Bioinformatics Analysis on lncRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles for Novel Biological Features of Valvular Heart Disease with Atrial Fibrillation
2021-04-02
Abstract—The biological features of the valvular heart disease with atrial fibrillation (AF-VHD) remain unknown when involving long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs).This study performed system analysis on lncRNA and messenger RNA (mRNA) expression profiles constructed by using bioinformatics methods and tools for biological features of AF-VHD.Fold change and t-test were used to identify differentially expressed (DE) lncRNAs and mRNAs.The enrichment analysis of DE mRNAs was performed.The subgroups formed by lncRNAs and nearby mRNAs were screened,and a transcriptional regulation network among lncRNAs,mRNAs,and transcription factors (TFs) was constructed.The interactions between mRNAs related to lncRNAs and drugs were predicted.The 620 AF-VHDrelated DE lncRNAs and 452 DE mRNAs were identified.The 3 lncRNA subgroups were screened.The 665 regulations mediated by lncRNAs and TFs were identified.The 9 mRNAs related to lncRNAs had 1 or more potential drug interactions,totaling 37 drugs.Of these,9 drugs targeting 3 genes are already known to be able to control or trigger atrial fibrillation (AF) or other cardiac arrhythmias.The found biological features of AF-VHD provide foundations for further biological experiments to better understand the roles of lncRNAs in development from the valvular heart disease (VHD) to AF-VHD.
1.Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common supraventricular arrhythmias disorder associated with an increased risk of the heart failure,dementia,and stroke.The stroke is one of the greatest hazards of AF[1].The research by Wolfet al.indicated that the stroke rate among those who have the non-valvular heart disease with AF was 5.6 times higher than normal people,and that among patients who have the valvular heart disease with atrial fibrillation (AF-VHD) was 17.6 times higher than normal people.Strokes caused by AF-VHD were also much more serious[2].Therefore,understanding the biological features of AF-VHD at the molecular level is important for improving the diagnosis,treatment,and prognosis of this disease.
Some efforts have been made in identifying biomarkers of AF-VHD and the mechanism behind AF-VHD.For example,9 genes were related to the development of fibrosis and 8 genes were related to an increased risk of thromboembolic events in chronic AF-VHD patients[3].The expression level of miR-1202 showed the largest change in AF with mitral stenosis[4].There was no detectable effect of chronic AF on the microRNA expression in the left atria tissue,but the microRNA expression in the right atria was strongly influenced by AF[5].Fenget al.combined microRNAs with gene expression profiles to predict 45 specific microRNAs related to AF-VHD using an asymmetric principal component analysis algorithm.These predicted microRNAs provided new insight into further experimental study and the molecular mechanism leading to the development of AF-VHD[6].
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are defined as transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides that are not translated into protein[7].Recent evidence has shown that lncRNAs participate in a variety of important regulatory processes,such as silencing of the X chromosome[8],genomic imprinting[9],chromatin modification[10],[11],and transcriptional activation[12].More recent studies have shown that lncRNAs play important roles in the occurrence and development of AF and some AF related diseases,such as the coronary artery disease,dilated cardiomyopathy,diabetes,and cardiomyopathy[13].NONHSAT040387 and NONHSAT098586 were the most up-regulated and down-regulated lncRNAs in patients with AF,respectively.The oxygen transporter activity and protein heterodimerization activity were speculated to be involved in AF pathogenesis[14].A total of 579 differentially expressed (DE) lncRNAs and 349 DE messenger RNAs (mRNAs) were identified in pulmonary vein sleeves between the patients with the mitral valve disease and dilated left atria who developed long standing persistent AF and the patients with the mitral valve disease and dilated left atria who were in a normal sinus rhythm (SR)[15].Furthermore,increasing evidence has shown that the transcriptional regulatory circuits of lncRNAs and transcription factors (TFs) play important roles in controlling cell differentiation,cell proliferation,and embryonic stem cell identification[16]-[18].For example,interactions between lncRNAs and TFs can control the pluripotency and differentiation of embryonic stem cells[16].The plasma levels of lncRNA H19 and LIPCAR were significantly increased in patients with the coronary artery disease[19].H19 knockdown increased the PA2G4 expression and suppressed apoptosis in cardiomyocytes to improve the left ventricular structure and function[20].Further,H19 was confirmed to reduce the VDAC1 expression and inhibit apoptosis in cardiomyocytes[21]and to inhibit autophagy in cardiomyocytes by epigenetically silencing of DIRAS3[22].However,the biological features of AF-VHD remain unknown when involving lncRNAs.
Here,we used Arraystar Human lncRNA and mRNA Arrays to construct genome-wide lncRNA and mRNA expression profiles of the valvular heart disease (VHD) and AF-VHD.We then integrated these large-scale datasets to identify AF-VHD-related DE lncRNAs and mRNAs,which further were done enrichment analysis for functions of DE mRNAs associated with AF-VHD.Next,the subgroup analysis of lncRNAs and the identification of interactions among DE lncRNAs,DE mRNAs,and TFs were performed for understanding the biological features of AF-VHD when involving lncRNAs.Finally,the interactions between mRNAs related to lncRNAs and drugs were predicted.
2.Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This experiment was approved by the Ethics Review Board of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC) and all patients gave informed consent.The investigation complied with the principles that governed the use of the human tissue outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki.
