Molecular-scale drug delivery systems loaded with oxaliplatin for supramolecular chemotherapy
2021-05-14JieYangDihuaDaiLianjunMaYingWeiYang
Jie Yang,Dihua Dai,Lianjun Ma*,Ying-Wei Yang*
International Joint Research Laboratory of Nano-Micro Architecture Chemistry, College of Chemistry, and Department of Endoscopics, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
ABSTRACT Smart strategies that can decrease the side effect and enhance the therapeutic efficacy of chemotherapy are in urgent need to meet the special demands of cancer therapy.Herein,two water-soluble macrocyclic hosts, i.e., a carboxylated leaning tower[6]arene (CLT6) and a carboxylated [2]biphenyl-extended pillar[6]arene (CBpP6), are used to load chemotherapy drug oxaliplatin (OxPt) by forming inclusion complexes (OxPtCLT6 and OxPtCBpP6) through host-guest interactions.Interestingly, OxPt can be released from the macrocyclic cavities of these drug delivery systems(DDSs)via the competitive binding effect of spermine (SPM) because of the stronger binding abilities of CLT6/CBpP6 toward SPM as compared with OxPt,leading to enhanced cytotoxicity on SPM-overexpressed cancer cells,such as breast cancer MCF-7 cells.Moreover, compared to free OxPt, due to the low concentration of SPM in normal cells, OxPtCLT6 and OxPtCBpP6 demonstrated a decreased cytotoxicity on liver L02 cells, which is beneficial for reducing the side effect of anticancer drug during chemotherapy.Such a strategy might be extended to other antitumor drugs and water-soluble macrocycles with suitable cavity sizes to achieve controllable drug delivery and enhanced anticancer ability in supramolecular chemotherapy
Keywords:Drug delivery system Host-guest chemistry Macrocyclic chemistry Supramolecular chemotherapy Supramolecular chemistry
As a widely used method for cancer treatment, chemotherapy still suffers from some intrinsic disadvantages such as low selectivity, tumour resistance and undesired side effects, which seriously weaken the therapeutic effect [1–3].Considering the miserable shortcomings of chemotherapy, the development of effective drug delivery systems(DDSs)to improve the therapeutic effect and realize the controlled release of anticancer drugs is of great significance [4–7].In the last few decades, various DDSs,including inorganic nanomaterials, organic nanocarriers, and organic-inorganic nanohybrids have been designed and extensively fabricated [8–13].Notably, the synthesis and decoration of inorganic nanomaterials are not difficult,but their biodistribution,biodegradation,metabolic mechanisms and immunogenicity need to be comprehensively studied and clearly understood[14–16].On the other hand, organic carriers with the engaging features of biodegradability and biocompatibility are capable of carrying drugs via physical encapsulation or covalent bonding, but will cause unpredictable drug loading and premature drug leakage[17–19].Thus,the emergence of organic nanocarriers with predictable drug loading capacity can satisfy the demands of controllable drug delivery as well as enrich the toolbox of DDSs [20,21].
As a kind of host molecules that can selectively accommodate molecules or ionic guests via host-guest interactions,supramolecular macrocycles have been widely used to construct dynamic multifunctional materials [22–26].Taking advantages of the noncovalent interactions between various hosts and guests,supramolecular macrocycles bearing highly tuneable combinations and intelligent stimuli-responsive properties are widely developed for gas capture and separation [27,28], sensing and detection [29–33], supramolecular self-assembly [34–36] and controlled drug delivery [37–42].Particularly, as a new group of synthetic macrocycles, pillar[n]arenes (n=5–15) [43–47], especially pillar [5,6]arenes and their derivatives, have been widely used in biomedicine due to their appropriate cavity sizes and good biocompatibility[48–53].Based on the original features of pillar[6]arene,it leads to further breakthroughs to extend the application of supramolecular chemistry,however,there are still some deficiencies that need to be optimized in terms of synthesis yield, cavity backbone adaptability and variability of substituent numbers[54].In order to tackle this problem, in 2016–2018, our group successfully designed and reported two novel macrocyclic arenes,namely a[2]biphenyl-extended pillar[6]arene(BpP6)and a leaning tower[6]arene (LT6), with high synthetic yield, good cavity adaptability, less substituents and prominent guest binding capability [55,56].The rigid backbone and large cavity endow BpP6 with prominent properties, such as the purification of petrochemicals and detection of hazardous substances.Meanwhile, water-soluble cationic BpP6 and LT6 possessed good recognition capabilities for sulfonate guests in aqueous solutions.On the other hand,owing to the adaptability of cavity adaptability and variability of substituent numbers,both LT6 and BpP6 possess enhanced guest binding capabilities [56,57].On the basis of the abovementioned studies and the unique properties of watersoluble supramolecular macrocycle derivatives [58–60], we envision that utilizing ionic LT6/BpP6 to construct novel DDSs would be an efficient strategy for anticancer drug delivery.
