植物钙依赖性蛋白激酶及其相关蛋白激酶CDPKs/CRKs的研究进展
2020-10-09何乐平张蕾
何乐平 张蕾
摘要 作为细胞第二信使,Ca2+协调着植物对各种生理反应的感知。钙离子传感器向下游传递钙信号并引发级联反应,调控植物生长发育以及对环境的响应等过程。钙依赖性蛋白激酶在Ca2+介导的信号转导中起重要作用。综述了近年来植物CDPKs/CRKs相关研究进展,包括分子结构和作用机制、表达模式、亚细胞定位和生物学功能,旨在为CDPKs/CRKs相关研究提供参考。
关键词 钙依赖性蛋白激酶;钙依赖性蛋白激酶相关蛋白激酶;调控机制;生物学功能
中图分类号 Q946 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2020)18-0026-05
Abstract As a second messenger in cell, Ca2+ coordinates the perception of plant for a variety of physiological reaction. The calcium ion sensor transmits calcium signal and triggers a cascade reaction to regulate plant growth and development. Calcium dependent protein kinases play important roles in Ca2+ mediated signal transduction. This paper reviewed the related research progress in plant CDPKs and CRKs, including molecular structure and mechanism, expression patterns, subcellular localizations and biological functions. Hence, the purpose of this review is to provide reference for related research on CDPKs/CRKs.
Key words Calciumdependent protein kinases;CDPKrelated kinases;Regulation mechanism;Biology function
Ca2+作为第二信使,协调植物对内外界多种生理反应的感知[1]。Ca2+传感器接受钙信号,将化学信号转化为细胞的生理生化反应。植物主要有4种Ca2+传感器:钙调素(Calmodulin,CaM)及其类似蛋白(CaMlike proteins,CMLs)、钙依赖性蛋白激酶(Calciumdependent protein kinases,CDPKs or CPKs)及其相关的蛋白激酶(CDPKrelated kinases,CRKs)、钙调磷酸酶B类似蛋白(Calcineurin Blike protein,CBL)、钙和钙调素依赖性蛋白激酶(calciumand calmodulin-dependent protein kinases,CCaMKs)[2]。目前对CDPKs的研究较为深入,研究表明CDPKs/CRKs存在复杂的调控模式,在植物发育及多种胁迫响应中均扮演重要角色。笔者综述了近年来植物CDPKs/CRKs相关研究进展,旨在为CDPKs/CRKs相关研究提供参考。
1 CDPKs/CRKs的分子结构和作用机制
CDPKs存在于植物、绿藻和单细胞原生生物中[3]。拟南芥、水稻、玉米和棉花中分别含有34、31、40和41个CDPK基因[4-8];拟南芥、水稻、白楊、番茄和辣椒中分别含有8、5、9、6和5个CRK基因[4,9-12]。对于CDPKs和CRKs分子结构以及激酶活性调控的研究主要集中在拟南芥。
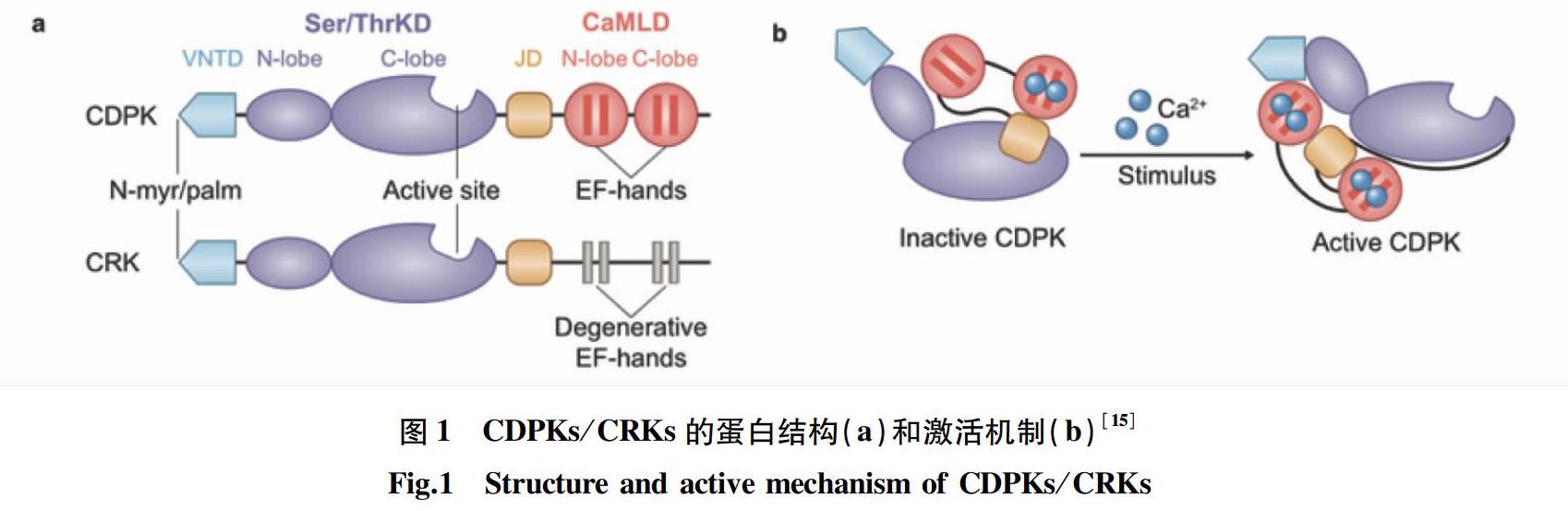
CDPKs蛋白包含4个结构域:N端可变结构域(variable N-terminal domain,VNTD)、Ser/Thr蛋白激酶域(Ser/Thr protein kinase domain,PKD)、自抑制连接域(junction domain,JD)和C端具有EF手型结构的类钙调素调控结构域(CaM-like regulatory domain,CaMLD)[13-15]。CRKs C端的EF手型结构已经退化,其他结构与CDPKs相似[16]。CDPKs/CRKs的蛋白结构见图 1a。