3.Materials
In the construction of the genome-wide lncRNA and mRNA expression profiles,we used the atrial appendage tissue of five VHD patients with chronic AF and five VHD patients with SR.The clinical characteristics of patients are shown in Table 1,in which the group data are shown as mean ± SD where SD denotes the standard deviation;gender data are summarized as the female/male;LAD represents the left atrium diameter;RAD denotes the right atrium diameter;LVD is the left ventricle diameter;RVD is the right ventricle diameter;EF is the ejection fraction.The VHD and AF-VHD groups were comparable in the mean age and gender distribution (49 ± 2 years and 49 ± 5 years,80% female and 60% female,respectively).VHD and AF-VHD had similar ejection fractions(60% ± 5% and 59% ± 8%,respectively).AF-VHD patients had a greater tendency to the left atrial dilation and left ventricle dilation,but the differences were not statistically-significant (t-test).The AF duration of AF-VHD patients was between 2 months and 29 months with an average of 11 ± 11 months.
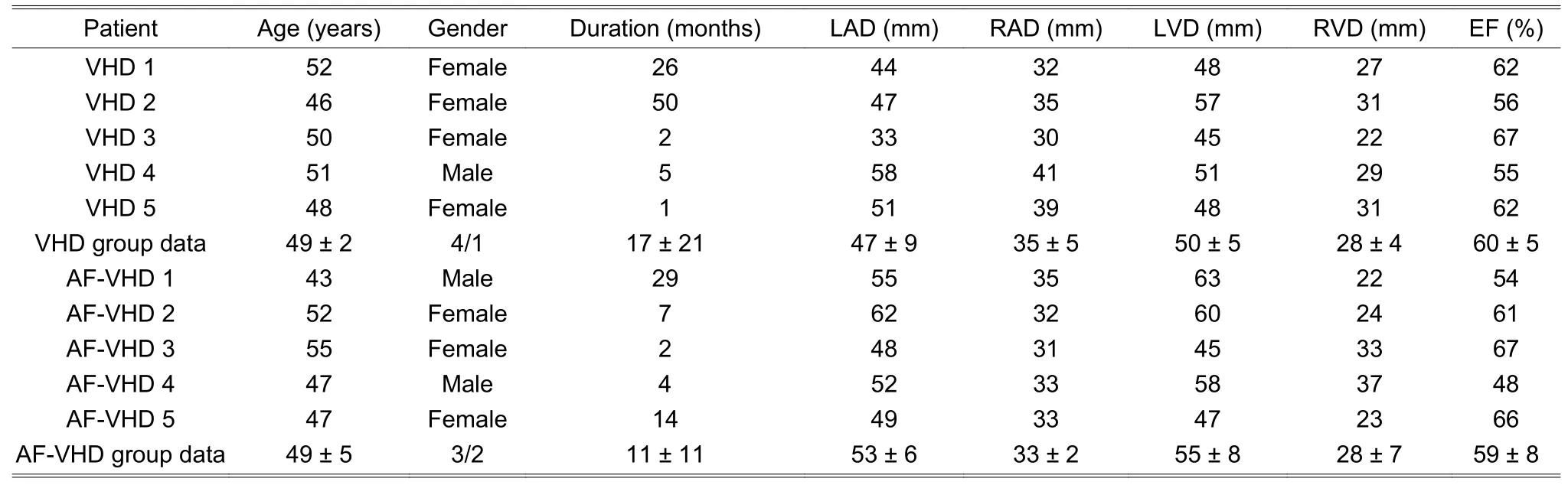
Table 1:Clinical characteristics of patients
The atrial appendage tissue was collected from VHD and AF-VHD patients undergoing heart surgery at the Affiliated Hospital,Medicine School,UESTC,Chengdu.In all cases,the tissue removed at surgery was placed immediately in ice-cold saline.The surgically removed tissue (the thickness of less than 0.5 cm) was immersed in the tubes containing the RNAlater solution (Invitrogen) within 10 min of excision and then it was stored at -4 °C all night.RNAlater was removed after overnight treatment and the samples were stored at-80 °C until lncRNA and mRNA arrays analysis.
4.Methods
4.1.Microarray Experiment
mRNA was purified from total RNA after removal of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) (mRNA-ONLY™ Eukaryotic mRNA Isolation Kit,Epicentre).The RNA quantity and quality were measured by NanoDrop ND-1000.The RNA integrity was assessed by standard denaturing agarose gel electrophoresis.The Arraystar Human lncRNA Microarray V3.0 was used to detect lncRNAs and coding transcripts.The Agilent Feature Extraction software (version 11.0.1.1) was used to analyze the acquired array images.Quantile normalization and subsequent data processing were performed with the GeneSpring GX v12.1 software package (Agilent Technologies).After quantile normalization of the raw data,the data of lncRNAs and mRNAs were used in further data analysis.The original microarray data files have been deposited in Gene Expression Omnibus(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo) and the accession number was GSE113013.
4.2.Identification of DE lncRNAs and DE mRNAs
The fold change andt-test were used to identify DE lncRNAs and DE mRNAs.Statistically significant DE lncRNAs and DE mRNAs satisfiedF≥2.0 andP≤0.05,whereFis the fold change andPis the P-value.The multi-test corrections for the P-values were performed by the Benjamini Hochberg method (false discovery rate(FDR) smaller than 0.23).
4.3.Function Analysis of DE mRNAs
We used topGO[23]to perform Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of DE mRNAs (P≤0.05).The functions are described in three aspects:Biological process,cellular component,and molecular function.Similarly,we performed Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis to obtain important biological pathways enriched by DE mRNAs (P≤0.05).