Herein, we firstly designed and synthesized two macrocyclic receptors as molecular-scale biocompatible drug carriers, namely carboxylated leaning tower[6]arene (CLT6) and carboxylated [2]biphenyl-extended pillar[6]arene(CBpP6),for the in vitro delivery of anticancer drug oxaliplatin (OxPt) (Fig.1).Through the hostguest interactions,OxPt guest was spontaneously encapsulated in the cavities of CLT6 or CBpP6 host to construct host-guest complex of OxPtCLT6 or OxPtBpP6 with a stoichiometry of 1:1.The association constants were calculated as (1.150.08)103L/mol and (2.290.19)102L/mol, respectively.In addition, spermine(SPM), overexpressed in MCF-7 cancer cells, could also be encapsulated into CLT6 and CBpP6 cavities to develop 1:1 SPMCLT6 or SPMCBpP6 complex.Moreover, because of the stronger binding abilities between both two macrocycles and SPM with a binding constant of(4.590.82)104L/mol for SPMCLT6 and (2.640.61)104L/mol for SPMBpP6, respectively, OxPt could be released from OxPtCLT6 or OxPtCBpP6 complex, and SPM was simultaneously bound in the corresponding cavities of hosts,causing enhanced cytotoxicity on MCF-7 cells.Interestingly,compared with free OxPt, such two complexes also exhibited a reduced toxicity on L02 cells,which was attributed to the low SPM content in normal L02 cells.
The synthetic routes to CLT6 and CBpP6 were shown in Fig.S1(Supporting information).According to our previous report, CLT6 and CbBpP6 were synthesized by demethylation, etherification and hydrolysis of LT6 [32,56].Subsequently, after a facile neutralization, CLT6/CBpP6 host with eight carboxylate groups were obtained in satisfactory yields, which have been characterized by1H NMR,13C NMR and MALDI-TOF-MS spectroscopy(Figs.S2–S6 in Supporting information).

Fig.1.Schematic illustration of the preparation of CLT6/CBpP6(n=1,2,respectively)DDS and its application for in vitro OxPt delivery.(A)Synthetic route to CLT6.(i)BBr3,DCM,room temperature;(ii)BrCH2COOEt,NaH,THF,reflux;(iii)NaOH,H2O,THF,reflux;(iv)HCl;(v)NaOH,H2O.(B,C)OxPtCLT6 was prepared via host-guest complexation of CLT6 host and anticancer drug OxPt, showing a reduced toxicity on normal cells and an enhanced cytotoxic effect on cancer cells.

Fig.2.(A) 1H NMR spectra(400 MHz,298 K):(1)OxPt(5.00 mmol/L)in D2O;(2)mixture solution of OxPt and CLT6(5.00 mmol/L);(3)CLT6(5.00 mmol/L)in D2O.(B)Partial 2D ROESY spectrum(600 MHz,298 K)of CLT6(5 mmol/L)with OxPt(5 mmol/L)in D2O with a mixing time of 300 ms.(C) 1H NMR spectra of different radios of CLT6 and OxPt(from top to bottom: CLT6:OxPt=10:0, 9:1, 8:2, 7:3, 6:4, 5:5; 4:6, 3:7, 2:8 1:9 and 0:10).(D) Job’s plot analysis of CLT6 and OxPt.
