Case Study:Interviewing,Assessing,and Analyzing a Second Language Learner
2021-01-11
College of Foreign Languages,Xinjiang University,Xinjiang,China Email:jhuamei2019@yeah.net
[Abstract]This study aims to investigate how L2 learners are affected by various internal and external factors in terms of their learning outcomes.Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory(1978)is adopted to analyse L2 learning of the research subject based on interviews and questionnaires examining the participant’s L2 proficiency.The results indicate that it is necessary to achieve a balance between the Ideal L2 Self and the ought L2 Self.Secondly,one’s personality is closely related to L2 anxiety.Lastly,learners’language metacognition and learning autonomy are essential factors determining their learning achievements.
[Keywords]L2 Proficiency;Sociocultural Theory;Internal Factors;External Factors
Introduction
The difficulty of L2 learning lies in the variation of learners’performance even under the same instruction due to the influence of various internal and external factors.Hence,the analysis of the potential factors affecting the performance of L2 learning is of a necessity for assisting L2 learners in adjusting their learning according to specific situations.This study aims to investigate how L2 learners are affected by various internal and external factors in terms of their learning outcomes.Specifically,Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory(1978)is adopted to analyse L2 learning of the research subject based on interviews and questionnaires examining the participant’s L2 proficiency.As a result,three main conclusions are drawn from the findings of the study.Firstly,it is necessary to achieve a balance between the Ideal L2 Self and the ought L2 Self,while the importance of the ideal L2 self for L2 learning should be emphasized.Secondly,one’s personality is closely related to L2 anxiety.Lastly,learners’language metacognition and learning autonomy are essential factors determining their learning achievements.
Participant
Enrolled in the TESOL programme at a University in London,a 27-year-old female student pseudo-named sunny was selected as the participant.Her mother tongue is Chinese as she was born and raised in China.In 2019,she gained a score of 7.5 in the IELTS test.According to the IELTS scale(2020),“7”means“good use”.In other words,a score of 7 means that the test taker has achieved an operational command of the tested language in spite of occasional errors.Thus,her language proficiency is proved to be the C1 level,which is above the standard of good use(Cambridge English Scale,2020).
Methodology
Conducted on ZOOM,the interview is divided into two phases,namely the pre-interview phase and the whileinterview phase.Considering the fundamental role of vocabulary in language acquisition(Zimmerman,1997),I invited sunny to receive a test of her vocabulary size on the website called“My Vocabulary Size”before the online interview so as to measure her L2 proficiency.Researchers are allowed to observe the learner’s basic linguistic knowledge such as the vocabulary size and pronunciation through the bottom-up approach(Vandergrift,2009).In the while-interview phase,she was required to complete a picture description task,which involves making statements based on pictures by learners(Nation&Newton,2009,p.30).For the purpose of mitigating her anxiety and strengthening her confidence,she was allowed to examine each picture for one minute and then ask questions related to the pictures.Then,she was offered one or three minutes to make pre-task planning that can affect learners’performance(Mochizuki&Ortega,2008)and help candidates prepare for the task“both psychologically and linguistically”(Li et al.,2015).Li et al.(2015)also suggest that the optimal time for pre-task planning is from 1 to 3 minutes,especially for accuracy and fluency.Subsequently,the participant was required to describe each picture within 1 minute.The participant was stimulated to express the content faster by an increase in time pressure,which is a typical strategy used in the 4/3/2 activity(Thai&Boers,2016).Different from 4/3/2 activity,this study has no repetition work as the test is not for improving her language fluency.Besides,the simple repetition work is not challenging for the participant whose language proficiency level is“C1”(Cambridge English Scale,2020).Instead,this study adopted a more difficult picture description task,which assigned the participant three different pictures with the difficulty level ranging from simple,medium,and hard.In this case,ample data can be collected,thereby contributing to a comprehensive analysis of her language proficiency.Following the picture description task,20 questions were posed to identify the possible factors facilitating her language proficiency and language learning.In the end,data of the interview was transcribed and coded to summarize the findings and propose implications for improving the participant’s language proficiency and determining factors that contribute to her success in second language acquisition.