4.4.Subgroup Analysis of DE lncRNAs
The nearby mRNAs of lncRNAs can be the potential target regulated by that lncRNA in cis-regulation.When the distance between mRNA and lncRNA was less than 300 kbp,their position was considered to be near[24].The Arraystar Human lncRNA Microarray V3.0 mainly collected information about lncRNAs from multiple databases,including the reference sequence (RefSeq),University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC),GENCODE,lncRNA database (lncRNAdb),RNA database (RNAdb),non-coding RNA expression database (NRED),long intergenic non-coding RNA (lincRNA) catalogs,ENCODE CAGE clusters,PolyA-seq,deep RNA-seq,and capture seq data repositories.Some lncRNAs and nearby mRNAs in the databases have been grouped according to their position relationships,e.g.,antisense lncRNAs,enhancer lncRNAs,and lincRNAs.The existing studies illustrated that different neighborhood relations between lncRNAs and mRNAs might reveal different regulation patterns of lncRNAs[12],[25],[26].For example,antisense lncRNAs can induce epigenetic changes of chromatin and DNA to affect the expression of the corresponding sense mRNA[25].Enhancer lncRNA is a region of DNA that can enhance gene transcription.lncRNAs from this region are referred to as enhancer-like lncRNAs and may change the expression of nearby protein-coding genes[12].Therefore,we screened the subgroups of DE lncRNAs and nearby mRNAs through searching the above databases using DE lncRNAs and DE mRNAs.
4.5.ldentifying lnteractions among DE lncRNAs,DE mRNAs,and TFs
Transcription of mRNA requires a combination of specific TFs with regulatory sequences to open the transcription program.TF is a key regulatory factor in the gene expression.lncRNA can also activate or inhibit the gene expression by binding to the promoter sequences of mRNA[27],[28].Thus,there possibly exists an interaction that lncRNAs share common TF-binding sites (TFBS) in mRNA sequences with TFs.In this study,these lncRNA-mRNA-TF interactions were defined as lncRNA associated triplets (LncATs),which reveals another regulation relationship of lncRNAs.So far,LncATs have not yet been fully understood.However,some studies have found that there is a transcriptional regulation mediated by lncRNA and TF,which can be explained well in biology as detailed below[27],[28]:1) lncRNA binds with the promoter region of the corresponding mRNA to form a trimer,which inhibits the binding of TFs and induces gene silencing;2) TF binds with the promoter region of the corresponding mRNA before lncRNA,which can inhibit the binding of lncRNA and block lncRNA to regulate mRNA.
To find LncATs,we first extracted the promoter sequences of mRNA from the database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).Then,the match tool in the TRANSFAC database was used to match the promoter sequences and TFBS for establishing the regulation between TF and mRNA (denoted by TF-mRNA).To ensure the accuracy of matching,only those TFs from the human genome with a core score of 1.00 and a matrix fraction greater than 0.95 were chosen[29].
Next,the co-expressed relationships between DE lncRNAs and DE mRNAs were established.The Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) was calculated based on the expression value between each DE lncRNA and DE mRNA pair.The threshold was set as PCC >0.95 or PCC <-0.95,and FDR was controlled at the threshold of 0.05 (the Benjamini and Hochberg algorithm).We indicated the relationship between lncRNA and mRNA using lncRNA-mRNA.
Finally,we blended lncRNA-mRNA and TF-mRNA pairs to build a transcriptional regulatory network among lncRNAs,mRNAs,and TFs.LncATs could be identified from the network.
4.6.Analyzing lnteractions between mRNAs Related to lncRNAs and Drugs
We investigated whether the nearby mRNAs of lncRNAs and mRNAs in LncATs interact with the drugs associated with AF or other cardiac arrhythmias by querying the Drug Gene Interaction database (DGIdb)[30].
5.Results
5.1.DE lncRNAs and DE mRNAs from Microarrays
We found that 262 lncRNAs and 169 mRNAs were significantly up-regulated and that 358 lncRNAs and 283 mRNAs were significantly down-regulated between the AF-VHD and VHD groups (see Additional File 1 for DE lncRNAs and Additional File 2 for DE mRNAs).Fig.1 is two volcano plots displaying the statistical significance of DE lncRNAs and DE mRNAs between AF-VHD and VHD.The horizontal axis represents log2F.The vertical axis represents -lgP.Each point denotes a biological molecule.The color of the point is used to tell whether biological molecules are DE.The red squares indicate DE lncRNAs or DE mRNAs with statistical significance.

Fig.1.Volcano plots:(a) lncRNA and (b) mRNA.
5.2.GO Enrichment Analysis of DE mRNAs
The results of GO analysis of down-regulated mRNAs are shown in Additional File 3,from which the most significant ten terms of the biological process (BP),cellular component (CC),and molecular function (MF) are shown in Fig.2 (a) to Fig.2 (c),respectively.

Fig.2.Results of GO analysis of DE mRNAs:Top ten terms of down-regulated mRNAs of (a) BP,(b) CC,and (c) MF;Top ten terms of up-regulated mRNAs of (d) BP,(e) CC,and (f) MF.Count is the number of genes in a term.P represents the credibility of the enriched term.
