不同氮浓度对薏苡幼苗生长和光合特性的影响
2020-11-02王红娟於春路献勇江本利胡积送余黎明朱加保闫晓明
王红娟 於春 路献勇 江本利 胡积送 余黎明 朱加保 闫晓明


摘要:【目的】探討不同氮浓度和品种差异对苗期薏苡生长和光合特性的影响,为阐明薏苡响应氮营养的机理及指导合理施氮提供理论依据。【方法】以皖薏1号和皖薏2号为材料进行水培试验,以NH4NO3为氮源,设4个氮水平(0、5、15和25 mmol/L)处理,处理后第4、8、12和16 d测定不同处理薏苡幼苗的地上部干重、根冠比、叶绿素含量、光合速率和叶绿素荧光参数。【结果】整个培养过程中,皖薏1号表现出茎细、叶窄、叶色偏浅,皖薏2号表现出茎粗、叶宽、叶色偏深,与皖薏1号相比,皖薏2号的株高相对偏低。2个皖薏品种5~25 mmol/L处理的地上部干重、叶绿素(a+b)含量、叶绿素a/b、净光合速率(Pn)、光系统Ⅱ最大光能转换效率(Fv/Fm)整体上高于0 mmol/L处理,而根冠比低于0 mmol/L处理。在整个培养过程中,皖薏1号的地上部干重随着氮浓度的增加逐渐增加,表现为0 mmol/L处理<5 mmol/L处理<15 mmol/L处理<25 mmol/L处理;皖薏2号的地上部干重随着氮浓度的增加呈先升高后降低的变化趋势,表现为0 mmol/L处理<5 mmol/L处理<25 mmol/L处理<15 mmol/L处理。不同培养时间下,5~25 mmol/L处理间的幼苗根冠比无显著差异(P>0.05,下同)。在0 mmol/L处理下,同一培养时间皖薏2号的地上干重和根冠比高于皖薏1号。2个品种除培养第4 d的叶绿素(a+b)含量为15 mmol/L处理最高外,其他培养时期的叶绿素(a+b)含量均随着氮浓度的增加而逐渐升高,且培养8~16 d时15和25 mmol/L处理的叶绿素(a+b)含量显著高于0 mmol/L处理(P<0.05,下同),相同条件下皖薏1号的叶绿素(a+b)含量均低于皖薏2号。皖薏1号5~25 mmol/L处理幼苗的Pn差异不显著,但均显著高于0 mmol/L处理;皖薏2号幼苗的Pn随着氮浓度的增加先升高后降低,均为15 mmol/L处理幼苗的Pn最高,且显著高于0 mmol/L处理。皖薏1号的Fv/Fm随着氮浓度的增加整体上呈升高趋势,皖薏2号的Fv/Fm随着氮浓度的增加呈先升高后降低的变化趋势。【结论】不同薏苡品种的最适氮浓度存在差异,25 mmol/L或更高氮浓度较适宜皖薏1号幼苗生长,15 mmol/L氮浓度较适于皖薏2号幼苗生长。皖薏2号表现出氮高效品种特征。
关键词: 氮浓度;薏苡;水培;幼苗生长;光合特性
中图分类号: S519.01 文献标志码: A 文章编号:2095-1191(2020)08-1925-07
Effects of different nitrogen concentrations on seedling growth and photosynthetic characteristics of coix
WANG Hong-juan1, YU Chun1, LU Xian-yong1, JIANG Ben-li1, HU Ji-song1,
YU Li-ming2, ZHU Jia-bao1*, YAN Xiao-ming1*
(1Institute of Cotton Research, Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Hefei 230001, China; 2Anhui Hui Nong Ecological Food Co.,Ltd., Chizhou, Anhui 245108, China)
Abstract:【Objective】In the present study, the effects of different nitrogen concentrations and varieties on seedling growth and photosynthetic physiology of different cultivars of coix were studied to provide theoretical basis for elucida-ting the mechanism of coixs response to nitrogen nutrition and guiding rational nitrogen application. 【Method】The hydroponic experiment was carried out with Wanyi 1 and Wanyi 2 as materials, NH4NO3 was used as the nitrogen source, and four nitrogen levels (0, 5, 15 and 25 mmol/L) were set. Coix seedling dry weight, root-shoot ratio, chlorophyll content, net photosynthetic rate and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters were determined at 4,8,12 and 16 d after treatment. 