Molecular Cloning, Bioinformatics Analysis and Transcriptional Expression of Virulence-related Gene (exsA) of Vibrio alginolyticus
2021-03-05*
*
1. College of Fisheries, Guangdong Ocean University, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Pathogenic Biology and Epidemiology for Aquatic Economic Animals, Key Laboratory of Diseases Controlling for Aquatic Economic Animals of Guangdong Higher Education Institutions, Zhanjiang 524088, China; 2. Faculty of Chemistry and Environmental Science, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang 524088, China
Abstract [Objectives] The purpose was to investigate the function and mechanism of exsA gene in type III secretion system of Vibrio alginolyticus.[Methods]The full length of exsA was cloned using molecular biology techniques to analyze its biological information. Fluorescence quantitative PCR technology was used to analyze the expression of exsA after different media stress. [Results] The exsA gene contains an open reading frame (ORF) of 861 bp, encoding 286 amino acids. The physico-chemical analysis shows that the molecular structural formula is C1442H2267N393O441S12, the theoretical molecular weight is 32.549 kD, the theoretical pI value is 6.0, and the protein is non-hydrophilic and unstable. The gene does not contain a transmembrane region, and there is no obvious signal peptide. The prediction result of protein subcellular localization shows that the protein is inside the cell. The deduced amino acid sequence and constructed phylogenetic tree show that V. alginolyticus has a close relationship with Vibrio antiquarius. The qPCR results show that the expression level of exsA in different media is different, highest in TSB medium containing bile salts, followed by DMEM medium, and lowest in ordinary TSB medium. [Conclusions] The gene sequence, molecular structure and isoelectric point of exsA, as well as its expression in three different media were obtained.
Key words Vibrio alginolyticus, exsA, Type III secretion system, Bioinformatics analysis
1 Introduction
Vibrio
alginolyticus
(Vibrionaceae:Vibrio
) is a halophilic and facultative anaerobic gram-negative bacterium. It is a common marine pathogen. The reproduction and growth of the bacterium has certain requirements for pH (6-9) and temperature (17-35 ℃). In 1973, it became clear thatV
.alginolyticus