Results
Participant’s L2 speech proficiency
As indicated by Brown(2000),the overall assessment of language learners’oral proficiency is generally related to their conversational proficiency performance in interviews.Accordingly,this study analyzed the participant’s L2 proficiency from four dimensions,including comprehensibility,fluency,pronunciation,and vocabulary based on her performance in the interview.
Comprehensibility
Comprehensibility is used for assessing the degree of difficulty in understanding a speaker’s utterance(Derwing& Munro,1997).According to“the global and analytic scales of L2 English comprehensibility”(Isaacs et al.,2018),the subject’s L2 comprehensibility level can be classified as level 5,namely the highest level of comprehensibility.The overall explanation for Level 5 comprehensibility demonstrates that the understanding of L2 speakers under level 5 comprehensibly effortless(Isaacs et al.,2018).It is not difficult to understand the subject’s response in both interview and picture description tasks.Also,this result is in line with the participant’s performance in the IELTS test.A score of 7 in the IELTS speaking test indicates that her overall speaking proficiency is good(IELTS Scale,2020).
Comprehensibility involves an overall construct built by listeners’perception(Suzuki&Kormos,2020).Despite overall good comprehensibility,there are few problems in the subject’s speech.In general,a negative assessment of comprehension refers to linguistic inability to understand(e.g.a lack of specific vocabulary knowledge)and misinterpretation of the interviewer’s questions(Brown,2000).The participant described the first and second pictures fluently in the description task while looked up several unknown English words in her mobile dictionary before describing the third picture as it is more complex than the first and second pictures with more figures and complicated plots.Also,since 2 questions out of 20 are long during the interview,the participant asked me to repeat and paraphrase the question to gain an accurate understanding of the questions.
Fluency
Fluency is usually defined as the eloquence and smoothness of one’s speech or writing(De Jong et al.,2012).In particular,oral fluency refers to a speaker’s ability to produce eloquent and smooth speech with few cessations hesitations,or reformulations”(Suzuki & Kormos,2020).However,it is hard to quantify speech fluency due to its multivariable composition(Martins et al.,2007).
Generally,there is a close relationship between speed fluency and a listener’s perception of fluency(Bosker et al.,2013).Speech rate and pauses are used to distinguish the fluency of a speech(Kerschensteiner et al.,1972).The common way of computing the speech rate is the number of words produced or syllables per minute(Kerschensteiner et al.,1972).However,in this short interview,no ample data is available for computing the subject’s speech rate.Thus,the total number of fillers such as uh and um was recorded in this study to analyse pauses and repetition in the participant’s speech(Derwing et al.,2004)as the number of pauses can also be used for measuring the fluency of a speech(Kerschensteiner et al.,1972).Although Sunny paused when thinking and organising her answers,these fillers would not influence the subject’s fluency for me because these are rare phenomena in her speech and these fillers actually make her speech sounds more natural.
Vocabulary and grammar
Vocabulary and grammar were found to be applicable to the evaluation of the language proficiency level(De Jong et al.,2012),especially the lexical knowledge that plays a core role in formulating theoretical views on speaking ability(Saito et al.,2016).Hence,the improvement of learners’oral proficiency requires the learning and expansion of their vocabulary(Adolphs&schmitt,2003).According to the subject’s vocabulary test result,a vocabulary size of at least 9,700 English word families is sufficient for an adequate understanding of L2 discourses(Adolphs&schmitt,2003).However,the vocabulary size website can only test the participant’s receptive vocabulary size rather than the productive vocabulary size,which is also an important aspect in L2 learning and closely related to one’s speaking and writing ability.The score of participants’productive vocabulary tests can significantly predict their speaking scores(Uchihara & Saito,2019).Considering the common way of measuring lexical richness and lexical variation is the type-token ratio(TTR)(Read,2000),I transcribed the subject’s picture-description task and calculated the TTR of the spoken text,which is(85/156)54.5%.Although the lexical richness of a text is positively correlated with the TTR(Williamson,2014),the TTR is also closely related to the length of the text.Therefore,the TTR may not serve as an objective and real reference for the measurement of the subject’s L2 productive vocabulary size.Also,the vocabulary of a spoken text may be less diverse than that of a written text because simultaneous communication leaves little time of thinking for speakers.In a word,further tests of the subject’s productive vocabulary need to be considered.