【Result】During the entire cultivation process, Wanyi 1 showed thinner stems, narrower leaves, and lighter leaf color, and Wanyi 2 showed thicker stems, wider leaves, and darker leaf color. Compared with Wanyi 1, the plant height of Wanyi 2 was relatively lower. The above-ground dry weight, chlorophyll(a+b) content, chlorophyll a/b ratio, net photosynthetic rate(Pn), photosystem II maximum light energy conversion efficiency(Fv/Fm) of the two cultivars treated with 5-25 mmol/L nitrogen were generally higher than those under 0 mmol/L treatment, while the root-shoot ratio was lower than those under 0 mmol/L. During the entire cultivation process, the dry weight of the shoots of Wanyi 1 gradually increased with the increase of nitrogen concentration, showing 0 mmol/L treatment<5 mmol/L treatment<15 mmol/L treatment<25 mmol/L treatment; the dry weight of the shoots of Wanyi 2 increased first and then decreased with the increase of nitrogen concentration,showing 0 mmol/L treatment<5 mmol/L treatment<25 mmol/L treatment<15 mmol/L treatment. There was no significant difference in seedling root-shoot ratio among 5-25 mmol/L nitrogen treatments under different culture time(P>0.05, the same below). Under 0 mmol/L nitrogen treatment, the above-ground dry weight and root-shoot ratio of Wanyi 2 were higher than those of Wanyi 1 at the same culture time. Except for the highest chlorophyll(a+b) content of 15 mmol/L treatment on the 4th day of cultivation, the chlorophyll(a+b) content of the two cultivars increased gradually with the increase of nitrogen concentration. The chlorophyll(a+b) content of 15 and 25 mmol/L treatments was significantly higher than that of 0 mmol/L treatment(P<0.05, the same below) on 8-16 d of culture. Under the same conditions, the content of chlorophyll(a+b) in Wanyi 1 was lower than that of Wanyi 2. The Pn of the seedlings of Wanyi 1 treated with 5-25 mmol/L nitrogen was not significantly different, but were all significantly higher than that of the 0 mmol/L treatment. The Pn of the seedlings of Wanyi 2 increased firstly and then decreased with the increase of nitrogen concentration, the Pn of seedlings treated with 15 mmol/L was the highest, and it was significantly higher than that with 0 mmol/L treatment. The Fv/Fm of Wanyi 1 showed an overall upward trend with the increase of nitrogen concentration. The Fv/Fm of Wanyi 2 first increased and then decreased with the increase of nitrogen concentration. 【Conclusion】All the results indicate that the optimum nitrogen concentration for different coix cultivars is different, and the optimum nitrogen concentration for Wanyi 1 is 25 mmol/L or higher, while the 15 mmol/L culture is suitable for the growth of Wanyi 2 seedlings. Wanyi 2 shows the characteristics of high-efficiency nitrogen cultivar.