could be pathogenic to humans, and by contaminating food, it causes people’s diarrhea and wound infection.V
.alginolyticus
is a conditional pathogen, and is very harmful to China’s aquaculture. When the aquaculture environment is bad and the immune function of aquatic animals is low,V
.alginolyticus
is prone to outbreak. In particular, it can make turbot, large yellow croaker, grouper,etc
. get ill, and can also infect shrimpand shellfish. Therefore, in recent years, many researchers have begun to study the molecular biology ofV
.alginolyticus
to find out the prevention and control methods to solve the harm ofV
.alginolyticus
to aquaculture.V
.alginolyticus
has no spore or capsule, but planktonicV
.alginolyticus
can adhere to the surface of media and produce a large number of extracellular products to package and aggregate individual colonies into micro colonies. With the continuous increase of extracellular products, individual microcolonies gradually connect to form a stable biofilm, soV
.alginolyticus
can resist bad environments and multiply.The pathogenic factors ofV
.alginolyticus
are mainly divided into four categories: adhesin, outer membrane proteins (OMPs), extracellular products (ECP) and siderophores.V
.alginolyticus
contains eight different protein secretion systems, named T1SS-T8SS.T3SS is a non-signal peptide-dependent secretion pathway, which is in the shape of a "needle". It is mainly composed of apparatus proteins, translocon proteins, effector proteins, regulation proteins and chaperones. The infection process of T3SS virulence system is very complicated. The whole process is completed through interaction and tight regulation of about 40 proteins and a secretion channel with a diameter of about 2 nm. The principle is to deliver the effector protein to the host cell to induce pathological changes such as rapid apoptosis or self-phagocytosis, rounding and osmotic swelling of the host cell. The study results of Zhou Xiaohuishow that the regulation ofT
3SS
1 gene expression inVibrio
parahaemolyticus
is controlled by the interaction between ExsA, ExsD and ExsD; and ExsA is necessary to induceT
3SS
1 gene transcription, and it directly interacts with the promoter sequence of theT
3SS
1 gene and participate in the positive regulation of Vp1656 expression and secretion. However, Gao Ruxiafound that the ExsA ofPseudomonas
aeruginosa
