Regenerative Therapeutic Applications of Mechanized Lipoaspirate Derivatives
2020-08-29ShaohengXIONGQiruiWANGLihongQIUJizhongYANGChenggangYI
Shaoheng XIONG ,Qirui WANG ,Lihong QIU ,Jizhong YANG ,Chenggang YI*
1 Department of Plastic Surgery,Xijing Hospital,Fourth Military Medical University,No.15 Changle Western Road,Xi'an,Shaanxi,710036,China
2 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital,Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine,639 Zhi Zao Ju Road,Shanghai,200011,China
SUMMARY Autologous adipose tissue is one of the most commonly used fillers.Plastic surgeons are increasingly using it in aesthetic or reconstructive surgery owing to its abundant source,easy availability,and minimal invasiveness.Increasing amount of evidence has shown its reparative ability rather than just filling utility due to the presence of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) that exhibit multipotential differentiation and paracrine characteristics.However,traditional enzymatic isolation of ADSCs is often difficult in clinical settings,limiting its application.Recently,with the development of mechanical techniques for preparation of lipoaspirates,bioactive adipose tissue can be successfully identified and isolated.Such components with therapeutic potential might also be helpful in tissue repair and regeneration.In this article,we introduced several types of mechanized lipoaspirates derivatives (such as emulsified fat,adipose extracellular matrix (ECM),and cell-free extraction) and their applications from bench to bedside.
KEY WORDS Adipose-derived stem cells; emulsified fat; extracellular matrix; cell-free extraction
INTRODUCTION
Since the fat tissue used for autologous fat transplantation is obtained from the target itself,there is no risk of allergic reaction and immune rejection,along with abundant sources,simple operation,easy access,excellent tissue compatibility,low damage to the donor area,low price,and reusability post-transplantation.Autologous fat presents with several advantages such as natural comfort for the patient,and is preferred by plastic surgeons as a filler.Further studies have revealed isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue,which were later termed as adipose stem cells.Some studies have found that fat stem cells have multidirectional differentiation ability,self-renewal ability,and paracrine function,and can secrete a variety of growth factors.At present,autologous fat is being increasingly used not for the filling but for regenerative therapy benefit due to the presence of abundant adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs)in it,which possess multipotential differentiation ability and paracrine function,and can secrete a variety of growth factors.
Compared within vitroADSC expansion,the preparation method of stromal vascular fraction (SVF) cells is simple and does not require anin vitroculture,expansion,and contact with animal serum,and thus,takes less time.However,the SVF prepared by the traditional enzyme digestion method has many shortcomings,which renders ADSCs useless in further regenerative medicine.Traditional enzymatical isolation of SVF cells often takes 30 min to 1 h for digestion,which may lead to biological contamination during the preparation.In addition,the purification of ADSCs is time-consuming and needs specific laboratory equipment,which would delay the treatment of patients.Since Tonnard invented ADSCs after mechanized fat treatment in 2013[1],he has found a clinically simple method for obtaining stem cells,which makes ADSCs more useful in clinical regenerative treatment.Moreover,recent studies have emphasized that mechanical stress could be effectively enhancing the secretion ability and change the phenotype of ADCSs that promote angiogenesis[2,3].So,the mechanical forces during the fat preparation processes may remarkably affect its regenerative properties.Further research has shown that other components in the adipose tissue after mechanical treatments,including the extracellular matrix(ECM) and liquid components,might also play a role in regenerative treatment.There are now a variety of mechanized fat derivatives that play an essential role in regenerative treatment.This article aims to introduce the regenerative applications of mechanized lipoaspirate derivatives.
EMULSIFIED FAT
Nanofat
Nanofat was a revolutionary product and was first obtained by Tonnard in 2013[1].The “nanofat” is a kind of a supermicrofat rather than a real nanoscale.Different scales of lipoaspirates (mainly divide into macrofat,microfat,and nanofat) could be prepared by using different side holes of the liposuction cannula.Macrofat was isolated by cannula with large side holes (3 mm in diameter),while microfat and nanofat are collected by cannulas with smaller side holes (no more than 1 mm in diameter).Moreover,compared to microfat,an additional mechanical emulsification procedure is required for to obtain nanofat.Specifically,the emulsified fat was prepared followed by 30 passes shifting,which was achieved by two 10 mL syringes and a Luer-Lok connector,and finally,the emulsified fat was filtered over a sterile nylon cloth to produce nanofat.During the preparation procedures,most of the mature adipocytes were destroyed,leaving the ADSCs and oil that could be smoothly injected intradermally using a 27-gauge needle.