Key words: nitrogen; coix; hydroponics; seedling growth; photosynthetic characteristics
Foundation item: Key Research and Development Projects of Anhui(1804a07020114); Major Science and Techno-logy Projects of Anhui(18030701181)
0 引言
【研究意义】薏苡(Coix lacryma-jobi L.)是禾本科(Gramineae)薏苡属(Coix)草本植物。早在夏朝至春秋战国时期,薏苡是我国一种重要的粮食作物,后因生产限制逐渐被取代,退居为半野生的药用植物(杨万仓,2007)。薏苡除具有健脾利湿、清热排脓作用外,还具有抗癌等功效(杨爽等,2011)。此外,随着对薏苡保健美容功效认识的深入,薏苡的经济价值逐渐被开发出来,并广泛应用于食品、保健品及化妆品等领域,市场需求不断提高(吴庆华等,2014)。我国是最大的薏苡生产国和出口国(刘国庆等,2015),但由于长期以来科研投入较少,薏苡的生产还存在很多问题,在薏苡的施肥管理上通常仅凭经验,而施肥不足和过量施肥均不利于薏苡生长。因此,研究合理施肥,尤其是氮素营养与薏苡生长和光合特性的关系,对薏苡种植的增产增效及生态保护均具有重要意义。【前人研究进展】氮肥用量不仅能影响植物的生物量,也会对光合性状产生影响。不同供氮水平会改变植物的生长指标、叶绿素含量、光合速率和叶绿素荧光参数等,适宜的氮水平能有效提高植物的生长和光合指标(陈静等,2013;周志强等,2015;李亚静等,2016)。同一作物不同品种间氮效率存在差异,不同品种对相同施氮量的响应也不同。阮新民等(2010)研究表明,单株干物质重可作为水稻苗期氮素效率高低的筛选指标。安久海等(2014)研究表明,氮高效水稻品种更能适应低氮环境,低氮条件下,氮高效品种的叶绿素含量、地上部分干质量、根长及净光合速率(Pn)均显著高于氮低效品种。杜保见等(2014)研究表明,小麦苗期的地上部生物量和地下部生物量可作为氮效率苗期筛选的重要指标。王小纯等(2015)研究表明,氮高效小麦品种耐低氮胁迫能力更强。合理施用氮肥能有效提高薏苡产量,而氮肥用量过低或过高均不利于薏苡的增产(陈雄鹰,2008;陈光能等,2015;周棱波等,2016)和植株健壮(陈光能等,2015)。周棱波等(2016)研究发现,复合肥施用量对薏苡产量和Pn有极显著影响,产量和Pn均随着施肥量提高呈先升高后降低的变化趋势。此外,氮效率与光合性状密切相关,氮高效品种具有光合优势(魏海燕等,2009;李敏等,2015;尹晓明和李辰,2019)。Nghiem等(2018)研究表明,与氮低效薏苡品种相比,氮高效品种在分蘖期、抽穗期、成熟期的光合速率和叶绿素含量更高,且在生育后期衰减更慢,但薏苡的氮素利用效率与叶绿素荧光参数无显著相关关系。【本研究切入点】目前关于氮素营养与薏苡生长和光合特性关系的研究较少,尤其是氮水平对不同品种薏苡幼苗生长和光合特性影响的研究鲜有报道。【拟解决的关键问题】通过室内水培的方式对不同氮浓度下的薏苡幼苗进行研究,探讨不同氮浓度和品种差异对苗期薏苡生长和光合特性的影响,为阐明薏苡响应氮营养的机理和指导合理施氮提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1. 1 试验材料
供试薏苡品种为安徽省地方品种皖薏1号和皖薏2号,由安徽省农业科学院棉花研究所提供。品种间外观差异明显,种性稳定,纯度较高,适于试验研究。
1. 2 試验方法
选取饱满的薏苡种子经75%酒精消毒30 s,2% NaClO消毒10 min,蒸馏水洗涤3次,每次5 min,均匀播种于灭菌沙土中。8 d后选取生长均匀一致且已有次生根的薏苡幼苗,切断带种子的初生根,以免水培过程中长菌造成试验材料损失(在预试验水培过程中,无论剥壳与否,大量幼苗因为种子位置长菌导致死亡),洗净根系用海绵固定于孔径0.8 cm的泡沫板中,置于长19.0 cm、宽13.5 cm、高8.0 cm的避光塑料盒内,用Hoagland营养液培养2周后进行不同氮浓度处理。
参照张志良和瞿伟菁(2003)的方法配置处理营养液,除氮源外的营养液组成为:2.5 mmol/L MgSO4·7H2O、2 mmol/L KH2PO4、5 mmol/L KCl、5 mmol/L CaCl2·2H2O、0.02 mmol/L Na2-EDTA·2H2O、0.02 mmol/L FeSO4·7H2O、6.7 μmol/L MnSO4·H2O、0.3 μmol/L CuSO4·5H2O、0.8 μmol/L ZnSO4·7H2O、46.3 μmol/L H3BO3、0.6 μmol/L H2MoO4。以 NH4NO3为氮源,设4个氮水平(0、5、15和25 mmol/L)处理,每处理重复3次。处理开始后每4 d更换1次营养液并测定1次相关指标,即处理后第4、8、12和16 d连续测定4次。