Positive regulation of T-cell migration,positive regulation of lymphocyte migration,negative regulation of viral genome replication,response to type I interferon,etc.were enriched in BP;myofibril,contractile fiber,cell projection,etc.were enriched in CC;protein binding,potassium-transporting ATPase activity,hydrolase activity,etc.were enriched in MF.The results of GO analysis of up-regulated mRNAs are shown in Additional File 4,from which the top ten terms of BP,CC,and MF are shown in Fig.2 (d) to Fig.2 (f),respectively.Oxygen transport,response to stimulus,positive regulation of multicellular organism growth,etc.were enriched in BP;hemoglobin complex,cytosolic part,axon part,extracellular space,etc.were enriched in CC;oxygen transporter activity,serinetype activity,receptor activity,etc.were enriched in MF.
5.3.KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DE mRNAs
UnderP≤0.05,the pathways enriched by down-regulated and up-regulated mRNAs are shown in Additional File 5.The top ten significant terms enriched by 283 down-regulated mRNAs are shown in Fig.3 (a),including arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy,circadian entrainment,and cholinergic synapse.The top ten significant terms by 169 up-regulated mRNAs are shown in Fig.3 (b),including adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes,antigen processing and presentation,and cAMP signaling pathway.SelectionCounts is the number of genes in a pathway term andPrepresents the credibility of an enriched pathway term in Fig.3.

Fig.3.Participant pathways of DE mRNAs:(a) down-regulated and (b) up-regulated mRNAs.
5.4.Three Subgroups of DE lncRNAs Existed nearby DE mRNAs
We mined three subgroups of lncRNAs according to the positional relationships between DE lncRNAs and nearby DE mRNAs,which are antisense lncRNAs (see Table 2),enhancer lncRNAs (see Table 3),and lincRNAs(see Table 4).In these tables,it is worthy to note that the sequence name represents the sequence identifier of lncRNA;regulation denotes which group has greater or lower intensity values than the other;RNA length is the length of lncRNA;nearby gene symbol is the symbol of the nearby coding gene of lncRNA;txStart and txEnd are the beginning and end of a transcript of lncRNA,respectively;nearby gene txStart and nearby gene txEnd are the beginning and end of a transcript of mRNA,respectively.The distances between lncRNAs and their cis-regulated mRNAs are presented in Fig.4.The positions of lncRNAs and their nearby mRNAs in the antisense lncRNAs subgroup overlap,so the distance between them is zero.

Table 2:Information of antisense lncRNAs

Table 3:Information of enhancer lncRNAs
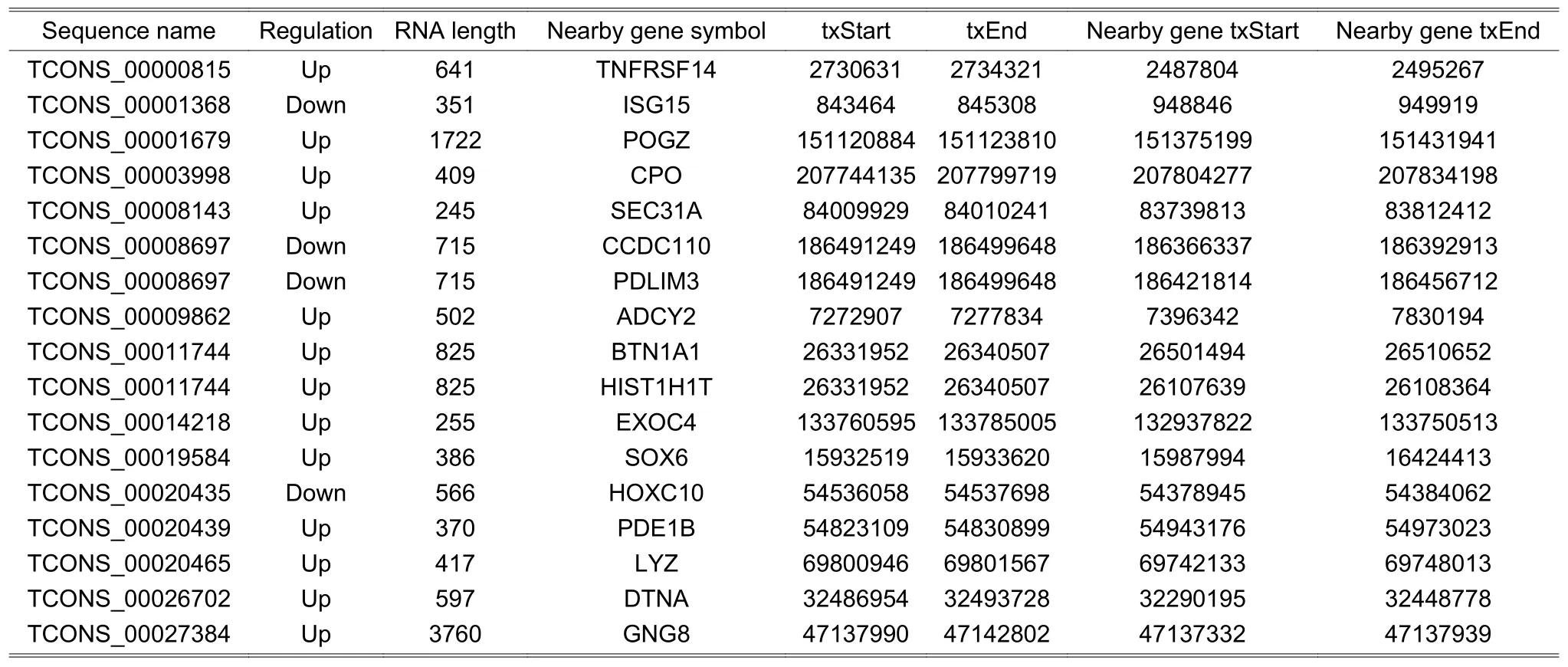
Table 4:Information of lincRNAs
5.5.ldentified LncATs
We firstly identified 8472 lncRNA-mRNAs and 113 TF-mRNAs using the proposed method,shown in Additional File 6.Secondly,we blended lncRNA-mRNAs and mRNA-TFs to build a transcriptional regulatory network with DE lncRNAs,DE mRNAs,and TFs as the nodes.In total,there were 917 nodes (496 lncRNAs,381 mRNAs,and 40 TFs) and 8585 edges in this network.Finally,665 LncATs were identified (see Additional File 7) and used to construct an LncAT regulation network (see Fig.5),which included 250 nodes (188 lncRNAs,30 mRNAs,and 32 TFs) and 344 edges.In Fig.5,the circle represents lncRNA,the hexagon indicates TF,and the five-pointed star indicates mRNA.The red color and flesh color indicate up-regulated and down-regulated lncRNAs or mRNAs,respectively.The line represents the relationship of lncRNA-mRNA or TF-mRNA.The existing research can support that some LncATs were associated with the development from VHD to AF-VHD (see Section 6).