CDPKs的N端具有较高比例的脯氨酸、谷氨酰胺、丝氨酸和苏氨酸(PEST)序列,这些序列可以进行快速的蛋白降解[14]。VNTD区氨基酸序列多样,长度各异,保守性低。拟南芥CDPKs的VNTD区序列长度最短只有25个氨基酸,最长达180个氨基酸[17]。VNTD区参与底物特异性识别过程。NtCDPK1与RSG互作,而AtCPK9不与RSG互作,但含有来源于NtCDPK1的VNTD区的重组AtCPK9可与RSG互作,这表明NtCDPK1的VNTD区在特异性识别底物RSG的过程中发挥了重要作用[18]。研究发现多数CDPKs N端具有参与蛋白膜结合的豆蔻酰化或棕榈酰化位点,暗示VNTD区参与CDPKs膜结合过程[19]。
CDPKs蛋白的PKD区保守性高,含有Ser/Thr磷酸化位点,关键氨基酸突变往往会使激酶失活[4]。PKD区分为2个球形结构,分别是N-lobe和C-lobe,前者对Ca2+的亲和性低于后者[13]。CRKs除含有Ser/Thr激酶活性,还具有极高的酪氨酸自磷酸化活性且可以磷酸化底物的酪氨酸位点[20]。
CDPKs上的JD区保守性高,主要作为假底物结合在CDPKs的激酶区[14]。
正常情况下,JD区与C-lobe的催化位点结合,作为假底物维持CDPKs处于低基础激酶活性状态。当植物受到光照、低温或高温、高盐、干旱、激素甚至病原体等刺激时,细胞内形成特异性Ca2+信号,Ca2+与EF手型结构直接结合,改变了CDPKs的构象,暴露出激酶活性位点,激活激酶活性(图1b);此外,PKD区结合ATP或GTP并转移γ-磷酸基团到受体羟基残基,激活底物,从而引发植物多种生理反应[15,21-22]。近年研究显示在部分CDPKs上具有CaM结合位点并在体外试验中证明了二者的相互作用,体外激酶试验显示CaM可抑制这一类CDPKs Ca2+依赖性的激酶活性[23]。
大部分CRKs C端的EF手型结构退化,因此不受Ca2+直接调控,但由于部分CRKs具有CaM结合区,所以CRKs的激酶活性会受到Ca2+和CaM的协调控制[24-25]。
磷酸化作用是影响CDPKs/CRKs激酶活性的另一个重要因素。AtCPK28第228和318 位的丝氨酸位点突变使其不能发生自磷酸化作用,降低了激酶活性。除典型的Ser/Thr磷酸化位点,CRKs和第Ⅳ类CDPKs还具有Tyr磷酸化位点[23,26]。
CDPKs/CRKs可以被泛素化修饰。Teng等[27]、樊莉娟等[28]、邓亚男等[29]研究结果显示,拟南芥中CRK5的蛋白水平通过DWD蛋白介导被泛素化降解;AtTR1可以对AtCPK28和AtCPK32进行体外多泛素化修饰;过表达E3泛素连接酶ABRv1通过单泛素化AtCPK3,可以提高拟南芥耐旱性[27-29]。
2 CDPKs/CRKs的表达模式和亚细胞定位
转录组分析结果显示CDPKs具有不同的表达模式,表明CDPKs在植物细胞中功能的多样性[6]。一些CDPKs呈现泛表达模式,而另一些CDPKs则特异性表达在植物的某些器官或组织中。如NtCDPK1在烟草根、茎、花中表达,叶中不表达[30];AtCPK12在拟南芥大部分组织包括根、茎、叶等均有表达,但在种子中无法检测到[31];AtCPK17/20/34仅在花粉中表达,调控花粉管生长[32-33];AtCPK3/6则在保卫细胞中大量表达,调节气孔运动[34];BnCDPK1主要在油菜叶片中表达,油菜花中表达量很低,种子等其他组织表达量适中[35]。CRKs的表达模式也因其种类而异。番茄LeCRK1在叶、茎 、花中均有表达,但在成熟果实中表达量最高[36]。qRT-PCR结果表明AtCRK5在花中表达量最高,茎中表达量最低[37]。
CDPKs/CRKs在细胞中的定位与其功能密切相关。CDPKs的亚细胞定位模式多样,包括细胞质、细胞核、细胞膜、内质网、过氧化物酶体、脂质体等,暗示其功能的多样性[6,38]。多数CDPKs在细胞膜处均有分布,与其N端的酰基化修饰有关,其中棕榈酰化位点与细胞膜形成可逆的稳定结合,豆蔻酰化位点形成的则是不可逆的松散结合[39]。豆蔻酰化或棕榈酰化位点的突变会改变CDPKs的膜定位。AtCPK16定位于细胞膜,当发生G2A突变后,阻断了该蛋白发生豆蔻酰化修饰,AtCPK16则定位于叶绿体;当该蛋白发生C4S突变阻断其发生棕榈酰化修饰后,则表现为核定位[40];AtCPK3定位于细胞膜,G2A位点突变阻断其发生豆蔻酰化修饰,在细胞质中也可以检测到点突变的AtCPK3[41]。部分CRKs是細胞核或细胞质定位,其他均为膜定位。目前研究表明所有AtCRKs均具有N端酰基化位点[6],除AtCRK6的亚细胞定位尚不清楚,其他7个AtCRKs在细胞膜处均有分布[42-43]。