1. 3 测定项目及方法
1. 3. 1 根冠比测定 取幼苗3株,吸干植株根部水分,分成地上和地下两部分,105 ℃杀青0.5 h,80 ℃烘干至恒重并测量。根冠比=地下部干重/地上部干重。
1. 3. 2 叶绿素含量测定 采用分光光度计法测定叶绿素含量,以95%酒精为浸提液,在665、649和470 nm下比色,计算叶绿素含量,3次重复。
1. 3. 3 光合指标测定 用LI-6400便携式光合仪(美国LI-COR公司),于8:00—11:00测定主茎倒2叶的Pn。由于薏苡幼苗叶片窄于所用的标准叶室,选取叶片中段均匀一致的区域进行测定,并根据叶宽计算实际测量面积,从而得到相对准确的Pn,测定光强为600 μmol/(m2·s)。
叶绿素是光系统的重要组成部分,是光合作用过程中的主要色素,可吸收、传递和转化光能,直接影响植物的光合作用。叶绿素的含量及比例是植物适应和利用环境因子的重要指标(张利等,2001)。有研究表明,过高或过低的供氮水平均会影响植物的叶绿素含量(周志强等,2015),但也有研究结果显示随着氮水平提高,植物的叶绿素含量不断提高(郭盛磊等,2005)。本研究中,2个薏苡品种多数培养时间下幼苗的叶绿素(a+b)含量均随着氮浓度的增加逐渐升高,表明氮素增加能提高薏苡幼苗叶绿素(a+b)含量。同时,皖薏1号在培养第4、8 和12 d时25 mmol/L处理的叶绿素a/b最高,皖薏2号在培养第4、8和12 d时15 mmol/L处理的叶绿素a/b最高,表明随着氮浓度的提高,不同品种薏苡幼苗的表现存在差异,可能与不同品种的适宜氮浓度不同有关。本研究结果与Kitajima和Hogan(2010)研究发现的供氮不足会降低紫绣球叶片单位面积的总叶绿素含量,提高叶绿素a/b的研究结果存在一定差异,可能是由于本研究是室内试验,光照强度较弱,光照条件是否会对试验结果产生影响还有待深入研究。
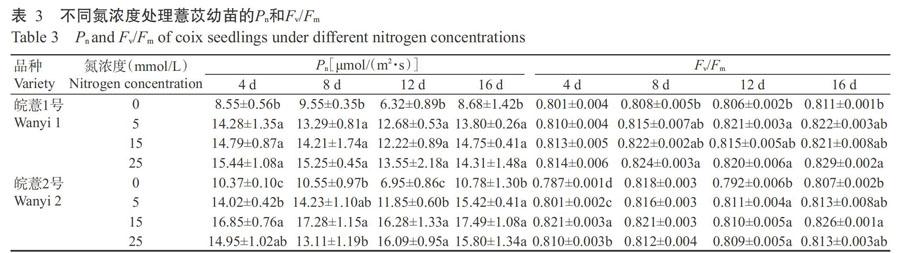
氮素对植物的光合速率有明显影响,而光合速率可直观反映植物的光合能力。前人研究表明,随着供氮素水平提高,植物的光合速率随之提高,但氮素供给过高时光合速率不再提高,甚至会有降低趋势(郭盛磊等,2005;张艾英等,2015;刘剑钊等,2019)。本研究中,皖薏1号在培养第4 、8和12 d时,均是25 mmol/L处理的Pn最高,而皖薏2号的Pn则先升高后降低,表明随着氮浓度的升高,不同薏苡品种幼苗的光合速率变化存在差异,可能与不同品种的适宜氮水平不同有关。
叶绿素荧光在氮素营养的研究中已得到广泛应用(张旺锋等,2003;李强等,2015;朱荣等,2017)。研究表明,氮缺乏会降低Fv/Fm(Huang et al.,2004),增加供氮可使Fv/Fm回升,但当供氮达一定水平后Fv/Fm变化幅度较小(郭盛磊等,2005)。也有研究表明,随着氮供给水平增加,Fv/Fm会先升高后降低(陈静等,2013;周志强等,2015;李亚静等,2016)。本研究中,在无氮培养条件下,2个薏苡品种的Fv/Fm大多低于含氮培养条件,缺氮胁迫明显降低了薏苡的最大光能转换效率。在含氮培养条件下,除培养第12 d外,皖薏1号的Fv/Fm整体上随着氮浓度增加有升高趋势,皖薏2号的Fv/Fm先升高后降低,与Pn的变化趋势相似,应该同样受不同品种适宜氮浓度的影响。
同一作物不同基因型间的氮素吸收利用率通常存在明显差异。前人研究认为,氮高效品種更能适应低氮环境(安久海等,2014;王小纯等,2015),苗期的植株生长情况可作为品种氮效率的筛选指标(阮新民等,2010;杜保见等,2014)。在相同条件下,氮高效品种常具有光合优势和较好的生长发育指标。Nghiem等(2018)研究表明,氮高效薏苡品种在各生育期功能叶片的光合速率和叶绿素含量均明显高于氮低效品种。本研究中,在0 mmol/L无氮处理下,皖薏2号较皖薏1号有更高的地上生物量和根冠比,且在相同培养条件下,皖薏2号较皖薏1号也有更高的叶绿素含量和Pn。因此,推测皖薏1号的氮效率较低,而皖薏2号的耐低氮能力相对较强,氮效率较高。
4 结论
不同薏苡品种的最适氮浓度存在差异,25 mmol/L或更高浓度较适宜皖薏1号幼苗生长,15 mmol/L氮浓度较适于皖薏2号幼苗生长。与皖薏1号相比,皖薏2号的耐低氮胁迫能力更强,表现出氮高效品种特征。
参考文献:
安久海,刘晓龙,徐晨,崔菁菁,徐克章,凌凤楼,张治安,武志海. 2014. 氮高效水稻品种的光合生理特性[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),42(12):29-38. [An J H,Liu X L,Xu C,Cui J J,Xu K Z,Ling F L,Zhang Z A,Wu Z H. 2014. Photosynthetic physiological characteristics of rice varieties with high nitrogen use efficiencies[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University(Natural Scien-ce Edition),42(12):29-38.]
