基于双模LPFG折射率不敏感双参量传感器
2021-04-12王向宇乔学光禹大宽
王向宇,乔学光,禹大宽
基于双模LPFG折射率不敏感双参量传感器
王向宇1,乔学光2*,禹大宽1
1西北工业大学陕西省光信息技术重点实验室,陕西 西安 710072;2西北大学物理学院,陕西 西安 710069
环境折射率和环境温度变化是影响光纤应变测量误差的主要因素。本文利用双模光纤纤芯双模式(LP01和LP11)支持特性设计了一款环境折射率不敏感的双模光纤(DMF)长周期光纤光栅LPFG)应变传感器。设计了传感器模型结构,制作了最优化参数的传感器样品。实验测试了DMF-LPFG传感结构对外部环境中应变、温度和折射率的响应。通过在单模光纤上用紫外激光刻写的布拉格光栅(FBG)解决了环境温度的交叉影响。轴向应变实验结果表明,该新型结构传感器在0 με~840 με应变范围内其轴向应变灵敏度可以达到-5.4 pm/με,该灵敏度值相比较于普通LPFG有很大提高。温度在25 ℃~80 ℃范围内其灵敏度为58.86 pm/℃,表现出较好的线性度。同时,传感器对环境折射率变化表现出不敏感特性。通过采用双参数矩阵对少模LPFG和FBG的应变和温度灵敏度进行处理,可以实现双参数的同时解调。该新型复合光栅结构具有良好的传感性能和工程应用前景。
双模光纤;长周期光纤光栅;布拉格光栅;应变传感器;温度补偿
1 引 言
光纤光栅(Fiber grating, FG)器件作为一种新型的光无源器件,表现出了独特的物理和光学性能,如体积小,波长响应快,抗电磁干扰,以及具有全光纤网络兼容性等[1-2]。长周期光纤光栅(Long period fiber grating, LPFG)的研究已有几十年的时间,其中,采用高频CO2激光刻写LPFG技术的提出,对丰富LPFG的设计和制备,提高信号传输质量,以及实现批量生产都具有非常重要的意义。虽然,现在LPFG的制备手段已经非常丰富,如飞秒激光刻写[3]、热诱导刻写[4]、光纤周期性拼接[5]、以及电弧放电等方法[6],但是由于高频CO2激光刻写技术具有效率高、成本低和制备结构稳定等优点,依然是最普遍采用的一种写制技术。目前,LPFG不仅能够在单模光纤上实现,并且随着新型光纤的出现其应用变得更加丰富,例如被研制出的基于新型特种光纤的有多芯光纤光栅[7]、保偏光纤光栅[8]、光子晶体光栅[9]和少模光栅[10]等。由于不同光纤具有不同的传感特性,因此在不同类型的光纤上刻写的LPFG也将会实现不同的传感性能。
