Research on Chemical Prevention and Control against Stem Base Rot of Sweet Potato
2021-02-26LiuYenanLiuWeimingHeXianbiaoHuangLifei
Liu Yenan,Liu Weiming,He Xianbiao*,Huang Lifei
1.Taizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Linhai 317000,China;2.Taizhou Vocational College of Science&Technology,Taizhou 318020,China;3.Crop Research Institute of Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement,Guangzhou 510640,China
Abstract [Objective]The paper was to effectively control stem base rot of sweet potato.[Method]Chemical prevention and control test against stem base rot of sweet potato were conducted for consecutive three years from 2016 to 2018.[Result]The use of carbendazim or carbendazim+mancozeb,and carbendazim+embamycin had significant control effect on stem base rot of sweet potato.However,the applied concentration should be higher than the recommended concentration.Especially the concentration of 50% carbendazim WP should be no more than 300 times,and the prevention and control effect of 100 times dilution would be better.[Conclusion]The types and concentrations of prevention and control agents are determined in the test,which will provide certain basis for chemical prevention and control against stem base rot of sweet potato.
Keywords Sweet potato;Stem base rot of sweet potato;Pathogen;Chemical prevention and control
Sweet potato is an important dryland crop,widely cultivated in more than 100 countries and regions as food,feed and industrial raw materials[1].China is one of the largest sweet potato producers in the world[2-3].With the development of economic society and the improvement of living standard,people are paying more and more attention to the nutritional health care and medicinal value of sweet potato.The tuber,petiole and stem tip of sweet potato all have high nutritional value[4],and have complete kinds of amino acids and relatively balanced protein nutrition.Lysine,which is deficient in cereals,is higher in sweet potato[5-6].Sweet potato also contains anti-cancer mucus protein, dehydroepiandrosterone and selenium,etc.[7-8].It is generally considered that sweet potato is a good nutritional food and health food.
As an important dry grain crop in Taizhou,sweet potato has gradually become the local characteristic cash crop in recent years.Currently,there are many sweet potato varieties suitable for different uses in Taizhou.For example,there are fresh food types,among which there are high carotene content,soft sweet taste,sweet powder and other types[9-11],and there are premature mini fresh purple sweet potato and premature mini fresh red skin orange flesh sweet potato[12-17].There are also high-starch sweet potatoes suitable for starch production,high-sugar varieties suitable for food processing[9-10],and vegetable sweet potatoes suitable for stem tip processing[18].In addition,Taizhou has rich traditional sweet potato processing industries,such as vermicelli and potato chips,which further promotes improvement and sustainable development of sweet potato industry.
However,the stem base of sweet potato became brown(or black)in several counties(districts)in Taizhou since 2010,and gradually died out.Potato blocks rotted in the middle and late stage,and the yield of sweet potato decreased significantly,with the loss of 20%-50% in light cases and almost no harvest in severe cases,which seriously affected the income of potato farmers.Since 2012,stem base rot of sweet potato has been aggravating year by year and spreading obviously,which leads to the decrease of planting area of sweet potato year by year and seriously affects the development of local sweet potato industry.
Since2011 when stem base rot of sweet potato was first found,we had conducted a series of prevention and control test against the disease.The incidence rates of stem base rot and yield loss of sweet potato could not be reduced by using different tillage systems(six tillage systems,five different pre-cropping systems)and by using different 4-year rotation patterns at fixed point(interval of 2 years,rotation of 2-4 stubbles).The agricultural measures including cutting of virus-free seedlings,plastic film mulching and application of organic fertilizer could not alleviate the damage of stem base rot of sweet potato.Appropriately postponing cutting period of sweet potato to around the end of June could reduce the yield loss to a certain extent[19].Meantime,survey and pathogen identification of stem base rot of sweet potato was performed[20].The pathogens of 127 samples collected from 51 villages(endemic area of sweet potato)in Taizhou City(Yuhuan County,Wenling City,Sanmen County,Linhai City,Huangyan District),Wenzhou City(Leqing City,Dongtou County,Yongjia County),Lishui City(Suichang County),Hangzhou City(Lin’an District),Ningbo City(Ninghai County)were isolated and identified.According to pathogenicity,morphological characteristics,ITS and 16SrDNA sequence analysis of pathogens,eight pathogenic bacteria including Dickeya dadantii,Sclerotium rolfsii,Fusarium verticillioides,F.solani,Diaporthe batatas,Phomopsis destruens and F.javanicum were identified.In addition,a few other pathogenic bacteria and fungi had been isolated,such as Rhizoctonia solani AG-4HG-1[19,21].After prevention and control test of southern blight of sweet potato in 2013[22]and preliminary investigation on chemical prevention and control of stem base rot of sweet potato in 2015[19],more detailed prevention and control tests against stem base rot of sweet potato was conducted for three consecutive years from 2016 to 2018[23-24].In this study,the experimental results of three consecutive years were summarized to make a comprehensive analysis and discussion on chemical prevention and control of stem base rot of sweet potato.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Materials (i)Varieties.Zheshu 13 was the sweet potato variety used in three years.
