Network pharmacology-based elucidation of molecular biological mechanisms of Kanglaite injection for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
2020-10-10BoWenXuShiXinLiJieLiXiaoXiaoZhangLuChangCaoJingYuanWuWenChaoDan
Bo-Wen Xu, Shi-Xin Li, Jie Li, Xiao-Xiao Zhang, Lu-Chang Cao, Jing-Yuan Wu, Wen-Chao Dan
1. Guang'anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China
2. Graduate School of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
Keywords:Kanglaite injection Non-small cell lung cancer Coix seed Network pharmacology Molecular biology Mechanistic studies
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the effective compounds, potential targets and molecular mechanism of Kanglaite injection (KLTi) in the treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) based on network pharmacology. Methods: The active compounds and targets of KLTi which extracted and isolated from Coix Seed were screened by Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP). The related genes of NSCLC were obtained by searching the Human Gene Database (GeneCards) and Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM). The candidate targets of KLTi in the treatment of NSCLC were obtained after extracting the intersection network. The "drug-component-targetdisease" network was constructed with the help of Cytoscape 3.7.2. The Protein- Protein Interaction networks were constructed on the STRING platform and core network modules were screened. The Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis of candidate genes were performed using Metascape platform, and a "pathway-target- compounds" network was constructed to further screen key genes and active compounds. Results: A total of 11 compounds, 22 candidate targets, 206 GO functions and 12 KEGG pathways were obtained. Conclusion: The active compounds of KLTi in the treatment of NSCLC are stigmasterol, stigmasterol α1 and ergosterol. The key targets are PGR, NCOA2, PTGS2, NR3C2, and PTGS1. The core GO functions included receptor activity and binding, neuronal signal transmission and hormone stimulation; KEGG mainly involves cancer pathways, neuroactive ligand-receptor interactions and calcium signaling pathways. This study reveals the molecular biological mechanism of KLTi in the treatment of NSCLC, which is speculated to be related to neuroendocrine, providing a new basis and therapeutic direction for subsequent clinical application and experimental research.
1. Introduction
Primary bronchogenic carcinoma ranks first in the incidence of tumors. According to the global cancer data in 2018[1], the incidence of lung cancer accounts for 11.6% and the mortality rate accounts for 18.4%. It is the most common refractory malignant tumor in the world, of which Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) accounts for about 85%. Most patients have advanced disease at the time of diagnosis[2]. Surgery and chemoradiotherapy are commonly used in modern medical treatment of NSCLC, but the 5-year survival rate is 5%. It is often associated with adverse reactions or drug side effects and reduces the quality of life of patients. Therefore, it is of great clinical significance and practical value to seek an alternative or adjuvant therapy with less side effects and good efficacy.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) plays an active role in reducing the recurrence and metastasis of NSCLC, reducing the toxic and side effects of treatment, and improving the quality of life and survival of patients. Kanglaite injection (KLTi) is an extract of Coix seed. Studies[3] have confirmed that it acts on G2 + M phase of tumor cells, induces apoptosis and necrosis of tumor cells, and also inhibits the formation of metastases. At the same time, it can improve the immune function of the body and have attenuation and synergism for a variety of tumor treatment methods, but the specific molecular biological mechanism is not yet fully understood and needs to be further studied.
TCM has the characteristics of multiple targets, multiple pathways, and multiple compounds. If a single pathway mechanism study cannot reflect the integrity and multiorientation of TCM in the treatment of diseases, this study introduces a network pharmacology research method with multidirectional regulatory pathways. Network pharmacology is based on the theory of systems biology, emphasizing the multi-way regulation of a certain pathway, analyzing the relationship between the compounds by constructing a network, paying attention to the key nodes in the network, which can systematically elaborate the material basis and mechanism of action of traditional Chinese medicine and compound prescription. At present, it is mostly used in the fields of mechanism of action research and new drug development of traditional Chinese medicines and compound prescriptions[4], and is also widely used in tumors[5]. Therefore, in this study, network pharmacology was used to predict and explore the molecular biological mechanism of KLTi intervention in NSCLC, providing a methodology and theoretical basis for integrative medicine diagnosis and treatment and basic experimental research, and the workflow is shown in Figure 1.