多参数测量是光纤传感技术未来发展的必然趋势,尤其是在工程化应变传感应用中往往存在环境折射率改变干扰、温度串扰问题,因此有效补偿温度带来的测量误差非常重要。少模LPFG的包层模式对外界折射率比较敏感,因此环境中折射率的变化会对测量带来偏差。环境中温度的变化会引起少模LPFG周期的变化以及多种模式有效折射率的变化。双模光纤的纤芯仅传输两种较低阶模式,因此比SMF在模式控制和分析上具有更高的容量和灵活性。同时,由于LPFG全光纤结构具有更紧凑和灵活的特点,当满足相位匹配条件时,两个模式之间的转换具有非常高的效率,并且模式转换处的谐振波长对应变和温度敏感。利用这一特性,提出了基于双模光纤的LPFG传感器。通过对双模LPFG结构复合FBG,能够解决温度和应变的解耦问题。
本文设计和实现了一款DMF-LPFG级联SMF-FBG的复合传感结构。理论分析了传感器的模式耦合机理,实验研究了该传感器的应变特性、温度特性和对环境折射率的响应特性。研究发现,理论分析和实验结论表现出了较好的一致性。其中,在0 με~840 με应变范围内该少模LPFG的轴向应变传感灵敏度可以达到-5.4 pm/με。在25 ℃~80 ℃温度范围内该传感器的温度灵敏度达到58.86 pm/℃。在不同气体环境中测量的光谱移动量为0。同时,实验分析了SMF-FBG的应变特性、温度特性和折射率敏感特性。结果表明,在0 με~840 με应变范围内FBG的应变传感灵敏度达到1.2 pm/με,在25 ℃~80 ℃温度范围内该传感器的温度灵敏度达到10.13 pm/℃,在不同气体环境中测量的光谱移动量为0。在应变和温度解耦部分,通过监测LPFG和FBG波长的变化带入双参数矩阵可以实现两种物理量的解耦。
2 结构及制备
图1(a)给出了新型复合传结构的结构图,其中双模LPFG的长度为20 mm,刻写的FBG长度为10 mm。双模LPFG采用高频CO2激光刻写,衰减波长为1530 nm,周期为=800 μm,周期数为=20。本结构中采用紫外曝光技术在LPFG右侧刻写中心波长为1550 nm的FBG。通过分析可知,DMF-LPFG结构对应变和温度会有响应,同时FBG的波长也会受到环境温度和应变的影响,故选择简单的双参数矩阵可以实现对于两种物理量的解耦。
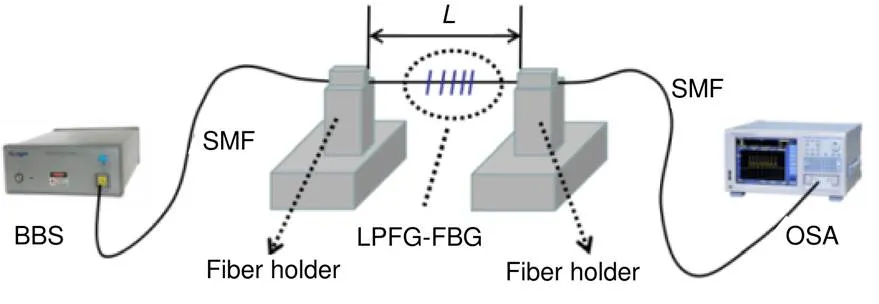
本文对SMF-FBG不再作详细介绍,主要研究DMF-LPFG的设计原理和制备过程。DMF-LPFG的光谱是谐振波长为LP01模式和LP11模式转换的结果,为了证明这一点,需要设计一个验证性的实验。美国Optilab公司生产的TWL-C-R型号可调谐激光器输出窄带激光=1536 nm,当光经过SMF-双模光纤后光场模场分布图如图1(b)所示;通过SMF-双模LPFG如图1(c)所示;在双模LPFG后面添加偏振片后被红外CCD捕获,此时可从红外CCD中查看光斑图像,如图1(d)和1(e)所示。图1(f)是制备的LPFG结构图,可以发现激光直接加工的表面会出现一定塌陷,这就形成了非对称的LPFG结构。
