Bottom dross defect and its transformation behavior during the galvannealing process
2020-10-13,,
, ,
1)Research Institute,Baoshan Iron & Steel Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai 201999,China;2) State Key Laboratory of Development and Application Technology of Automotive Steels (Baosteel),Shanghai 201999,China;3) Baosteel-NSC Automotive Steel Sheets Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai 200941,China
Abstract: Bottom dross obtained from zinc bath and the typical bottom dross defects on galvanized and galvannealed coating were metallographically investigated.Galvannealing simulations with different holding time were conducted,and the bottom dross transformation behavior during the galvannealing process was revealed.The fast diffusion between bottom dross particles and the surrounding zinc occurs during the galvannealing process,resulting in the formation of an Al-containing Zn-Fe intermetallic outburst structure at the defect position.The thicker and harder coating will cause a shiny spot on the coating surface and a deep dent on the substrate after being temper rolled.
Key words: hot-dip galvanizing; bottom dross; galvannealing
1 Introduction
Dross is a popular surface defect on hot-dip galvanized (GI) and galvannealed (GA) steel sheets.As the dross defects cause pimple defects easily on the surface of stamped parts,they ruin the appearance of the painting.Therefore,dross defect is among the unacceptable defects on GI- and GA-exposed panels.
Dross comprises Fe,Al,and Zn.Iron is mainly obtained from the residual iron chippings on steel sheet surfaces,dissolved iron from the steel strips,or immersion rollers.Based on its composition,dross can be divided into two categories,top and bottom dross[1].In addition to the oxides of Zn and Al,the top dross is a ternary intermetallic compound of Fe2Al5Znxor Fe2Al5-xZnx(η phase).Owing to its higher Al content,the density of the top dross is lower than that of the zinc bath;therefore,it floats on the surface of the zinc bath.Bottom dross is an intermetallic compound of Fe and Zn and may contain FeZn7(δ1phase),FeZn10Alx(δ phase),and FeZn13(ζ phase)[2].Due to its higher Fe content,the density of the bottom dross is larger than that of a zinc bath and therefore is usually deposited at the bottom of a zinc pot.However,the bottom dross can easily be stirred up by a rotating sink roll in the zinc bath,resulting in the bottom dross defect on the coated steel sheet.The composition of the top and bottom dross is shown in Table 1[3- 4].
The aluminum level in the zinc bath affects the type of dross.When the effective Al is greater than 0.14%,the stable dross particles are that of top dross.When the effective Al is below 0.14%,the stable dross particles are that of bottom dross.Therefore,the bottom dross can build up during the production of galvannealed coating[1].The key element in minimizing bottom dross generation is the stability of the bath with respect to both the temperature and aluminum content.A sudden drop in temperature can cause the formation of bottom dross,and a sudden increase in the aluminum content can generate excess top dross[1].Upon continuous galvanizing lines (CGL),which pro-duce both GI and GA sheets,the bath stability will be disturbed during product transition.Gradually increasing the Al content during the transition process from GA to GI would transform some of the bottom dross into top dross,and the reaction is shown as follows:
2FeZn10+5Al→Fe2Al5Znx+(20-x)Zn
(1)
Dross defects on GI and GA steel sheets appear as dark or shiny spots;it is difficult to distinguish whether they are top or bottom dross particles through macroscopic characteristics.The dross defect on GI coating can be identified through Al,Fe,and Zn contents in the defect location.How-ever,in the case of the dross defect on GA coating,only the top dross can be easily identified through the Al content;the bottom dross is difficult to be determined owing to the proximity of the Fe content to the surrounding galvannealed coating.
Furthermore,the existing literature focuses on the formation mechanism and control of dross in the zinc pot[5-7].However,the transformation behavior of bottom dross particles in the coating during the galvannealing process after the strip moves out of the zinc bath and its effect on the surrounding coating are still unclear.The main purpose of this study is to comprehensively study the bottom dross in a zinc bath on the industrially produced GI and GA coatings and laboratory-galvannealed coatings with different alloy contents.This study establishes the transformation behavior of bottom dross during the galvannealing process.
2 Materials and experimental procedures
There is no secret to why our marriage has lasted while so many others have failed. There is no formula for success that I can offer, other than to express at the most important feature of our relationship is that it has never lost the sense of romance3 that bloomed when we first met. Too often marriage kills the romance that was born in the courtship of a relationship. To me, I have always felt that I am still courting Patricia, and therefore the romance has never died.