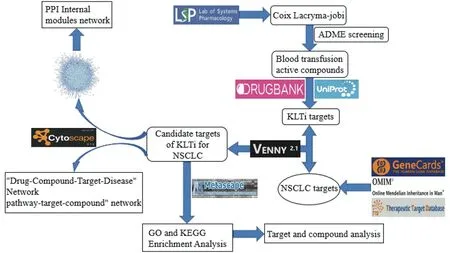
Figure 1 Study workflow
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Active Compounds and Target Screening of KLTi
Search the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP, http://tcmspw.com/tcmsp.php), all compounds of KLTi, or Coix seed, were screened. Because KLTi is a traditional Chinese medicine injection and does not involve oral availability (OB), according to the ADME screening principle, drug-likeness (DL) refers to the degree of similarity with known drugs, so the screening conditions are determined as DL ≥ 0.18. The effective compounds with anti-tumor activity confirmed in previous literature studies were also collected to supplement and improve the prediction results and obtain candidate compounds. The candidate compounds were deposited in the DRUGBANK database (Version 5.1.5, https://www.drugbank.ca/), the drug target was matched in and analyzed by Uniprot database (https://www.uniprot.org/), corrected to the standard gene name.
2.2 NSCLC target retrieval
“Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer” was used as a keyword, in the Human Gene Annotation Database (Genecards, https://www.genecards.org/), the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM, https://omim.org/), treatment target database (TTD, http://db.idrblab.net/ttd/), and other search targets, the obtained disease targets are summarized and duplicate values are removed, so as to establish NSCLC target datasets.
2.3 Acquisition of Common Targets between Drugs and Diseases
With the help of Venny (Version 2.1.0, https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/), intersecting the drug predicted target with the disease target to obtain a common target, which can be considered as a candidate target for KLTi in the treatment of NSCLC.
2.4 Constructing the "Drug-Compound-Target-Disease" Network
The drug compounds and candidate targets were imported into Cytoscape 3.7.2 to construct a "drug-compound-target-disease" network, in which the "node" indicated the drug, component, target and disease, and the "edge" indicated the relationship between the two. Cytoscape built-in Network Analyzer tool is used to analyze the network, focusing on the degree of the node, that is, the size of the node. The more biological functions involved, the higher the importance, so as to study the more important compounds and targets in KLTi and their relationship.
2.5 Construction of target protein interaction network
To further interrogate the interactions among candidate target proteins, STRING (Version 11.0, https://string-db.org/), to construct a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network. BioGrid6, InWebIM7, OmniPath8 and other databases were used for PPI mining analysis. If the subnetwork contained 3 to 500 proteins, the molecular complex detection algorithm (MCODE) was applied to identify densely connected network features to further screen the core network nodes.
2.6 Pathway Enrichment Analysis
The Metascape platform (http://metascape.org/), which is powerful and integrates multiple authoritative databases such as GO, KEGG, and Uniprot for pathway enrichment analysis of gene targets, and is updated monthly to ensure the accuracy of the data. GO and KEGG analysis of candidate targets can be performed with the help of this platform, and gene ontology (GO) includes three parts: molecular function (MF), biological process (BP) and cellular component (CC) to interpret anti-tumor biological processes of key targets; Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis to study the main anti-tumor signaling pathways involved in key targets. Based on the relevant targets mapped by KEGG results, a "pathway-target-compound" network was constructed to further screen the key target genes and active compounds of KLTi in the treatment of NSCLC.
3. Results
3.1 Acquisition of KLTi Active Compounds
Coix seed was searched in TCMSP database with DL ≥ 0.18, and 18 active compounds were obtained. Although some compounds have low DL value, it has been confirmed in the literature that these compounds have good biological activity and have a clear effect on NSCLC, so Olein and MBOA[6] were supplemented, and a total of 20 active compounds were included in the study.
3.2 Acquisition of targets
A total of 36 drug targets were obtained by target screening of active pharmaceutical compounds with the help of DRUGBANK. NSCLC was searched in Genecards, OMIM, and TTD databases, which resulted in 4180, 471, and 245 targets, respectively, and duplicate values were summarized and removed, resulting in a total of 4531 disease targets. The drug was intersected with the disease target by Venny 2.1.0 to obtain 22 common targets, and 11 effective compounds were obtained by target mapping for further basic research, as shown in Figure 2, Tables 1 and 2.