3 14-3-3蛋白对CDPKs/CRKs的调控
CDPKs可以与脂质或14-3-3蛋白相互作用来调节激酶活性。脂质可以增加CDPKs对底物的亲和性[44],而CDPKs与14-3-3蛋白的作用关系更为复杂。一方面,14-3-3蛋白可以直接调节CDPKs激酶活性,调控其稳定性。研究表明14-3-3蛋白可以在体外促进AtCPK1/21/23的激酶活性但不影响其钙敏感性,同时抑制AtCPK3在细胞内的降解[45-47]。另一方面,14-3-3蛋白也可以作为CDPKs的底物发挥作用[48-49]。
4 CDPKs的生物学功能
4.1 CDPKs调控植物生长发育
研究表明CDPKs参与调控植物根、茎、叶的发育。MtCDPK1对于苜蓿根毛的正常生长必不可少,抑制 MtCDPK1基因表达会导致根长和根毛长度变短[50];OsCDPK5和OsCDPK13在根皮层细胞大量表达,诱导OsRBOHH介导的ROS生成,保证水稻在淹水条件下根系通气组织正常形成[51]。同时沉默NaCDPK4和NaCDPK5导致转基因植株茎发育异常,生长受阻[52];AtCPK28在维管和分生组织大量表达,参与调控茎基部节间次生生长和木质部发育,cpk28突变体严重矮化[26]。敲除烟草NtCDPK1基因导致新生叶片细胞形态异常和过早死亡[53];AtCPK3磷酸化的RhoGDI1通过调节ROP信号通路来调控拟南芥幼苗形态和叶表皮细胞发育[54]。
CDPKs参与调控植物开花、花粉萌发及花粉管生长、种子发育等过程。AtCPK33与bZIP转录因子FD相互作用并磷酸化FD是成花素复合体形成的关键,AtCPK33功能缺陷导致开花延迟[55]。AtCPK2/4/6/11/14/16/17/20/24/26/32/34在花粉中表达[15,56-57],其中 AtCPK11/24通过抑制SPIK介导的K+内流抑制花粉管生长[58];AtCPK2/6/20通过激活SLAH3、ALMT12/13/14介导的NO3-和苹果酸盐外流促进花粉管生长[33,59];Atcpk17/Atcpk34双突变体花粉管顶端极化生长存在缺陷[32,60];过表达AtCPK32引起花粉管尖端Ca2+浓度增加并伴随花粉管尖端膨胀[61]。OsCPK21-RNAi转基因植株在花药发育第10期时花粉发育严重缺陷,花粉细胞死亡[62]。OsCPK31过表达转基因植株种子灌浆期提前,成熟期缩短,表明OsCPK31对水稻种子的灌浆和成熟有重要作用[63];OsCDPK1在种子发育中期大量表达,负调控直链淀粉含量、胚乳透明度和种子大小[64]。
4.2 CDPKs参与调控植物激素信号通路
CDPKs参与调控赤霉素(Gibberellin,GA)生物合成或信号通路。CDPKs参与GA合成主要是通过影响GA20-氧化酶(GA20ox)和GA3-羟基化酶(GA3ox)来调控活性GA的合成[65]。AtCPK28促进GA3ox1合成,增加活性GA水平,正调控GA稳态[26]。NtCDPK1使bZIP转录因子RSG失活,下调GA20ox1,负调控GA稳态[66-67]。OsCDPK1负调控GA20ox1和GA3ox2的表达,抑制GA合成[68]。NtCDPK1与14-3-3蛋白的非磷酸化基序结合,调节叶鞘生长[18]。此外,外源GA处理后,OsCDPK13、NtCPK4、IiCDPK2表达均上调[69-71]。
CDPKs参与生长素转运过程。AtCPK3/4磷酸化马铃薯糖蛋白相关磷脂酶AtPLA IVA和IVB调控生长素信号通路[72]。体外试验表明StCDPK1可以磷酸化生长素运输载体StPIN4从而调控生长素水平[73]。
CDPKs响应乙烯信号并影响乙烯生物合成。StCDPK5可以被乙烯诱导表达,在番茄花梗脱落过程中发挥重要作用[74]。AtCDPK16通过磷酸化ACC合成酶AtACS7,参与调控拟南芥根的向重力性[75]。
CDPKs响应茉莉酸(Jasmonic Acid,JA)信号并参与调控JA生物合成。NtCDPK4和NtCDPK5响应JA信号,影响JA早期生物合成 [76]。Atcpk28突变体生长缓慢,JA相关基因表达量升高,JA代谢物增加[77]。
CDPKs参与ABA诱导的气孔运动和响应ABA信号。AtCPK13主要在保卫细胞表达,响应ABA信号,通过磷酸化并抑制2个K+内流通道:AtKAT1和AtKAT2,使气孔开放[78]。AtCPK6通过磷酸化ABA响应元件结合因子,正调控ABA信号和耐旱性[79]。AtCPK9通过调控离子通道活性,负调控ABA介导的气孔运动[80]。OsCPK9/12/21已被证实可以响应ABA信号[81-83]。