can affect its activity, which in turn affects the toxicity of the bacterium. The research on the T3SS protein secretion system is constantly progressing, and studying the regulation mechanism ofV
.alginolyticus
ExsA will inevitably provide a data basis for the study of the T3SS system.2 Materials and methods
2.1
Materials
2.1.1
Vector and strain.V
.alginolyticus
virulent strain HY9901was isolated from diseased red snapper fish in Zhanjiang waters of Guangdong Province. The cloning vector pMD18-T was purchased from Takara Bio Inc.2.1.2
Main reagents. ExTaq
DNA polymerase was purchased from Takara Bio Inc. Bacterial genomic DNA extraction kit and DNA gel recovery kit were purchased from Tiangen Biotech (Beijing) Co., Ltd. The remaining reagents (analytically pure) were imported or domestically produced. The PCR primer synthesis and sequencing were completed by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. The concentration of the antibiotic used (ampicillin, Ap) was 100 μg/mL.2.2
Methods
2.2.1
Extraction of total DNA ofV
.alginolyticus
strain HY9901.V
.alginolyticus
strain HY9901 was inoculated in TSB medium (2% NaCl) and shaking-cultured at 28 ℃ for 18 h. An appropriate amount of the bacterial liquid was transferred into a centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 10 000 rpm/min for 1 min, and the bacterial cells were collected. According to the kit instruction, genomic DNA was extracted and store at -20 ℃ for later use.2.2.2
Cloning ofexsA
gene. A pair of primers was designed according to the full genome sequence ofV
.alginolyticus
registered on Genbank (ACCESSION: GU074526) (upstream primer S: ATGGATGTGTCAGGCCAACTA; downstream primer A: TCATT-TCGCGATAGCCACTTG). The extracted total DNA ofV
.alginolyticus
strain HY9901 was used as a template. The PCR reaction conditions were as follows: pre-denaturation at 95 ℃ for 5 min; denaturation at 95 ℃ for 30 s, annealing at 65 ℃ for 30 s, 72 ℃ for 60 s, 32 cycles; extending at 72 ℃ for 10 min. After examined by 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis, the PCR product was recovered with gel DNA recovery kit.2.2.3
Sequencing of PCR products. In line with relevant instructions, the PCR product was aligned to the pET32a(+) vector, transformed intoEscherichia
coli
DH5α competent cells, and screened on Ap+/LB plates containing IPTG/X-Gal, and positive clones were selected and sent to Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. for sequencing.2.2.4