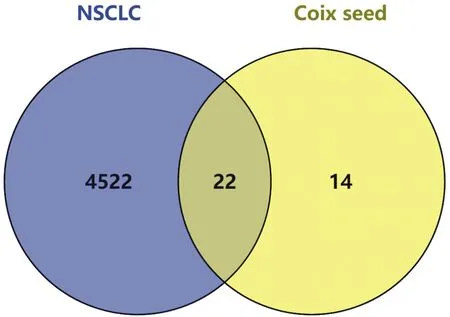
Figure 2 Veeny of drugs and disease targets

Table 1 11 potential active compoundss in KLTi
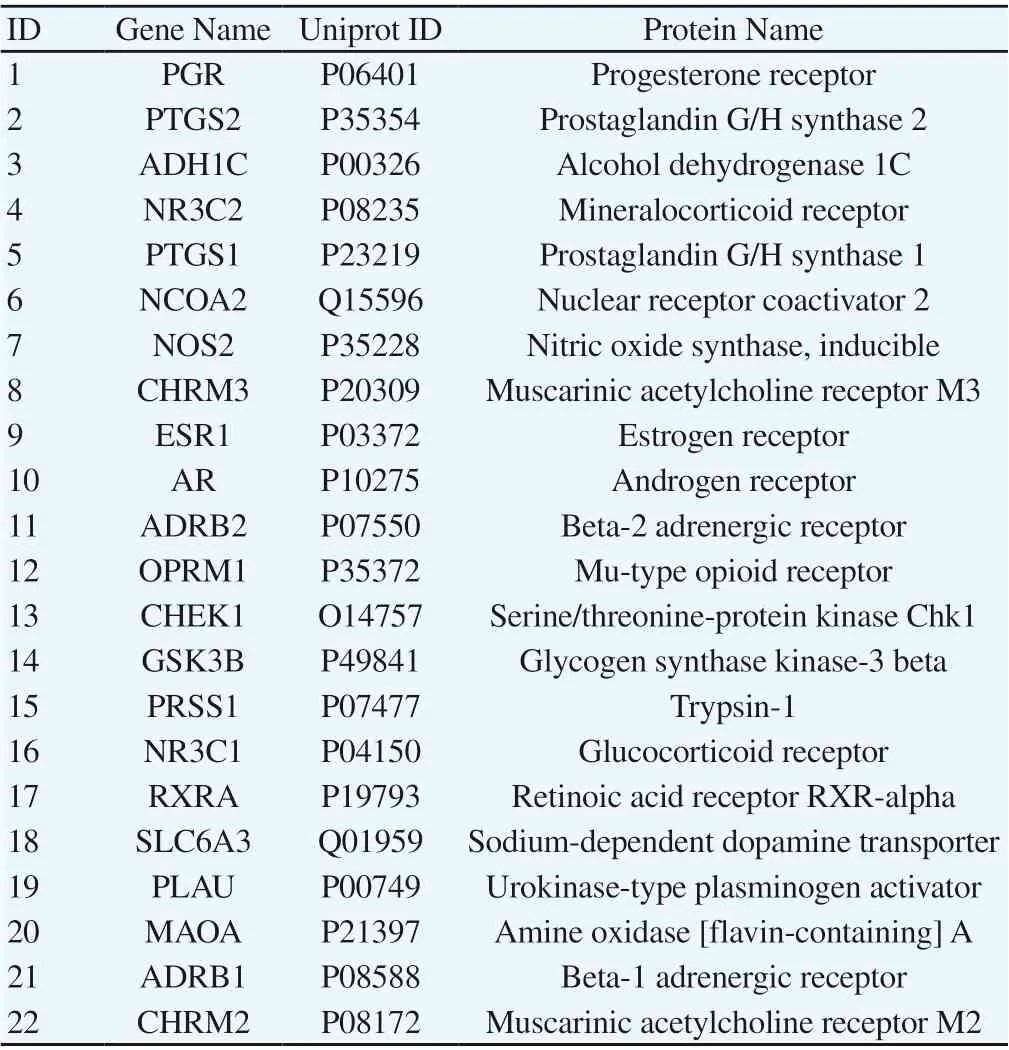
Table 2 22 Potential Targets for KLTi in NSCLC
3.3 Construction of "Drug-Compound-Target-Disease" Network
For the above potential active compounds and targets, the "drugcompound-target-disease" network was constructed with the help of Cytoscape3.7.2, as shown in Figure 3. The network consists of 35 nodes and 160 edges, and the size of the nodes represents the corresponding Degree. Using Network Analyzer in Cytoscape to analyze node metrics, the top four compound metrics were stigmasterol, omaine, sitosterol alpha1, and ergosterol, which corresponded to 15, 12, 5, and 5, respectively, which may be the more important active compounds of KLTi in the treatment of NSCLC; the top five target metrics were PGR, NCOA2, PTGS2, NR3C2, and PTGS1, which corresponded to 8, 7, 6, 5, and 5, respectively.