4.3 CDPKs参与植物生物胁迫反应
植物进化出了有效的免疫系统来抵御各种病原微生物的攻击。在第一层防御中,病原微生物信号(microbe-associated molecular patterns,MAMPs)被植物细胞膜上的模式识别受体(pattern recognition receptors,PRRs)感知,引起机体免疫反应(pattern-triggered immunity,PTI):ROS的增加或诱导致病相关基因表达等[84-85]。在PTI信号通路中,PRRs感知MAMPs会引发激酶介导的复杂信号反应,包括MAPK级联反应和CDPKs介导的信号转导[86-87]。
过表达AtCPK1可诱导水杨酸积累和水杨酸调控的防御抗病基因的组成型表达,从而对病原体感染具有广谱保护作用[88]。当病原体感染拟南芥时,AtCPK5被快速激活并磷酸化NADPH氧化酶AtrbohD,激活植物防御机制;AtCPK5在exo70B1介导的自身免疫中也发挥重要作用[89-90]。OsCPK18-OsMPK5通路抑制防御相关基因表达,负调控水稻对稻瘟病的抗性,过表达OsCPK4可以提高水稻抗病性[91-92]。
4.4 CDPKs参与植物非生物胁迫反应
研究表明,干旱、高温、低温、盐胁迫均可引起CDPKs特异性表达[93]。通过对寒冷、干旱和盐胁迫条件下的水稻进行微阵列分析,发现6个OsCDPK基因(OsCPK4/10/12/13/15/21)表达上调,1个(OsCPK1)表达下调[5,94]。
干旱引发的植物细胞反应包括通过调节保卫细胞来诱导ABA介导的气孔运动、通过积累渗透物质调节渗透压、通过ROS稳态调节氧化损伤[95-96]。干旱条件下,OsCPK9过表达转基因植株,通过调节渗透压诱导气孔关闭,提高花粉活性和小穗育性[82];OsCPK10通过调节过氧化氢(H2O2)酶的积累和脂质过氧化水平,保护了细胞膜的完整性,提高了水稻对H2O2的解毒能力,增强了水稻的耐旱性[97]。
盐胁迫通过积累Na+和Cl+导致胞内离子不平衡,使植物发生氧化应激反应,同时还会增加植物体内ROS的产生[98]。AtCPK27和AtCPK12通过调节离子稳态和ROS稳态提高植株耐盐性[99-100]。OsCPK21与OsGF14e相互作用并在Tyr-138位点磷酸化OsGF14e,通过对OsGF14e的转录后调控来响应ABA信号和盐胁迫[101]。ZmCPK11通过调节Na+和K+的体内平衡以及稳定光系统Ⅱ来提高转基因拟南芥植株的耐盐性[102]。
CDPKs参与植物响应冷胁迫和热激反应。水稻OsCPK17以蔗糖合酶和质膜固有蛋白为底物,是冷应激反应所必需的[103];OsCPK24通过Ca2+信号通路,抑制谷氨酰胺多辛(OsGrx10),使其维持较高的谷胱甘肽水平和磷酸化状态,正调控水稻对冷胁迫的响应[104]。香蕉MaCDPK7是热激诱导的果实成熟和冷胁迫的正调控因子[105]。
5 CRKs的生物学功能
CRKs在调控植物生长发育、响应生物和非生物胁迫中发挥重要作用。
拟南芥crk5突变体根长和侧根数目减少,根的向重力性改变。研究表明AtCRK5通过磷酸化PIN2參与根的向重力性生长[37]。此外,研究发现连续光照使拟南芥crk1突变体出现严重的表型缺陷(侏儒症和萎黄病),暗示拟南芥CRK1可能参与了光调控的植物生长发育[42]。SlCRK6正调控番茄对Pst DC3000和核盘菌(Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)的调控[106]。
6 结语
截至目前,CDPKs的作用机制以及生物学功能等研究已相对成熟,但其底物的多样性还有待进一步发现。研究发现CDPKs与14-3-3蛋白间的调控关系十分复杂,但二者的交叉磷酸化调节机制以及这种调节作用对下游靶基因的影响还需要进一步探究;同时,关于二者是如何保持信号的特异性并引起特异性应答反应,目前也知之甚少,有望成为今后科学工作者致力研究的方向。
与CDPKs相比,CRKs生物学功能的信息非常有限。鉴于CRKs和CDPKs高度同源,希望该研究对CDPKs研究进展的总结,能够为相关科研工作者研究CRKs的功能提供思路和方向。
参考文献
[1] DODD A N,KUDLA J,SANDERS D.The language of calcium signaling[J].Annual review of plant biology,2010,61:593-620.