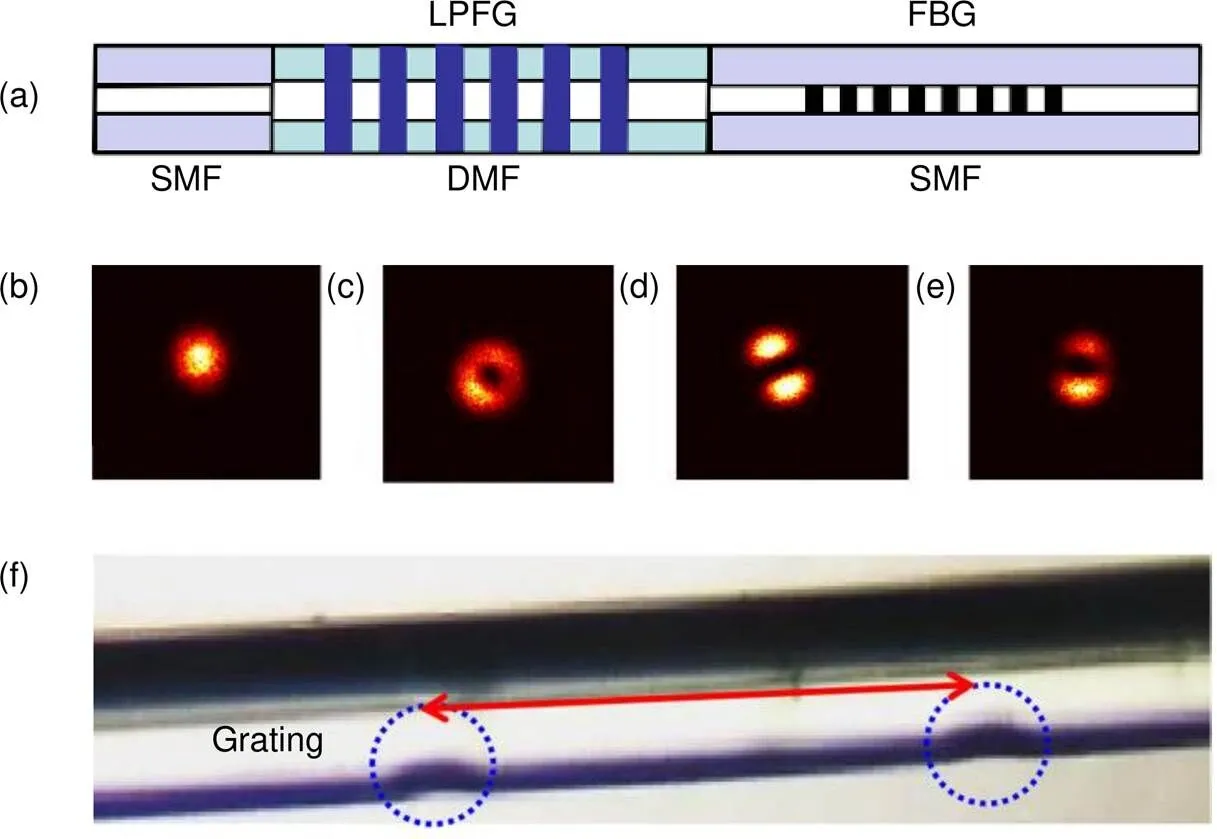
图1 (a) 传感器结构;(b) 激光经过单模-少模后测量的场分布;(c) 激光经过单模-少模-LPFG后测量的场分布;(d), (e) 激光经过单模-少模-LPFG-偏振片后测量的场分布;(f) LPFG的显微镜图像
本文采用ATLEX-FBG CO2激光器刻写系统制备DMF-LPFG,可调谐输出功率为0~30 mW,通过聚焦透镜汇聚成宽度最小达到10 μm的光斑,如图2所示。首先在单模光纤中间熔接一段长度为2 cm的双模光纤,然后将光纤一端固定在微位移平移台上,另一端悬挂一个5 g的砝码,并且确保双模光纤处于聚焦透镜下。LPFG制备过程中需要时时检测光谱的变化,因此要连接光源和光谱仪。本文采用的CHINA-FIBER宽带光源(amplified spontaneous emission,ASE)输出波长范围为1250 nm~1650 nm,光源输出光功率最大为100 mW。测量过程使用的光谱仪型号是YOKOGAWA AQ6370 (optical spectrum analyzer, OSA),纵坐标能量最小分辨率是0.01 dB,横坐标波长最小分辨率是10 pm。
实验中刻写的周期为800 μm的LPFG的光谱图如图3中红色曲线所示,在1536 nm的波长处出现了一个明显的谐振波长。实际传感中为了提高检测速度要求使用的光源范围越窄越好,而LPFG的衰减谷位于1520 nm~1570 nm区间内且光谱稳定性好,因此后面直接讨论该区间的光谱情况。
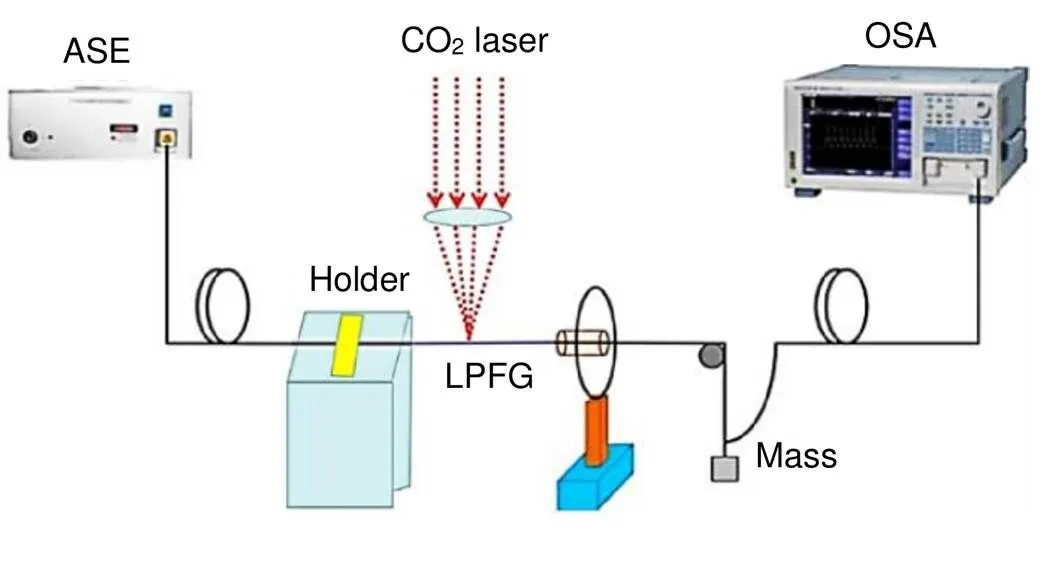
图2 DMF-LPFG写制的实验装置
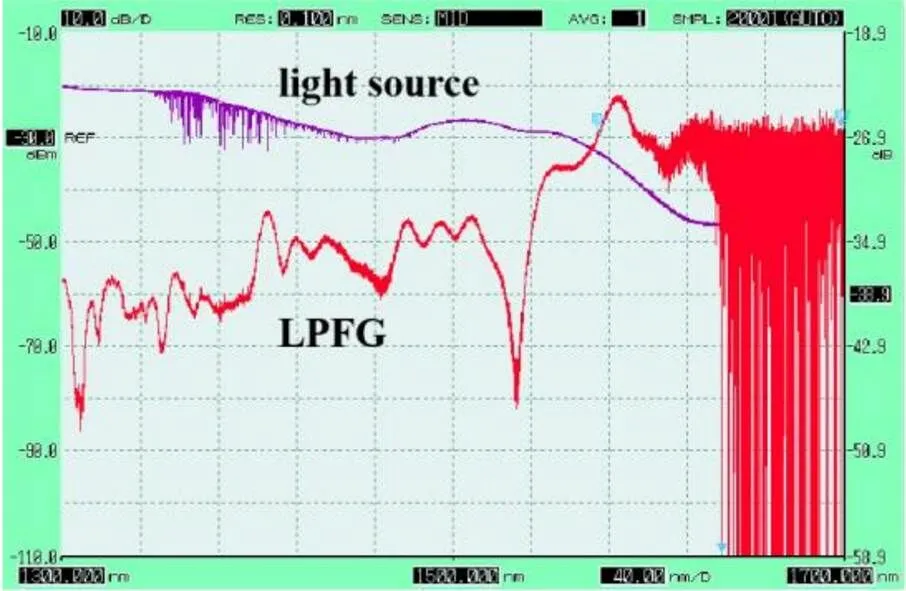
图3 DMF-LPFG的透射光谱
3 传感原理
本文采用折射率阶跃型的双模式少模光纤,即仅只允许LP01和LP11模式传输,这样排除了SMF-DMF-SMF结构产生模间干涉现象的可能。入射光从SMF的一端入射,由于SMF中只存在唯一的模式LP01且模式本身具有的正交特性,因此光从SMF传输到DMF中时,LP01不会耦合成为非对称的LP11。当光在DMF中遇到非对称的LPFG结构时,将发生LP01到LP11模式的转换现象。