Meta-analysis on clinical efficacy of Simiao Yong'an decoction in treatment of peripheral arterial occlusive diseases
2020-10-10JinPengJingYueZhangYiLiuZhiXinCheng
Jin-Peng Jing, Yue Zhang, Yi Liu, Zhi-Xin Cheng
1. Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Med,Jinan,250014,China
2. Affiliated hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Med, Jinan,250014,China
Keywords:Simiao Yong'an decoction Peripheral arterial occlusive disease Meta analysis
ABSTRACT Objective: To systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Simiao Yong'an Decoction in the treatment of peripheral occlusive disease(PAOD). Methods: Eight randomized controlled clinical trials(RCT) of Simiao Yong'an Decoction in the treatment of PAOD were searched and screened from domestic and foreign databases (all from database construction to March 2020).The quality of the retrieved original studies was evaluated according to the evaluation criteria of Cochrane Handbook 5.1.0,and the included studies were meta-analyzed by RevMan5.3 software. Results: A total of 350 articles were retrieved,among which 14 studies met the inclusion criteria,with a total sample size of 1254 cases. The results of meta-analysis showed that:compared with conventional western Med,combined with Simiao Yong'an Decoction on the basis of western Med treatment can significantly improve the total clinical response rate of patients[RR=1.20,95%CI (1.14,1.27),P<0.00001],improve ankle brachial index(ABI) level[MD=0.79,95%CI (0.66,0.92),P<0.00001] and toe brachial index(TBI) level[RR=0.13,95%CI(0.10,0.16), P<0.00001],decreased c-reactive protein levels[MD=-8.55,95%CI(-8.99,-8.11),P< 0.00001] and LDL levels [MD=-0.41,95%CI(-0.62, -0.19),P=0.0002],and increased HDL levels[MD=0.32(0.22,0.43),P<0.00001].There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of adverse reactions[RR=0.50]95%CI(1.15,1.64),P=0.25]. Conclusion: Simiao Yong'an Decoction combined with conventional western Med is more effective than conventional western Med in the treatment of PAOD.However,in view of the limitations of the quality of the analyzed literature,the positive results obtained in this study still need to be further verified by a large sample and multi-center clinical trial with a reliable research program.
1. Introduction
Peripheral occlusive disease(PAOD) refers to a group of diseases with limb ischemia as the common manifestation except aorta,coronary artery and cerebral artery[1],most of the lesions are in the lower limb arteries.Mainly includes the occlusive arterial sclerosis(ASO),thromboangiitis obliterans(TAO) and diabetic limb arterial occlusion(DAO).In recent years,the incidence of PAOD has been significantly increasing,the incidence of arterial occlusive diseases of the lower extremities alone has reached 30% worldwide[2,3].The risk of cardiovascular death in PAOD patients is 3 times that of non-paod patients[4].It is characterized by difficult treatment,long course of disease,and high disability and mortality,the quality of life of patients was severely reduced[5,6].China is currently facing the serious challenge of an aging society, and it is predictable that the number of PAOD patients will increase, bringing a huge burden to the social economy of China.
Although there is no record of the disease name of PAOD in ancient Chinese Med books,according to its manifestations, it can be classified into the categories of "vessel bi-disease" and "gangrene"[7].Although the pathogenesis and pathological changes of ASO,TAO and DAO are different, the total pathogenesis of TCM can be summarized as the deficiency in origin and excess in superficiality[8,9].There are similarities in clinical manifestations,especially in the development of extremity gangrene,the local manifestations of "heat,toxic and blood stasis" as the main pathogenesis,at this time,the syndrome differentiation for toxic heat flourishing and blood stasis resistance.Simiao Yong'an Decoction as the treatment of toxic heat flourishing of degangrene classic prescription,its heat-clearing and detoxifying, invigorating blood circulation and analgesia effect on this pathogenesis.In recent years,although there have been a number of randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTS) which have proved that Simiao Yong'an Decoction can effectively treat PAOD,but due to the small sample size of RCT,different effect scales and lack of systematic evaluation related to its efficacy and safety,there is no conclusive conclusion yet.Therefore,the purpose of this study is to systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Simiao Yong'an Decoction in the treatment of PAOD,so as to provide a useful reference for the clinic.
2. Research data and methods
2.1 Inclusion criteria
2.1.1 Research types
In the RCT literature on the treatment of PAOD with Simiao Yong'an Decoction, the words "random" or "random control" or "random assignment" can be found in the literature,regardless of whether blind method is used or not,and the language is not limited.