3.4 Constructing the PPI Network
The PPI network map was constructed by placing 22 candidate targets in STRING, excluding 2 free target proteins (no interacting proteins), see Figure 4. The PPI network contains 20 targets and 44 edges, of which NR3C1, ESR1, PTGS2, AR, PGR and so on have more interaction relationships, which lays a foundation for further study of the function between each target.
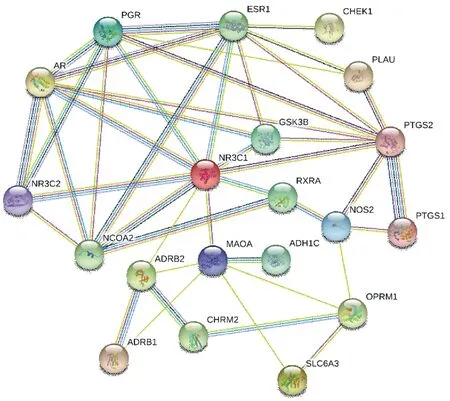
Figure 4 PPI Network Diagram
Since the roles of proteins in PPI networks are reciprocal and often classified as undirected graphs, there are regions of high partial density in their complex networks, and the networks within this region have high biological significance. Therefore, to more precisely analyze the mechanism of action of KLTi in the treatment of NSCLC, it is necessary to further identify the characteristics of the intrinsic core network after obtaining the core PPI network. The densely connected network relationships were analyzed by the Molecular Complex Detection Algorithm (MCODE), see Figure 5. According to the P value, the biological processes of the three best scores in the PPI network were retained and functionally described, respectively, 3.

Figure 5 PPI Internal Core Network Module Diagram
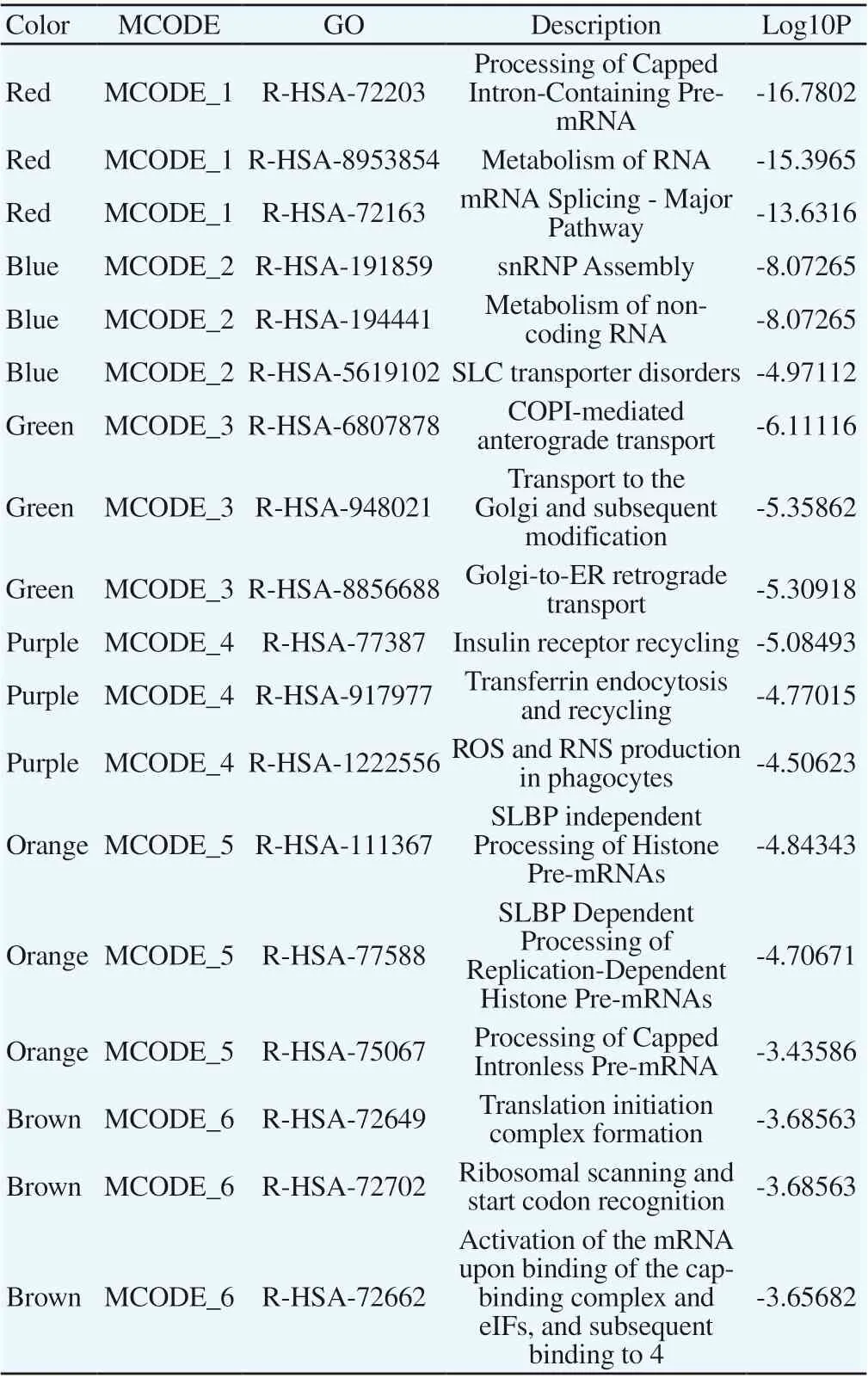
Table 3 Functional description of core network modules within PPI (top 3)
3.5 Enrichment Analysis