在DMF和输出SMF的熔接点处,已经存在的LP11模式并不能耦合成LP01模式而进入到输出SMF中,也就不能通过FBG被光谱仪接收。本文提出的DMF-LPFG结构能够有效实现模式转换,在光谱中得到透过损耗波谷。该新型结构传感器模式耦合发生在光纤纤芯当中,因此DMF-LPFG结构对环境折射率变化不敏感,适合在不同折射率环境中对温度和轴向应变进行测量。其结构中用到的非对称双模LPFG仅仅涉及到LP01和LP11模式之间的相互耦合,因此双模LPFG的相位匹配条件则表示为
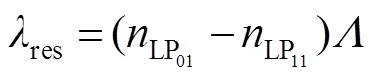
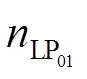
双模LPFG周围温度发生变化时,光纤的热光效应和热膨胀将会起作用。因此,当温度发生改变时,LPFG的纤芯折射率和包层折射率会随之改变,光栅周期由于热胀冷缩也将发生改变,这会导致LPFG的谐振波长发生漂移。DMF-LPFG的温度灵敏度公式可以表示为
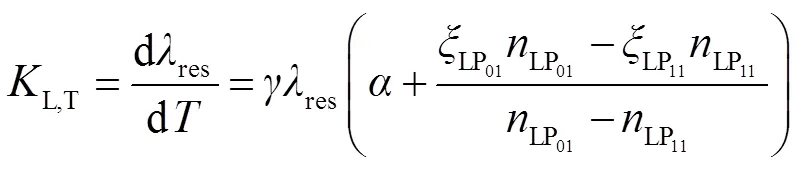
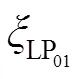
当双模LPFG受到轴向应变时,其光栅性质的改变与普通LPFG相似。因此,在假设其他条件不变时,通过监测DMF-LPFG波长的漂移量可以实现对外界轴向应变的测量。DMF-LPFG的轴向应变灵敏度为
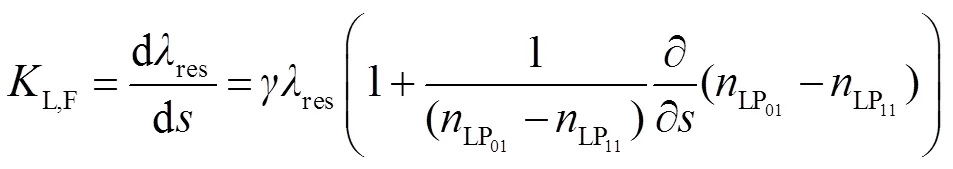
通过以上分析可知,弹光效应主要决定该新型DMF-LPFG结构的轴向应力应变灵敏度。
当温度和应变等参量发生改变时,会引起B的线性变化。根据耦合模式理论,B满足:
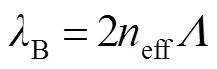
其中:B是FBG波长,eff为所使用的光纤纤芯的有效折射率,是对应的光栅周期。
FBG的温度灵敏度可以表示为
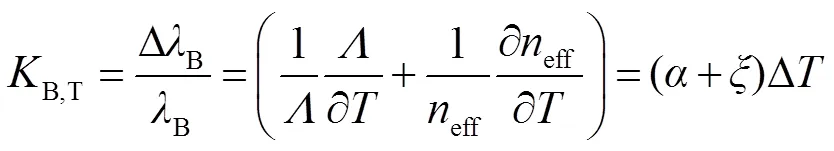
其中:为刻写光纤的热膨胀系数,为刻写光纤的热光系数。
FBG的应变灵敏度可以表示为
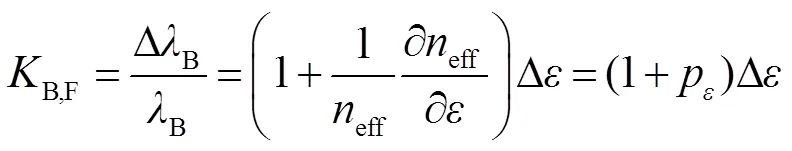
为了实现环境温度与应变的双参数解耦,将刻写有LPFG的双模少模光纤与SMF熔接,熔接之后用紫外激光在SMF上刻写FBG。在测量过程中,当环境温度改变了Δ,应变改变了Δ,ΔL和ΔB分别代表监测的少模LPFG和FBG的波长所对应的波长变化量。可以得到该结构的双参数矩阵为
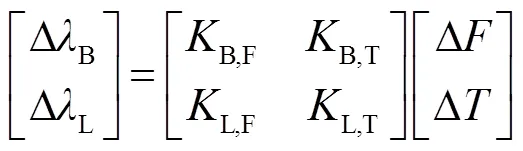