2.1.2 Research object
Patients clearly diagnosed with PAOD(TAO,DAO,ASO),whether or not specific diagnostic criteria are explicitly mentioned.The patient's condition and the type of TCM syndrome differentiation are not limited,and the patient's age,region, occupation and ethnic group are not limited.
2.1.3 Intervention
The control group was treated with conventional western Med, and the treatment group was taken orally in combination with Simiao Yong'an Decoction on the basis of the control group.The specific types of western Med are not limited; Treatment course, drug source, dose and dosage form were not restricted in both groups.
2.1.4 Final indicator
The included study must include clinical total efficiency or the ankle brachial index(ABI),secondary outcome indicators included toe brachial index(TBI),c-reactive protein(CRP),low density lipoprotein (LDL),high density lipoprotein(HDL) and the adverse reaction rate.
2.2 Exclusion criteria
2.2.1 The data is unknown, and the author cannot be contacted to obtain the literature;
2.2.2 Review, experience summary, case reports, animal experiments and other non-clinical research literature;
2.2.3 The experimental group was the literature of Simiao Yong'an Decoction combined with other traditional Chinese Med measures;
2.2.4 Literature with obvious errors;
2.2.5 Outcome indicators are not consistent with the literature.
2.3 Literature retrieval
Computer retrieval of CNKI,VIP,wanfang data knowledge service platform,CBM, PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science.Chinese database search terms include Simiao Yong'an Decoction,arteriosclerosis obliterans,thromboangiitis obliterans,diabetic limb arterial obliterans, lower limb artery occlusion, arteriosclerosis of the lower limbs,peripheral o c c l u s i v e d i s e a s e,v e s s e l b i-d i s e a s e, g a n g r e n e, ASO,DLASO,TAO,DAO,LEAD,PAD,PAOD.According to the characteristics of different databases,English database search words are searched by combining MeSH or Emtree subject words with free words.Search words are peripheral occlusive artery diseases,arteriosclerosis obliterans,obliterans, arteriosclerosis,T hromboangiitis obliterans,Buerger 's diseases,Buergers diseases, Thromboangitis obliterans,Simiao Yong'an Decoction,Simiao Yongan Decoction,Si- Miao-Yong-An,etc.The retrieval time of each database is from creation to March 2020. Manual retrieval "Chinese Journal of Integrative Med","Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Med","Chinese Journal of Surgery of Integrated Traditional and Western Med" and other related journals.In addition, relevant conference papers,academic papers,included references and other gray documents have been searched in the above database.Taking PubMed as an example, the retrieval strategy is as follows:#1peripheral occlusive artery disease, #2arteriosclerosis obliterans[Mesh],#3obliterans or arteriosclerosis,#4#2 or #3, #5#1 or #4,#6thromboangiitis obliterans[Mesh],#7Buerger's Disease or Buergers Disease or Thromboangitis Obliterans or Buerger Disease or Disease Buerger's or Disease Buerger,#8#6 or #7,#9#5 or #8,#10 Simiao Yong'an Decoction or Simiao Yongan Decoction or Si-Miao-Yong-An,#11#9 and #10.
2.4 Literature screening and data extraction
Two researchers independently screened literatures based on inclusion and exclusion criteria and extracted relevant data.If there is any objection,the third researcher shall assist to solve it.The final indicator included the first author,sample size,random methods, intervention measures,treatment cycle,outcome indicators,etc.
2.5 Quality evaluation of literature
Using the "risk of bias assessment" in Cochrane evaluation manual Handbook5.1.0 to evaluate,it mainly includes the following 7 aspects:①random sequence generation(selection bias);②allocation concealment(selection bias);③blinding of participants and personnel(implementation bias);④blinding of outcome assessment(detection bias);⑤incomplete outcome data(attrition bias);⑥selective reporting(reporting bias);⑦other bias.According to the evaluation criteria,three quality outcomes of "low risk of bias","high risk of bias" and "uncertain risk of bias" were judged.All the above mentioned literatures were evaluated independently by 2 researchers.If there was any objection,the third researcher would help to solve it.
2.6 Statistical analysis
RevMan5.3 software was used for statistical analysis of the data.Relative risk (RR) and 95%confidence intervals(95%CI) were used to represent the dichotomous variables.Mean difference(MD) and 95%CI were used for continuous variables.For the included studies,I2was used for heterogeneity test.When the heterogeneity test results were small(P>0.10,I2≤50%),the fixed effect model was used for Meta analysis.If there is a large statistical heterogeneity(P<0.10,I2>50%),the random effect model is adopted,and subgroup analysis,sensitivity analysis or meta regression were performed according to the possible heterogeneity factors to minimize heterogeneity. If the heterogeneity is too large or the data source cannot be found, the meta-analysis is abandoned and only the qualitative analysis is performed.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.If the final indicator of a certain outcome index is ≥10, funnel plot is used to analyze whether there is publication bias.