To investigate the host-guest interactions between the two macrocycles and OxPt,1H NMR experiments were performed.As shown in Fig.2A,upon addition of 1.0 equiv.of CLT6,all the proton signals(Ha,Hb,Hc,Hdand He)of OxPt showed considerable upfield shifts(andppm,respectively),reflecting the shielding effect of macrocyclic cavity on OxPt.Meanwhile, the downfield shifts of proton signals (H1, H2, H3, H4and H5)in CLT6 were attributed to the deshielding effect caused by OxPt.Besides,the similar changes(=andppm for Ha,Hb,Hc,Hdand Heof OxPt,respectively)were also observed in the OxPtCBpP6 complex (Fig.S7 in Supporting information).Subsequently, the host-guest interactions between CLT6/CBpP6 and OxPt were further investigated by 2D ROESY spectroscopy.Clearcorrelationsbetweenphenyleneprotons(H1,H2and H3) in CLT6 or phenylbenzene protons (H1, H2, H3and H4) in CBpP6 and cyclohexyl protons(Ha,Hb,Hc,Hdand He)in OxPt were displayed, indicating the inclusion complexation between CLT6/CBpP6 and OxPt (Fig.2B and Fig.S8 in Supporting information).Furthermore,inordertoverifytheformationofhost-guestcomplex,the 2D diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy (DOSY) experiments were conducted.The results showed that the weight-average diffusion coeffcients (D) of OxPtCLT6 and OxPtCBpP6 were determined to beandrespectively, which were lower than that of OxPtillustrating the formation of host-guest complex( Figs.S9 and S10 in Supporting information).All the above experiments proved the formation of the host-guest complexes(OxPtLT6,OxPtBpP6)between the anticancer drug OxPt and CLT6 (or CBpP6) with an electron-rich cavity.