In her speech,there are other linguistic issues such as morphological appropriateness errors.According to Saito et al.,(2016),morphological appropriateness errors could be related to the use of verb tense.For example,some verb tense errors were found in Sunny’s answer,“he seems to be the little girl’s father and he wanted(wants)to rescue the cat”.Nevertheless,these grammatical errors would not affect the comprehensibility of her production as grammar only accounts for 10% in rating L2 comprehensibility.Moreover,mistakes are common in oral English communication of L2 learners as speaking as the productive knowledge of L2 is harder than the receptive knowledge to master.
Pronunciation
The research subject’s English pronunciation is decent and comprehensible.In addition to the correct pronunciation of the vowels and consonants in her speech,both of the segmental and super-segmental elements are standard and natural(Derwing,2012).Also,she is in good command of her speech rhythm.These results conform to her speaking achievements in the IELTS test.According to IELTS speaking criteria(2020),test takers are evaluated in four aspects,including lexical resources,oral fluency and coherence,grammatical knowledge,and pronunciation.A score of 7 in her IELTS speaking test suggests the official recognition of her speaking performance by IELTS examiners.Also,her vocabulary size of 9,700 word families is far larger than that stipulated in the lexical standard for L2 learners.As a result,she has a high awareness of segments that have contributed to her acquisition of L2 pronunciation(Saito et al.,2018).
Participant’s L2 learning experiences and contexts(External factors)
Daily L2 use
Sunny revealed in the interview that she uses the L2 on a daily basis.Before her study in London,she worked as an English teacher who needed to instruct students in English.Now the life and study in London require her to use L2 more frequently.The overseas experience provides Sunny with more opportunities to use English and has an impact on her L2 learning results due to massive exposure to L2 contexts that are considerably different and favourable for second language acquisition(Jaekel et al.,2017).Also,Thompson & Lee(2014)indicated that overseas experience could improve language proficiency in both linguistic and non-linguistic ways regardless of its duration.
It is worth mentioning that the subject’s boyfriend is a Londoner who can’t speak Chinese and thus has created an ideal L2 learning environment in that they have to communicate in English.To some extent,this relationship also strengthens her determination and self-esteem in learning and improving her L2.As she said,“Allen(her boyfriend’s name)helps me to proofread my assignments,but I don’t want him to look down upon me,so I study harder now.”Generally speaking,the degree of L2 learners’self-esteem is positively correlated with their level of L2 proficiency(Hashemian,2012).
The role of the learner’s age
The subject’s age of learning usually plays an important role in deciding her L2 learning results.At the age of four,she began to learn English in kindergarten where she benefited from learning a second language at an early age in terms of long-term language learning.According to Lenneberg’s(1967)critical period hypothesis(CPH),it is possible to normally acquire a language through mere language exposure during a certain period.Also,young learners who are highly motivated and hold positive attitudes towards L2 learning(Graham et al.,2016)will be less perplexed by language anxiety(Johnstone,2009).For instance,she was attracted by online English learning at an early age when she could have access to online resources and never get tired of this way of learning.In particular,she indicated that her experience of taking online phonetics courses with a foreign teacher at the age of 6 greatly improved her L2 pronunciation and helped her develop a nativelike accent(Abrahamsson,2012).Currently,she still feels most confident about her pronunciation among all the aspects of language skills.