从上式中可以发现,当得到少模LPFG和FBG温度响应灵敏度及应变响应灵敏度,同时从OSA得到该结构反射谱波长变化量,结合式(7)可以计算出外界环境中温度的变化量和施加应变的变化量,最终实现环境温度和应变的双物理量的解耦。
4 实验及结果分析
4.1 DMF-LPFG应变传感
应变传感实验装置如图4所示。首先将传感结构放置在微位移平台上并连接好应变测量系统,实验中受轴向应变的部分长度=14.3 cm。通过调节三维位移平台,使得新型复合光栅结构在轴向受到拉伸,即复合结构受到轴向上应变作用,在轴向上每次使复合结构拉伸的轴向形变量为0.02 mm,则每次提供的应变量为0.02 mm/14.3 cm=140 με。图5(a)展示了LPFG结构的应变响应。由图可得,随着应变增大,双模LPFG的谐振波长发生红移,谐振波长处的透过率单调减小。图5(b)展示了LPFG结构的谐振波长与应变的关系曲线。图中红色数据点为LPFG在不同轴向应变下的波长值,黄色数据表示强度衰减变化。从图中可以发现,该新型结构传感器在0 με~840 με轴向应变范围内,其灵敏度达到-5.4 pm/με,相比在SMF上用CO2激光刻写的LPFG,其轴向应变灵敏度具有较大的提高。
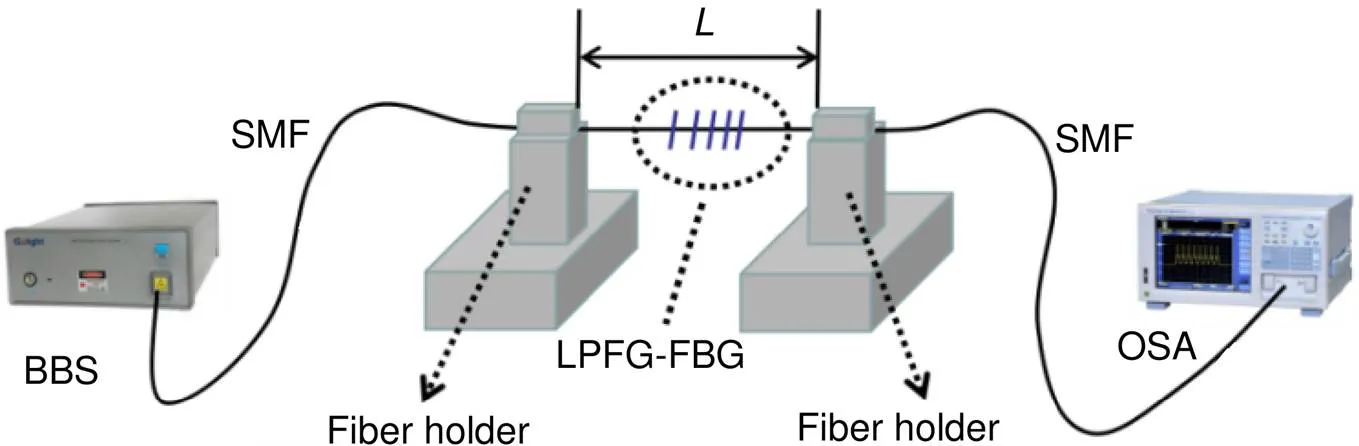
图4 应变测量装置
4.2 温度传感
在轴向应变测量时一般伴随着温度串扰,因此对该结构进行了温度测试。将传感器分装好拉直并固定在温箱中,温箱的温度从室温开始上升,25 ℃逐步到80 ℃,其响应的温度分辨率为0.1 ℃。在不同的温度步长下记录传感器透射光谱的波长变化,其对应的实验光谱如图6(a)所示。当温度升高时,双模LPFG的谐振光谱红移。将不同温度值下的对应波长进行线性拟合,可以得到少模LPFG的温度灵敏度达到58.86 pm/℃。在温度测量过程中对FBG的响应也进行的测试,实验结果表明,FBG的应变灵敏度为1.2 pm/με,温度灵敏度是10.13 pm/℃。将LPFG与FBG谐振波长的变化情况代入式(7)中,即可计算出外界环境中温度与应变的变化值,从而达到同时测量温度和应变的目的,如式(8)所示:
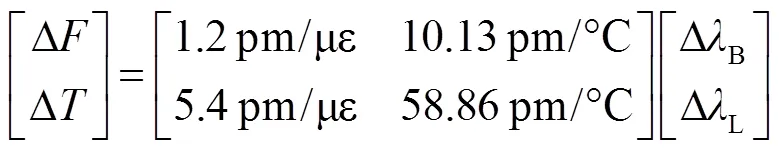
4.3 折射率特性分析
本文提出的非对称LPFG-FBG复合结构中的FBG对环境折射率不敏感,是由于其刻写在纤芯区,但是LPFG的栅格在包层区也存在,这是分析LPFG环境折射率敏感特性的必要性。首先,原理上是由LP01模式和LP11模式之间的相互耦合产生的1536 nm处的损耗谷,因此根据双模LPFG的耦合模公式,可以得到设计的非对称DMF-LPFG结构对外界环境折射率的灵敏度公式为