3. Results
3.1 Literature retrieval and screening results
A total of 350 articles were retrieved from the relevant retrieval database,3 articles were retrieved from the English database,and the rest were all Chinese literatures.After checking the weight of NoteExpress,157 pieces are screened out. According to inclusion and exclusion criteria,167 titles and abstracts were read and screened out.After further reading,12 papers were screened out and 14 papers were finally included.
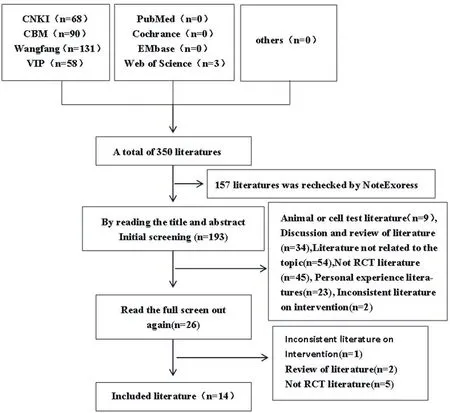
Fig.1 Literature screening process
3.2 Situation of included research
A total of 1254 patients were included, including 627 in the experimental group and 627 in the control group.In the experimental group,the intervention measures were Simiao Yong'an Decoction combined with a specific western Med or applied alone on the basis of conventional treatment.The treatment period varies from 28 to 120 days.The baseline data of each treatment group and the control group were compared,and there was no statistical significance(P<0.05).The specific basic information is shown in table 1.

Table1 Basic information included in the research
3.3 Risk of bias
All the included studies reported baseline level,showing no statistical significance(P>0.05).Blind method,sample size estimation and random allocation concealment were not reported.All patients did not terminate or withdraw from the follow-up in advance.5 references[10,14,20,21,23] adopted the random number table method,while the rest adopted the random method but were not specified.The literature was evaluated using the "risk of bias assessment" in Cochrane Handbook5.1.0.The specific risk assessment of bias is shown in figure 2.
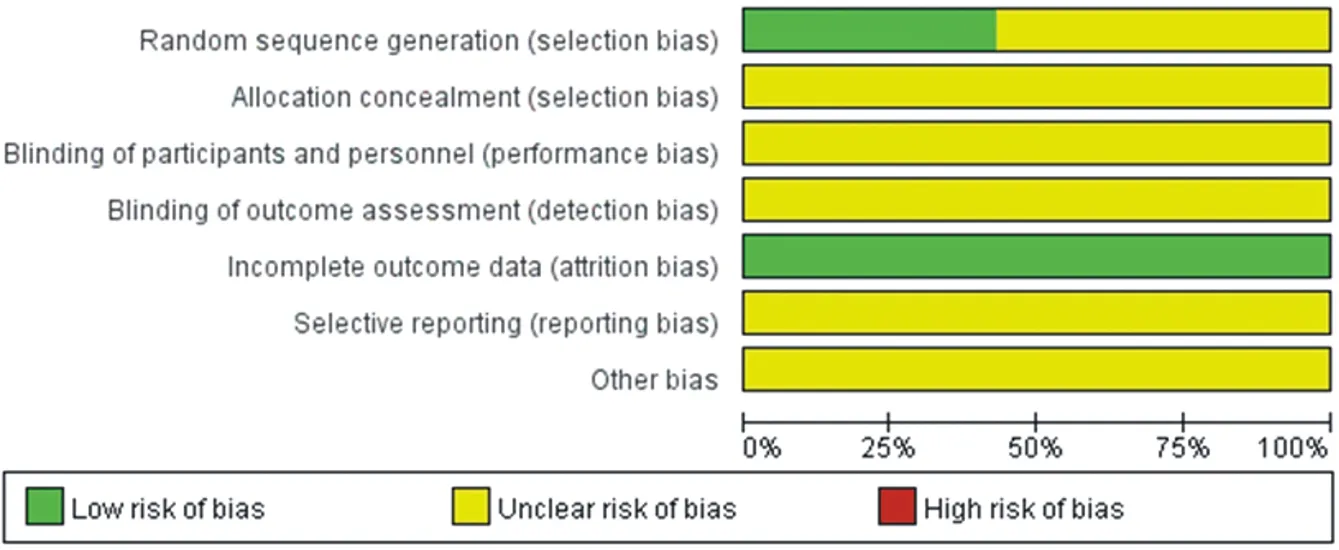
Fig.2 Percentage of projects included in the study that pro- duced a risk of bias
3.4 Meta-analysis
3.4.1 Clinical total efficiency
In the included literature,eleven studies[10.11,12,13,14,16,18,19,20,21,22] reported total clinical efficacy,with a total of 972 patients,486 patients in the experimental group and 486 patients in the control group.Heterogeneity analysis of the included data shows that:P=0.93,I2=0%,it shows that the included literatures have good homogeneity,so the fixed effect model is used for analysis.Metaanalysis showed that compared with conventional western Med,the combination of Simiao Yong'an Decoction could significantly improve the total clinical efficiency of PAOD patients,and the difference was statistically significant [RR=1.20,95%CI (1.14,1.27),Z=6.42(P<0.00001)].As shown in figure 3.