(ii)Fungicides.The fungicides used in three years are displayed in Table 1.The five agents used in 2017 were those with relatively good prevention and control effects and no phytotoxicity in the field among the nine agents used in 2016[23],and field chemical prevention and control test was performed with further optimized design.The agents and design ideas in 2018 were similar to those in 2017.
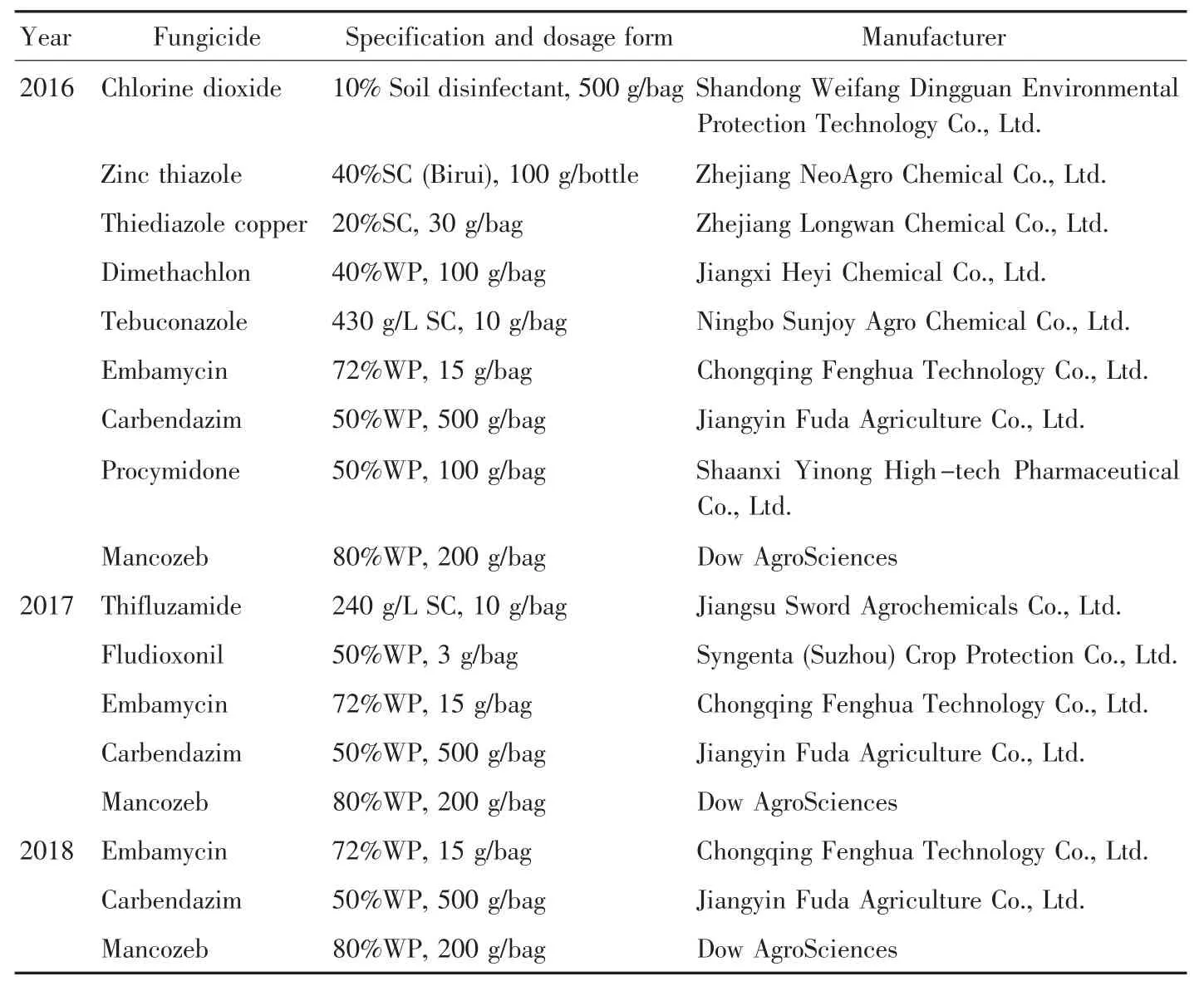
Table 1 Agents used in the test
1.2 Experimental sites The test was conducted in Shaxixia Village,Dongcheng Town,Linhai City,Zhejiang Province from June 25 to November 18,2016,June 18 to November 20,2017 and May 21 to November 8,2018,respectively.The test plot was flat,with sandy loam and medium fertility.