Table 2 Sample list
Samples with a dimension of 120 mm×220 mm were cut from sample 3 and alcohol was used to clean the sample surface before it was reheated.Galvannealing simulation was conducted on the Iwatani hot-dip galvanizing simulation equipment.After the bottom dross defects were circled by a mark pen,samples were heated to 540 ℃ with a heating rate of 4 K/s and held for different periods to obtain different iron contents in the coating.Sample 4,which was under-galvannealed,was held for 1 min,and sample 5,which was over-galvan-nealed,was held for 3 min.
The cross section of sample 1 was prepared and examined using a Zeiss scanning electron micro-scope (SEM) coupled with energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS).Cross sections were prepared and detailed examinations were made for samples 2-5,including coating surface morphology,substrate surface morphology after the zinc coating was removed by 10%HCl solution containing methena-mine as an inhibitor.A Veeco surface profilometer was used to examine the surface profile.Note that the same bottom dross defect could not be simultaneously used to prepare the substrate surface and the cross section of the coating;therefore,the sample numbers shown in Table 2 included multiple samples of the same type.
3 Results
3.1 Bottom dross in the zinc bath
After the zinc coating was removed using a 10%HCl solution with an added inhibitor,a dent on the substrate was observed.The 3D surface profile shown in Fig.4(c) illustrates that the depth of the dent was 20-30 μm.As shown by the arrow in Fig.4(d),indentations caused by polygonal hard particles were observed at the bottom of the dent.Such a characteristic can be used as evidence to determine that the origination of the dent was the pressed-in bottom dross.
The as-received bottom dross defect on the GA coating appears as small shiny spots,the diameters of which are generally less than 1 mm.The 3D surface profile shown in Fig.4(a) illustrates that the surface of the spot was 4-6 μm higher than that of the surrounding normal coating.The surface morphology in Fig.4(b) shows that the surface of the defect spot was much smoother than that of the normal coating.The typical ξ and δ phases on the surface of normal GA coating were not observed at the defect spot.
The mound then opened, and his youngest daughter came out of it, and said, Why, father! why are you not coming in to see me? Oh, said he, if I had known that you lived here, and had seen any entrance, I would have come in
3.2 Bottom dross defect on the GA coating
Forty fields of view with a magnification of 50× were selected to perform the quantitative metallo-graphic analysis of bottom dross particles.The area percentage of the bottom dross particles on the cross section was 50%-60%.The distribution of the equivalent diameter of the particles is shown in Fig.3.The maximum equivalent diameter was approximately 800 μm,and the equivalent diameter of most of the bottom dross particles was between 0 and 300 μm.
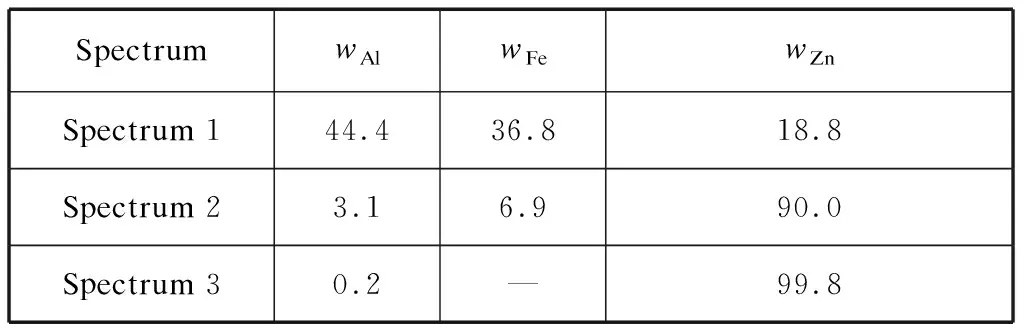
Table 3 EDS results of the as-received bottom dross %
The SEM morphology and energy spectrum analysis results of the as-received bottom dross taken from the bottom of the zinc pot are shown in Fig.2 and Table 3.The shapes of the bottom dross particles were irregular polygons,and the energy spectrum showed that the approximate composition (mass percentage) was Zn-7%Fe-3%Al,which was very close to FeZn10Alxreported by McDermid[3].At higher magnifications,some small top-dross particles were observed to be embedded in some large bottom dross particles.The energy spectrum of these top-dross particles showed that the approximate composition (mass percentage) was 44%Al-37%Fe-19%Zn,which was close to Fe2Al5Znxreported by McDermid[3].