However,it has to be admitted that older language learners make progress faster in the classroom for the possible reason of their high-level cognitive maturity and strong abilities to learn a language from explicit instructions(Muñoz,2006).This is also the reason why Sunny believes that her language proficiency improved a lot after becoming a middle school student.
Learning strategy
It can be learnt from the interview that the subject’s language metacognition is strong.She is clear about appropriate learning strategies for improving her L2 learning.
Compared to incidental learning,the subject prefers explicit learning as she mentioned,“I’m not so good at picking them up incidentally,my learning experience and method is more like intentionally.”
Apart from teachers’explicit instructions in the classroom,self-study is also a way of language learning frequently adopted by her.She is good at taking advantage of online resources,such as“Magoosh”,“Rosseta Stone”,and“Coursea”to enhance her self-study.These online courses provide both meaning-focused and form-focused activities that further assist her in L2 learning.Besides,the application of computer-assisted language learning(CALL)can promote the autonomous learning of learners and significantly raise their linguistic awareness by adjusting learners’input,gauging learning progress,reflecting on their learning results,and optimising them(Collentine,2011,cited in Wach,2012).
Factors affecting the participant’s L2 learning outcomes(Internal factors)
Motivation and Willingness to Communicate(WTC)
Affective factors such as motivation and willingness to communicate play an important role in acquiring a language(Yashima,2002).Specifically,willingness to communicate(WTC)has been considered as an important predictor of communication frequency(Zarinabadi,2011).In the interview,Sunny presented a strong willingness to communicate,especially in a casual context where she can communicate with classmates and foreign friends.
At the same time,Sunny manifested strong motivation in L2 learning according to her“Motivation Questionnaire”with a score of 6(highest)on the Ideal L2 self and 4 on to the ought L2.In particular,the Ideal L2 self is closely related to one’s motivated behaviours(Saito et al.,2018).Ideal L2 Self,which is defined as the self-image of an ideal user that a learner wants to develop(Dörnyei,2005),can help set L2 learners’future goals,thus contributing to L2 learners’future development.In Sunny’s case,she had a short experience of participating in an exchange programme as a student in the United States when she was 16.The novel environment and atmosphere there deeply attracted her,thereby further stimulating her integrative motivation(Gardner & Lambert,1959).As she recalled,she expected to integrate into the local community and“study or work in an international environment in the future”.She also joined the English debating club in College to practice and improve her English.In the debate club,she had great admiration for her teammate Lin who performed well in English debating.As Sunny said,“I wish I could become Lin someday,she can debate with others in English fluently and logically.Can you believe that,she can keep debating in English for 7 minutes!”Then she was encouraged by this admiration to learn English abroad.
The ought self is related to those characteristics desired by learners for meeting certain expectations and avoiding negative learning outcomes in the future(Saito et al.,2018).In the interview,Sunny mentioned that her father had high expectations of her and was strict about her English learning even when she was a kid by continuously emphasising the importance of English.Sunny recalled that she made all her efforts to win her father’s praise and had contradictory feelings towards her father.On one hand,she desired the approval and praise from her father.On the other hand,she hated him for pressuring her so hard.This complex emotion had affected her attitude toward language learning when she was young.Fortunately,she gradually gained pleasure from this process as she found the charm of English.
