Introduction Performance of New Labor-saving Grape Variety Miguang in Southern Guangxi and Its Two-harvest-a-year Cultivation Technique
2020-09-01JiayuHANYingZHANGXiongjunCAORongrongGUOLingLINChangfuCHENG
Jiayu HAN, Ying ZHANG, Xiongjun CAO, Rongrong GUO, Ling LIN, Changfu CHENG
Grape and Wine Research Institute, Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Nanning 530007, China
Abstract In order to alleviate the difficulty of labor employment for grape cultivation Guangxi, Nanning Comprehensive Experiment Station of China Grape Industry Technology System introduced the labor-saving variety Miguang, made an observation and record of the botanical characteristics, fruit traits, phenology, disease resistance, and yield of the new grape variety. Finally, it summarized the two-harvest-a-year cultivation technique of the labor-saving grape variety Miguang.
Key words Labor-saving grape, Miguang, Two-harvest-a-year, Introduction
1 Introduction
At present, the main grape varieties planted in Guangxi are Shine-Muscat Grape, Xiahei, Kyoho (Jufeng) Grape,etc. These varieties need too much labor in several key stages, and it is difficult to achieve the goal of high efficiency[1]. In recent years, a large amount of labor has been exported from Guangxi, and grape cultivation is dominated by middle-aged and elderly men and women. The labor efficiency is not high and the labor force is becoming increasingly short. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to introduce grape varieties that save labor and are easy for flowering. Miguang grape is a hybrid of European and American hybrids cultivated by Chinese scholars Zhao Shengjianetal. in 2003 with Kyoho as the female parent and Zaoheibao as the male parent. It has a beautiful bunch shape, thinning-free, does not need plant growth regulator, has large berries, the appearance is beautiful, the quality is excellent, the management is labor-saving, belongs to the middle-early maturing variety. Its traits have relatively high stability, and the indicators are also outstanding[2]. In 2014, Miguang grape variety was approved by Hebei Province with the number of Hebei SSV-VV-020-2013. Nanning Comprehensive Experiment Station of China Grape Industry Technology System introduced it to Mingyang Double-harvest Vineyard Variety Area Experimental Orchard of Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences in 2016 and carried out the two-harvest-a-year cultivation technique research.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 General situation of experimental siteThe experiment was performed in Mingyang Double-harvest Vineyard Demonstration Base of Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences. In February, 2016, it introduced and cultivated 2 667 m2of Miguang grape with a plant row spacing of 3 m×6 m. The experimental site is 64.2 m above sea level, with an average annual temperature of 22 ℃, annual sunshine 1 617.3 h, annual rainfall of 1 240.7 mm, soil organic matter 1.89%, pH 6.22, total nitrogen 0.135%, total phosphorus 0.064%, and total potassium 0.838%. In 2017, Miguang grapes started fruiting.
2.2 Experimental methodsSelected three normal-growing Miguang grapes, and observed the phenological period of the variety for three consecutive years starting in February 2017, and made a systematical observation for its field botanical traits[3]. At the maturity stage, conducted research and analysis of fruit quality and related indicators. Randomly selected 30 grape plants, counted the number of grape bunches, then randomly selected 10 clusters of large, medium and small bunches, calculated the average single bunch weight, and calculated the yield per hectare according to the row spacing of the plants. The organic acid content and soluble solid content of the fruit were determined using ATAGOD’s PAL-BXIACID2 sugar acid analyzer. Percentage of woody shoots(%)=Number of woody shoots/Number of bud burst×100; Percentage of bearing shoots(%)=Number of bearing shoots/Number of woody shoots×100.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Botanical traitsMiguang grape belongs to European and American varieties. The tips of the young shoots are half-open, anthocyanin intensity is medium, young leaves are reddish, mature leaves are green, upper and lower sides are covered with medium dense prostrate hairs. Leaf is cordate, medium, 5 lobes, upper sinuses are deep, the base is elliptic, and lower sinuses is shallow to medium deep. The sex of flower is hermaphrodite and diploid. The vigor of plant growth is strong, the maturity of woody shoot is high.