1.3 Experimental design Ten treatments were designed in 2016,while nine treatments were designed in 2017 and 2018(Table 2).The plots sprayed with only water were set as control.The corresponding seedling soaking of each treatment before cutting had not been conducted in 2016.Root irrigation should be carried out on the cutting day,but due to light to moderate rain on that day,it was delayed to the fifth day after cutting,and the soil was first relaxed and then watered.According to the product instructions,chlorine dioxide soil disinfectant in treatment 1602 was diluted with water and sprayed on ridge back on the day before cutting potato seedlings,and then plastic film was covered and pressed tightly all around.Root irrigation treatment during cutting in 2017 and 2018 referred that sweet potato seedlings were first immersed in corresponding treated liquids for about 1 min,and slightly drained before cutting;after cutting,the liquids were evenly poured at the base of potato seedlings.Spraying referred that after cutting sweet potato seedlings,sweet potato was sprayed at base with the agents in Table 2 from July to the initial incidence.The three spraying in 2016 were on July 12 (no infected plants were found in the field),July 21 and July 29,respectively.The three spraying in 2017 were on July 15 (no infected plants were found in the field),July 26 and August 3,respectively.The three spraying in 2018 were on July 26 (no infected plants were found in the field),August 7 and August 15,respectively.
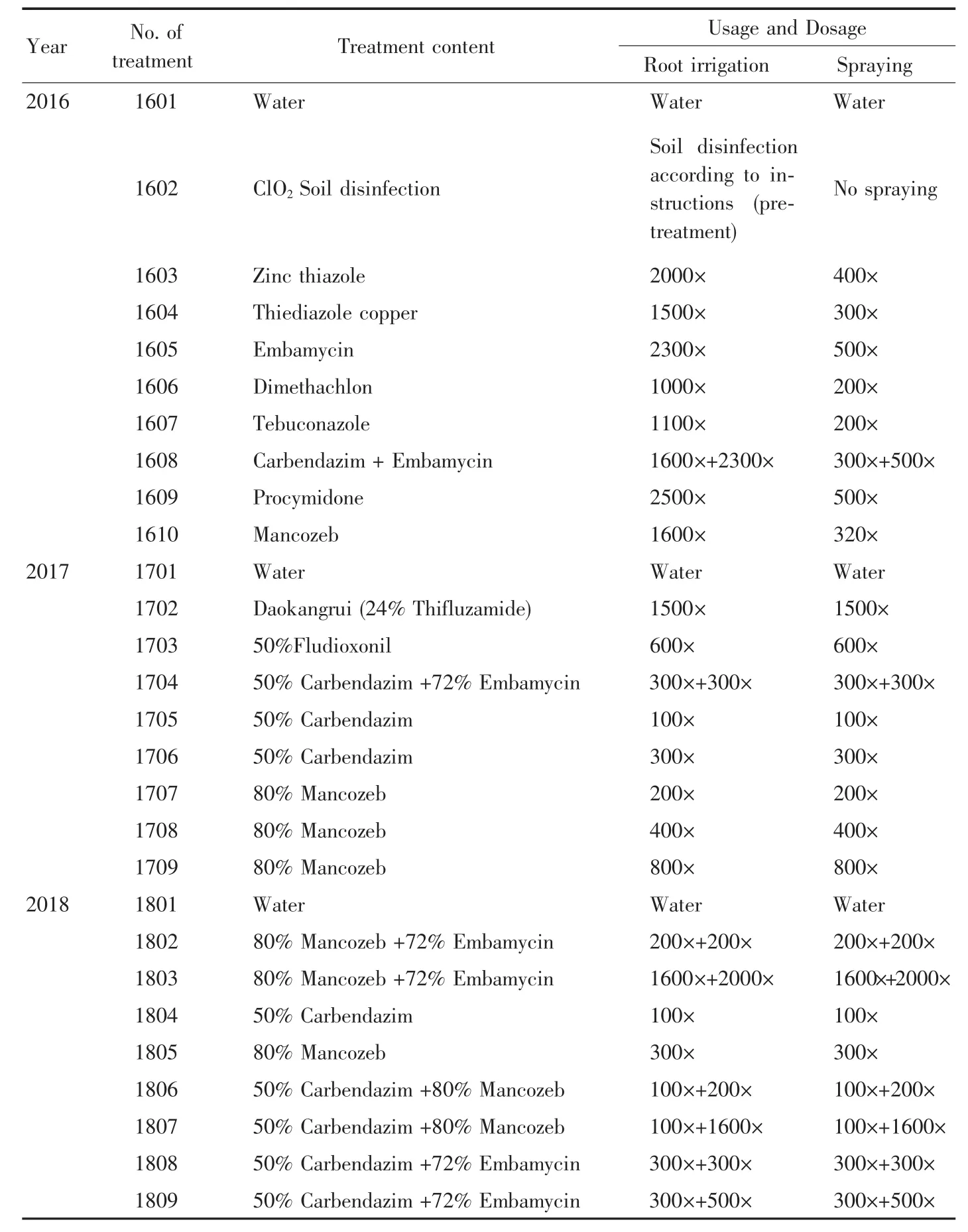
Table 2 Experimental design
From 2016 to 2018,the net areas of experimental plots were 13.00,9.60 and 12.47 m2,respectively.All treatments were in randomized block arrangement,and each treatment was repeated three times.Protection lines were set around plots.Before cutting of sweet potato every year,600 kg/hm2of ternary-compound fertilizer(N-P2O5-K2O=17-17-17)was used as basal fertilizer at one time,and no other fertilizer was applied during the whole growing period.