The cross-sectional morphology is shown in Fig.5.Corresponding to the results shown in Fig.4,a slightly higher exposed coating surface and a relatively deeper dent in the substrate were observed.The maximum coating thickness at the bottom dross defect was ap-proximately 55 μm,which is much thicker than that of the surrounding coating.The maximum depth of the dent on the substrate was approximately 45 μm.The EDS results listed in Table 4 reveal that the coating at the defect position contained 2%-4% of Al in addi-tion to Zn and Fe.The Al content was higher than that of the coating at the normal position,which was close to FeZn10Alxpresented in Reference [3] and was also close to the composition of the as-received bottom dross obtained from the zinc pot.A small number of top-dross particles were observed locally,as marked by symbol+1 in Fig.5(b),and the EDS results are listed in Table 4.It is necessary to note that except for the small top-dross particles in Fig.5(b),the other areas exhibited a constant morphology.Therefore,it is dif-ficult to distinguish whether the defect area was bottom dross or normal zinc coating.This should be an intermetallic phase formed through the diffusion reaction of the bottom dross and zinc coating.
3.3 Bottom dross defect on GI coating
The characteristics of the bottom dross defect on the GI coating are shown in Fig.6.Similar to the characteristics of the bottom dross defect on the GA coating,the spot was approximately 5-7 μm higher than that of the surrounding coating.With higher magnifications,slight scratches and minor amounts of contamination were observed on the defect surface.Therefore,it appeared as a small dark spot on the GI coating.By controlling the zinc dissolving time,substrates with and without residual bottom dross were obtained.As shown by the surface profile of the residual bottom dross in Fig.6(c),the height of the bottom dross was close to that of the surrounding substrate,indicating that it was pressed onto the substrate in the zinc bath.Around the bottom dross,a narrow ring-shaped dent with a maximum depth of 20-30 μm was observed.Based on the morphology shown in Fig.6(d),there was still some residual zinc around the bottom dross.When the bottom dross was completely removed using an HCl solution,a dent with a maximum depth of 60-70 μm was observed on the substrate.
The enlargement of the bottom dross on the substrate and the cross section of the bottom dross defect are shown in Fig.7.The EDS results for the particles marked by symbols +1,+2,and +3 are shown in Table 5.Elemental mappings of the cross section are shown in Fig.8.The residual dross contained both bottom and top dross,among which the bottom dross had a larger volume fraction.From the cross section in Fig.7(b),the thickness of the defect was 40-50 μm,which was much thicker than that of the normal coating.Also,the bottom dross was adjacent to the substrate,and the top dross,which was above the bottom dross,was much adjacent to the coating surface.Owing to the higher Al content in the top dross,it appeared dark in the backscattered electron image.However,the contrast of the bottom dross was remarkably close to the GI coating.The bottom dross having a polygon shape contained many cracks,indicating that the bottom dross was more brittle than the GI coating.
3.4 Simulated bottom dross defect
The surface profile comparison of the same bottom dross defect before and after galvannealing simulation is shown in Fig.9.As the strip was skin-passed in CGL,any raised spot was flattened through the skin-pass roll.Therefore,the height difference between the defect spot and the surrounding coating was small,which was only 5-7 μm higher.However,a deeper dent (as shown in Fig.6) was formed on the substrate.After it was reheated to 540 ℃ and held for 1 min,an obvious pimple was formed at the bottom dross defect position.The maximum height difference reached 40-50 μm.As shown in Fig.9(c),both the heights at the positions of 0.75 mm and 2.0 mm along the length direction were lower than the other positions and were also lower than the original height of the as-received bottom dross defect on the GI coating.Metal movement from the edge to the center of the bottom dross defect probably occurred during the galvannealing process.