Bioinformatics analysis ofexsA
ofV
.alginolyticus
strain HY9901. Sequence homology comparison and similarity analysis were performed using NCBI (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi).DNAMAN was used for amino acid homology analysis. ExPASy Proteomics Server (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/) was used to deduce amino acid sequence, determine open reading frame (ORF), predict calculated molecular weight (Mw
) and theoretical isoelectric point (pI
),etc
. Through SignalP 4.0 Server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP), signal peptide sequence was predicted. TMHMM Server 2.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM) was applied to predict the transmembrane domain. SoftBerry-Psite (http://linux1.softberry.com/berry.phtml?Topic=psite&group=rograms & subgroup = proloc) was used to predict the distribution of functional sites in the amino acid sequence. The promoter was analyzed with Promoter 2.0.PSORT II Prediction (http://psort.hgc.jp/form2.html) was adopted to predict subcellular location. Using Clastal 2.0 and MEGA 5.0, phylogenetic tree was constructed with neighbor-joining method. SWISS-MODEL (http://www.swissmodel. expasy.org/) was used to construct three-dimensional structure. Kegg (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/) was used to analyze the pathways involved. In the STRING database (http://string.embl.de/), protein network interactions were searched.2.2.5
B cell epitope prediction of ExsA ofV
.alginolyticus
strain HY9901. The Chou-Fasman method was used to predict the secondary structure of the protein. Parameters were predicted separately with Kyte-Doolittle (hydrophilicity), Karplus-Schulz (flexibility), Emini (surface accessibility) and Jameson-Wolf (antigenicity). The prediction result of each parameter was analyzed. Finally, combined with DNAstar software, the B cell epitope of ExsA protein ofV
.alginolyticus
strain HY9901 was determined.2.2.6
Expression differences ofexsA
gene in different media. The expression ofexsA
gene in different media was determined using quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR).V
.alginolyticus
strain HY9901 withOD