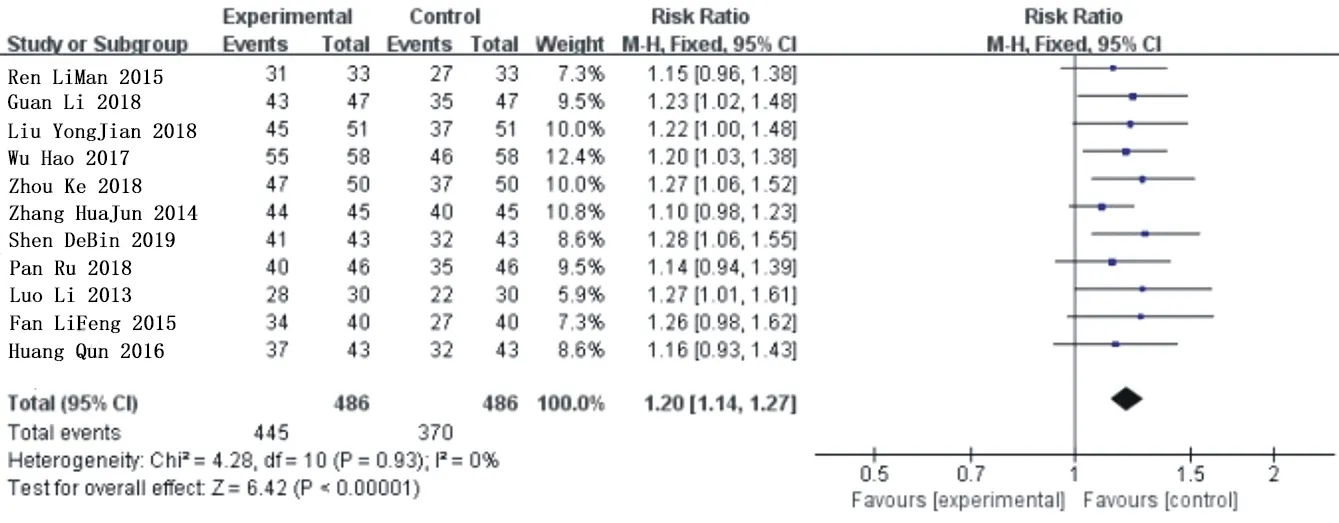
Fig.3 Forest chart of comparison in total clinical response rate
3.4.2 ABI
There are 11 studies[10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,21,23] describes the ABI changes before and after the treatment with a total of 974 patients,and there were 487 cases in the experimental group and control group.Heterogeneity analysis shows:P=0.40,I2=4%.It indicates that the included research has good homogeneity, so the fixed-effect model can be used for analysis.Meta-analysis showed that the combined application of Simiao Yong'an Decoction significantly improved patients' ABI level compared with conventional western Med treatm ent[MD=0.79,95%CI(0.66,0.92),Z=11.87 (P<0.00001)].As shown in figure 4.