The 22 candidate targets were subjected to GO and KEGG enrichment analysis by Metascape platform. The GO results showed that a total of 206 GO terms showed enrichment, including 154 biological processes, 23 cellular compositions, 29 molecular functions, and 12 signaling pathways enriched by KEGG. According to the ranking of P values, the top 12 were selected to draw the bubble Chart in R language, as shown in Figure 6.To the left of each figure is the top enrichment name, the color of bubbles from red to blue represents the Qvalue values from small to large, the bubble represents the gene count of this pathway, and the horizontal axis represents the ratio of genes of this pathway to the overall input genes. From Figure 6-A, B, C, the main GO processes involved are receptors activity and binding, such as nuclear receptor, hormone, transcription factor and neurotransmitter. Transmission of neuronal signals, hormone stimulus, and synaptic transmission are also included, and KLTi is predicted to regulate hormone and neurotransmitter levels to play a role in intervening NSCLC.
In the KEGG results shown in Figure 6-D, including Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes, Calcium signaling pathway, Thyroid hormone signaling pathway, classical pathway in cancer, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, and cAMP signaling pathway.
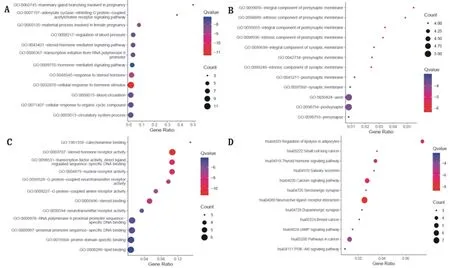
Figure 6 GO + KEGG Bubble Plot
To further reveal the relationship between signaling pathways and candidate targets and compounds, a "pathway-target-compound" network was constructed, as shown in Figure 7. From the network, it can be seen that PTGS2, PGR, ADRB2, NCOA2, ADRB1, PTGS1 have a large Degree and are key targets. Compounds, on the other hand, are consistent in the "drug-compound-target-disease" network and also corroborate with the results of the PPI network.