1.4 Data processing Field incidence investigation,disease classification standard and actual prevention and control effect calculation referred to the literature[23].Data were statistically analyzed using Duncan’s new multiple range method.
2 Results and Analysis
2.1 Effects of different agents on field incidence rate of sweet potato stem base rot After root irrigation and three times of stem base spraying in 2016,the incidence rates of stem base rot in different treatments are shown in Table 3.No disease strains were found in the previous two investigations.In the field investigation on August 11,there were three treatments with initial incidence,including 1601,1604 and 1606.On August 22,there were three more treatments with initial incidence,including 1602,1605 and 1609.After August 31 when long drought was terminated,it began to rain in plots,the field humidity increased,and high temperature and high humidity accelerated the incidence.The investigation on September 7 showed that except 1607,1608 and 1610,there were six treatments with incidence,and the disease was worsened.On October 23,plants were individually examined in three repeats of each treatment(survey data on October 23 in Table 3 were average values of three repeats,and significance test was conducted accordingly).The survey results demonstrated that field incidence rate was the lowest in treatment 1608(30.00%)and the highest in control 1601(96.91%).Analysis of variance (ANOVA)showed that the incidence rates had extremely significant difference among treatments except for treatments 1602 and 1605,which were significantly lower than that of the control.After seedling soaking,base spraying posterior to cutting and three times of stem base spraying in 2017,the incidence rate of treatment 1705 was the lowest(70.69%),which was significantly lower than those of other treatments;followed by treatment 1704,with the incidence rate of 89.99%,which had no significant difference with treatments 1706 and 1707,but was significantly lower than treatments 1702,1703,1708,1709 and control 1701,and the incidence rate of treatment 1702 and control was 100%(Table 4).
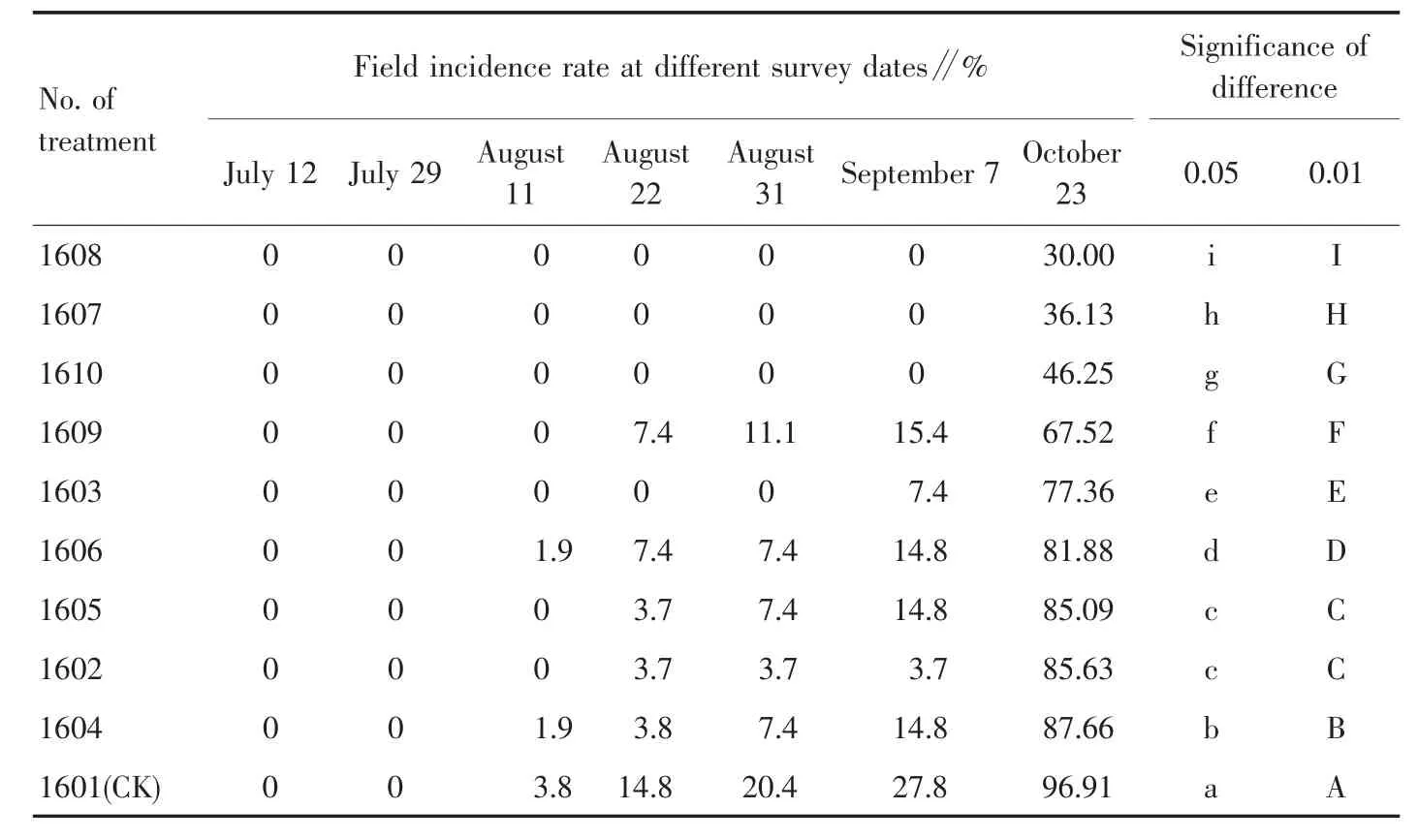
Table 3 Field incidence rate of sweet potato stem base rot over different periods in 2016
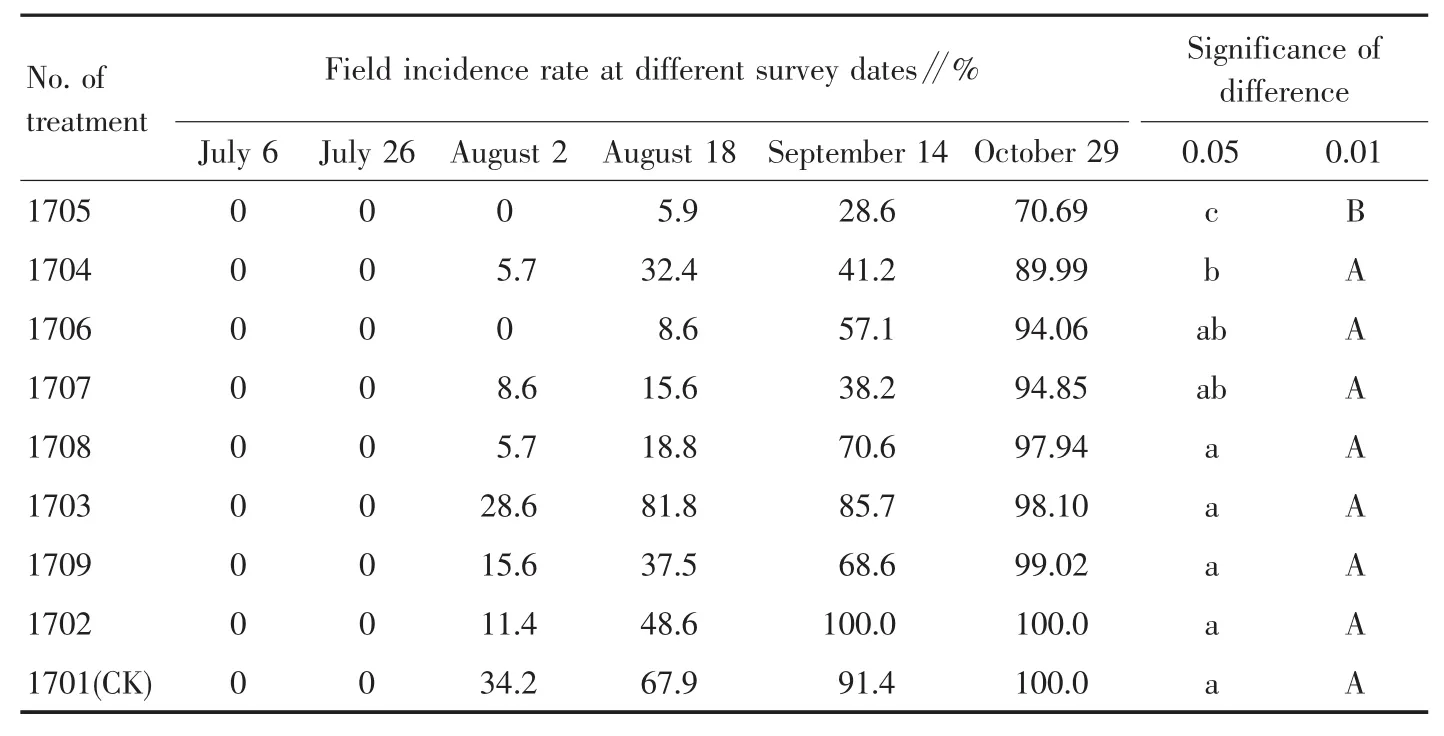
Table 4 Field incidence rate of sweet potato stem base rot over different periods in 2017
The first survey of field incidence rate of sweet potato in 2018 was conducted on August 7,that is,before the second spraying of sweet potato stem base.The last survey of field incidence rate on September 27(the incidence of sweet potato plants was not individually investigated before the harvest of sweet potato in 2018)showed that the incidence rate of treatment 1807 was the lowest(47.6%);the incidence rates of treatments 1804,1806,1808 and 1809 were around 70%;the incidence rates of treatments 1802 and 1805 were 80.0% and 96.9%,respectively;and the incidence rates of control and treatment 1803 reached 100%(Table 5).