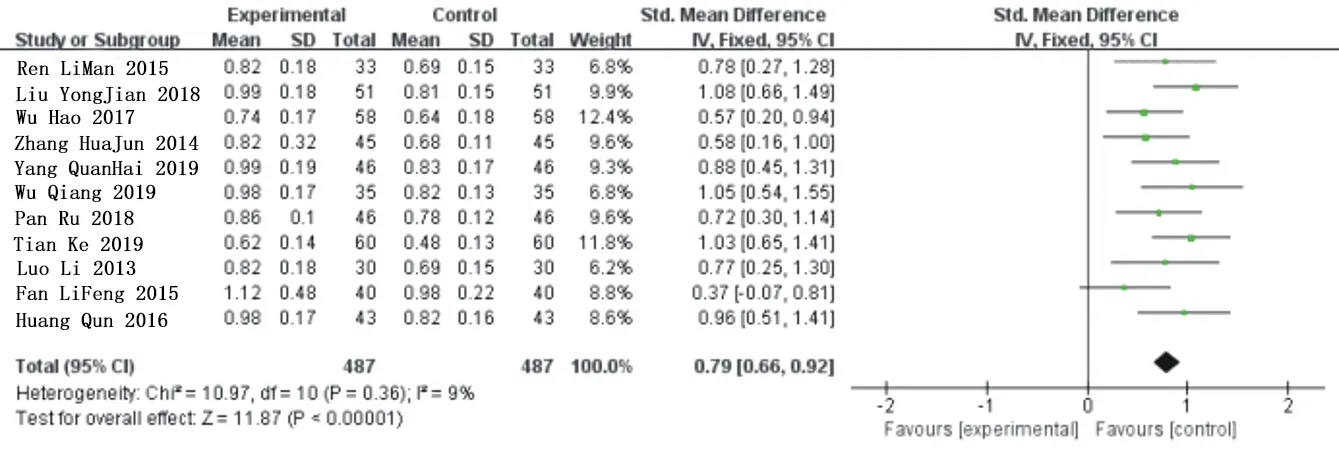
Fig.4 Forest chart of comparison in ABI
3.4.3 TBI
Three studies[14,17,19] reported the improvement of TBI,with a total of 284 patients, including 142 in the experimental group and 142 in the control group.Heterogeneity analysis shows:P=0.61,I2=0%,so the fixed effect model was used for meta-analysis. The results showed that compared with the traditional western Med treatment, the TBI level of patients could be significantly improved with Simiao Yong'an Decoction,and the difference was statistically significant [RR=0.13,95%CI(0.10,-0.16),Z=8.11(P<0.00001)].As shown in figure 5.

Fig.5 Forest chart of comparison in TBI
3.4.4 CRP
There were 3 studies[20,22,23] reported on the changes of patients before and after treatment with CRP, a total of 278 patients, including 139 in the experimental group and the control group.Heterogeneity analysis shows: P=0.05.I2=68%.The heterogeneity was relatively large,and after sensitivity analysis,1 study[22] was removed,the heterogeneity was significantly reduced(P=0.96,I2=0%).The remaining two studies were meta-analyzed by using the random effects model.The results showed that compared with the traditional western Med treatment,the combination of Simiao Yong'an Decoction could significantly reduce the CRP level of patients[MD=-8.55,95%CI(-8.99,-8.11),Z=37.87(P<0.00001)].As shown in figure 6 and figure 7.
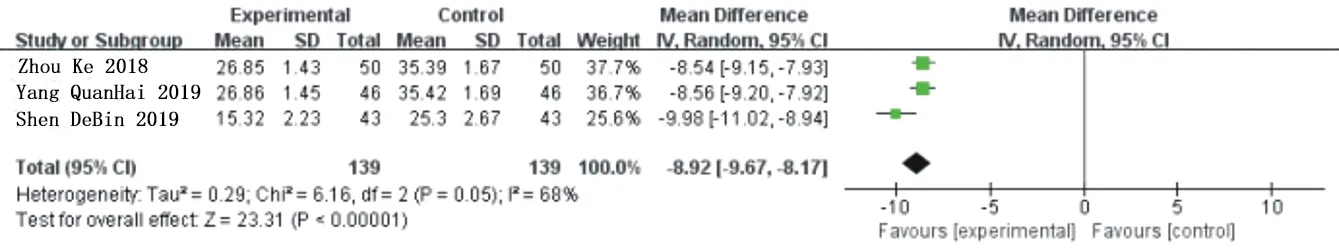
Fig.6 Forest chart of comparison in CRP(1)
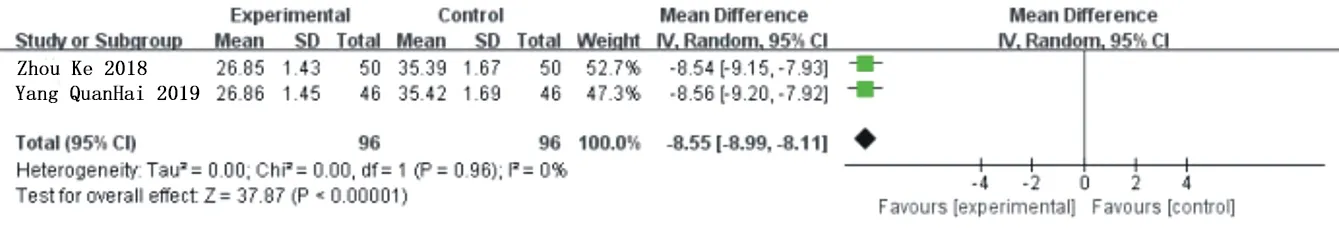
Fig.7 Forest chart of comparison in CRP(2)
3.4.5 LDL
Five studies[11,12,15,17,20] reported improvement of LDL in a total of 484 patients, including 242 patients in the experimental group and the control group.Heterogeneity analysis showed that:P=0.0004,I2=80%.No source of heterogeneity was found by sensitivity analysis,so the random effect model was used for meta-analysis of all studies.The results showed that compared with traditional western Med,Simiao Yong'an Decoction could significantly reduce the level of LDL,and the difference was statistically significant[MD=-0.41,95%CI(-0.62,-0.19),Z=3.75(P=0.0002)].As shown in figure 8.