[2] XU W W,HUANG W C.Calciumdependent protein kinases in phytohormone signaling pathways[J].International journal molecular sciences,2017,18(11):2346-2361.
[3] HAMEL L P,SHEEN J,SEGUIN A.Ancient signals:Comparative genomics of green plant CDPKs[J].Trends in plant science,2014,19:79-89.
[4] HRABAK E M,CHAN C W,GRIBSKOV M,et al.The Arabidopsis CDPKSnRK superfamily of protein kinases[J].Plant physiology,2003,132(2):666-680.
[5] RAY S,AGARWAL P,ARORA R,et al.Expression analysis of calciumdependent protein kinase gene family during reproductive development and abiotic stress conditions in rice(Oryza sativa L.ssp.indica)[J].Molecular genetics and genomics,2007,278(5):493-505.
[6] BOUDSOCQ M,SHEEN J.CDPKs in immune and stress signaling[J].Trends in plant science,2013,18(1):30-40.
[7] MA P D,LIU J Y,YANG X D,et al.Genomewide identification of the maize calciumdependent protein kinase gene family[J].Applied biochemistry and biotechnology,2013,169(7):2111-2125.
[8] LI L B,YU D W,ZHAO F L,et al.Genomewide analysis of the calciumdependent protein kinase gene family in Gossypium raimondii[J].Journal of integrative agriculture,2015,14(1):29-41.
[9] ASANO T,TANAKA N,YANG G,et al.Genomewide identification of the rice calciumdependent protein kinase and its closely related kinase gene families:Comprehensive analysis of the CDPKs gene family in rice[J].Plant and cell physiology,2005,46(2):356-366.
[10] ZUO R,HU R B,CHAI G H,et al.Genomewide identification,classification,and expression analysis of CDPK and its closely related gene families in poplar(Populus trichocarpa)[J].Molecular biology reports,2013,40(3):2645-2662.
[11] WANG J P,XU Y P,MUNYAMPUNDU J P,et al.Calciumdependent protein kinase(CDPK)and CDPKrelated kinase(CRK)gene families in tomato:Genomewide identification and functional analyses in disease resistance[J].Molecular genetics and genomics,2016,291(2):661-676.
[12] CAI H Y,CHENG J B,YAN Y,et al.Genomewide identification and expression analysis of calciumdependent protein kinase and its closely related kinase genes in Capsicum annuum[J].Frontiers in plant science,2015,6:737.
[13] CHRISTODOULOU J,MALMENDAL A,HARPER J F,et al.Evidence for differing roles for each lobe of the calmodulinlike domain in a calciumdependent protein kinase[J].Journal of biological chemistry,2004,279(28):29092-29100.
[14] KLIMECKA M,MUSZYNSKA G.Structure and functions of plant calciumdependent protein kinases[J].Acta biochimica polonica,2007,54:219-233.
[15] DELORMEL T Y,BOUDSOCQ M.Properties and functions of calciumdependent protein kinases and their relatives in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].New phytologist,2019,224:585-604.
[16] HARPER J F,BRETON G,HARMON A.Decoding Ca2+ signals through plant protein kinases[J].Annual review of plant biology,2004,55(1):263-288.
[17] TAKAHASHI Y,ITO T.Structure and function of CDPK:A sensor responder of calcium[M]∥LUAN S.Coding and decoding of calcium signals in plants.Berlin:Springer,2011:129-146.
[18] ITO T,NAKATA M,FUKAZAWA J,et al.Phosphorylationindependent binding of 1433 to NtCDPK1 by a new mode[J].Plant signaling and behavior,2014,9(12):1-3.
[19] RUTSCHMANN F,STALDER U,PIOTROWSKI M,et al.LeCPKl,a calciumdependent protein kinase from tomato,Plasma membrane targeting and biochemical characterization[J].Plant physiology,2002,129(1):156-168.
[20] NEMOTO K,TAKEMORI N,SEKI M,et al.Members of the plant CRK superfamily are capable of transand autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues[J].The Journal of biological chemistry,2015,290(27):16665-16677.
[21] KUDLA J,BATISTIC O,HASHIMOTO K.Calcium signals:The lead currency of plant information processing[J].The plant cell,2010,22:541-563.
[22] LIESE A,ROMEIS T.Biochemical regulation of in vivo function of plant calciumdependent protein kinases(CDPK)[J].Biochimica et biophysica acta(BBA)molecular cell research,2013,1833(7):1582-1589.
[23] BENDER K W,BLACKBURN R K,MONAGHAN J,et al.Autophosphorylationbased calcium(Ca2+)sensitivity priming and Ca2+/calmodulin inhibition of Arabidopsis thaliana Ca2+dependent protein kinase 28(CPK28)[J].Journal of biological chemistry,2017,292(10):3988-4002.
[24] POPESCU S C,POPESCU G V,BACHAN S,et al.Differential binding of calmodulinrelated proteins to their targets revealed through highdensity Arabidopsis protein microarrays[J].Proceedings of the national academy of sciences,2007,104(11):4730-4735.
[25] WANG Y,LIANG S,XIE Q G,et al.Characterization of a calmodulinregulated Ca2+dependentproteinkinaserelated protein kinase,AtCRK1,from Arabidopsis[J].Biochemical journal,2004,383:73-81.