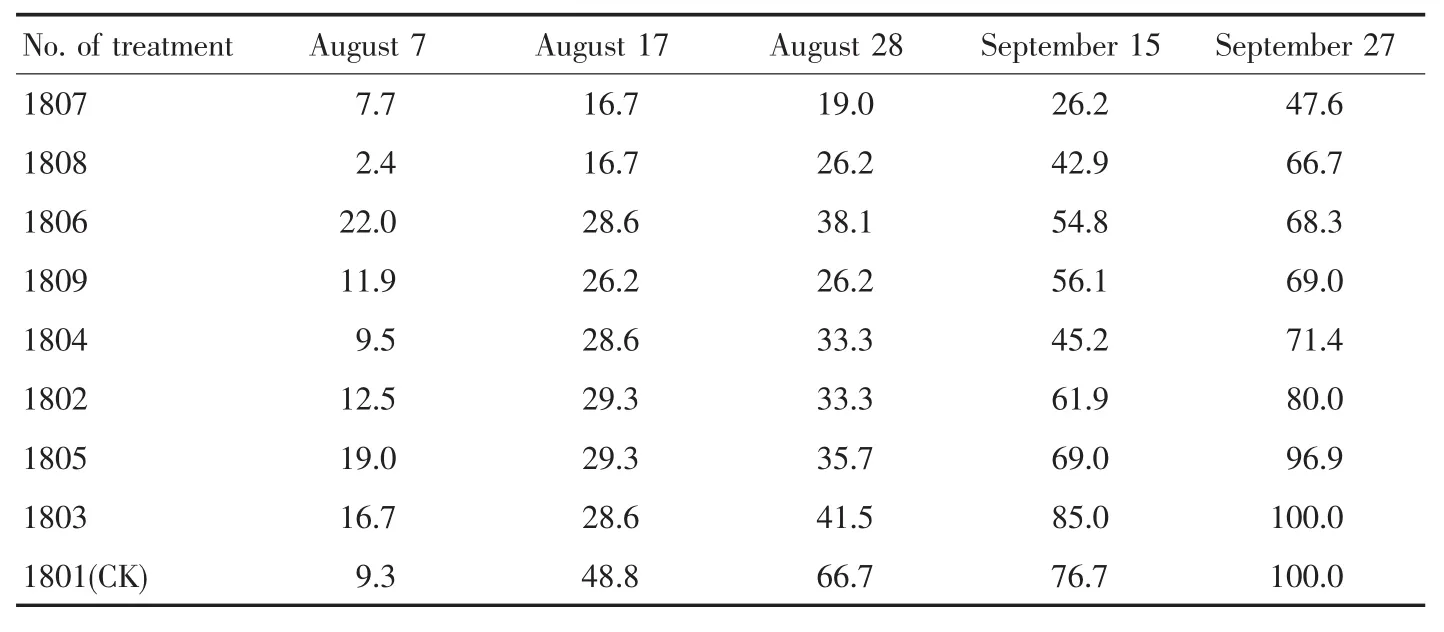
Table 5 Field incidence rate of sweet potato stem base rot over different periods in 2018 %
2.2 Effects of different agents on disease index and control effect in the field Statistical analysis of disease index and control effect of each treatment in 2016(Table 6)demonstrated that the disease index and control effect of treatment 1608 were 18.9 and 77.7% respectively,showing the lowest disease index and the best control effect.The treatments 1607 and 1610 also had low disease index and good control effect.There was no significant difference in disease index among treatments 1608,1607 and 1610,but all of which were significantly lower than other treatments.There was no extremely significant difference among treatments 1608,1607 and 1610,but the disease indexes of treatments 1608 and 1607 were extremely lower than those of other treatments.