3.2 Fruit traitsThe first-crop fruit of Miguang grape has dense bunch, round berry, crisp berry skin, and purple black berry. The flesh is moderately sweet and sour, crisp, has a strong muscat flavor, and has no cracked fruit. The single bunch weight is 700.28-730.56 g, berry width is 2.01-2.26 cm, berry length is 1.98-2.11 cm, and single berry weight is 8.63-9.18 g. The maximum single bunch weight is 923.13 g, and the maximum single berry weight is 12.5 g. The second-crop fruit of Miguang grape has round berry, crisp berry skin, and purple red berry. The flesh is moderately sweet and sour, crisp, has a strong muscat flavor. The average single bunch weight is 655.40-684.96 g, the average berry width is 1.86-1.89 cm, and the average berry length is 1.78-1.83 cm, average single berry weight is 8.39-8.91 g, maximum single bunch weight is 750.25 g, and maximum single berry weight is 11.3 g. According to the 3-year data, the single bunch weight of the second-crop grape is slightly less than that of the first-crop grape, the muscat flavor is more intense than the first-crop grape, the skin color is darker than the first-crop grape, the soluble solids are significantly higher than the first-crop grape, but organic acid content is higher than the first-crop grape, and the solid acid ratio is lower (Table 1).

Table 1 Fruit traits and yield of two crops of Miguang grape in Nanning in different years
3.3 Growth and bearing habitsThe first bunch of Miguang grape is generally in the fourth and fifth nodes, and the second bunch is mainly in the fifth and sixth nodes. For the first-crop fruit, the percentage of bud burst is 83.5%-89.82%, the percentage of woody shoots is 94.15%-98.87%, the percentage of bearing shoots is 90.15%-92.68%, and the bearing coefficient is 1.74-1.89. For the second-crop fruit, the percentage of bud burst is 84.37%-89.60%, the percentage of woody shoots is 90.78%-94.35%, the percentage of bearing shoots is 91.35%-93.23%, and the bearing coefficient is 1.33-1.42. These indicate that the bearing coefficient of the second-crop fruit is lower than that of the first-crop fruit (Table 2).
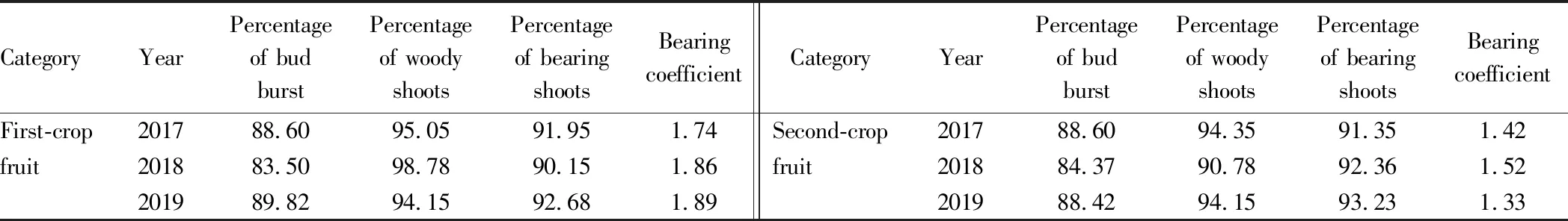
Table 2 Growth and bearing habits of Miguang grape in Nanning in different years %
3.4 Phenological periodIn Nanning, Miguang grape started bud burst in February and flowered in mid-March. The fruits gradually began to change color in mid-May and matured in the following month. In the first half of August, the second crop was pruned and germination was carried out according to the relevant specifications. In the next month, it bloomed and the fruit matured in December. Generally, the beginning date of woody maturity is in June. On the whole, the first-crop fruit takes about 130 d from the bud burst to the maturity, and the second-crop fruit takes about 120 d (Table 3).