[26] MATSCHI S,WERNER S,SCHULZE W X,et al.Function of calciumdependent protein kinase CPK28 of Arabidopsis thalianain plant stem elongation and vascular development[J].The plant journal,2013,73(6):383-396.
[27] TENG H J,GUO Y,WANG J Q,et al.WDRP,a DWD protein component of CUL4based E3 ligases,acts as a receptor of CDPKrelated protein kinase 5 to mediate kinase degradation in Arabidopsis[J].Journal of plant biology,2016,59:627-638.
[28] 樊莉娟,陳彩丽,朱旭辉,等.拟南芥AtTR1对AtCPK 28和AtCPK 32的体外泛素化修饰研究[J].四川大学学报(自然科学版),2017,54(3):617-622.
[29] 邓亚男,刘志斌,王健美,等.过表达E3泛素连接酶ABRvl通过泛素化CPK3提高拟南芥干旱耐受[J].四川大学学报(自然科学版),2018,55(3):613-618.
[30] YOON G M,CHO H S,HA H J,et al.Characterization of NtCDPK1,a calciumdependent protein kinase gene in Nicotiana tabacum,and the activity of its encoded protein[J].Plant molecular biology,1999,39(5):991-1001.
[31] ZHAO R,SUN H L,MEI C,et al.The Arabidopsis Ca2+dependent protein kinase CPK12 negatively regulates abscisic acid signaling in seed germination and postgermination growth[J].New phytologist,2011,192(1):61-73.
[32] MYERS C,ROMANOWSKY S M,BARRON Y D,et al.Calciumdependent protein kinases regulate polarized tip growth in pollen tubes[J].The plant journal,2009,59(4):528-539.
[33] GUTERMUTH T,LASSIG R,PORTES M T,et al.Pollen tube growth regulation by free anions depends on the interaction between the anion channel SLAH3 and calciumdependent protein kinases CPK2 and CPK20[J].The plant cell,2013,25(11):4525-4543.
[34] MORI I C,MURATA Y,YANG Y Z,et al.CDPKs CPK6 and CPK3 function in ABA regulation of guard cell Stype anionand Ca2+permeable channels and stomatal closure[J].PLoS Biology,2006,4(10):1749-1762.
[35] ZHANG Q P,WEN L,WANG F,et al.Cloning and expression analysis of calciumdependent protein kinase BnCDPKl in Brassica[J].Journal of plant genetic resources,2014,15(6):1320-1326.
[36] LECLERCQ J,RANTY B,SANCHEZBALLESTA M T,et al.Molecular and biochemical characterization of LeCRK1,a ripeningassociated tomato CDPKrelated kinase[J].Journal of experimental botany,2004,56(409):25-35.
[37] RIG G,AYAYDIN F,TIETZ O,et al.Inactivation of plasma membranelocalized CDPK related kinase 5 decelerates PIN2 exocytosis and root gravitropic response in Arabidopsis[J].The plant cell,2013,25(5):1592-1608.
[38] SIMEUNOVIC A,MAIR A,WURZINGER B,et al.Know where your clients are:Subcellular localization and targets of calciumdependent protein kinases[J].Journal of experimental botany,2016,67(13):3855-3872.
[39] RESH M D.Trafficking and signaling by fattyacylated and prenylated proteins[J].Nature chemical biology,2006,2(11):584-590.
[40] STAEL S,BAYER R G,MEHLMER N,et al.Protein Nacylation overrides differing targeting signals[J].FEBS Letters,2011,585:517-522.
[41] MEHLMER N,WURZINGER B,STAEL S,et al.The Ca2+dependent protein kinase CPK3 is required for MAPKindependent saltstress acclimation in Arabidopsis[J].The plant journal,2010,63(3):484-498.
[42] BABA A I,RIG G,AYAYDIN F,et al.Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana CDPKrelated kinase family:AtCRK1 regulates responses to continuous light[J].International journal of molecular sciences,2018,19(5):1282.
[43] MAJERAN W,LE CAER J P,PONNALA L,et al.Targeted profiling of A.thaliana subproteomes illuminates new co and posttranslationally Nterminal myristoylated proteins[J].The plant cell,2018,30(3):543-562.
[44] DIXIT A K,JAYABASKARAN C.Phospholipid mediated activation of calcium dependent protein kinase 1(CaCDPK1)from chickpea:A new paradigm of regulation[J].PLoS One,2012,7(12):1-8.
[45] CAMONI L,HARPER J F,PALMGREN M G.1433 proteins activate a plant calciumdependent protein kinase(CDPK)[J].FEBS Letters,1998,430:381-384.
[46] VAN KLEEFF P J M,GAO J,MOL S,et al.The Arabidopsis GORK K+channel is phosphorylated by calciumdependent protein kinase21(CPK21),which in turn is activated by 1433 proteins[J].Plant physiology and biochemistry,2018,125:219-231.
[47] LACHAUD C,PRIGENT E,THULEAU P,et al.1433regulated Ca2+dependent protein kinase CPK3 is required for sphingolipidinduced cell death in Arabidopsis[J].Cell death and differentiation,2013,20:209-217.
[48] SWATEK K N,WILSON R S,AHSAN N,et al.Multisite phosphorylation of 1433 proteins by calciumdependent protein kinases[J].Biochemical journal,2014,459:15-25.