However, the money he obtained in this way enabled him to buy the Queen her flock of sheep, as well as many of the other things which go to make life pleasant, so that they never once regretted their lost kingdom
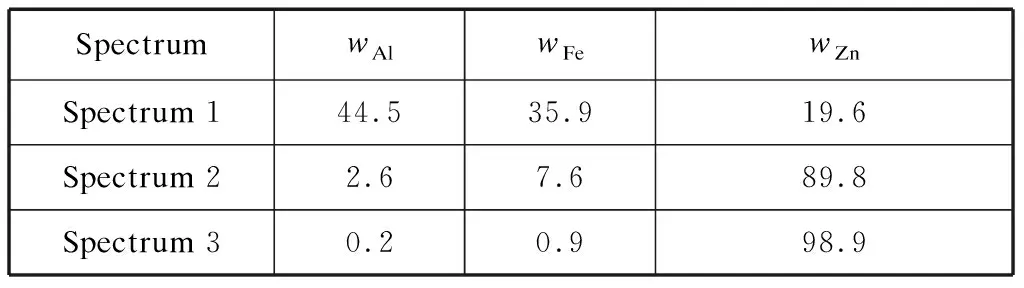
Table 5 EDS results of the bottom dross defect on the GI coating%
The cross section of the simulated under-galvannealed dross defect is shown in Fig.10.It further confirmed the results of the surface profile measurement in Fig.9.The maximum thickness at the center of the dross defect was close to 80 μm.A higher surface of the coating and a deeper dent in the substrate were observed.It indicated that an outburst reaction would occur at the defect position during the galvannealing process.The existence of bottom dross promoted the diffusion between Zn and Fe.The maximum depth of the dent was approximately 30 μm.If the sample was skin-passed like the indus-trial GA coating,the pimple would be flattened,and a deeper dent would be formed on the substrate.
But when they heard that she had only come to be with them for a short time, and then must go back to the Beast s palace for ever, they lamented loudly
The enlargement of the squared area in Fig.10(a) is shown in Fig.10(b).The EDS results for different points as marked by symbols from +1 to +3 are listed in Table 6.Three phases with different com-position were observed.The dark particles adjacent to the coating surface were identified as top dross containing a large amount of Al and Fe.The second phase,which exhibited the largest volume fraction,contained approximately 10%Fe,2%Al,and balanced zinc.The morphology and composition were still the same as those of the bottom dross.The third one contained much lower Fe and Al;it was the residual pure-zinc phase with insufficient zinc-iron diffusion.
The boy made one of those hand signs at me as I was about to leave. I asked his sister if your brother is so smart then why is he doing things like that with his hands? She told me that he was saying that he loved me with his hands. I didn t say anything back to her at all because I didn t believe her. People can t talk with their hands and everybody knows that. People can only talk with their mouth.

Table 6 EDS results of the marked points in Fig.10 %
In the first hot-dip galvanizing step,when a piece of bottom dross is brought to the strip,a spot defect will be formed on the GI-coated steel strip.It comprises a large number of bottom dross particles,a small number of top dross particles,and zinc liquid.When a hard polygon bottom dross particle is pressed onto the strip as it contacts with the sink rolls,an indentation with a similar polygon shape will be printed on the substrate.The pressed-in bottom dross may prevent the formation of an inhibition layer at the coating/substrate interface.The existence of bottom dross may also influence the coating weight control when it passes through the air knife,resulting in several times thicker coating at the bottom defect position.As a result,pimple spots on the coating with corresponding dents on the substrate have been formed before the steel strip is galvannealed.
From the cross section shown in Fig.11(c),the normal coating exhibited a layered structure.It comprised δ,Γ1,and Γ phases from the top surface to the substrate.The EDS results of spectra 5-7 revealed that the Al content in the Γ1phase was slightly higher than that in δ and Γ phases.Such a difference was probably caused by the initial inhibition layer at the interface of the coating and substrate on the as-received sample.As it was obtained from the transition process from GA to GI,Al content in the bath was slightly higher than the normal Al content in the GA bath.Therefore,higher Al content in Γ1phase was from the Fe2Al5inhibition layer.Al content in the Γ1phase in Fig.11(a) (spectrum 4) was lower than that in the Γ1phase in Fig.11(c) (spectrum 6),which could be attributed to the missing inhibition layer at the position,wherein the pressed-in bottom dross prevented the reaction between Al in the bath and Fe dissolved from the substrate.It may further promote the diffusion of Zn and Fe in the defect location during the alloying process and accelerate the formation of the outburst structure.