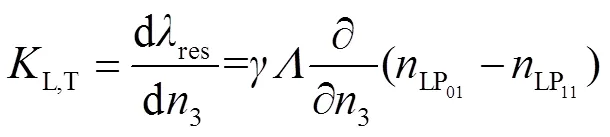
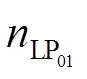
5 结束语
本文提出了新型DMF-LPFG与SMF-FBG级联结构光纤传感器,实现了对温度与应变的同时测量。详细介绍了DMF-LPFG的制备过程、传感机理和实验结果。实验结果表明,在0 με~840 με应变范围内该LPFG的应变传感灵敏度达到-5.4 pm/με,在25 ℃~80 ℃温度范围内该传感器的温度灵敏度达到58.86 pm/℃,在不同气体环境中测量的光谱移动量为0,并且给出了FBG-LPFG的双参数解调矩阵。通过理论和实验证明了复合结构的环境折射率不敏感特性,这对于抵抗环境干扰具有重要意义。本文提出的复合光栅结构具有良好的传感性能和工程应用前景。
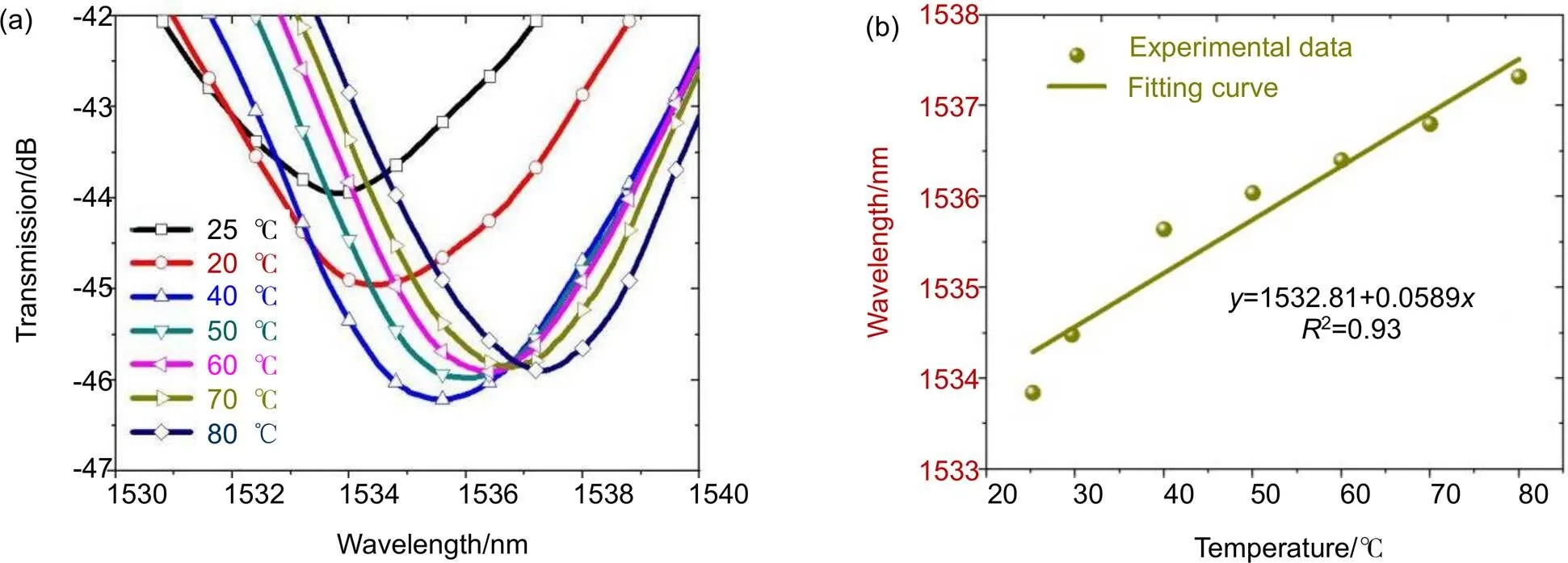
图6 温度测量实验数据。(a) 光谱随温度漂移;(b) 温度灵敏度拟合
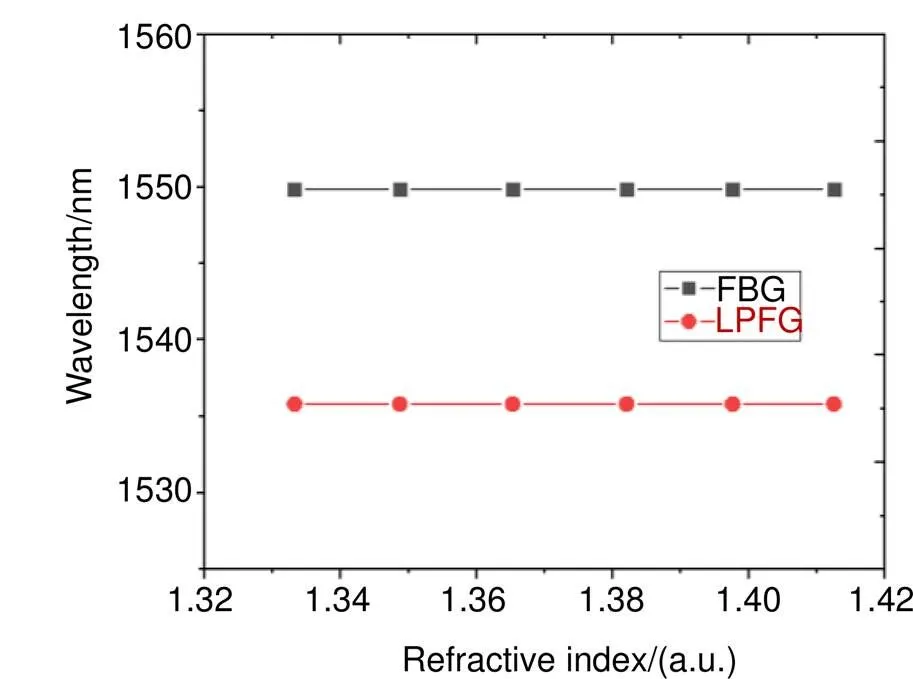
图7 折射率测量实验数据
[1] Vengsarkar A M, Lemaire P J, Judkins J B,. Long-period fiber gratings as band-rejection filters[J]., 1996, 14(1): 58–65.
[2] James S W, Tatam R P. Optical fibre long-period grating sensors: characteristics and application[J]., 2003, 14(5): R49–R61.
[3] Liao C R, Wang Y, Wang D N,. Femtosecond laser inscribed long-period gratings in all-solid photonic bandgap fibers[J]., 2010, 22(6): 425–427.
[4] Martinez-Rios A, Monzon-Hernandez D, Torres-Gomez I. Highly sensitive cladding-etched arc-induced long-period fiber gratings for refractive index sensing[J]., 2010, 283(6): 958–962.