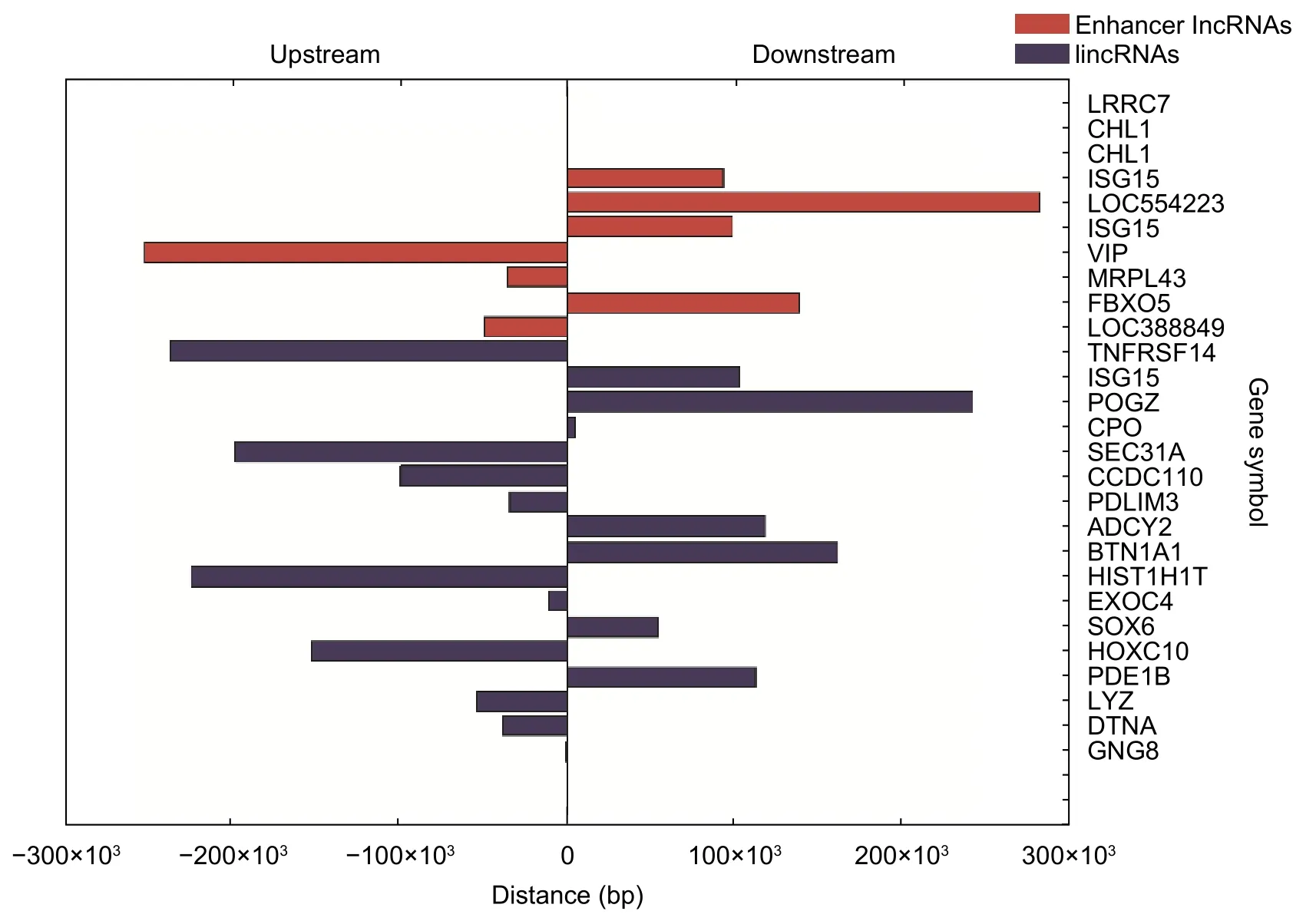
Fig.4.Distances between lncRNAs and their nearby mRNAs.Upstream means that the nearby mRNA is at the upstream of lncRNA,and downstream means that the nearby mRNA is at the downstream of lncRNA.