What! said the woman, I am the King, and you are nothing but my husband; will you go this moment? go at once! If he can make a King he can make an emperor. I will be Emperor; go instantly. So he was forced to go. As the man went, however, he was troubled in mind, and thought to himself, It will not end well; it will not end well! Emperor is too shameless! The Flounder will at last be tired out.
Al content in the δ phase in Fig.11(a) (spec-trum 3) was higher than that in Fig.11(c) (spectrum 5).Such a difference indicated that the δ phase in the defect position was mainly the product formed through the diffusion between zinc and bottom dross particles.As the enlargement is shown in Fig.11(b),another change was observed at the edge of the top-dross particle.The Al content at the edge (spectrum 2) was lower than that at the center (spectrum 1),implying that the diffusion between the top-dross particle and the adjacent bottom dross or zinc also occurred during the galvannealing pro-cess.It could be the second source of the increased Al content in the δ phase.
The samples used in this study are listed in Table 2 and their macroscopic appearances are shown in Fig.1.The as-received samples were collected from the No.2 CGL in Baosteel.Sample 1 was the bottom dross obtained from the bottom of the zinc pot during the production of GA coating.Sample 2 was a common bottom dross defect on the GA coating.Sample 3 was a bottom dross defect on the GI coating,which was produced in the transition process from GA to GI.
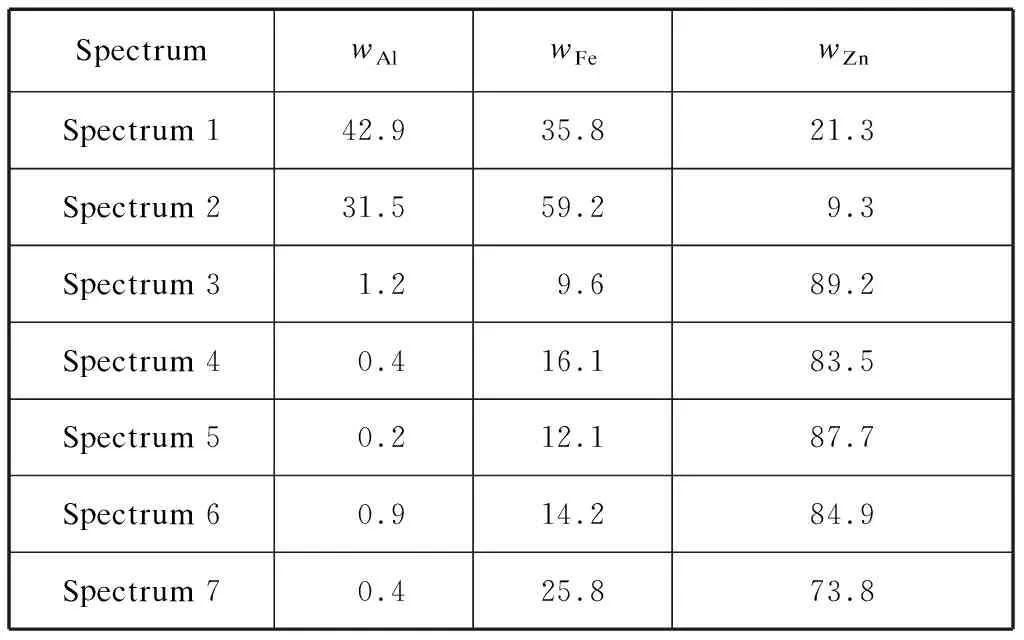
Table 7 EDS results of the marked points in Fig.11 %
4 Discussion
Based on the metallographic investigation on bottom dross defects in different stages,their transformation behavior during the galvannealing process is revealed.A schematic of the transfor-mation of bottom dross defect from GI to GA is shown in Fig.12.
The bottom dross in the zinc bath mainly comprises Fe and Zn,and it also contains 2%-3%Al.They have irregular polygon shapes,and most of their equivalent diameters are between 0 and 300 μm.These bottom dross particles tend to gather to form a cluster of bottom dross.Some small-size top-dross particles that contain much higher Al and Fe are embedded in some bottom dross particles.A GA zinc bath in which Al is lower than 0.14% is favorable for cluster formation.It may cause bottom dross defects when the operation is inappropriate.
