digital age depends on the application of digital technology, and the application of digital technology in agricultural production, circulation and consumption requires supporting infrastructure. In agricultural production, there is still a lack of high-quality digital monitoring terminals, and the penetration and utilization rate of digital technology applications in agricultural production is not high. Although China’s third agricultural census data points out that the Internet has covered 89.9% of the country’s rural areas, some agricultural production bases such as family farms in the rural areas have not yet been fully covered. In the circulation and consumption, only 25.1% of the rural areas in China have e-commerce distribution stations, and there are still gaps in platforms such as digital logistics and agricultural consumption information services.3.2 Development of agricultural digital economy lacking high-quality agricultural and digital talents
Talents are the foundation of social and economic development, and various forms of rural economic development are inseparable from agricultural production and management personnel. As a new type of agricultural economic development format that has grown up under the background of the Internet, the agricultural digital economy requires high technological and cultural literacy for the required talents. However, according to China’s third agricultural census data, in 2016, 7.1% of China’s agricultural production and management personnel had a high school or technical secondary school education, and only 1.2% had a college degree or above. It can be seen that well educated agricultural talents and digital talents are extremely scarce, which limits the continuous innovation and development of the rural economy in the era of digital economy.3.3 Lack of in-depth integration of digitalization and agricultural digital economy
The most important carrier in the development of the digital economy is digital technology. However, according to the development data of the digital economy of the three industries released by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, the current integration of digital technology and the rural economy is still not satisfactory, and the development of agricultural digital economy significantly lags behind industrial digital economy and service industry digital economy. The main reason is that the current digital technology talents are still mainly engaged in electronic information technology, and not many engaged in agricultural production. At the same time, most digital technical talents lack a deep knowledge and understanding of agricultural production, which has also led to the problem of low effectiveness of agricultural digital scientific and technological achievements.4 Policy recommendations for digital economy to empower rural revitalization
The promotion of rural revitalization in the era of digital economy is inseparable from rural digital construction. Based on the background, in order to accelerate the high-quality development of rural revitalization in China, it is necessary to innovate the development model of agricultural economy and realize the deep integration of digital economy and agricultural economy to promote the development of rural revitalization. At the same time, rural revitalization is a systematic project. China needs to analyze concrete problems in the development of agricultural economy and make full use of digital technologies such as big data capture to analyze the difficulties and challenges faced in the process of rural revitalization and development. On the innovative path of digital economy empowering rural revitalization, the government can consider taking measures from the following three aspects.
(i) It is recommended to speed up the construction of rural digital infrastructure to lay a solid information and physical foundation for the development of agricultural digital economy. The Chinese government should accelerate the construction of new rural infrastructure. While promoting the construction of rural informatization infrastructure such as the Internet and e-commerce platforms, it should also promote the optimization and upgrading of traditional physical infrastructure such as water conservancy and road transportation, improve the scalability of infrastructure for the development of agricultural digital economy and continuously consolidate the hardware foundation for the deep integration of digital economy and agricultural economic development.
(ii) It is recommended to formulate and promulgate corresponding talent policies to increase support for the cultivation of compound talents in digitalization and agriculture. At present, the development of China’s agricultural digital economy urgently needs compound talents who master both digital technology and agricultural production knowledge. While developing agricultural digital terminals, they can deeply integrate digital information such as professional agricultural production knowledge, agricultural product circulation, and rural e-commerce sales. The government should encourage highly-educated talents to participate in the development of the agricultural digital economy, continuously improve the digital literacy of agricultural production and management personnel, and formulate corresponding incentive mechanisms to increase the enthusiasm of agricultural entities to participate. The government should also use agricultural colleges and universities as the main body of teaching and scientific research, and agricultural production bases as the practice and output platform, promote the integration of production, education and research to build a reasonable and complete digital agricultural talent training system.
(iii) It is recommended to strengthen the top-level design of agricultural digital economy development, and promote the in-depth integration of digital economy and agricultural economy. China’s digital economy is still in the initial stage of development, the relevant national policy documents are scattered, and the legal system needs to be improved. The government should strengthen the systematic construction of the agricultural digital economy policy system, increase support for the agricultural digital economy, establish a feasible and effective agricultural digital economy incentive mechanism and development effect evaluation system, and implement regular dynamic evaluations of the construction of the agricultural digital economy to increase support for those with excellent evaluation results, and order re-evaluation after a deadline for rectification if the evaluation results are unqualified. In addition, the government should also improve the corresponding laws and regulations in the construction of agricultural digital economy, provide effective legal protection and a good policy environment for various problems and difficulties that may arise in its development process.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Landscape Advantages and Application of Groundcover Ornamental Bamboo
- Research Progress on Bacteriostasis of Nano Selenium
- Plant Cultivation Device in Intelligent Agricultural Greenhouse
- Reform of Teaching Mode for College Students’ Financial Literacy Training under General Education: Taking Yangtze University as an Example