陈光能,魏心元,李祥栋,周小松,陆秀娟,唐虎. 2015. 不同氮肥运筹对薏苡生长及产量形成的影响[J]. 耕作与栽培,(5):38-39. [Chen G N,Wei X Y,Li X D,Zhou X S,Lu X J,Tang H. 2015. Effects of N fertilizer rate on growth and yield formation of Jobs tears[J]. Tillage and Cultivation,(5):38-39.]
陈静,刘连涛,孙红春,张永江,王占彪,李存东. 2013. 氮素水平对棉花幼苗生长和光合特性的影响[J]. 棉花学报,25(5):403-409. [Chen J,Liu L T,Sun H C,Zhang Y J,Wang Z B,Li C D. 2013. Effects of nitrogen concentrations on cotton(Gossypium hirsutum L.) seedling growth and photosynthetic characteristics[J]. Cotton Science,25(5):403-409.]
陈雄鹰. 2008. 不同施氮量和种植密度对薏苡产量的影响[J]. 福建农业科技,(3):58-59. [Chen X Y. 2008. Effects of different nitrogen application rate and planting density on the yield of Jobs tears[J]. Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology,(3):58-59.]
杜保见,郜红建,常江,章力干. 2014. 小麦苗期氮素吸收利用效率差异及聚类分析[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,20(6):1349-1357. [Du B J,Gao H J,Chang J,Zhang L G. 2014. Screening and cluster analysis of nitrogen use efficiency of different wheat cultivars at the seedling stage[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer,20(6):1349-1357.]
郭盛磊,阎秀峰,白冰,于爽. 2005. 供氮水平对落叶松幼苗光合作用的影响[J]. 生态学报,25(6):1291-1298. [Guo S L,Yan X F,Bai B,Yu S. 2005. Effects of nitrogen supply on photosynthesis in larch seedlings[J]. Acta Ecolo-gica Sinica,25(6):1291-1298.]
李敏,罗德强,江学海,周维佳,姬广梅,王学鸿,李树杏. 2015. 高产氮高效籼稻品种的光合生产特性[J]. 中国稻米,21(4):65-67. [Li M,Luo D Q,Jiang X H,Zhou W J,Ji G M,Wang X H,Li S X. 2015. Dry matter production characteristics of rice cultivars with high yield and high N use efficiency[J]. China Rice,21(4):65-67.]
李强,罗延宏,余东海,孔凡磊,杨世民,袁继超. 2015. 低氮胁迫对耐低氮玉米品种苗期光合及叶绿素荧光特性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,21(5):1132-1141. [Li Q,Luo Y H,Yu D H,Kong F L,Yang S M,Yuan J C. 2015. Effects of low nitrogen stress on photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of maize cultivars tolerant to low nitrogen stress at the seedling stage[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer,21(5):1132-1141.]
李亞静,姜燕琴,韦继光,曾其龙,於虹. 2016. 不同氮浓度对兔眼蓝浆果不同品种幼苗生长和光合生理的影响[J]. 植物资源与环境学报,25(2):65-71. [Li Y J,Jiang Y Q,Wei J G,Zeng Q L,Yu H. 2016. Effects of different nitrogen concentrations on growth and photosynthetic phy-siology of seedlings of different cultivars of Vaccinium ashei[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment,25(2):65-71.]