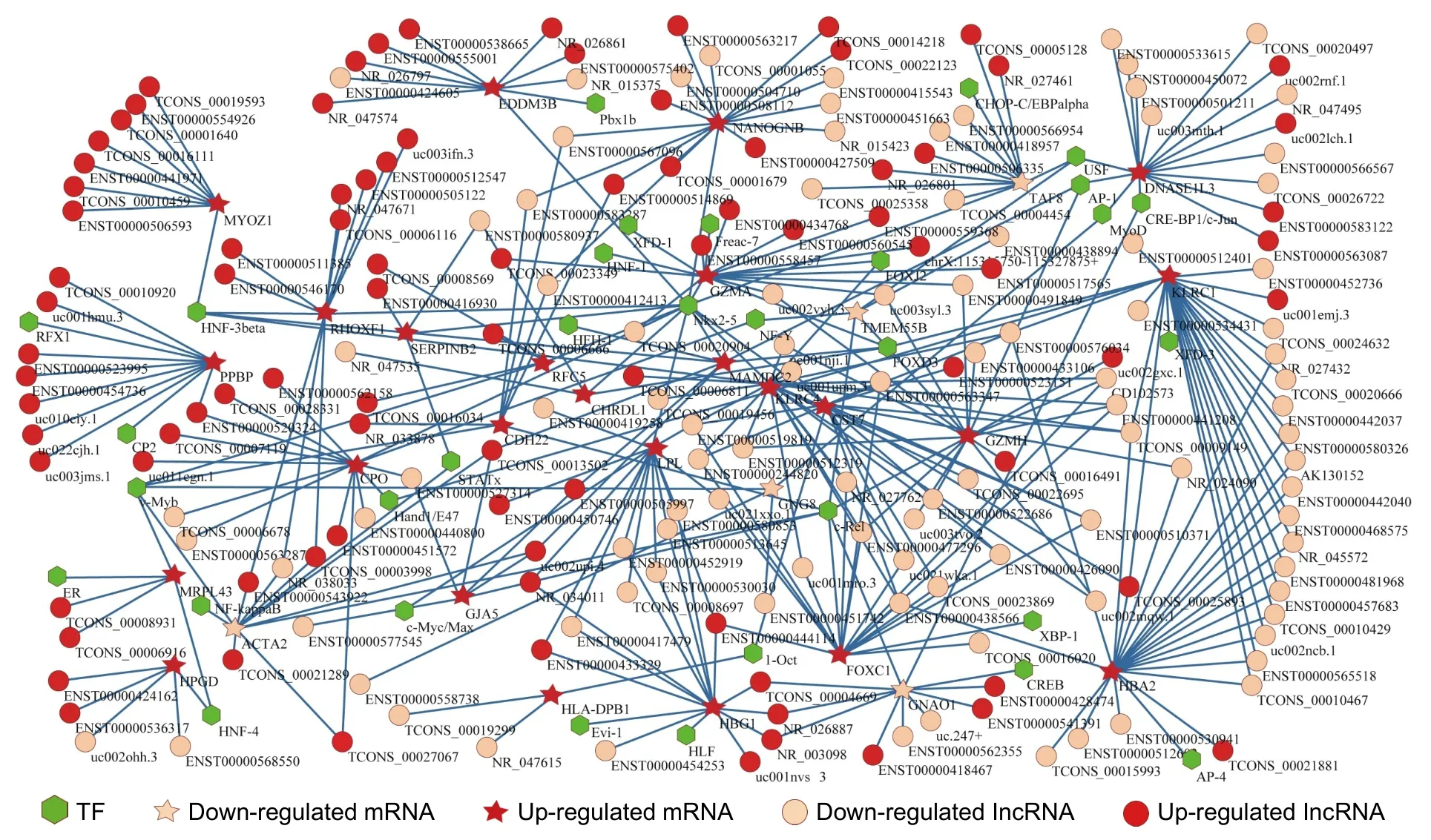
Fig.5.LncAT regulation network.
5.6.lnteractions between mRNAs Related to lncRNAs and Drugs
In these 51 mRNAs related to lncRNAs,including nearby mRNAs of lncRNAs in three subgroups and mRNAs in LncATs,we found 9 mRNAs (ISG15,VIP,PDE1B,LYZ,GZMA,LPL,GJA5,SERPINB2,and HPGD) which had 1 or more potential drug interactions,totaling 37 drugs.Of these,9 drugs targeting 3 genes (VIP,PDE1B,and LYZ)are already known to be able to control or trigger AF or other cardiac arrhythmias.Table 5 shows the predicted interactions of 9 mRNAs with drugs and related lncRNAs.Bold indicates the drugs related to AF or other cardiac arrhythmias.

Table 5:Predicted interactions of 9 mRNAs with drugs and related lncRNAs
6.Discussion
6.1.Comparison with Existing Work
AF-VHD-related lncRNAs have not been reported yet to our knowledge.In the previous study,169 genes were identified to be DE between AF-VHD and VHD patients[3].Only 3 genes (TNNT1,LDB3,and SERPINB2) are the same between DE gene lists of Lamiraultet al.[3]and this study.TNNT1 genetic and epigenetic variations are associated with the coronary artery disease[31].The tenecteplase targeting SERPINB2 is a drug to treat acute myocardial infarction[32].AF could be induced by the coronary artery disease and is a risk of myocardial infarction[13],[33].One reason for a low overlap could be that individual differences in patients led to the differences in the gene expression.Another possible reason is the difference between the two sample groups.For example,our samples came from the Asian patient group,but the compared samples came from the European patient group.The third reason is that different microarray platforms and bioinformatics tools were used.