of 0.5 was inoculated in DMEM (high sugar medium), 0.05% bile salt TSB and ordinary TSB at a ratio of 1∶100, respectively. After culturing at 28 ℃ for 12 h, bacterial liquids were collected. RNA was extracted to synthesize cDNA for qRT-PCR reaction. Based on the conservative sequence ofexsA
gene, specific primers were designed for qRT-PCR analysis. The 16S rRNA gene was selected as the control gene. SYBR Green I was used as the marker. The primers used in the PCR reaction are shown in Table 1.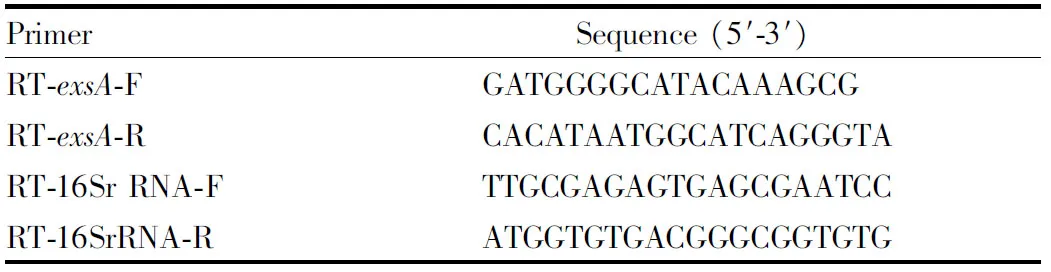
Table 1 Primers for quantitative real-time PCR
3 Results and analysis
3.1
Cloning
of
gene
A specific band of approximately 861 bp was obtained by PCR amplification (Fig.1). The sequencing results show that theexsA
gene contains an open reading frame (ORF) of 861bp, encoding 286 amino acids (Fig.2). The accession number in GenBank is MN385414.3.2
Analysis
of
physical
and
chemical
properties
of
ExsA
ExPASy software was used to analyze the ExsA protein ofV
.alginolyticus
strain HY9901. The results show that the total number of atoms is 4 555, the molecular structure is CHNOS, the theoretical molecular weight is 32.549 kD, the theoreticalpI
value is 6.0, the instability coefficient is 53.96 (greater than the threshold value of 40, indicating that the properties are unstable, that is, the protein is unstable), the fat coefficient is 89.30, the overall average coefficient of hydrophilicity is -0.278, the total number of acidic amino acid residues (Asp + Glu) is 35, the total number of basic amino acids (Arg + Lys) is 30, and the N-terminal is methionine (Met).The half-life of expression in yeast andE
.coli
is greater than 20 and 10 h, respectively, and the half-life of expression in mammalian reticulocytesin
vitro
is 30 h.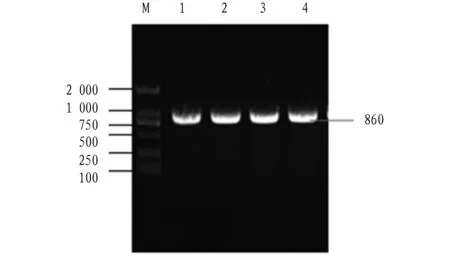
Note: M, DL 2000 DNA marker; 1-4, PCR products.
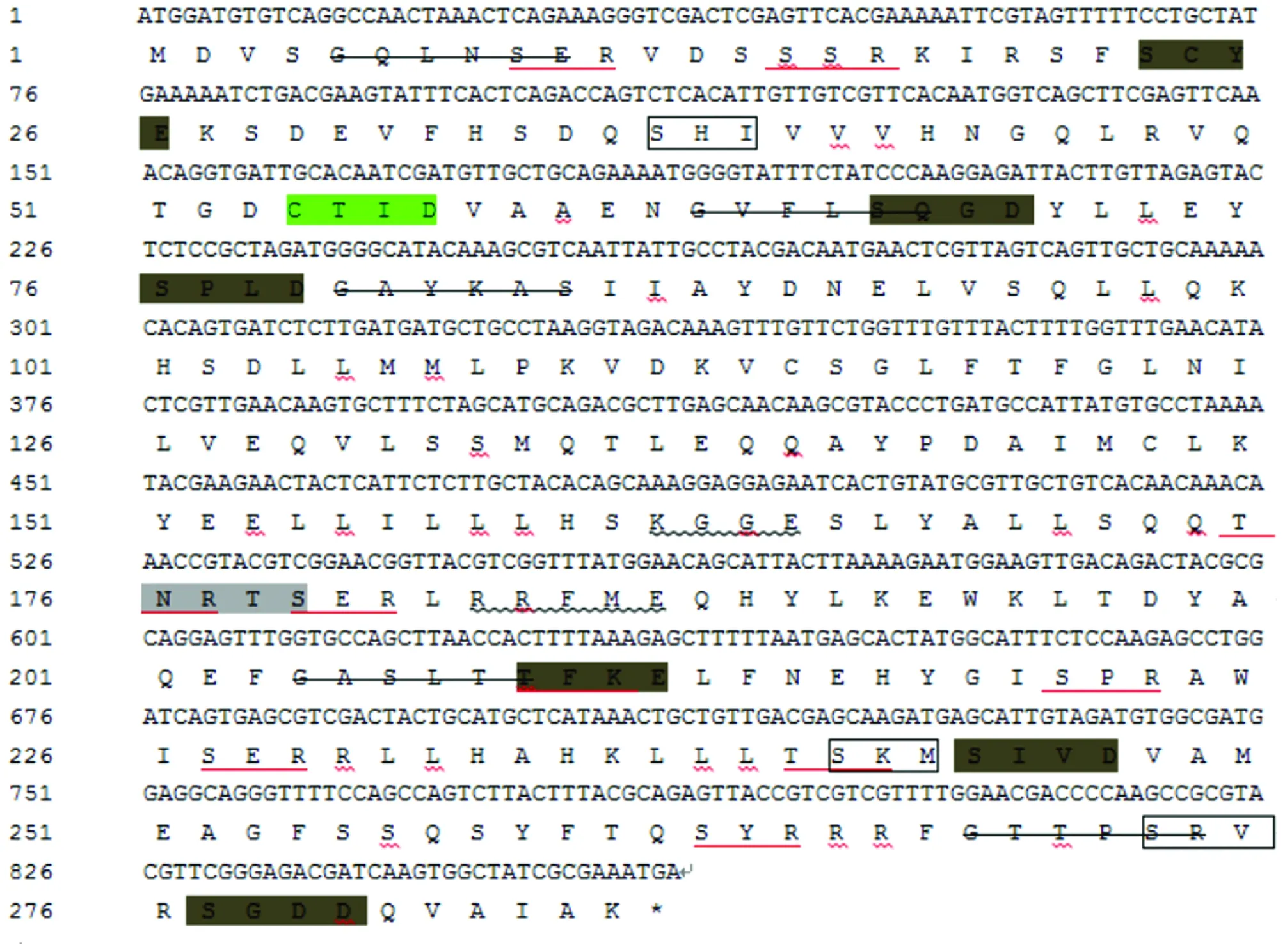
Note: *represents terminator; the light gray shade is the N-glycosylation site; the red underlined part is the phosphorylation site of protein kinase C; the dark gray shade is the phosphorylation site of casein kinase II; the underlined wavy line represents the phosphorylation site of tyrosine kinase; the strikethrough represents the myristoylation site; the green shade is the prenyl binding site; and the box represents the C-terminal targeting signal site of microbody.
3.3
Sequence
analysis
of
ExsA