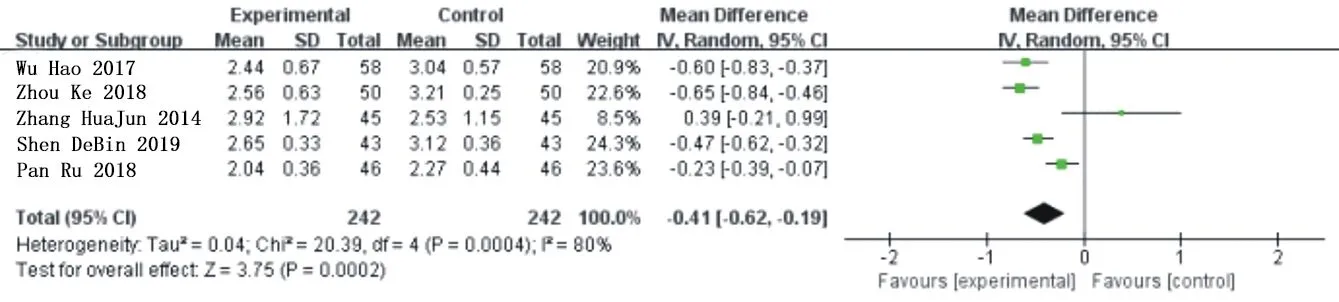
Fig.8 Forest chart of comparison in LDL
3.4.6 HDL
Five studies[11,12,15,17,20] recorded the improvement of HDL before and after treatment,with a total of 484 patients,and 242 patients in the experimental group and the control group.Heterogeneity analysis showed that:P=0.09,I2=51%.It indicates that there is a certain heterogeneity,so the random effect model was used for meta-analysis. The results showed that compared with the conventional western Med treatment, the combination of Simiao Yong'an Decoction could significantly improve the HDL level of the patients,and the difference was statistically significant [MD=-0.33,95%CI(0.22,0.43),Z=6.16(P<0.00001)].As shown in figure 9.
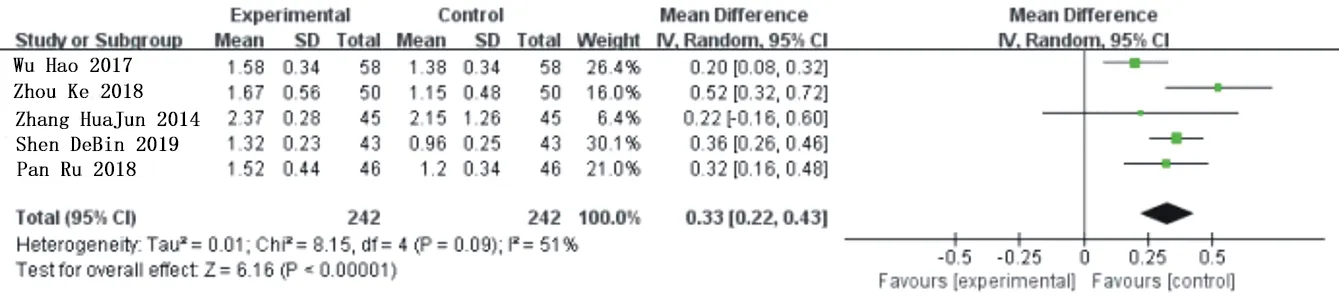
Fig.9 Forest chart of comparison in HDL
3.4.7 adverse reaction rate
Seven articles[11,13,15,18,19,21,23] reported the incidence of adverse reactions after intervention,with a total of 642 patients,including 321 in the experimental group and 321 in the control group.Three studies[11,13,15] reported that no adverse reactions occurred after treatment in the two groups.One study[12] mentioned that one case of abnormal liver function and pne case of abnormal kidney function occurred in the experimental group during the treatment,and the adverse symptoms were relieved in a short time,bue it didn't affect the research.Three studies[18,21,23] mentioned that two patients had symptoms such as nausea or itchy skin in the control group. Heterogeneity analysis showed that:P=0.35,I2=10%,so the fixed effect model was used for meta-analysis.The results showed that there was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse reactions between Simiao Yong'an Decoction and conventional western Med[RR=0.50,95%CI(1.15,1.64),Z=1.14(P=0.25)].As shown in figure 10.