刘国庆,李伟,李海权,张嘉楠,相金英,韩玉翠,耿玲玲,侯升林. 2015. 薏苡生物学研究进展[J]. 河北农业科学,19(4):1-5. [Liu G Q,Li W,Li H Q,Zhang J N,Xiang J Y,Han Y C,Geng L L,Hou S L. 2015. Research pro-gress of biology in Coix lacryma-jobi[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural Sciences,19 (4):1-5.]
刘剑钊,袁静超,周康,梁尧,闫孝贡,张洪喜,任军,蔡红光. 2019. 不同氮肥施用水平对春玉米光合特性及产量构成的影响[J]. 玉米科学,27(5):151-157. [Liu J Z,Yuan J C,Zhou K,Liang Y,Yan X G,Zhang H X,Ren J,Cai H G. 2019. Effect of different nitrogen fertilizer application rates on photosynthetic characteristic and yield of spring maize[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences,27(5):151-157.]
Nghiem Tien Chung,江立庚,孔飞扬,Bui Ngoc Anh. 2018. 不同薏苡品种光合特性及其与氮素利用效率的关系[J]. 中国农业大学学报,23(11):31-39. [Nghiem T C,Jiang L G,Kong F Y,Bui N A. 2018. Photosynthetic characte-ristics and its relationship with nitrogen utilization efficien-cy of different coix cultivars[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University,23(11):31-39.]
钱燕萍,祝遵凌. 2016. 氮素营养对欧洲鹅耳枥幼苗生长及光合特性的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),44(6):71-78. [Qian Y P,Zhu Z L. 2016. Effects of nitrogen nutrition on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Carpinus betulus seedlings[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition),44(6):71-78.]
阮新民,施伏芝,罗志祥,佘德红. 2010. 水稻苗期氮高效品种评价与筛选的初步研究[J]. 中国稻米,16(2):22-25. [Ruan X M,Shi F Z,Luo Z X,She D H. 2010. Evaluation and screening of nitrogen efficient varieties in rice seedling stage[J]. China Rice,16(2):22-25.]
孫利涛. 2008. 施肥对杨树生长及生理特性的影响[D]. 南京:南京林业大学:18-21. [Sun L T. 2008. Effects of fertilization to the growth and physiological characteristic of poplar[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Forestry University:18-21.]
王小纯,王晓航,熊淑萍,马新明,丁世杰,吴克远,郭建彪. 2015. 不同供氮水平下小麦品种的氮效率差异及其氮代谢特征[J]. 中国农业科学,48(13):2569-2579. [Wang X C,Wang X H,Xiong S P,Ma X M,Ding S J,Wu K Y,Guo J B. 2015. Differences in nitrogen efficiency and nitrogen metabolism of wheat varieties under different nitrogen levels[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,48(13):2569-2579.]
魏海燕,张洪程,马群,戴其根,霍中洋,许轲,张庆,黄丽芬. 2009. 不同氮肥利用效率水稻基因型剑叶光合特性[J]. 作物学报,35(12):2243-2251. [Wei H Y,Zhang H C,Ma Q,Dai Q G,Huo Z Y,Xu K,Zhang Q,Huang L F. 2009. Photosynthetic characteristics of flag leaf in rice genotypes with different nitrogen use efficiencies[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica,35(12):2243-2251.]
吴庆华,韦荣昌,林伟. 2014. 薏苡栽培技术研究进展[J]. 现代中药研究与实践,28(4):75-78. [Wu Q H,Wei R C,Lin W. 2014. Research progress of loquat cultivation technology[J]. Research and Practice on Chinese Medicines,28(4):75-78.]
杨爽,王李梅,王姝麒,郭晓江,任冬梅. 2011. 薏苡化学成分及其活性综述[J]. 中药材,34(8):1306-1312. [Yang S,Wang L M,Wang S Q,Guo X J,Ren D M. 2011. Summarization of the chemical components and activities of radon[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,34(8):1306-1312.]
杨万仓. 2007. 中国薏苡遗传改良研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报,23(5):188-191. [Yang W C. 2007. A review on coix genetic improvement in China[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,23(5):188-191.]