Personality
Personality factors play an important role in determining one’s language acquisition(see e.g.Dewaele,2013).A personality test called Ten-Item Personality Inventory-(TIPI)was used for identifying Sunny’s personality as a brief measurement of the Big-Five personality domains.As a hierarchical model of personality traits,the big-five framework provides five broad factors that represent personality at the broadest level of abstraction(Gosling et al.,2003).Results are shown below,see Figure 1:
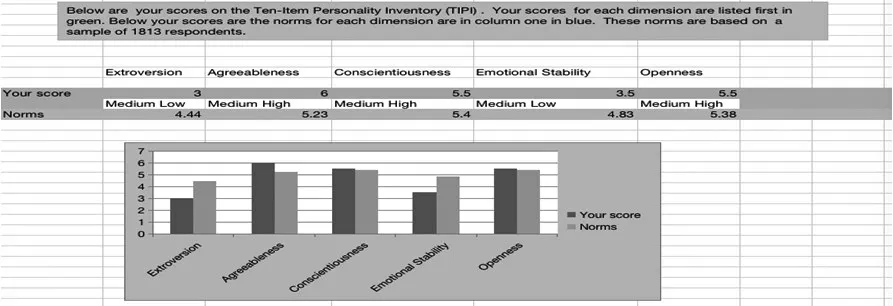
Figure 1 The participant’s TIPI results
In terms of extroversion,she gained a score of 3,which is below the mean of 4.44 and indicates that she is somewhat introverted.She also self-reported that she was reserved and quiet instead of being extraverted and enthusiastic.
Generally speaking,extroverts perform better in language fluency while introverts perform better in language accuracy(Ożańska-Ponikwia&Dewaele,2012).This statement is in line with Sunny’s L2 learning process.The interview demonstrated that she paid more attention to accuracy during language learning as she believes“accuracy is very important”.
Aptitude
Sunny’s“talents”can help explain her success in L2 learning.Although she didn’t take the“LLAMA”test,she believes that she has“talents”in language learning to some extent.For example,she is good at analysing language and memorising vocabulary quickly.In particular,she can imitate different accents vividly due to her sensitivity to language.
However,it should be noted that language aptitude is not a predictor of one’s ability to learn a second language but a predictor of the possible rate of one’s learning progress(Dörnyei,2006)under optimal conditions.Learners with higher levels of talents or abilities tend to be more successful in language learning under good conditions.
Emotion and Interest
The subject showed a strong interest in English.Interest plays a critical role in gaining educational achievements as it can influence learners’“behaviour,involvement,and learning”(Amiryousefi,2018).Learners with greater interest are expected to be more willing to devote their mental efforts and commitment to self-regulated learning activities(Pintrich&Zusho,2002).
With regard to the emotion involved in L2 learning,she gained enjoyment and confidence from learning English according to the result of her“Foreign Language Anxiety&Enjoyment”questionnaire(Dewaele et al.,2018).
Empirical researchers demonstrate that learners’beliefs,attitudes,and emotions are closely related to language learning processes and outcomes(Wesely,2012).Apart from her affection for English learning,the subject’s affection for her L2 teachers is also favourable for her learning because“a well-loved teacher can boost students’enthusiasm for learning during classes”(Dewaele et al.,2018).Yet,she still encountered anxiety slightly during her L2 learning,especially when she had to deliver a presentation or speech in front of the class.Overall,her enjoyment surpassed her language anxiety.
Discussion
The study aims to identify the possible factors that contribute to the success of the subject’s L2 learning by examining the subject’s language proficiency from various perspectives.Based on the analysis of her language proficiency,it can be concluded that Sunny is an advanced language learner whose success in L2 learning results from both internal and external factors.In Table 1,an overview of Sunny’s L2 proficiency is presented,together with those internal and external factors that influence her L2 learning.