[5] Bai Z Y, Zhang W G, Gao S C,. Compact long period fiber grating based on periodic micro-core-offset[J]., 2013, 25(21): 2111–2114.
[6] Rego G, Okhotnikov O, Dianov E,. High-temperature stability of long-period fiber gratings produced using an electric arc[J]., 2001, 19(10): 1574–1579.
[7] Jiang Y H, Fu H W, Zhang J L,. Simultaneous measurement of transverse pressure and temperature based on multi-core fiber cascaded with fiber Bragg grating[J]., 2017, 46(1): 0106002. 蒋友华, 傅海威, 张静乐, 等. 基于多芯光纤级联布喇格光纤光栅的横向压力与温度同时测量[J]. 光子学报, 2017, 46(1): 0106002.
[8] Chu J L, Shen C Y, Feng Q,. Simultaneous measurement of strain and temperature based on a long-period grating with a polarization maintaining fiber in a loop mirror[J]., 2014, 20(1): 44–47.
[9] Yang M W, Wang D N, Wang Y,. Long period fiber grating formed by periodically structured microholes in all-solid photonic bandgap fiber[J]., 2010, 18(3): 2183–2189.
[10] Liu Q, Bi W H, Fu X H,. Refractive index sensing characteristic of superimposed long period gratings on few mode fiber[J]., 2018, 47(1): 0106001.
刘强, 毕卫红, 付兴虎, 等. 基于少模光纤长周期光栅叠栅的折射率传感特性[J]. 光子学报, 2018, 47(1): 0106001.