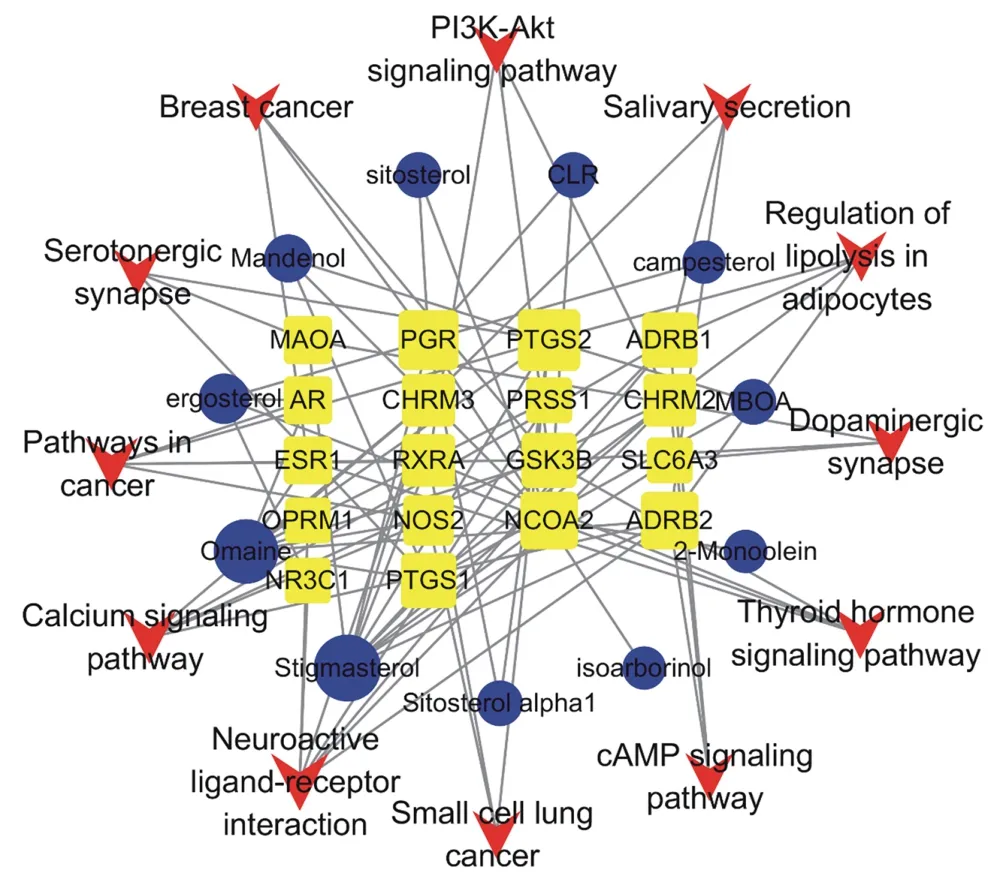
4. Discussion
NSCLC is an important type of lung cancer, which belongs to the category of "lung accumulation" in traditional Chinese medicine. It is mostly caused by deficiency of vital qi, invasion of evil toxin, damage to the lung, lung loss and purging, and imbalance of water metabolism; lung qi deficiency, daughter disease and mother, spleen deficiency is loss of health and transport, endogenous phlegmdampness, wet turbid flow, qi block, and blood stasis and toxin. The disease is based on deficiency, phlegm, dampness, blood stasis, and poison, and is mainly treated with supplementing qi and nourishing yin, eliminating phlegm and detoxifying[7]. KLTi has the functions of supplementing qi and nourishing yin, eliminating symptoms and dispersing stasis. It is suitable for primary cell lung cancer with deficiency of both qi and yin and dampness due to spleen deficiency that is not suitable for surgery. Combined with chemoradiotherapy, it can synergize and reduce toxicity, and has anti-cachexia and analgesic effects on advanced tumors. ShenNongBenCaoJing contains: "Coix seed, sweet taste, slightly cold. Attending muscle cramps, can not bend and stretch, rheumatism, under the gas. "Coix seed is the genus of nemi valley, long summer and autumn, white color can enter the lungs, taste sweet and medium, sexual cold can clear heat, endowment Yangming gold soil essence. Coix seed taste Gan Yi stomach, and the shape, cultivate soil to win water, Gan Yi wet, purge water and benefit soil, so good cultivate soil to generate gold. Discussion "hot and humid, big tendons short, small tendons long", to Yangming main moisten Zongjin, Zongjinrun is Zhujin self-harmony, Coix seed cold to clear away heat and dampness, slow tendons urgent, flat cramp can be analgesic. Gold can make the wind, earth can win wet, the treatment of rheumatism and phlegm and dampness knot but do not hurt the positive. The lung belongs to the gold and the main qi, Job's tears endowment Yangming gold qi, so it can righting qi to reduce adverse qi, the function of supplementing qi and nourishing yin, clearing away heat and dampness, and tonifying the shape, Sanjie pain. It is commonly used to treat patients with advanced NSCLC. Studies have confirmed that it can effectively improve the clinical symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, pain, quality of life and degree of bone marrow suppression[8].