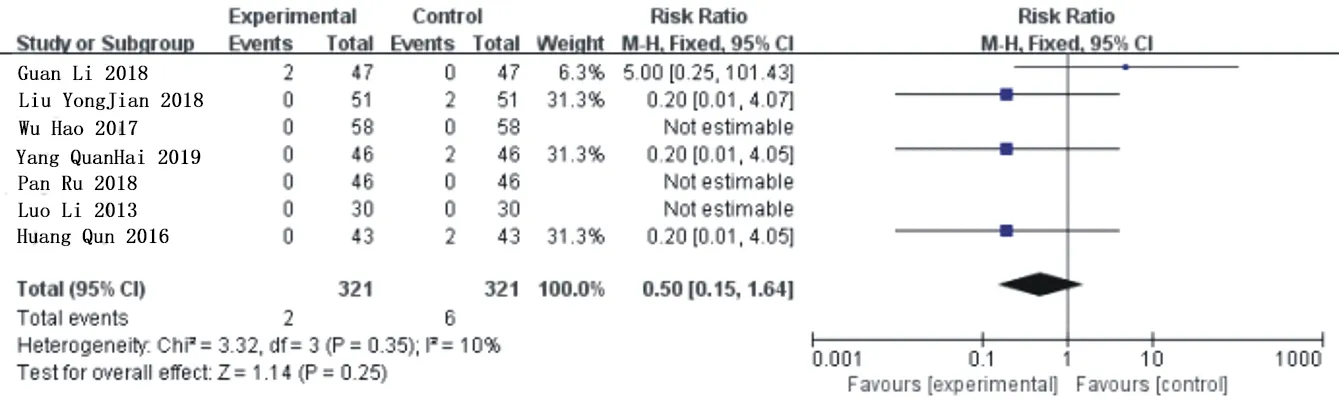
Fig.10 Forest chart of comparison in the incidence of adverse reactions
3.5 Publication bias analysis
Funnel plots were used to analyze the publication bias of clinical total response rate and ABI.It shows that the funnel plot is basically symmetrical,and all of them are within the range of the interval.It can be considered that the publication bias is small and the results are more reliable.As shown in figure 11 and figure 12.
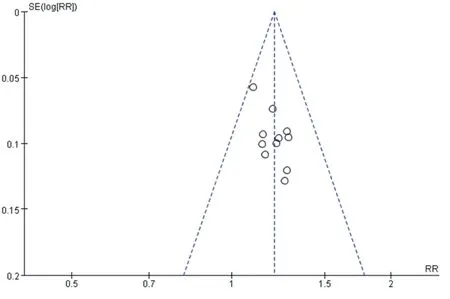
Fig.11 Funnel chart of total clinical response rate
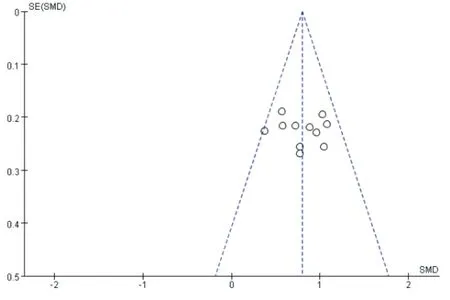
Fig.12 Funnel chart of ABI
3.6 Sensitivity analysis
According to the results of meta-analysis of Simiao Yong'an Decoction in the treatment of PAOD, sensitivity analysis was conducted on each final indicator.,The studies included in the outcome indicators were removed one by one and the meta-analysis was conducted again.The heterogeneity of the final indicator CRP decreased significantly after excluding the study.The heterogeneity of residual outcome indicators did not change significantly.There was no conclusive change in the meta-analysis of all final indicator,which indicated that the sensitivity of the overall analysis results was low and the conclusion was credible.