Some terms of GO that we enriched using DE mRNAs have been previously reported to be related to AF in literature[34]-[37].For example,myofibril is associated with the systolic function,contractile fiber,and hydrolase activity,and the potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity is related to potassium channels.The atrial systolic dysfunction is one of the causes of AF.The atrial systolic dysfunction occurs both after short-term and chronic AF.The systolic dysfunction is associated with myocardial fibrosis[34].In the study of AF,Gelderet al.found that the systolic dysfunction was most likely associated with the changes in the atrial myocytes,which can reflect the structural changes.This change in the atrial myocytes may be induced by the hydrolysis of proteins[35].The decrease in the atrial effective refractory period (AERP) has benefits for initiation of reentrant arrhythmias,such as AF.AERPs were significantly shorter in patients with persistent and paroxysmal AF.Protein levels of L-type calcium channels were correlated positively with AERP,and it showed a remarkable reduction[36],[37].The shortening of AERP can also be caused by the increase in the conductivity of potassium ions.Several mRNA and protein levels of potassium channels were significantly decreased in patients with persistent AF.It has been declared that the changes in the electrophysiology of AF were mainly caused by the decreases in L-type calcium channels,but the decrease in potassium channels played a secondary role in allowing myocardial cells to adapt to the high rate and counteract the shortening of AERP[37].ACTA2 in LncATs was enriched in the contractile fiber.Guoet al.found that people with ACTA2 mutations can have a diversity of vascular diseases,including the premature onset of the coronary artery disease and premature ischemic strokes[38].The coronary artery disease is a risk factor for AF[39].AF increases the risk of strokes[1].TCONS_00027067,ENST00000543922,TCONS_00021289,TCONS_00003998,TCONS_00013502,uc002upi.4,and NR_038033 were co-expressed with ACTA2 in LncATs.These lncRNAs may be related to AF by acting ACTA2.
Right ventricular cardiomyopathy causing arrhythmia and cholinergic synapse pathways enriched by DE mRNAs have been reported to be related to arrhythmia or AF in literature[40],[41].The pathological features of right ventricular cardiomyopathy are the gradual loss of cardiomyocytes and the replacement of fibrous plaques[40].This disease can cause arrhythmia,heart failure,and sudden death.Animal experiments showed that isopropyl epinephrine and acetylcholine can increase the induction of AF[41],[42].Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter and can specifically act on all kinds of cholinergic receptors,while the sympathetic nerve and vagus nerve have a synergistic effect on the occurrence of AF[43],[44].The nearby mRNA ADCY2 and GNG8 of lncRNAs in the lincRNAs subgroup were enriched in the cholinergic synapse pathway.The up-regulated TCONS_00009862 and TCONS_00027384 may be associated with AF by regulating their nearby mRNA ADCY2 and GNG8 in the cholinergic synapse pathway.GNAO1 and GNG8 in LncATs were enriched in the cholinergic synapse pathway.NR_026887,ENST00000541391,ENST00000418467,NR_003098,TCONS_00004669,ENST00000428474,uc.247+,and ENST00000562355 were co-expressed with GNAO1 in LncATs.ENST00000558738 and ENST00000451742 were co-expressed with GNG8 in LncATs.These lncRNAs may be involved in AF by acting GNAO1 or GNG8 in the cholinergic synapse pathway.
6.2.lncRNAs in Different Subgroups
lncRNAs can regulate the expression of protein-coding genes at multiple levels,such as the transcriptional regulation and post-transcriptional regulation[45].Based on the positional relationships between lncRNAs and protein-coding genes in the genome,lncRNAs can be divided into multiple subgroups.From our datasets,we mined three subgroups of lncRNAs from the identified DE lncRNAs:Antisense lncRNAs,enhancer lncRNAs,and lincRNAs (see Tables 2 to 4).The existing related studies can partially support our results.In the lincRNA subgroup,PDLIM3 and DTNA were predicted to be the nearby mRNAs of TCONS_00008697 and TCONS_00026702,respectively.Although the direct association of PDLIM3 and DTNA with AF-VHD has not previously been reported,several studies have shown that PDLIM3 and DTNA are related to the risk factors of AFVHD,e.g.,PDLIM3 plays an important role in myocyte stability,growth,and remodeling processes[46].PDLIM3-deficient mice developed cardiomyopathy,structurally resembling human arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy that can cause arrhythmia[47].One mutation in DTNA has been identified in noncompaction of the left ventricle,which is the recognized primary cardiomyopathy[48].Noncompaction of the left ventricle clinically contains cardiac systolic and diastolic disorders that are associated with arrhythmias[49].In this study,the expression levels of PDLIM3 and DTNA were significantly up-regulated in AF-VHD patients compared with VHD patients.Hence,TCONS_00008697 and TCONS_00026702 were possibly associated with the development of AF-VHD by acting on PDLIM3 and DTNA,respectively.