SignalP 4.1 Server was used to predict the N-terminal signal peptide structure of ExsA amino acid sequence, and no signal peptide was found between amino acids. The prediction results of TMHMM Server v. 2.0 show that no transmembrane domain was found. The prediction results of SoftBerry-Psite (predict protein) show that the amino acid sequence contains one N-glycosylation site,10 protein kinase C phosphorylation sites, 6 casein kinase II phosphorylation sites,3 tyrosine kinase phosphorylation sites, 5 N-myristoylation sites, one isopentenyl binding site, and 3 microbial C-terminal targeting signals. The prediction results of protein subcellular localization show that the probabilities of ExsA being distributed in plasma membrane, cytoplasm, vacuole, mitochondrion, endoplasmic reticulum, vesicle and nucleus are 4.3%,43.5%, 4.3%, 13.0%,4.3%, 13.0% and 17.4%, respectively.3.4
Homology
and
evolution
analysis
of
exsA
BLAST analysis found thatV
.alginolyticus
exsA
has high homology withexsA
of other species, and the homology withVibrio
antiquarius
is up to 97%. Similarity analysis shows thatexsA
inVibrio
is conserved (Fig.3).Using the neighbor-joining method of MEGA 5.0, a phylogenetic tree was constructed by combining the deduced ExsA amino acid sequence ofV
.alginolyticus
with those of other microorganisms. The results show that the ExsA ofV
.alginolyticus
strain HY9901 andV
.antiquaries
belong to the same cluster, indicating that they are closely related (Fig.4), consistent with the traditional morphological and biochemical characteristics classification results.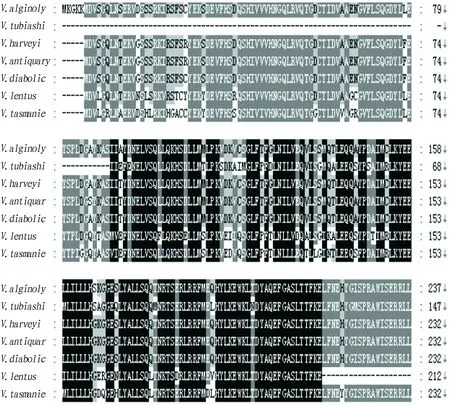
Fig.3 Homology analysis of deduced amino acid sequences of exsA gene
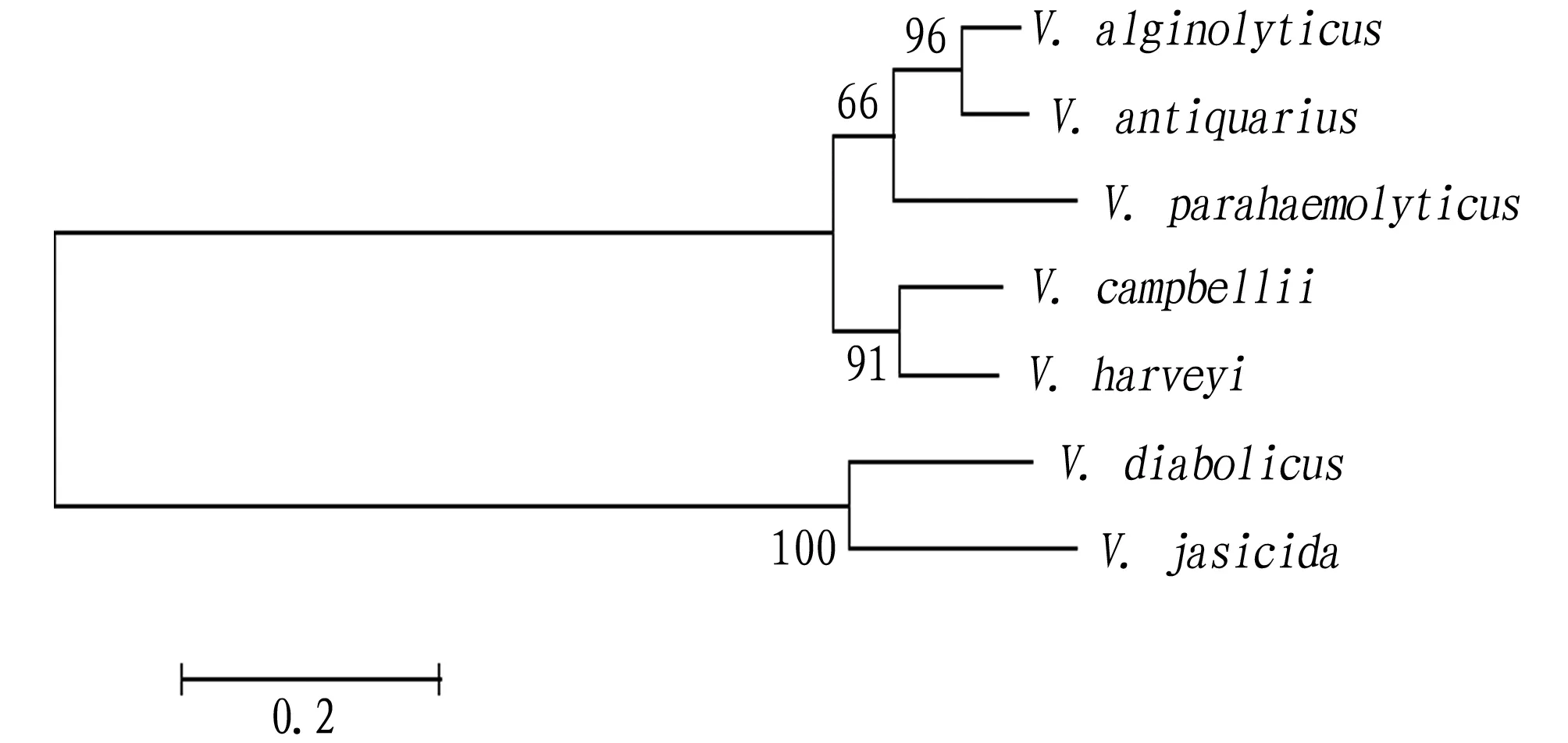
Fig.4 Phylogenetic tree of ExsA amino acid sequences based on NJ method
3.5
Prediction
of
functional
domain
and
secondary
structure
of
ExsA
SMART was used to predict the functional domain of ExsA. It is found that ExsA has a main functional domain HTH_GNTR (Fig.5). The secondary structure of ExsA was predicted using SOPMA. The results show that in the secondary structure of ExsA,α-helix, random coil, extended strand and β-fold account for 44.06%, 22.38%, 20.28% and 13.29%, respectively (Fig.6).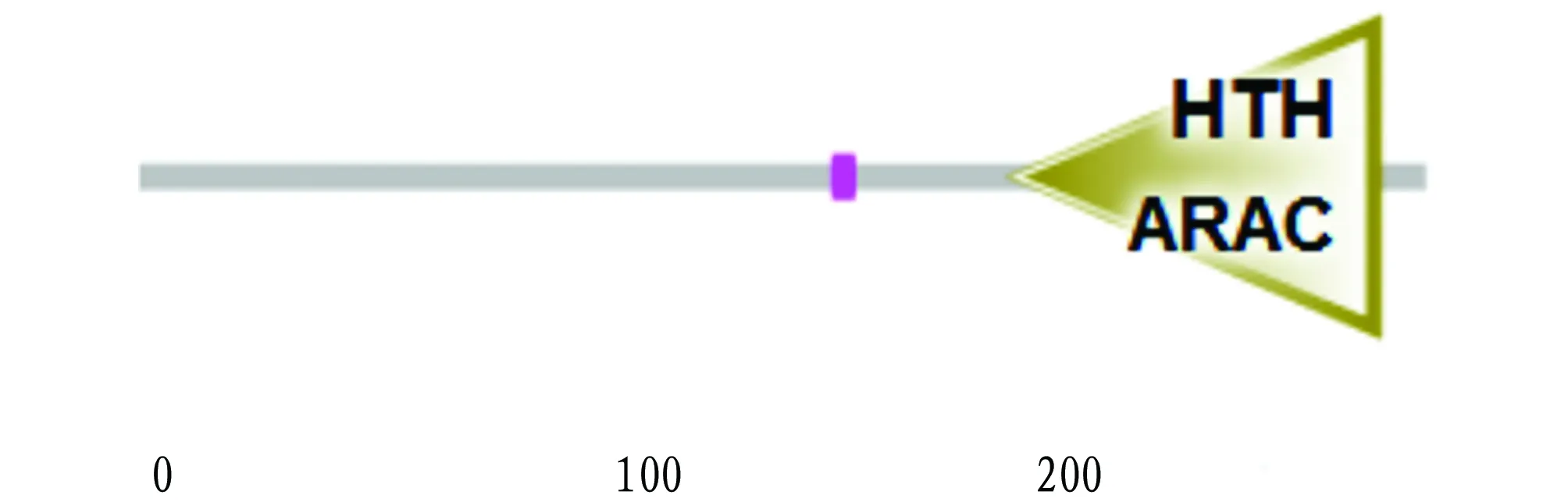
Fig.5 Domain prediction of ExsA protein
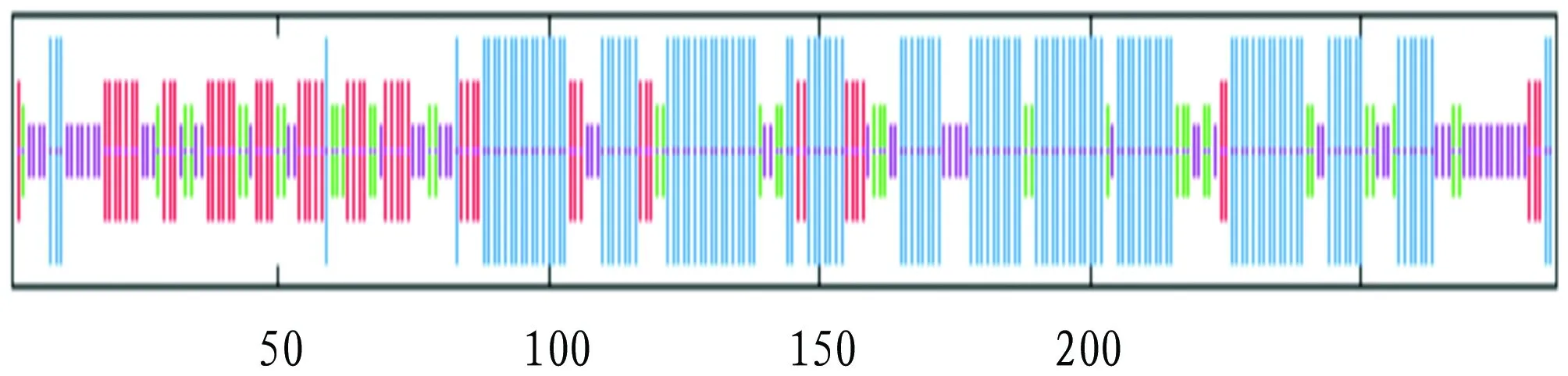
Note: blue line, α-helix; green line, β-fold; red line, extended strand; purple line, random coil.