4. Discussion
The Simiao Yong'an Decoction was first recorded in “Hua Tuo Shen Yi Mi Chuan”:“this disease occurs at the end of the finger or toe.It tickles first and then hurts...Internal Med with honeysuckle three liang,scrophularia ningpoensis Hemsl three liang,angelica sinensis two liang,glycyrrhiza,taking herbal decoction, even take ten when the cure.”Bao Xiang-ao named it Simiao Yong'an Decoction in “Yan Fang Xin Bian”in the qing dynasty[24].The formula is composed of honeysuckle, scrophularia ningpoensis Hemsl,angelica sinensis and glycyrrhiza. The four drugs are used in combination and the amount of strong special,playing the role of heat-clearing and detoxifying, invigorating blood circulation.The results of the meta-analysis showed that Simiao Yong'an Decoction could effectively reduce the levels of CRP and LDL in PAOD patients, increase the content of HDL, increase the ABI and TBI levels, increase the blood circulation in the lower limbs,and thus improve the overall clinical efficiency.Chronic inflammation and abnormal lipid deposition are directly or indirectly involved in the occurrence and development of PAOD.Modern studies have also proved that Simiao Yong'an Decoction can treat PAOD by inhibiting inflammatory response and correcting lipid metabolism disorders[25].The anti-inflammatory mechanism of Simiao Yong'an Decoction can be realized by regulating the nuclear factor-κB pathway,macrophage TLR4/MyD88 signal transduction pathway and other multiple pathways,and significantly reduced levels of inflammatory factors such as CRP,tumor necrosis factor-α,interleukin-6,and interleukin-1 in animal models[26,27,28].This reduces the release of inflammatory mediators.Simiao Yong'an Decoction has a good role in regulating blood lipid,significantly reducing the contents of LDL and triglyceride in rabbits of the AS model[29], and also increasing the HDL level in rats of the TAO model[30],thus inhibiting extracellular matrix degradation and lipid deposition.Currently,ABI is an effective non-invasive indicator for the diagnosis of PAOD [31].Combined with TBI,ABI can more accurately reflect the degree of distal limb ischemia[32].Studies have found that Simiao Yong'an Decoction can increase the rate of angiogenesis in DAO model rats and speed up the revascularization process[33],which may be related to the mechanism of Simiao Yong'an Decoction can improve ABI and TBI levels in PAOD patients.In addition,Simiao Yong'an Decoction can reduce the content of xanthine oxidase by increasing the levels of glutathione peroxidase,superoxide dismutase and nitric oxide synthase in the serum of AS model mice, and play the role of antioxidant stress[34].It can also improve the vascular remodeling and protect the vascular endothelium of model rats by inhibiting the proliferation of mononuclear macrophage antigen-1 and proliferating nuclear antigen[35].
Sensitivity analysis of all final indicator showed no conclusive change, indicating that the results were stable.The funnel plot is basically symmetrical,which indicates that the conclusion is reliable. However,the quality of the literatures included in this study is not so good,only 5 of which describe specific random methods. Allocation concealment and blind method are not mentioned in all literatures and the sample size was less than 200 cases.All the literatures studied are in Chinese,and there may be some publication bias.The long-term efficacy of Simiao Yong'an Decoction could not be judged due to only one literature report on the follow-up.Different clinical efficacy criteria were used in the study,which may interfere with the statistical results.The above limitations will interfere with the conclusion of the meta-analysis and affect the credibility of the research results.
In summary, on the basis of conventional western Med treatment,combined with Simiao Yong'an Decoction to treat PAOD can significantly improve the total clinical efficiency,inhibit the inflammatory response and reduce lipid deposition, improve the blood supply to the affected limb,and it is safe and worthy of clinical application.However,the sample size of this study is relatively small and the literature quality is not high.More high-quality,largesample,multi-center RCTS with rigorous scientific design and strict implementation in accordance with the standards need to be included to further verify the credibility of this study.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Mechanism of Ganlu Xiaodu MicroPill against COVID-19 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking method
- Toxicity effects of paclitaxel exposure on Caenorhabditis elegans
- The relationship between cellular immune level and diabetic foot in type 2 diabetic patients
- Clinical significance of TnI, hs-CRP and NT-proBNP in the diagnosis of myocardial damage in uremia patients
- Comparative study of 99Tc-MDP and zoledronic acid in the treatment of osteoporosis
- Clinical study on the treatment of bronchiectasis in remission period by embedding thread combined with Jianpi Qushi Huayu plaster