6.3.LncATs Associated with AF-VHD
We identified 665 LncATs (Fig.5 and Additional File 7) from our datasets,in which those LncATs including GJA5 and MYOZ1 (see Additional File 7) could be well explained to be likely related to AF-VHD according to the reports in the existing literature.Gap junctions allow the direct exchange of ions and small molecules between adjacent cells.Gap junction channels are the key channels to mediate the rapid action potential propagation between cardiomyocytes[50].Gap junction remodeling is a key component of the cardiac remodeling process[51].The gap junction protein isoforms in the human atria are connexin40 (Cx40),Cx43,and Cx45,among which Cx40 and Cx43 are found in the atrial myocytes[52].Several studies indicate that mutations and polymorphisms of GJA5 encoding human Cx40 are associated with AF[53],[54].Four heterozygous GJA5 mutations were identified in 4 of the 310 unrelated AF patients,respectively[53].Four novel heterozygous missense mutations in GJA5 were identified in 4 of the 15 idiopathic AF patients[54].One heterozygous missense mutation in Cx40 was identified in 1 of the 68 lone AF patients.The mutation was also presented in the proband's father with lone AF but it was not found in the unaffected family members[52].GJA5 remodeling may lead to abnormal electrical coupling to exert an effect on potential arrhythmogenic[55].AF risk variants,rs10824026 and rs3740293,were associated with the expression of MYOZ1[56],[57].These findings implicate that GJA5 or Cx40 mutants and MYOZ1 may play an important role in AF pathogenesis.From Additional File 7,we know that TCONS_00013502,ENST00000505997,uc002upi.4,ENST00000577545,and ENST00000527314 may affect AF-VHD with c-Rel for binding GJA5.Similarly,TCONS_00010459,ENST00000506593,TCONS_00019593,ENST00000441971,ENST00000554926,TCONS_00001640,and TCONS_00016111 may affect AF-VHD with HNF-3beta for binding MYOZ1.
6.4.About the Drugs Predicted by mRNAs Related with lncRNAs
The drugs targeting VIP,PDE1B,and LYZ are already known to be able to control or trigger AF or other cardiac arrhythmias[58]-[68].Some drugs (for example,omeprazole,lisinopril,flutamide,felodipine,pentoxifylline,and sucrose)could potentially impact AF via suppressing tachypacing-induced electrical remodeling[58],improving peak oxygen consumption in patients with chronic AF[59],regressing myocardial fibrosis[60],restoring the cardiac function after trauma-hemorrhage[61],attenuating the inflammatory and fibrosis process[62],ameliorating the cardiac fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction[63],and prevention or therapeutic treatment of the cardiac contractile dysfunction[64].Other drugs(such as felodipine and dipyridamole) could be used as single therapy for day-long management of arrhythmia[65]or cause AF[66].We also identified a number of drugs which have been used for the treatment of AF,such as digoxin and bepridil[67],[68].
6.5.Limitations
Several potential limitations of this study should be highlighted.First,the sample size is a limitation.The number of patients in VHD and AF-VHD groups is small,because careful screening and recruitment of patients is timeconsuming,which could be a reason that results in a small sample size.Results from this study could have been confirmed in larger cohorts of patients and in prospective studies.Second,the exact targeting molecules and pathways by alterations of lncRNAs leading to AF-VHD remain unclear.Although our bioinformatics analysis has identified some biological features of AF-VHD when involving lncRNAs,it is difficult to estimate the actual falsepositive rate for the prediction.Third,the screened target molecules were not verified by polymerase chain reaction owing to the lack of large samples.These results in this study are based solely on bioinformatics methods,and further experimental studies are essential to verify whether these biological features affect the development of AF-VHD.
7.Conclusions
We constructed transcription expression profiles of lncRNA and mRNA from patients,with VHD patients as the control group and AF-VHD patients as the experimental group.After the expression levels of lncRNA and mRNA were systematically analyzed and studied,we obtained 620 DE lncRNAs (262 up-regulated lncRNAs and 358 down-regulated lncRNAs) and 452 DE mRNAs (169 up-regulated mRNAs and 283 down-regulated mRNAs).The 3 lncRNA subgroups were screened.The 665 regulations mediated by lncRNAs and TFs were identified.The 9 mRNAs regulated by lncRNAs had 1 or more potential drug interactions,totaling 37 drugs.Of these,9 drugs targeting 3 genes are already known to be able to control or trigger AF or other cardiac arrhythmias.The found biological features of AF-VHD provide foundations for further biological experiments to better understand the roles of lncRNAs in the development from VHD to AF-VHD.
Appendix
The following additional files can be downloaded at http://www.journal.uestc.edu.cn or JEST ScienceDirect page:https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/journal-of-electronic-science-and-technology.
Additional File 1:DE lncRNAs.
Additional File 2:DE mRNAs.
Additional File 3:GO analysis of down-regulated mRNAs.
Additional File 4:GO analysis of up-regulated mRNAs.
Additional File 5:Pathways enriched by DE mRNAs.
Additional File 6:Predicted mRNA-TF and lncRNA-mRNA pairs.
Additional File 7:Identified LncATs.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to appreciate KangChen Bio-Tech Inc.,Shanghai for performing the microarray experiments and the support of the Scientific Platform Improvement Project of UESTC.
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Electronic Science and Technology的其它文章
- Annotation of miRNAs in the COVlD-19 Novel Coronavirus
- Molecules against COVlD-19: An in Silico Approach for Drug Development
- lmpact of Coronavirus Pandemic Crisis on Technologies and Cloud Computing Applications
- Identification of the Potential Function of circRNA in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Based on Mutual RNA-RNA and RNA-RBP Relationships Shown by Microarray Data
- lmage Classification with Superpixels and Feature Fusion Method
- Signal Acquisition and Processing Method for Capacitive Electromagnetic Flowmeter