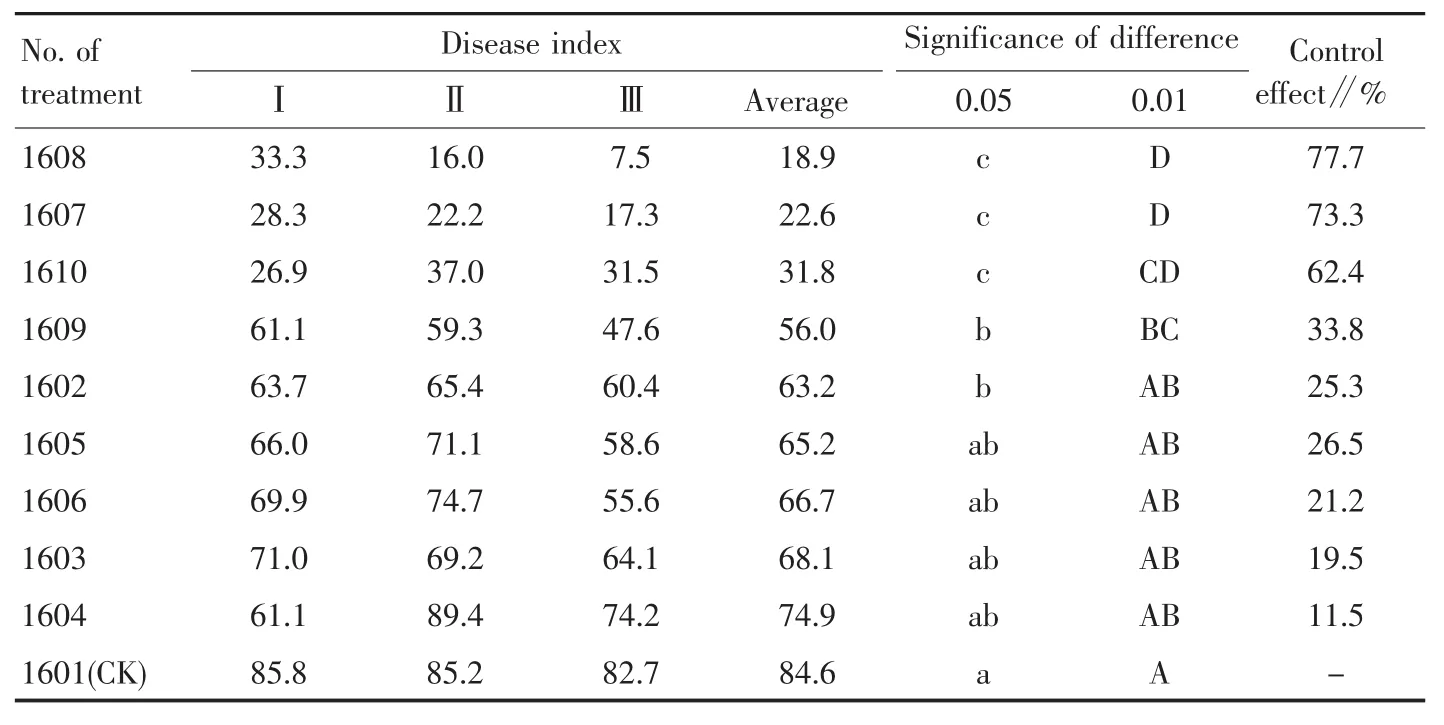
Table 6 Disease index and control effect of different treatments in 2016
Statistical analysis of disease index and control effect of various treatments in 2017(Table 7)showed that the disease index of treatment 1705 was the lowest(39.75),which was extremely lower than those of other treatments,and its control effect was the highest of 60.1%.The disease indexes of other treatments were above 73.6(treatment 1706 was 73.6),and the control effect was below 26.1%(treatment 1706 was 26.1%),all of which were not ideal.

Table 7 Disease index and control effect of different treatments in 2017
2.3 Effects of different agents on sweet potato yield As shown in Table 8,the yield of treatment 1608 was the highest in 2016,reaching 26 866.67 kg/hm2,which was increased by 13 292.31 kg/hm2(97.9%)compared with the control with the lowest yield.The yield of treatment 1608 was extremely higher than those of other treatments.The second largest yield was 25 061.54 kg/hm2in treatment 1607,which was close to the yield in treatment 1608,but the difference between the two reached an extremely significant level. The yields treated by other agents varied from 22 461.54 to 17 553.85 kg/hm2,which were extremely higher than the yield of the control.Further analysis showed that the order of treatments with yields in the first three positions was consistent with that of disease severity in the field.The treatment with the severest incidence also had the lowest yield.Treatments 1606 and 1604 had earlier and heavy incidence,so their yields were also relatively low.
In 2017,the yield of treatment 1705 was the highest,reaching 18 798.61 kg/hm2,which was increased by 389.51% compared with the control with the lowest yield of 3 840.28 kg/hm2;followed by treatments 1704,1706,1707,1708,1703,1709,1702 and 1701(CK).There were extremely significant difference in yield among treatments,and the yield of each treatment was extremely higher than that of the control(Table 8).Further analysis demonstrated that the correlation coefficient between yield and incidence rate was-0.77**;the correlation coefficient between yield and disease index was-0.80**;and the correlation coefficient between incidence rate and disease index was 0.96**.The incidence rate and disease index had extremely significant negative correlation with yield respectively,while the incidence rate had extremely significant positive correlation with disease index.