Refractive index insensitive two parameter sensor based on dual mode LPEG
Wang Xiangyu1, Qiao Xueguang2*, Yu Dakuan1
1Northwestern Polytechnical University, the School of Science, Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, Xi’an, Shaanxi 710072, China;2Northwest University, Department of Physics, Xi’an, Shaanxi 710069, China

(a) The structure of proposed sensor; (b) The measured field distribution emitted from DMF without LPFG; (c) The measured field distribution emitted from DMF-LPFG; (d), (e) The measured field distribution after passing through the LPFG-polarizer; (f) Microscopic image of LPFG
Overview:Fiber Bragg gratings (FGs) and long period fiber gratings (LPFGs) are novel passive optical devices, which have been investigated for decades due to their unique physical and optical properties. The proposal of high-frequency CO2laser writing LPFG technology is of great significance to enrich the design and preparation of the LPFG, improve the quality of signal transmission, and realize mass production. Multi-parameter measurement is an inevitable trend in the future development of optical fiber sensing technology. Especially, there are some problems such as the interference of environmental refractive index changes and temperature crosstalk for the application of engineering strain sensing. It is very important to effectively compensate the measurement error caused by temperature changes. The cladding mode of less-mode LPFGs is sensitive to the external refractive index, so the change in ambient refractive index will lead to the measurement deviation. The change in ambient temperature will cause the change of the LPFG period and the effective refractive index of various modes. The core of dual-mode fibers only transmits two low-order modes, so it has higher capacity and flexibility in mode control and analysis than that of single-mode fiber (SMFs). At the same time, compared with the SMF, the all fiber structure of the LPFG is more compact and flexible. Their conversion efficiency between the two modes is very high and the resonant wavelength at the mode conversion is sensitive to the strain and temperature when the phase matching condition is satisfied. Based on this characteristic, a LPFG sensor based on dual-mode fiber is proposed. The variation of ambient refractive index and ambient temperature is the main factor affecting the error of optical fiber strain measurement. In this paper, a strain sensor based on the dual-mode fiber (DMF) LPFG is designed. The sensor model structure was designed, and the sensor samples with optimized parameters were produced. The experiment tested the response of the DMF-LPFG sensing structure to the strain, temperature and refractive index in the external environment. Through the Bragg grating (fiber Bragg grating, FBG) written on the single-mode fiber with a UV laser, the cross effect of the ambient temperature is solved. The results of the axial strain experiment show that the axial strain sensitivity of the new structure sensor can reach -5.4 pm/με in the strain range of 0~840 με, which is greatly improved compared to the ordinary LPFG. The sensitivity is 58.86 pm/℃ in the temperature range of 25 ℃~80 ℃, showing good linearity. At the same time, the sensor is insensitive to changes in ambient refractive index. The dual-parameter matrix is used to process the strain and temperature sensitivity of the few-mode LPFG and FBG to achieve dual-parameter simultaneous demodulation. The new composite grating structure has good sensing performance and engineering application prospects.
Wang X Y, Qiao X G, Yu D KRefractive index insensitive two parameter sensor based on dual mode LPEG[J]., 2021, 48(3): 200247; DOI:10.12086/oee.2021.200247
版权所有©2021中国科学院光电技术研究所
Refractive index insensitive two parameter sensor based on dual mode LPEG
Wang Xiangyu1, Qiao Xueguang2*, Yu Dakuan1
1Northwestern Polytechnical University, the School of Science, Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Optical Information Technology, Xi’an, Shaanxi 710072, China;2Northwest University, Department of Physics, Xi’an, Shaanxi 710069, China
The variation of ambient refractive index and ambient temperature is the main factor affecting the error of optical fiber strain measurement. In this paper, a strain sensor based on the dual-mode fiber (DMF) long period fiber grating (LPFG) is designed. The sensor model structure was designed, and the sensor samples with optimized parameters were produced. The experiment tested the response of the DMF-LPFG sensing structure to the strain, temperature and refractive index in the external environment. Through the Bragg grating (fiber Bragg grating, FBG) written on the single-mode fiber with a UV laser, the cross effect of the ambient temperature is solved. The results of the axial strain experiment show that the axial strain sensitivity of the new structure sensor can reach -5.4 pm/με in the strain range of 0 με~840 με, which is greatly improved compared to the ordinary LPFG. The sensitivity is 58.86 pm/℃ in the temperature range of 25 ℃~80 ℃, showing good linearity. At the same time, the sensor is insensitive to changes in ambient refractive index. The dual-parameter matrix is used to process the strain and temperature sensitivity of the few-mode LPFG and FBG to achieve dual-parameter simultaneous demodulation. The new composite grating structure has good sensing performance and engineering application prospects.
dual mode fiber; LPFG; FBG; strain sensor; temperature compensation
National Programs for Science and Technology Development (61327012), National Natural Sciene Foundation of China (61735014), National Key Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Project (61927812), and National Key Research and Development Plan (2017YFB0405502)
10.12086/oee.2021.200247
TN253
A
* E-mail: xgqiao@nwu.edu.cn
王向宇,乔学光,禹大宽. 基于双模LPFG折射率不敏感双参量传感器[J]. 光电工程,2021,48(3): 200247
Wang X Y, Qiao X G, Yu D KRefractive index insensitive two parameter sensor based on dual mode LPEG[J]., 2021, 48(3): 200247
2020-07-04;
2020-10-19
国家科技攻关资助项目(61327012);国家自然科学基金资助项目(61735014);国家重大科研仪器研制资助项目(61927812);国家重点研究发展计划(2017YFB0405502)
王向宇(1977-),男,博士研究生,讲师,主要从事光纤传感与应用的研究。E-mail:wxy@xsyu.edu.cn
乔学光(1955-),男,博导,教授,主要从事光纤传感与应用的研究。E-mail:xgqiao@nwu.edu.cn