However,the filtration process might partly reduce the viability and the amount of ADSCs,and without this procedure,which is so-called nanofat 2.0,there will be a higher density of ADSCs and a better proliferation ability of ADSCs.Besides,the faster cell proliferation capacity could be beneficial in more rapid tissue repair and regeneration[4].
Using this mechanical isolation technique,we could easily and quickly separate ADSCs in the operating room without extra collagenase,special device,or timeconsuming extractions compared to the traditional enzymatic isolation of SVFs.This technique could be feasible for fat grafting owing to its convenience and presence of abundant amount of ADSCs,which could subsequently take part in the grafts' neovascularization via direct differentiation and secretion of various growth factors,which,in turn,improves the outcomes of fat grafting[5].
Except for the regenerative capacity of ADSCs in nanofat,intradermal injection also helps in expanding its clinical applications,such as skin rejuvenation,scar treatment,and wound healing,as it could be conveniently performed by a 27-gauge needle compared to the traditional structural fat that is difficult to inject directly.Previous studies have found that the skin texture can be improved after the traditional fat transplantation,which could be owed to the regenerative ability of ADSCs.Nanofat could be used to improve skin quality for facial rejuvenation of delicate parts,such as eyelids,lips,and wrinkles[6-8].Breaking the balance of fibers within the ECM could lead to aging process,which is often associated with wrinkles,rough texture,and atrophy.In addition,ADSCs have been proved to restore collagen synthesis and decrease elastosis[9].It was found that nanofat helps increase dermis thickness and neovascularization in an animal skin photo-aging model[10].Concentrated nanofat with condensed ADSCs,obtained by simple centrifugation,could effectively enhance the therapeutic ability of traditional nanofat[11].Moreover,nanofat offers a unique advantage in the treatment of scars.Scar tissue contains a lot of fibrotic tissue,and its texture is hard.Hence,the injection needle should be fine enough to inject the fat into the scar.Nanofat can pass through the 27G needle smoothly and the contact area with the scar is relatively large after the injection.Previously,clinic treatment has shown that nanofat injection softened the scars and improved the scar quality and patient satisfaction[12].In addition,condensed nanofat-assisted fat grafting is suitable for correcting the aesthetic and function of facial atrophic scars[13].
Although nanofat has various beneficial features,there are still some limitations in its clinical applications.First,it is a suboptimal filler mainly because with the application of mechanical shear force during preparation,most of the adipocytes in nanofat are destroyed,which results in their limited filling capacity.A small amount of oil and cell fragments can restore tissue regeneration by inducing inflammation and releasing growth factors.Cell fragments and released oil in nanofat are primarily responsible for an intense inflammatory reaction,resulting in edema and fibrous hyperplasia,thus affecting its clinical application.Besides,compared with granular fat or particulate fat,there are fewer ADSCs in nanofat.Further clinical applications of nanofat may need to be condensed.
SVF-Gel
The ratio of ADSCs in nanofat is low,and the extra oil component could lead to unsatisfactory results.Besides,previous studies have proved that traditional SVF cell or ADSCs suspensions would tend to be eliminate by immune system due to the lack of ECM protection,which lead to the unsatisfactory tissue retention rate and limits its therapeutical efficacy.Centrifugation can separate most of the fats and oils produced during the mechanical process,but some of the fats are still in the form of tiny lipid droplets in the chyle in a stable state.Simple centrifugation cannot destroy this steady state,and even increasing the centrifugation speed is inefficient in separation of oil.To reduce the level of extra oil components,and condense the amount of ADSCs to improve the regenerative efficacy of mechanized fat,researchers have used the principle of flocculation and precipitation to break the internal balance of nanofat.Based on Tonnard's study,novel processing methods was developed that condense the regeneratable components(ECM and SVF cells) and significantly discard most of the lipid and other unwanted components and remarkably increasing the density of ADSCs.The final product was called “extra-cellular matrix/SVF gel.” In short,Coleman fat was emulsified slowly (10 mL/s for 1 min) by shifting and the emulsified fat was filtered through a 500-mm removable mesh,and finally, after centrifugation(2,000×g,3 min),and the lower sticky substance under the oil layer was so-called ECM/SVF-gel[14].They stated that any substance that was processed via their protocol and met the following criteria could be considered as ECM/SVF gel:(1) a final volume of less than 15% of the initial volume; (2) more than 4.0 × 105 cells/mL of SVF cell; and (3) the final product could be injected through a 27-gauge needle.