尹晓明,李辰. 2019. 不同氮效率水稻品种叶片光合作用及氮利用特征的差异分析[J]. 作物杂志,(1):90-96. [Yin X M,Li C. 2019. Differences in leaf photosynthesis and assimilation of nitrogen between two rice cultivars diffe-ring in nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Crops,(1):90-96.]
张艾英,郭二虎,王军,范惠萍,李瑜辉,王丽霞,王秀清,程丽萍. 2015. 施氮量对春谷农艺性状、光合特性和产量的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,48(15):2939-2951. [Zhang A Y,Guo E H,Wang J,Fan H P,Li Y H,Wang L X,Wang X Q,Cheng L P. 2015. Effect of nitrogen application rate on agronomic,photosynthetic characteristics and yield of spring foxtail millet[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,48(15):2939-2951.]
张利,赖家业,杨振德,刘世贵. 2001. 八种草坪植物耐荫性的研究[J]. 四川大学学报(自然科学版),38(4):584-588. [Zhang L,Lai J Y,Yang Z D,Liu S G. 2001. Study on shade-tolerance characteristics of eight lawn plants[J]. Journal of Sichuan University(Natural Science Edition),38(4):584-588.]
张旺锋,勾玲,王振林,李少昆,余松烈,曹连莆. 2003. 氮肥对新疆高产棉花叶片叶绿素荧光动力学参数的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,36(8):893-898. [Zhang W F,Gou L,Wang Z L,Li S K,Yu S L,Cao L P. 2003. Effect of nitrogen on chlorophyll fluorescence of leaves of high-yielding cotton in Xinjiang[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,36(8):893-898.]
張志良,瞿伟菁. 2003. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 第3版. 北京:高等教育出版社:23-25. [Zhang Z L,Qu W J. 2003. Experimental guidance of plant physiology[M]. The 3rd Edition. Beijing:Higher Education Press:23-25.]
周棱波,汪灿,张国兵,徐燕,白俊霞,吴兰英,罗海,邵明波. 2016. 硫酸钾复合肥和种植密度对薏苡光合特性、农艺性状及产量的影响[J]. 作物杂志,(1):93-97. [Zhou L B,Wang C,Zhang G B,Xu Y,Bai J X,??Wu L Y,Luo H,Shao M B. 2016. Effects of potassium sulphate compound fertilizer and planting density on photosynthetic characteristics,agronomic traits and yield in Coix lacryma-jobi L.[J]. Crops,(1):93-97.]
周志强,彭英丽,孙铭隆,张玉红,刘彤. 2015. 不同氮素水平对濒危植物黄檗幼苗光合荧光特性的影响[J]. 北京林业大学学报,37(12):17-23. [Zhou Z Q,Peng Y L,Sun M L,Zhang Y H,Liu T. 2015. Effects of nitrogen levels on photosynthetic and fluorescence characteristics in seedlings of endangered plant Phellodendron amurense[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,37(12):17-23.]
朱荣,慕宇,康建宏,赵晶晶,吴宏亮. 2017. 不同施氮量对花后高温春小麦叶绿素含量及荧光特性的影响[J]. 南方农业学报,48(4):609-615. [Zhu R,Mu Y,Kang J H,Zhao J J,Wu H L. 2017. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on chlorophyll content and fluorescence characteristics of spring wheat under high temperature after anthesis[J]. Journal of Southern Agricultural Sciences,48??(4):609-615.]
Huang Z A,Jiang D A,Yang Y,Sun J W,Jin S H. 2004. Effects of nitrogen deficiency on gas exchange,chlorophyll fluorescence,and antioxidant enzymes in leaves of rice plants[J]. Photosynthetica,42(3):357-364.
Kitajima K,Hogan K P. 2010. Increases of chlorophyll a/b ratios during acclimation of tropical woody seedlings to nitrogen limitation and high light[J]. Plant,Cell & Environment,26(6):857-865.
(责任编辑 王 晖)
收稿日期:2019-12-06
基金项目:安徽省重点研究和开发计划项目(1804a07020114);安徽省科技重大专项(18030701181)
作者简介:*为通讯作者:朱加保(1976-),高级农艺师,主要从事特色经济作物及有害生物综合治理研究工作,E-mail:413380941@qq.com;闫晓明(1963-),研究员,主要从事农业生态环境及农产品质量安全研究工作,E-mail:5825116525@qq.com。王红娟(1987-),主要从事经济作物生物学和营养学研究工作,E-mail:whj14725@163.com