When the holding time was increased from 1 min to 3 min,an over-galvannealed sample was pre-pared.Here,the diffusion between Fe and Zn was completely sufficient.The cross section of the over-galvannealed bottom dross defect is shown in Fig.11,and the EDS results for different points marked by the symbols from +1 to +7 are listed in Table 7.Some top-dross particles were still located at the coating surface.The main part of the coating at the defect position contained approximately 10%Fe,1%Al,and balanced zinc.Except for two vertical cracks,no small cracks were observed.Moreover,no polygonal bottom dross particles were found.A layer of Γ1phase existed at the interface of the coating and substrate.It contained higher Fe content and lower Al content when being compared with the main part of the coating.
In the second galvannealing step,the coated steel strip moves into the galvannealing furnace and is soaked for several tens of seconds to finish the diffusion reaction between Zn and Fe.At the normal position,a layered coating structure having different Zn-Fe intermetallic phases is formed.Depending on the soaking temperature and period,one or two phases among ξ,Γ1,and Γ will also be found in addition to the δ phase.At the bottom dross defect position,the main diffusion reaction occurs between the bottom dross particles and the surrounding zinc.As the Al content in the bottom dross is higher than that in the normal coating,an Al-containing Zn-Fe inter-metallic phase is formed.Also,the higher diffusion rate between bottom dross and zinc results in the formation of an outburst structure,which further increases the coating thickness at the defect position.The zinc around the bottom dross supplies the zinc needed for the outburst structure formation.Therefore,the GA coating around the bottom dross defect is thinner than the normal coating.
During the galvannealing process,the diffusion between top dross particles and adjacent phases including bottom dross particles,zinc,or Zn-Fe intermetallic phases also occurs.Unlike the bottom dross,the top dross particles remain unchanged,and only a small amount of diffusion occurs at the edge of top dross particles when the soaking period is sufficiently long.
When the strip is skin-passed,the bottom dross defect is flattened,and it appears as a shiny spot.As it is still slightly higher than the surrounding coating,it can also be detected when the surface is polished using oil stone.Owing to its higher coating thickness and higher hardness,such a bottom dross defect will lead to pimple defects on the opposite side when the steel sheet is stamped.It will affect the surface quality of the panel;therefore,it is necessary to prevent the bottom dross in the zinc bath from being brought in the steel strip.To con-trol the bottom dross defect,some key points should be considered,including the stability of the bath temperature,the control of the strip entry temperature,the Al content in the zinc bath,and the cleanness of the strip steel.
When the hour for departure drew near the old mother went to her bedroom, and taking a small knife she cut her fingers till they bled;11 then she held a white rag12 under them, and letting three drops of blood13 fall into it, she gave it to her daughter, and said: Dear child, take great care of this rag: it may be of use to you on the journey. 14
5 Conclusions
Bottom dross in a zinc bath and bottom dross defects on GI and GA coatings were metallo-graphically investigated.Galvannealing simulations with different holding time were performed,and the bottom dross transformation behavior during the galvannealing process was revealed.The following conclusions can be drawn:
Together they formed Hands Across America- It Starts with You -an organization that encourages the public to learn sign language and has started making educational videos that use both deaf and hearing children together.
(1) A fast diffusion between bottom dross particles and the surrounding zinc occurs during the galvannealing process,resulting in the formation of an Al-containing Zn-Fe intermetallic outburst structure.
One day, after about two weeks, Harry and I were talking and I told him about my theory. If you ll just wait long enough, I said, you ll see her coming up those stairs some day. He turned and looked at the stairs as though he had never seen them before.,,,。“,”,“,。”,。
(2) Bottom dross defects on GA coating that appear as shiny spots have a thicker and harder coating and corresponding dents on the substrate.
(3) The coating morphology of the bottom dross defect shows a slight difference from that of the normal GA coating in the cross-sectional view.It can be distinguished by the Al content difference in the coatings.
(4) Some top dross particles remain in the defect and a diffusion reaction between top dross and the surrounding Zn-Fe intermetallic phase occurs when the galvannealing period is increased.
杂志排行
Baosteel Technical Research的其它文章
- Influence of sulfur on inclusion and pitting resistance of 316L stainless steel
- Mechanical and corrosion properties of N08825 CRA clad pipeline steel
- Research on material design and high-temperature friction and wear properties of new graphitic steel
- Theoretical study on the torque values of premium connections
- Causes of the formation of pit defects on the surface of the enamel layer