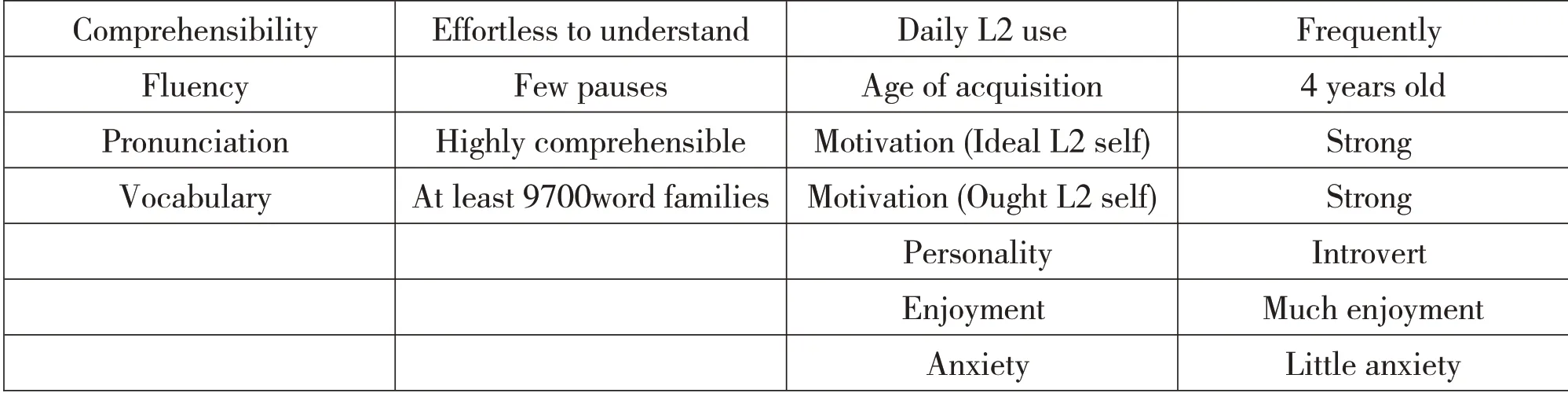
Table 1 The participant’s overall language proficiency
Apart from these factors,Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory can be used to explain the subject’s success in L2 learning.Vygotsky et al.(1978)divided learners’developmental levels into two parts,namely the“actual developmental level”and the“potential developmental level”,between which there is a zone of proximal development(ZPD).Although it is hard to judge whether the learner had passed ZPD and achieved the potential development level,one thing for sure is that whether the learner could complete the task independently could be observed.
In the current study,the subject not only received instruction from her teacher in the initial stage of her learning but also adopted various instruments to facilitate her L2 learning.With the assistance,she finished intractable tasks and improved her L2 step by step.However,it is worth mentioning that dependence on others did not directly result in her success.Normally,only a few learners can achieve a high level of L2 acquisition,even though all learners can seek help form instructors.
According to the theory,the ultimate goal of scaffolding instruction within the learner’s zone of proximal development(ZPD)used for tasks that a child or a less competent learner can accomplish with assistance rather than finishing them independently is to optimise learning and the development of the learner’s autonomy(Lantolf&Throne,2006).The literature on scaffolding indicates that the fading-out step of scaffolding constitutes an inseparable part of the scaffolding process(Lajoie,2005).Hence,a teacher’s assistance at first is not for providing assistance but developing learners’autonomous learning abilities.In this case,the subject’s learning autonomy has contributed to her success in L2 learning.
The essence of learners’autonomy is the ability to control the pace of one’s own learning process(Little,2007).As a factor that enables an individual to reach one’s“potential developmental level”(Vygotsky,1978),learners’autonomy must be supported by external environments,such as teachers,peers,facilities,and learning materials.Through the improvement on autonomous learning competence,learners can master the way of learning and thus achieve better academic performance.Furthermore,they can gain an in-depth understanding of the whole process of language learning.This study found that the subject consciously employed various appropriate and effective language strategies in her L2 learning.She also knew the way of effective self-learning and the goal of learning.Hence,language metacognition and a high level of learning autonomy competence are crucial for determining one’s language proficiency,which conforms to the findings of previous studies(Feryok,2013; Vickers & Ene,2006)that learners’autonomy helps develop a high degree of language proficiency and vice versa.Besides,language proficiency is positively correlated with the level of one’s metacognitive strategies.