[49] ORMANCEY M,THULEAU P,MAZARS C,et al.CDPKs and 1433 proteins:Emerging duo in signaling[J].Trends in plant science,2017,22:263-272.
[50] IVASHUTA S,LIU J Y,LIU J Q,et al.RNA interference identifies a calciumdependent protein kinase involved in Medicago truncatula root development[J].The plant cell,2005,17(11):2911-2921.
[51] YAMAUCHI T,YOSHIOKA M,FUKAZAWA A,et al.An NADPH oxidase RBOH functions in rice roots during lysigenous aerenchyma formation under oxygendeficient conditions[J].The plant cell,2017,29(4):775-790.
[52] YANG D H,HETTENHAUSEN C,BALDWIN I T,et al.Silencing Nicotiana attenuata calciumdependent protein kinases,CDPK4 and CDPK5,strongly upregulates woundand herbivoryinduced jasmonic acid accumulations[J].Plant physiology,2012,159(4):1591-1607.
[53] LEE S S,CHO H S,YOON G M,et al.Iteraction of NtCDPK1 calciumdependent protein kinase with NtRpn3 regulatory subunit of the 26S proteasome in Nicotiana tabacum[J].The plant journal,2003,33(5):825-840.
[54] WU Y X,ZHAO S J,TIAN H,et al.CPK3phosphorylated RhoGDI1 is essential in the development of Arabidopsis seedlings and leaf epidermal cells[J].Journal of experimental botany,2013,64(11):3327-3338.
[68] HO S L,HUANG L F,LU C A,et al.Sugar starvationand GAinducible calciumdependent protein kinase 1 feedback regulates GA biosynthesis and activates a 1433 protein to confer drought tolerance in rice seedlings[J].Plant molecular biology,2013,81(4/5):347-361.
[69] ABBASI F,ONODERA H,TOKI S,et al.OsCDPK13,a calciumdependent protein kinase gene from rice,is induced by cold and gibberellin in rice leaf sheath[J].Plant molecular biology,2004,55(4):541-552.
[70] ZHANG M,LIANG S,LU Y T.Cloning and functional characterization of NtCPK4,a new tobacco calciumdependent protein kinase[J].Biochimica et biophysica acta(BBA)Gene structure and expression,2005,1729(3):174-185.
[71] LU B B,DING R X,ZHANG L,et al.Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel calciumdependent protein kinase gene IiCPK2 Responsive to polyploidy from tetraploid Isatis indigotica[J].Journal of biochemistry and molecular biology,2006,39(5):607-617.
[72] RIETZ S,DERMENDJIEV G,OPPERMANN E,et al.Roles of Arabidopsis patatinrelated phospholipases a in root development are related to auxin responses and phosphate deficiency[J].Molecular plant,2010,3(3):524-538.
[73] SANTIN F,BHOGALE S,FANTINO E,et al.Solanum tuberosum StCDPK1 is regulated by miR390 at the posttranscriptional level and phosphorylates the auxin efflux carrier StPIN4 in vitro,a potential downstream target in potato development[J].Physiologia plantarum,2017,159(2):244-261.
[74] ZHANG X L,QI M F,XU T,et al.Proteomics profiling of ethyleneinduced tomato flower pedicel abscission[J].Journal of proteomics,2015,121:67-87.
[75] HUANG S J,CHANG C L,WANG P H,et al.A type III ACC synthase,ACS7,is involved in root gravitropism in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].Journal of experimental botany,2013,64(14):4343-4360.
[76] HETTENHAUSEN C,YANG D H,BALDWIN I T,et al.Calciumdependent protein kinases,CDPK4 and CDPK5,affect early steps of jasmonic acid biosynthesis in Nicotiana attenuate[J].Plant signal and behavior,2013,8(1):83-85.
[77] MATSCHI S,HAKE K,HERDE M,et al.The calciumdependent protein kinase CPK28 regulates development by inducing growth phasespecific,spatially restricted alterations in jasmonic acid levels independent of defense responses in Arabidopsis[J].The plant cell,2015,27(3):591-606.
[78] RONZIER E,CORRATGEFAILLIE C,SANCHEZ F,et al.CPK13,a noncanonical Ca2+dependent protein kinase,specifically inhibits KAT2 and KAT1 shaker K+ channels and reduces stomatal opening[J].Plant physiology,2014,166(1):314-326.
[79] ZHANG H F,LIU D Y,YANG B,et al.Arabidopsis CPK6 positively regulates ABA signaling and drought tolerance through phosphorylating ABAresponsive elementbinding factors[J].Journal of experimental botany,2020,71(1):188-203.
[80] CHEN D H,LIU H P,LI C L.Calciumdependent protein kinase CPK9 negatively functions in stomatal abscisic acid signaling by regulating ion channel activity in Arabidopsis[J].Plant molecular biology,2019,99(1/2):113-122.
[81] ASANO T,HAYASHI N,KOBAYASHI M,et al.A rice calciumdependent protein kinase OsCPK12 oppositely modulates saltstress tolerance and blast disease resistance[J].The plant journal,2012,69(1):26-36.
[82] WEI S Y,HU W,DENG X M,et al.A rice calciumdependent protein kinase OsCPK9 positively regulates drought stress tolerance and spikelet fertility[J].BMC Plant Biology,2014,14(1):1-13.