The mature fat cells in SVF-gel are almost completely destroyed,the oil is removed more extensively,and the ECM structure rich in vascular matrix fragments is relatively complete and highly concentrated.The average concentration of the SVF population can reach 4.5 times that of normal adipose tissue,while the amountof ADSCs was 6.3 times that of the original,and their multidirectional differentiation ability was not impaired.ECM,as a natural cell carrier,provides niches to SVF/ADSCs to ensure that ADSCs and other adherent cells are maintained at optimum condition for self-expansion and participation in tissue regeneration.Furthermore,
ECM can also protect ADSCs from being engulfed by macrophages in vivo,which ensures better cell survival rate.During SVF-gel preparation,although the fat cells are destroyed,the cell connection and ECM remain intact.
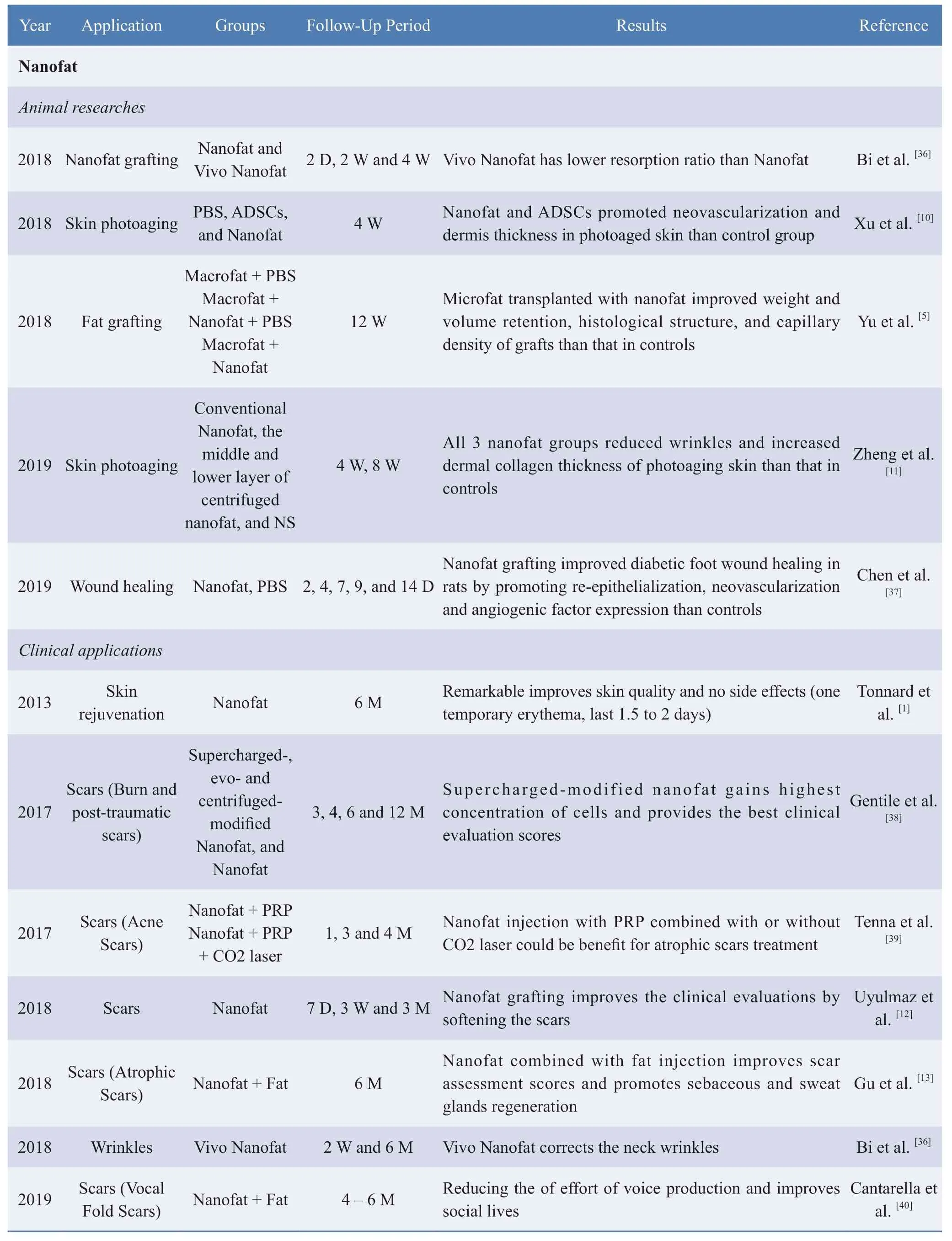
Table 1 The applications of Nanofat and ECM/SVF-gel from bench to bedsides
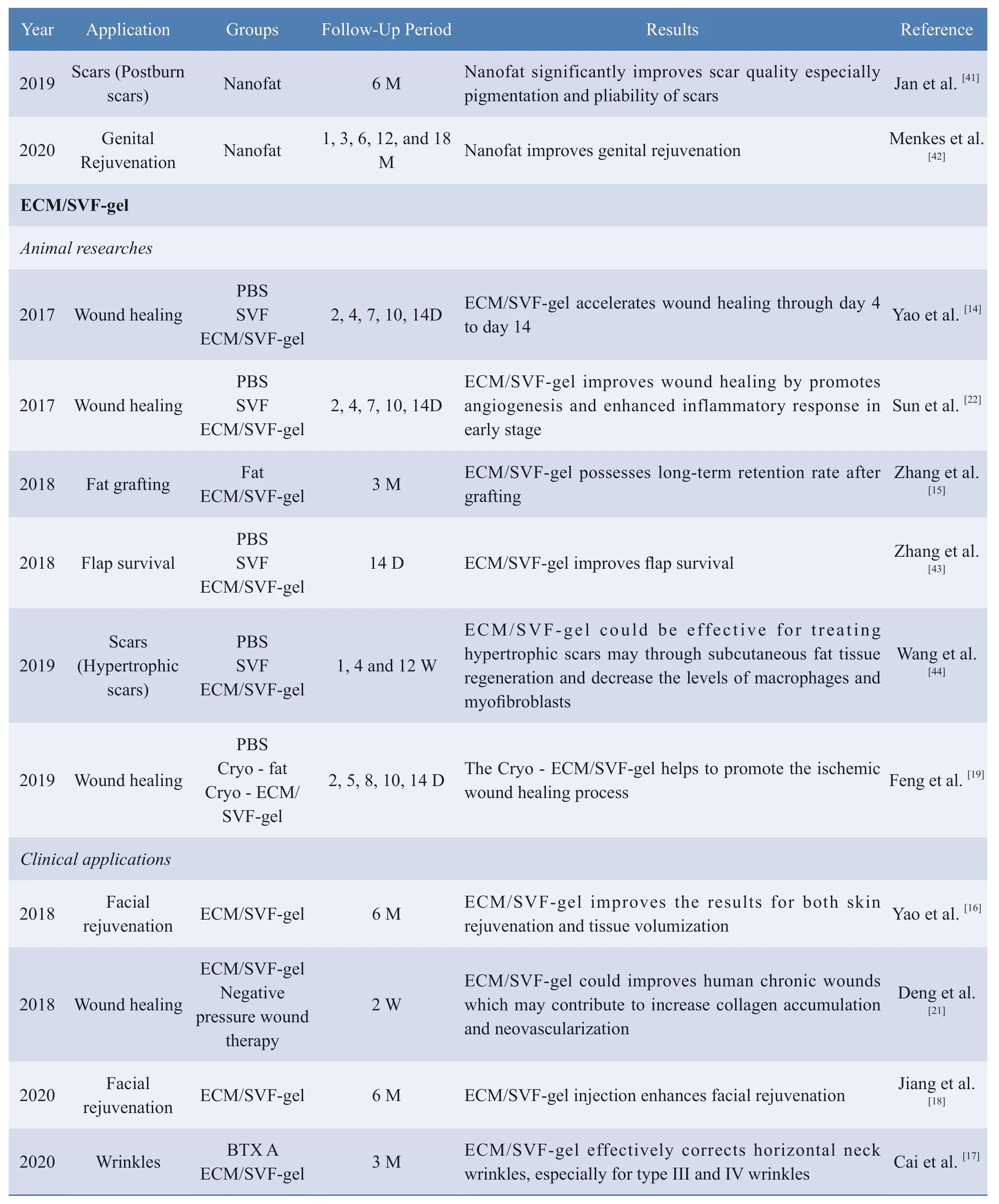
D,days; W:weeks; M:months; PBS,Phosphate Buffered Saline; ADSCs,Adipose derived stem cells; NS,Normal saline; PRP,Platelet rich plasma;ECM,Extracellular matrix; Cryo,Cryopreservation; BTX A,Botulinum toxin type A
SVF-gel has a filling function,and the same amount of SVF-gel and “standard Coleman” fat are injected into the back of nude mice.The former has a better longterm survival rate and gradually appears as normal fat tissue.Since mature adipocytes account for about 90%of the volume of adipose tissue,but the number of SVFs is less than 7%,after traditional fat transplantation,fragile mature adipocytes will be necrotic due to hypoxia,resulting in fat droplets occupying a large part of the graft,which hinders fat regeneration[15].SVF-gel is free of most of the “ineffective tissue” and fat,which facilitates complete stable tissue regeneration.However,during SVF-gel preparation,because the final fat volume is less than 15% of the original volume,it is impossible to prepare in large quantities,so it is currently only suitable for small area injections,such as facial filling[16-18],assisted-fat grafting[19],wound healing[20-22],and scar treatments[23].SVF-gel can promote the regeneration of subcutaneous adipose tissue and decrease the infiltrations of macrophages and myofibroblasts to inhibiting the proliferation of scar tissue.