Although KLTi is extracted from coix seed, the compounds of coix seed are complex, each component corresponds to many targets, and there may be synergistic or antagonistic effects between the targets, so it is difficult to elucidate the mechanism of action of KLTi in the treatment of NSCLC. Network pharmacology is based on various biological information databases, which can find the chemical compounds and protein targets of the traditional Chinese medicine, compound prescription or traditional Chinese medicine injection to be studied, and also contains the records of disease targets. Through the network analysis of drugs and diseases, it is conducive to explain the mechanism of action of traditional Chinese medicine and its compound prescription in the treatment of a disease, and network pharmacology emphasizes the pathway study of multiple targets, which is consistent with the overall concept of traditional Chinese medicine[9].
4.1 Potential active compounds
The "drug-compound-target-disease" network and the "pathwaytarget-compound" predict that stigmasterol, stigmasterol α1, ergosterol may be key active compounds and all belong to phytosterols.
Previous studies[10] have confirmed that plant sterols can reduce the risk of tumor incidence, curb tumor cell growth, promote apoptosis and regulate immune activity. Stigmasterol is an important component of plant sterol, including stigmasterol α1, which has significant anti-tumor, antioxidant, endocrine and other biological activities, can promote tumor cell injury, intervene tumor cell cycle to inhibit tumor growth[11]; stigmasterol can also reduce the risk of uterine fibroids induced by female sex hormones, can effectively inhibit the proliferation of rat uterine fibroid ELT3 cells and human uterine fibroid hUL cells[12]; and derivatives synthesized from stigmasterol also have certain anti-tumor characteristics, compared with adriamycin, the inhibition rate of tumor cells should be significantly improved[13]. Similarly, ergosterol[14] can cause different degrees of microangiopenia and a variety of apoptotic morphological changes in mouse tumor tissues, can inhibit tumor angiogenesis and regulate Bax and Bcl-2 protein expression[15]. However, modified ergosterol had a significant antitumor effect on A549 lung cancer-bearing mice, and the more significant the dose effect, it could also activate high expression of TNF-α in vivo [16]. For Omaine, there is no relevant clinical or experimental study, which may be another finding of KLTi intervention in NSCLC.
4.2 Key gene targets
For the genes, progesterone receptor (PGR), nuclear receptor coactivator 2 (NCOA2), prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 (PTGS2), mineralocorticoid receptor (NR3C2), and prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 (PTGS1) are considered to be key targets for KLTi intervention in NSCLC.
It is generally accepted that estrogen and progesterone receptors are widespread in NSCLC and have some association with tumor prognosis[17]. Beattie[18] also proposed that NSCLC is a sex hormone-dependent tumor, and concluded that high expression of sex hormones in the body can cause endocrine microenvironment disorders in the body, initiate the synthesis of receptor proteins with sex hormone biological activity, and enable cancer cells to obtain hormone-related growth characteristics. For example, estrogen and its enzymes in the synthesis process promote the survival of tumor cells, while ER antagonists have been shown to inhibit tumor growth in vitro and in vivo[19]. PGR is not expressed in normal lung tissues, but overexpressed in NSCLC[20], based on which inhibiting or blocking PGR expression has a certain role in the occurrence, development and prognosis of NSCLC.
Nuclear receptors can directly regulate target gene expression or interact with other proteins to affect intracellular signaling pathways, such as autophagy, and more than 10% of drugs belong to ligand drugs targeting nuclear receptors[21]. NCOA2 can promote the transcriptional activity of nuclear receptors and regulate a variety of metabolism in the body, especially for the regulation and treatment of various hormone-related tumors[22], such as progesterone, thyroid hormone, prostaglandins; it can also assist in the activation of transcription factors, induce the expression of inflammatory factors, and has the function of curbing the proliferation and migration of cancer cells. Intervention of the above molecules or protein receptors can inhibit the progression of NSCLC to a certain extent, providing a certain basis and support for the research and development of new drugs of traditional Chinese medicine, and there is a close interaction between hormone targets in the PPI network. Therefore, it is speculated that KLTi treatment of NSCLC may play an intervention role in hormone levels, which needs to be confirmed by further basic experimental studies.
4.3 GO analysis
GO results indicate that KLTi exerts its anti-NSCLC effect by regulating the activity and binding of receptors such as steroid hormone receptors, neurotransmitters, transcription factors, and G protein-coupled receptors[23].