Secondly,it is interesting to explore the reason for the subject’s anxiety and diffidence in L2 learning as an advanced and successful L2 learner.Generally,anxiety,which is negatively correlated with L2 achievements,may constitute a barrier to successful L2 learning.In this study,however,the subject’s L2 learning outcomes are not necessarily affected by her language anxiety as she gained an overall success in L2 learning.Meanwhile,it can be found that the subject was not confident with her language proficiency and always considered herself as an intermediate language learner,which,in turn,reflects her anxiety as anxious learners are more inclined to the underestimating of their language proficiency.Also,the short replies provided by Sunny to the interview questions are related to her language anxiety because learners with a high level of anxiety usually produce shorter communication units with fewer dependent clauses(Phillips,1992).According to Dewaele et al.(2008),foreign language anxiety is associated with learners’characters.It can be concluded from the data that the subject’s anxiety and diffidence resulted from her personality traits.This data is in accordance with the viewpoint of Gregersen&Horwitz(2002)who argue that perfectionists usually experience language anxiety as they set a higher standard for themselves when it comes to language learning and they present a high level of self-criticism(Gregersen & Horwitz,2002).Moreover,there is a positive correlation between the level of anxiety and the degree of perfectionism(Dewaele et al.,2008).
Thirdly,what deserves attention is that the subject is characterised by a high level of both the Ideal L2 self and the Ought L2 self.Thus,it is significant to discuss the relationship between the Ideal L2 self and the Ought L2 self.It has been widely acknowledged that motivation is one of the important factors that influence the rate and success of L2 learning.For L2 learners,their future self-image can be the main force of language learning(Dörnyei,1998).The findings of the study that motivation,especially that of strong Ideal L2 Self,positively influences the subject’s L2 learning are consistent with the research(Gardner & MacIntyre,1991; Saito et al.,2018)indicating that learners’motivation is closely related to their L2 learning outcomes.More importantly,Ideal L2 Self has been by far the most important component of the L2 motivation construct in many foreign language learning classrooms(Csizer&Dornyei,2005).Then in terms of the ought L2 self,it may bear a slight relationship with one’s own desires or wishes.Thus,conflicts may emerge due to differences between the ideal self and the ought self(Dörnyei,2009).For instance,in Asia countries where foreign language acquisition is highly exam-oriented,learners’efforts and persistence in L2 learning may be affected by the ought L2 self(Kormos et al.,2011).For the subject,she was deeply affected by her family expectation that constitutes a major factor influencing her motivation as she was always expected to gain high scores excellent results from her L2 learning.Fortunately,this Ought L2 Self did not conflict with her Ideal L2 Self,thereby resulting in her success in L2 learning.Thus,it is important to achieve a balance between the ideal self and the ought self as indicated by researchers(Siridetkoon & Dewaele,2018; Dörnyei,2009)that the Ideal L2 Self and the ought L2 Self interacts with each other.
Conclusion and Pedagogical Implications
To conclude,the interview was conducted in the current study to examine the subject’s language proficiency and possible factors influencing L2 learning outcomes.The findings of the study correspond to those of previous studies.Firstly,the Ideal L2 Self is extremely significant for L2 learning,and there should be a balanced relationship between the Ideal L2 Self and the Ought L2 Self.Secondly,there is a close relationship between L2 learners’personality and their anxiety with L2 learning.Lastly,learners’language metacognition and learning autonomy play a critical role in determining their learning achievements.Hence,implications can be summarized from the study that L2 learners should have clear expectations for their future self-image and keep the image alive,thus keeping being motivated.Besides,the development of one’s learning autonomy competence is of great importance.
杂志排行
Proceedings of Northeast Asia International Symposium on Linguistics,Literature and Teaching的其它文章
- Language Assessment Literacy and the Influential Factors:Evidence from a Survey of Middle School English Teachers in Chongqing
- Developing Critical Thinking in EFL Writing Class
- A Comparative Study on the Effects of Two Modes of Internet-based Feedback in EFL Writing Settings
- A Corpus-based Study on Conceptual Metaphor in T.S.Eliot’s Four Quartets
- Exploration of the SPOC-based Blended Teaching Model:Case Study of Business English Course
- The Study on CET-4 Writing and Writing Teaching Strategies Based on the Survey of CET-4 Writing Marking Teachers