[83] ASANO T,HAKATA M,NAKAMURA H,et al.Functional characterisation of OsCPK21,a calciumdependent protein kinase that confers salt tolerance in rice[J].Plant molecular biology,2011,75(1/2):179-191.
[84] BOLLER T,HE S Y.Innate immunity in plants:an arms race between pattern recognition receptors in plants and effectors in microbial pathogens[J].Science,2009,324(5928):742-744.
[85] WANG J Y,WANG S Z,HU K,et al.The kinase OsCPK4 regulates a buffering mechanism that finetunes innate immunity[J].Plant physiology,2018,176(2):1835-1849.
[86] BOUDSOCQ M,WILLMANN M R,MCCORMACK M,et al.Differential innate immune signalling via Ca2+ sensor protein kinases[J].Nature,2010,464:418-422.
[87] TENA G,BOUDSOCQ M,SHEEN J.Protein kinase signaling networks in plant innate immunity[J].Current opinion in plant biology,2011,14(5):519-529.
[88] COCA M,SAN SEGUNDO B.AtCPK1 calciumdependent protein kinase mediates pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis[J].The plant journal,2010,63(3):526-540.
[89] DUBIELLA U,SEYBOLD H,DURIAN G,et al.Calciumdependent protein kinase/NADPH oxidase activation circuit is required for rapid defense signal propagation[J].Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the United States of America,2013,110(21):8744-8749.
[90] LIU N,HAKE K,WANG W,et al.Calciumdependent protein kinase 5 associates with the truncated NLR protein TIRNBS2 to contribute to exo70B1mediated immunity[J].The plant cell,2017,29(4):746-759.
[91] XIE K B,CHEN J P,WANG Q,et al.Direct phosphorylation and activation of a mitogenactivated protein kinase by a calciumdependent protein kinase in rice[J].The plant cell,2014,26(7):3077-3089.
[92] BUND M,COCA M.Enhancing blast disease resistance by overexpression of the calciumdependent protein kinase OsCPK4 in rice[J].Plant biotechnology journal,2016,14(6):1357-1367.
[93] SCHULZ P,HERDE M,ROMEIS T.Calciumdependent protein kinases:hubs in plant stress signaling and development[J].Plant physiology,2013,163(2):523-530.
[94] DAS R,PANDEY G.Expressional analysis and role of calcium regulated kinases in abiotic stress signaling[J].Current genomics,2010,11(1):2-13.
[95] SINGH A,SAGAR S,BISWAS D K.Calcium dependent protein kinase,a versatile player in plant stress management and development[J].Critical reviews in plant sciences,2017,36:336-352.
[96] FOYER C H,NOCTOR G.Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling:A metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses[J].The plant cell,2005,17:1866-1875.
[97] BUND M,COCA M.Calciumdependent protein kinase OsCPK10 mediates both drought tolerance and blast disease resistance in rice plants[J].Journal of experimental botany,2017,68(11):2963-2975.
[98] ABDELGAWAD H,ZINTA G,HEGAB M M,et al.High salinity induces different oxidative stress and antioxidant responses in maize seedlings organs[J].Frontiers in plant science,2016,7:276.
[99] ZHAO R,SUN H L,ZHAO N,et al.The Arabidopsis Ca2+dependent protein kinase CPK27 is required for plant response to saltstress[J].Gene,2015,563:203-214.
[100] ZHANG H L,ZHANG Y N,DENG C,et al.The Arabidopsis Ca2+dependent protein kinase CPK12 is involved in plant response to salt stress[J].International journal of molecular sciences,2018,19(12):1-17.
[101] CHEN Y X,ZHOU X J,CHANG S,et al.Calciumdependent protein kinase 21 phosphorylates 1433 proteins in response to ABA signaling and salt stress in rice[J].Biochemical and biophysical research communications,2017,493(4):1450-1456.
[102] BORKIEWICZ L,POLKOWSKAKOWALCZYK L,CIES'LA J,et al.Expression of maize calciumdependent protein kinase(ZmCPK11)improves salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants by regulating sodium and potassium homeostasis and stabilizing photosystem II[J].Physiologia plantarum,2020,168(1):38-57.
[103] ALMADANIM M C,ALEXANDRE BRUNO M,ROSA MARGARIDA T G,et al.Rice calciumdependent protein kinase OsCPK17 targets plasma membrane intrinsic protein and sucrosephosphate synthase and is required for a proper cold stress response[J].Plant,cell and environment,2017,40(7):1197-1213.
[104] LIU Y,XU C J,ZHU Y F,et al.The calciumdependent kinase OsCPK24 functions in cold stress responses in rice[J].Journal of integrative plant biology,2018,60(2):173-188.
[105] WANG H B,GONG J J,SU X G,et al.MaCDPK7,a calciumdependent protein kinase gene from banana is involved in fruit ripening and temperature stress responses[J].The journal of horticultural science and biotechnology,2017,92:240-250.
[106] WANG J P,XU Y P,MUNYAMPUNDU J P,et al.Calciumdependent protein kinase(CDPK)and CDPKrelated kinase(CRK)gene families in tomato:Genomewide identification and functional analyses in disease resistance[J].Molecular genetics and genomics,2016,291(2):661-676.