Steroid hormones include sex hormones, corticosteroids, etc., and their receptors are nuclear transcription factors. Steroid hormone molecules cross the cell membrane and form hormone receptor complexes with them to enter the nucleus to affect target gene transcription and have an effect on cell differentiation and proliferation. Bi Hongdong[24] believed that 1,25 (OH) 2D3 binds to steroid hormone receptors, regulates drug metabolizing enzymes and endogenous substance transporters, exerts anti-tumor effects, and confirms that steroid hormone receptors have transcriptional activity, and if the signaling regulation of this receptor is disrupted, it will lead to the occurrence of a variety of malignant tumors, such as lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer and ovarian cancer. There was also a certain relationship between steroid binding protein and tumor. Chen Xiao[25] found that the expression of corticosteroid binding globulin was down-regulated in the plasma of NSCLC patients with multiple metastases, which was considered to be a marker protein for NSCLC metastasis. Liang Fenfen[26] found that 1,25 (OH) 2D3-related rapid response sterol binding protein is not only involved in calcium and phosphorus absorption, but also associated with tumor survival prognosis. And in the key biological processes, PGR, NR3C1, ESR1, AR, RXRA and other targets play an important hub role, which is basically consistent with the "drug-compound-targetdisease" network target, PPI network target, but also to establish the core position of these genes.
4.4 KEGG analysis
KEGG results showed that the regulatory pathways of KLTi in the treatment of NSCLC were mainly in neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction[27], calcium signaling pathway[28], regulation of adipocyte lipolysis[29], and thyroid hormone signaling pathway[30], while the above pathways were closely related to tumor proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis and angiogenesis.
There is an association between neuroactive ligand-receptor interactions and the risk of lung cancer development, and polymorphisms in chromosome 15q25.1 increase the risk of lung cancer development by affecting this pathway[31]. Shi[32]. found that for non-smoking female patients with lung adenocarcinoma, the down-regulated genes were mainly related to neuroactive ligandreceptor interactions. Ca2 + is one of the important small molecule signals regulating cell function. The high expression of NFATc2, a transcription factor of Ca2 + pathway, is also considered to be a novel regulator of the initial cell phenotype of lung cancer. Its high expression predicts poor tumor differentiation[33]. The increase of intracellular calcium concentration in cancer cells can also induce apoptosis[34].
Fat metabolism can also affect tumors. Hua[35]. found that inhibiting oncogenic factor Src can promote PPARγ expression, promote FABP4-mediated lipolysis, reduce lipid droplets, induce endogenous ROS levels, and inhibit tumor cell growth. It was also observed that elevated expression of lipolytic genes FABPR or LPL in lung cancer and renal cancer represented better survival and prognosis. In addition, metabolic abnormalities of tumor cells are also associated with drug resistance, Li[36]. found that paclitaxel-resistant A549 cells showed distinct metabolic characteristics from non-resistant cells, fatty acid inhibitors were able to increase the sensitivity of resistant cells to paclitaxel, and inhibition of lipolytic enzymes may be an effective treatment for resistant cells.
5. Conclusion
From this study, it can be seen that the active compounds of KLTi in the treatment of NSCLC may be stigmasterol, stigmasterol α1, ergosterol, etc., which are closely related to the activity and binding of receptors such as neurotransmitters, hormones and transcription factors, involving cancer pathways, neuroactive ligand-receptor interactions and calcium signaling pathways. We speculate that KLTi mainly intervenes in the occurrence and development of NSCLC by regulating neuroendocrine, providing a basis for further study on the mechanism of action and basic research of KLTi in the treatment of NSCLC. However, it is also necessary to design corresponding in vitro and in vivo experiments to verify the results of this study and enrich the molecular biological mechanism study of KLTi.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Mechanism of Ganlu Xiaodu MicroPill against COVID-19 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking method
- Toxicity effects of paclitaxel exposure on Caenorhabditis elegans
- The relationship between cellular immune level and diabetic foot in type 2 diabetic patients
- Clinical significance of TnI, hs-CRP and NT-proBNP in the diagnosis of myocardial damage in uremia patients
- Comparative study of 99Tc-MDP and zoledronic acid in the treatment of osteoporosis
- Clinical study on the treatment of bronchiectasis in remission period by embedding thread combined with Jianpi Qushi Huayu plaster