3.6
Subunit
structure
of
ExsA
The amino acid sequence of ExsA was submitted to the SWISS-MODEL program to automatically search for homologous proteins as templates, and the tertiary structure model of ExsA single subunit was obtained (Fig.7).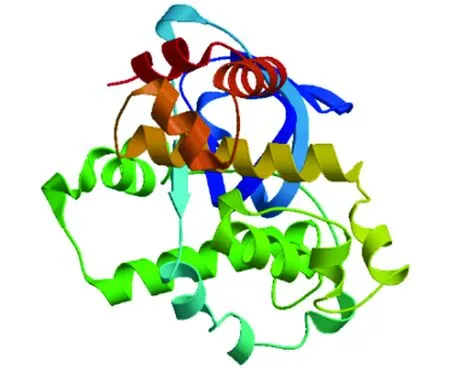
Fig.7 Tertiary structure model of single subunit of ExsA
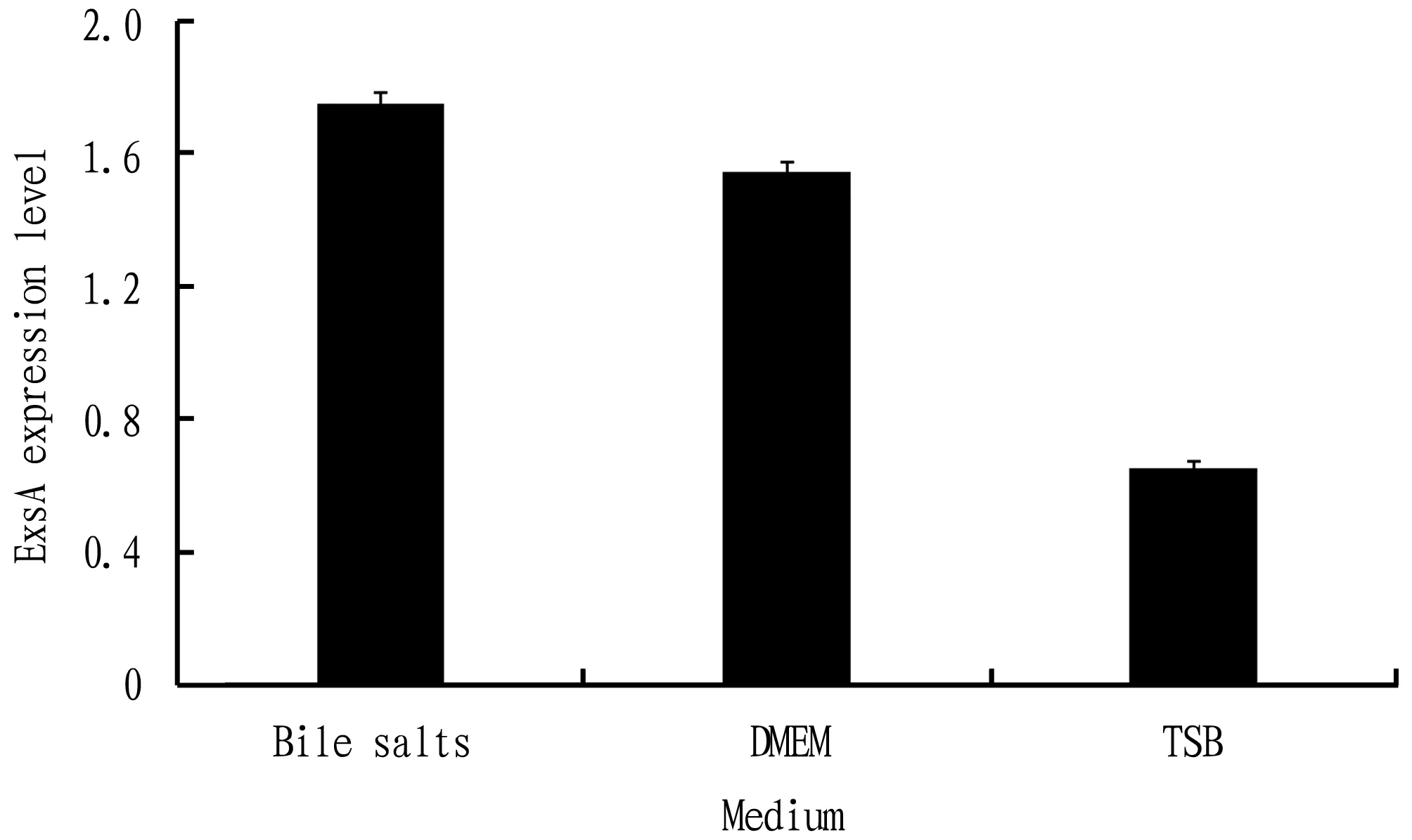
Fig.8 Expression level of exsA gene in different medium
3.7
Expression
analysis
of
Using quantitative real-time PCR technology, the expression ofV
.alginolyticus
exsA
after different media stress was determined. The result is shown in Fig.8. TheexsA
gene could be expressed in three different media, but the expression level was different, highest in TSB medium containing bile salts, followed by DMEM medium, and lowest in TSB medium.4 Discussion
V
.alginolyticus
is an important pathogen that causes diseases in marine aquaculture economic animals, causing greater economic losses to the industry. Currently, the domestic prevention and treatment of vibriosis still mainly relies on chemical drugs and antibiotics. The resulting environmental pollution, bacterial resistance and drug residues are becoming more and more serious. Therefore, looking for the main protective antigens and cloning their genes to express subunit vaccines with stronger immunogenicity and lower side effects have gradually attracted the attention of scholars.At present, the research onV
.alginolyticus
focuses on the isolation and identification of pathogens, pathological changes,etc
, but there are relatively few studies on its virulence-related genes. Research showsV
.alginolyticus
can produce adhesion factors, lipopolysaccharide, type III secretion system, outer membrane protein and other virulence factors. Studying the virulence-related genes ofV
.alginolyticus
and finding an ideal immune protective antigen for the immune prevention and treatment of vibriosis is the key to solving the problem.Bioinformatics analysis is an important method to analyze protein structure and function. It has been widely used in vaccine development. The prediction results of this study show that there is no signal peptide at the N-terminus of ExsA protein, so it can be inferred that ExsA protein is not a secreted protein. Protein phosphorylation can modify proteinsand is the key to regulating the cell cycle. It is a form of molecular switch. Due to lack of endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, ExsA protein inV
.alginolyticus