To further study the binding mode of macrocycle hosts and OxPt guest, Job’s plot analysis was conducted.1H NMR spectra of the mixture of CLT6 (or CBpP6) and OxPt with various molar ratios from 0:10 to 10:0 were recorded.According to the Job’s plot analysis for proton shift(Ha)of OxPt in various mixtures,the molar fraction of OxPt is 0.5 at the maximum,indicating the 1:1 binding stoichiometry between CLT6/CBpP6 and OxPt (Figs.2C and D, Fig.S11 in Supporting information).Meanwhile,1H NMR titration demonstrated that the association constants (Ka) of CLT6 (or CBpP6) and OxPt wereand (2.29)for OxPtLT6 and OxPtCBpP6, respectively(Figs.S12 and S13 in Supporting information).The biphenyl units in CBpP6 skeleton expanded the cavity size of CBpP6 and weakened the host-guest interaction between CBpP6 and OxPt,resulting in a smaller Kafor OxPtBpP6 [55].

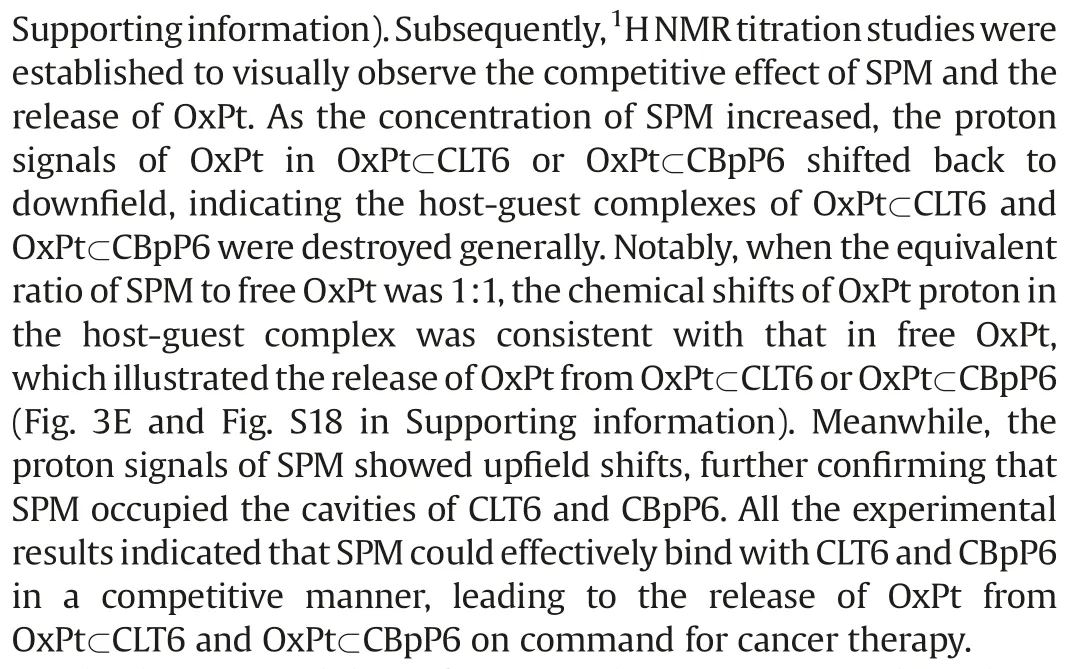
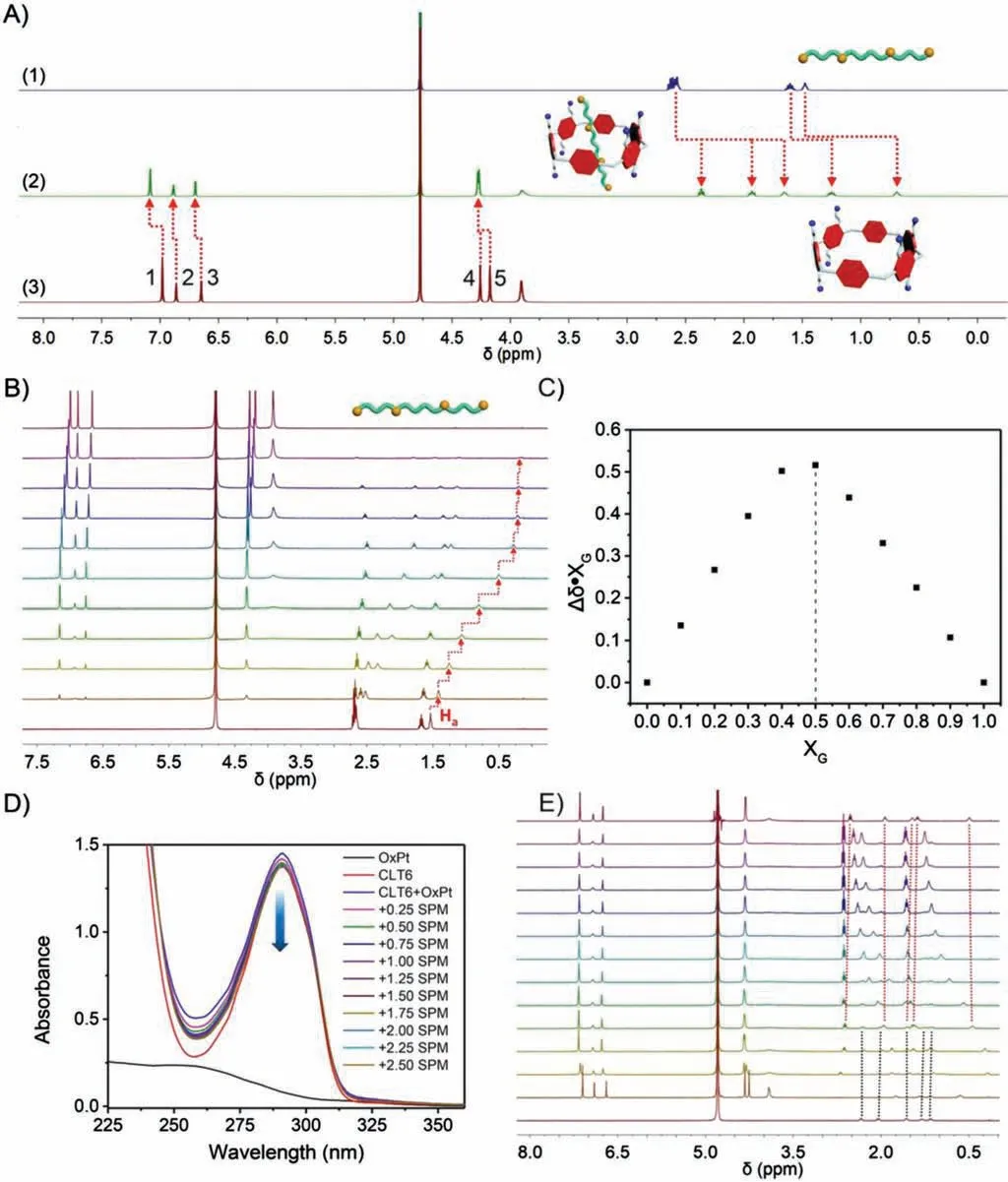
Fig.3.(A) 1H NMR spectra(400 MHz,298 K):(1)SPM(5.00 mmol/L)in D2O;(2)mixed solution of SPM and CLT6(5.00 mmol/L);(3)CLT6(5.00 mmol/L)in D2O.(B) 1H NMR spectra of different ratios of CLT6 and SPM(from top to bottom:CLT6:SPM=10:0, 9:1,8:2,7:3,6:4,5:5;4:6,3:7,2:8 1:9 and 0:10).(C)Job’s plot analysis of CLT6 and SPM binding.(D) UV–vis spectra of OxPt (100 mmol/L), CLT6 (100 mmol/L) and CLT6+OxPt (100 mmol/L) with different amounts (0-2.5 equiv.) of SPM.(E) 1H NMR spectra(400 MHz,298 K)of(from bottom to top)OxPt(0.5 mmol/L),CLT6+OxPt(0.5 mmol/L)with various amounts(0.2,0.4,0.5,0.6,0.8,1.0,1.2,1.4,1.6,1.8,2.0 equiv.)of SPM,and CLT6+SPM (0.5 mmol/L).