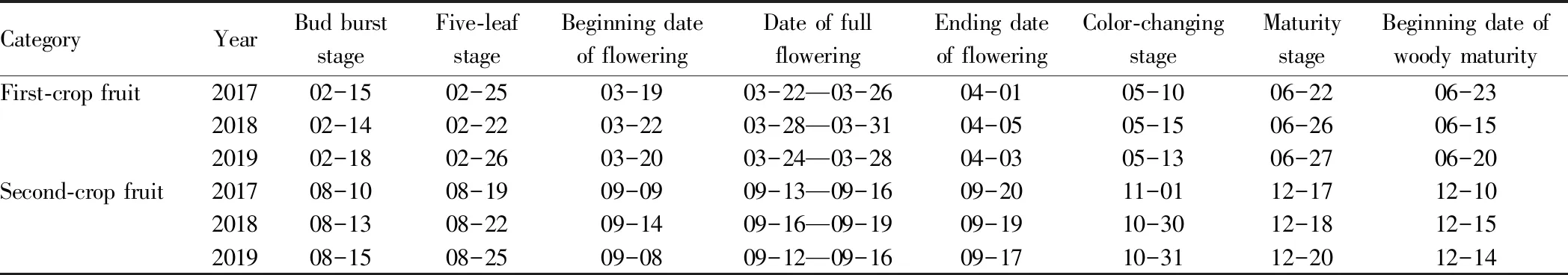
Table 3 Phenological period of Miguang grape in Nanning in different years (month-day)
3.5 Disease resistanceMiguang grape is a very typical European and American hybrid, and its disease resistance is similar to other European and American varieties planted in Nanning. During these four years of introduction and observation, various diseases were observed and recorded. Among them, the representative ones include gray mould, Thrips,etc. It was found that there was no difference from other grape varieties, but the red spider damage of the second crop is more serious, and it is necessary to strengthen prevention and control in key stages.
3.6 Comprehensive evaluationThe biggest characteristic of Miguang grape is that it does not need any growth regulator treatment, it is free of fruit preservation, and does not need fruit thinning. The berry size is uniform, clusters are natural, and it has strong muscat flavor. Miguang grape has strong disease resistance, relatively long fruit-bearing period, dense bunches, and can be transported for long distances. It is an ideal medium-early maturing variety for grape replacement. It can be cultivated according to the conditions of various regions for cultivation and has good promotion value.
4 Main points of two-harvest-a-year cultivation technique
4.1 Orchard construction and field plantingIt is necessary to choose sandy loam soil with good drainage and irrigation conditions and moderate soil acidity and alkalinity to build grape orchard, and try to avoid building orchard on contaminated plots. Before planting, dig a 80 cm × 80 cm × 70 cm planting hole, and then mix organic fertilizer: organic matter: soil into the planting hole at the ratio of 1∶1∶1. Before planting, the seedlings should be kept with 2-4 strong shoots and trimmed. The base roots can generally be left at 10 cm. The injured roots are cut at the wounded area. If the seedlings are relatively dry, soak them in clean water for one day. Seedlings should be planted as soon as they are ready. If they cannot be planted quickly, they should be covered with wet sacks or grass curtains. In order to reduce the spread of diseases and insect pests, especially quarantine pests, two-way disinfection is advocated, that is, seedling producers are required to disinfect seedlings before selling seedlings and users should disinfect them before planting. It is necessary to soak seedlings in higher concentrations of insecticides (such as phoxim) and fungicides (select targeted agents according to the main diseases in seedling supply areas) for half an hour, soak and rinse in clean water; ABT-3 rooting powder may be used to for soaking root system to improve rooting quantity and survival rate. When planting, placed the seedlings into the hole, which can be compacted with fertile topsoil, and raised by hand to make the roots stretch easily. When grafting seedlings, the grafting interface should be about 15 cm above the ground when planting, to avoid the scion rooting. Immediately after planting, water fully to increase the survival rate. After water seeping fully, fill the planting hole or cover with black mulch with soil between rows to moisturize and avoid weeding.
4.2 Pruning and germination technique for two-harvest-a-year cultivationAt 7-10 d before pruning, the second-crop fruit of Miguang grape can be sprayed with 300 times solution of Ethephon+500 times solution of standard (sulfur) to promote leaf yellowing and nutrient return, and irrigate with high nitrogen water soluble fertilizer (such as urea) once 30-60 kg/ha, and irrigate once a day to keep the soil moist and promote the growth of the root system, so as to facilitate uniform germination. Around late July, prune the bud eyes at the 6-9th nodes of bearing branches, and add 50% monocyanamide 40 times solution to the double-strength 6 000 times solution, and spray the cut-out bud eyes with a highly atomized sprayer. The pruning of the second-crop fruit is to prune 8-10 buds from the mother branch of the current year, and when using the dormancy breaking agent, only apply the agent to one bud of the top bud of the bearing branch, to promote it germinate, and the remaining buds on the branch are reserved for the bearing in the second year[4]. After promoting germination, continue irrigate little one time daily, to keep the soil moist till the bud burst.