cannot be glycosylated and acylated. However, it has no effect on phosphorylation modification.With the development of bioinformatics, using biological software to predict and screen antigens has become a research hotspot. For a long time, to explore the common antigen ofVibrio
, scholars’ research on this bacteria is mostly related to infection-related enzymes, attachment and colonization factors, transporters,etc
. However, there are few reports on ExsA ofV
.alginolyticus
. The amino acid sequence encoded byexsA
gene is highly conserved, and its similarity with otherVibrio
species is higher than 60%, which implies that the function ofexsA
gene is conserved. It is speculated that the ExsA protein ofV
.alginolyticus
may be a common antigen ofVibrio
, but it needs to be verified by prokaryotic expression, immunogenicity and immune protection, so as to find an effective common antigen for the prevention and treatment of vibriosis.The phylogenetic tree constructed shows thatV
.alginolyticus
strain HY9901 has a close relationship withV
.antiquarius
.5 Conclusions
In this study, theexsA
gene ofV
.alginolyticus
was cloned. The sequence analysis shows thatexsA
contains an open reading frame (ORF) of 861 bp, encoding a total of 286 amino acids. Its molecular structure is CHNOS, theoretical molecular weight is 32.549 kD, and theoreticalpI
value is 6.0. The protein does not contain a transmembrane region, is non-hydrophilic, and contains multiple sites.V
.alginolyticus
is found to be closely related toV
.antiquarius
. The ExsA protein ofV
.alginolyticus
has a main functional domain HTH_GNTR. The results of structural prediction show that in secondary structure, α-helix, random coil, extended strand and β-fold account for 44.06%, 22.38%, 20.28% and 13.29%, respectively. In different media, the expression level ofexsA
is highest in TSB medium containing bile salts, followed by that in DMEM medium, and lowest in TSB medium.杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Research on Quality Assurance System of Talent Cultivation in Higher Vocational Colleges from the Background of Enrollment Expansion
- Geographical Indication and Unique Production Technology of Zhengcheng Honeysuckle
- Thoughts on the Ways out of Breeding Industry under the Important Task of Ecological Civilization
- Development of Mountain Tourism in Central Yunnan in the Context of Rural Revitalization Strategy
- Exploration of Chinese Television Historical Comedy Drama Li Wei the Magistrate from the Perspective of Management
- A Non-toxic and Efficient Method for Extracting DNA and RNA from Peanut