The biocompatibility of CLT6 and CBpP6 was evaluated via cytotoxicity study on L02 cells and MCF-7 cells,and hemolysis test on red blood cells (RBCs).As shown in Fig.4A and Fig.S19A(Supporting information), 3-(40,50-dimethylthiazol-20-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay results showed high cells viability (>90%) after the cells incubated with CLT6/CBpP6 host at a concentration range offor 24 h,indicating good biocompatibility of CLT6.Moreover, the hemolysis rates of CLT6 and CBpP6 were well <10% even at a high concentration of 500suggesting its negligible destructiveness on RBCs(Fig.4B and Fig.S19B in Supporting information).


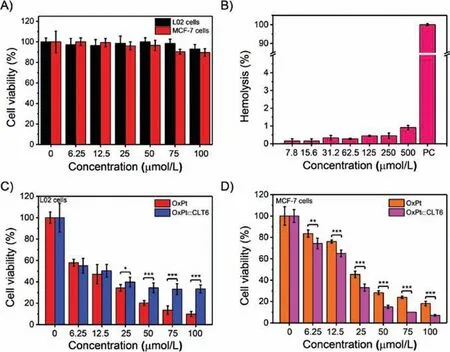
Fig.4.(A)Cell viabilities of L02 cells and MCF-7 cells treated by CLT6 host for 24 h.(B)Hemolysis test of CLT6(PC represents positive control group).Cell viabilities of(C)L02 cells and(D)MCF-7 cells incubated with free OxPt and OxPtCLT6 for 24 h(*P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001).
In summary, two water-soluble macrocyclic receptors, namely CLT6 and CBpP6,were designed as molecular-scale biocompatible drug carriers to build DDSs OxPtLT6 or OxPtCBpP6 with the marriage of anticancer drug OxPt via host-guest interaction for enhanced anticancer ability and reduced side effect in chemotherapy.OxPt could be spontaneously encapsulated in the cavity of CLT6/CBpP6 host to generate OxPtCLT6 or OxPtCBpP6 complex with a stoichiometry of 1:1,respectively.Compared with free OxPt,CLT6/CBpP6 possess higher binding ability with SPM, OxPt could be released from the two host-guest complexes through competitive substitution effect of SPM, gaining enhanced cytotoxicity on SPM overexpressed breast cancer MCF-7 cells.Interestingly, the decreased side effect was obtained on L02 cells due to the effective binding effect of the CLT6/CBpP6 host toward OxPt and the low SPM levels in L02 cells.This strategy might be extended to other antitumor drugs and water-soluble synthetic macrocycles with appropriate cavity sizes to realize controllable drug release and enhanced anticancer ability.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21871108), the Jilin Province-University Cooperative Construction Project–Special Funds for New Materials (No.SXGJSF2017-3), and the Jilin University Talents Cultivation Program for financial support.
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementarymaterialrelatedtothisarticlecanbefound,inthe online version,at doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.08.035.
杂志排行
Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- Quantitative assessment of rhodamine spectra
- Copper-cobalt-nickel oxide nanowire arrays on copper foams as self-standing anode materials for lithium ion batteries
- Design of activatable red-emissive assay for cysteine detection in aqueous medium with aggregation induced emission characteristics
- An aqueous zinc-ion hybrid super-capacitor for achieving ultrahigh-volumetric energy density
- Assembly and packing models of [Ti6Co12] ring based on the titanium-capped cobalt clathrochelates
- A stable Co(II)-based metal-organic framework with dual-functional pyrazolate-carboxylate ligand: Construction and CO2selective adsorption and fixation