4.3 Management of grape trellis and branchesMiguang grapes are cultivated in a straight line, with a north-south direction, trellis height is 1.9 m, and a plant row spacing of 3 m×6 m. Use bamboo to lead a single vine of the seedlings to grow upright. It is topped 20 cm below the trellis, leaving the top 2 vines on the trellis, both are topped at 60 cm, top 3 times continuously, to promote the growth of lateral buds. Top at 4-5 leaves of side buds for 3 times continuously, and remove remaining lateral shoots in time. For the new bearing shoots of the second-crop fruit, top at 6 leaves, keep one leaf of the lateral shoots, and keep 2-3 leaves of the lateral shoots for bunch node, and nutrition branches should be topped when grown to 8 leaves[5].
4.4 Bunch managementSince this variety is naturally fruiting, it does not need swelling agent, and greatly saves labor cost. It only needs flower thinning during the florescence. For the first-crop fruit, each bearing shoot keeps 1-2 bunches; for the second-crop fruit, each bearing shoot keeps one bunch, and the excess bunches should be should be removed manually. It is necessary to strictly control the yield to ensure the quality. At 3-4 h before bagging, spray Azoxystrobin, Cabrio, and Baobeigai one time.
4.5 Fertilizer and water managementAt seedling stage, apply the base fertilizer to completely decompose the organic manure, spray one time foliar fertilizer once every 5 d (alternately using COMPO foliar fertilizer and Nongjiufu). After the second year, it is necessary to apply fertilizer four times of during the growth cycle. The first fertilization is in the germination period, this time urea+high potassium water-soluble compound fertilizer is mainly adopted. The second fertilization is generally before the beginning of the flowering period. According to the situation, fertilizers mainly are N, P, K ternary compound fertilizer, water-soluble calcium fertilizer, to improve the speed of flowering. The third fertilization is completed during the fruit enlargement period, and some supplementary fertilizers are applied to increase the rate of fruit de-velopment. The last fertilization is completed before the color change period. At this time, spray Tenongjiufu+Guoshimei to grape roots, and spray potassium dihydrogen phosphate on the leaves to promote color change.
During cultivation of the second-crop fruit, the first fertilization is implemented with 15 t/ha biological organic fertilizer after harvesting of the first-crop fruit; the second fertilization is taken with 37.5 kg/ha of calcium magnesium phosphorus compound fertilizer at the inflorescence elongation period; the third to fifth fertilization should be the same as that for the first-crop fruit. During the cultivation management period, irrigate in combination with the fertilization at the germination period, around the beginning of flowering, and fruit expansion period for both the first-crop fruit and second-crop fruit. From the color changing to the maturity stage, strictly control the water to keep the soil moderately dry, and properly irrigate according to actual moisture condition for other stages.
4.6 Prevention and control of plant diseases and pestsThe disease resistance of this variety is not much different from most European and American grape varieties. In Nanning, attention should be paid to gray mould, powdery mildew, and anthracnose around the flowering period, and prevent and control other common diseases of grape during other stages.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Comparative Analysis of Semen between Debao Pony and American Pearl Pony
- Effect of Different Inoculation Methods on Pathogenicity of Fusarium proliferatum to Alfalfa
- Coupling Relationship between Integrated Land Consolidation and Farmland Scale Management in Villages over Coal Resources: A Case Study of Zezhou County in Shanxi Province
- Key Points of Breeding and Cultivation Techniques of Wushan Crisp Plum, a New Cultivar of Green Crisp Plum
- Return of Rural Migrants in Southwest China: An Empirical Study Based on 2010 Copies of Questionnaires
- Construction Approaches of Enterprise Innovation Network from the Perspective of Social Network