Table 8 Effects of different agents on sweet potato yield from 2016 to 2018
In 2018,treatment 1807 with the lowest incidence rate had the highest yield of 22 194.60 kg/hm2,which was increased by 14 822.24 kg/hm2(201.05%)compared with the control(7 372.36 kg/hm2),and the yield of treatment 1807 was also extremely higher than those of other treatments.The yields of treatments 1809 and 1808 were 20 491.85 and 19 786.15 kg/hm2,respectively,which were increased by 177.96% and 168.38% compared with the control,and the yield increase was extremely significant.The yield of treatment 1809 was higher than that of treatment 1808,but there was no significant difference.Except for treatment1807,the yields of treatment 1808 and 1809 were significantly higher than those of other treatments;the yields of other treatments were significantly higher than that of the control(Table 8).
3 Conclusion
The chemical prevention and control results of three consecutive years were basically consistent.Through the three years of study,it could be concluded that carbendazim,or carbendazim+mancozeb,carbendazim+embamycin had obvious prevention and control effect on stem base rot of sweet potato,and the applied concentration should be higher than the recommended concentration.Especially the concentration of 50% carbendazim WP should be no more than 300 times,and the prevention and control effect of 100 times dilution would be better.
4 Discussion
The results showed that carbendazim could not obtain obvious control effect unless the concentration was significantly higher than the recommended concentration.This is similar to the experimental results that azoxystrobin 100 times dilution received good control effect on stem base rot of sweet potato[19].However,the concentration is significantly higher than that recommended by some scholars[27-29],which needs to be further verified.
50% Carbendazim 100 times dilution used in 2017 received the best control effect,which was different from the conclusion that the application of carbendazim+embamycin had the best control effect on stem base rot of sweet potato in 2016.The test results in 2018 indicated that the mixture of carbendazim and mancozeb had better control effect than the mixture of carbendazim and embamycin,and low concentration of the same combination had better control effect than high concentration,probably attributed to the species of pathogen causing stem base rot of sweet potato or the major pathogen causing the incidence.In addition,it may also cause by experimental errors or other reasons,which needs to be further verified.In 2018,due to the drought in the early stage,the incidence posterior to cutting was delayed,while the incidence was earlier in the normal year.Therefore,the administration time should be advanced accordingly.
It was reported that the last registration certificate of embamycin expired on 14 June,2016,which would not be renewed[30].Therefore,alternative pesticides are still to be tested and determined,especially the screening of agents with good control effects against sweet potato bacterial and fungal diseases is more important.we have carried out a series of comprehensive prevention and control test on stem base rot of sweet potato since 2011.According to the summary and analysis of test results over the years,the author put forward the prevention and control strategies and pathways to prevent and control stem base rot of sweet potato:based on the selection and application of diseaseresistant varieties,supplemented by integrated use of other agricultural control and chemical control measures[19].Cooperative development of sweet potato diseaseresistant varieties breeding was conducted since 2015.In that year,among a large number of low-generation sweet potato materials, the low-generation material YA3008 (current name Zheshu 38)with better field disease resistance was selected by using the severe illness nursery of sweet potato stem base rot.In 2017,the resistance of Zheshu 38 were tested and demonstrated in five plots of sweet potato stem base rot in four counties and cities,and the results showed that the incidence rates of Zheshu 38 in five plots were significantly lower than those of other testing varieties (strains),and the yields of fresh potato reached 27 403.50-48 184.50 kg/hm2;the yields of Zheshu 13 or Xinxiang in five plots were reduced by 27.96%-84.42% compared with Zheshu 38.In 2018,the character of Zheshu 38 was verified in multiple points,and the demonstration was expanded,receiving obvious effect of increasing production and income.In Yao’ao demonstration area in Yuhuan City,the average yield of Zheshu 38 per 1.33 hm2reached 56 887.65 kg/hm2(incidence rate 9.5%),which was 138.52% higher than the average yield of Zheshu 13(23 850.00 kg/hm2,incidence rate 46.0%).
杂志排行
植物病虫害研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Integrated Prevention and Control Techniques of Infectious Diseases of Vegetables
- Disease-resistant Mechanism of Pepper against Root-Knot Nematode(Me1oidogyne spp.)
- Inhibitory Effects of Sixteen Fungicides on Mycelial Growth and Spore Germination of Monilinia fructicola
- Effects of Different Amino Acid Fertilizers on Growth,Development and Quality of Mini Watermelon under Substrate Cultivation
- Crystal Structure of Poly[(2,6-di(2’,4’-dicarboxylphenyl)pyridine-κ4 O:O′:O″:O′′′)-(μ2-1,4-bis(1-imidazolyl)benzene-κ2N:N’)cobalt(II)],C39H24Co2N7O8
- Morphological and Biological Characteristics of Rhynchaenus empopulifolis in Tai’an,China