After injection into the human body,SVF-gel has a low absorption rate and does not need to be over-injected.Compared with nano-fat,it can remove most of the invalid oil and cell debris,clearing the barrier of fat regeneration,and thus,can facilitate regeneration.SVFgel is ultra-concentrated nano-fat,whose preparation method is simple,and has both good regeneration and filling function.
CELL-FREE EXTRACTION
Fat Extract/Adipose Liquid Extract
More and more evidence have indicated that ADSCs play a role in regenerative therapy more because of their paracrine efficacy rather than direct differentiation[24].
ADSCs express multiple angiogenic factors,such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF),basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF),and transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-α)[25].It has been proved that ADSC-conditioned medium could improve the results of ischemic diseases[26].The clinical application of stem cells could be difficult because of some safety concerns.Thus,the cell-free therapy may be a viable alternative consideration.Moreover,recent study reveals that lipoaspirate covers abundant proangiogenic factors that can be directly applied without additional separation and purification[27].
Previous researches have demonstrated that nanofat contains a large number of cytokines and growth factor,which may account for its regenerative capabilities.However,the liquid fraction in it has always been ignored.The use of bioactive liquid fraction could theoretically avoid a series of problems such as the genetic stability of the collected cells,the efficacy and survival of the cells after grafting.Yu and colleagues have reported a kind of cell-free extraction.Briefly,rinsed lipoaspirate was centrifuged under 1200×g for 3 min,and the middle layer was obtained and emulsified.After one cycle of the freeze/thaw process,emulsified fat was centrifuged at 1200×g for 5 min.Collecting the third layer (fat extract,FE) and filtrating it through a 0.22-μm filter to remove tissue debris[28].Subsequent studies have proved that FE enhances the outcomes of fat transplantation which mainly contributes to its proangiogenic,anti-apoptotic and pro-proliferative effects on ADSCs[29].Besides,it can be used as a novel cell-free therapeutic strategy for a UVB-induced photoaging[30],and skin regeneration[31,32].
Another similar product named Adipose Liquid Extract(ALE) also shows therapeutic potential in tissue regeneration,and the ALE preparation method is similar to that of FE[33].ALE is a novel growth-factor-rich therapeutic agent that is cell-free and easy to produce.Besides,it is also able to induce angiogenesis and adipogenesis bothin vitroand in vivo,thus indicating that it could be used for wound repair and soft tissue regeneration.Still,more evidence are required to support its further clinical application.
Decellularized adipose tissue
Decellularized adipose tissue (DAT) provides scaffold material for tissue engineering to induce regeneration with the rapid development of tissue engineering technology.DAT is a bioactive ECM component obtained after the removal of fat and cellular components are removed from adipose tissue.DAT does not contain cellular components,can be allografted,and can be spontaneously induced into lipids in vivo,so it is considered to be ideal for soft tissue repair[34].It has already been proven to exhibit regenerative effects in both basic and clinical applications[35].
However,the limited in vivo adipogenic ability of DAT limits its wide clinical application,which is attributed to the loss and destruction of protein components in the ECM of adipocytes due to the use of several chemical reagents in the preparation process.Further studies are required to support the clinical applications of DAT.
CONCLUSION
Currently,autologous fat tissue is not only used as a filler but also as a regenerative material due to the presence of various bioactive components.Mechanical isolation methods have enabled to make it more operable in the clinic,and thus,have profoundly promoted its application in regenerative therapy.Still,more basic and clinical evidence is needed to support its application.
杂志排行
Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery的其它文章
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Axillary Web Syndrome:An Overview
- Biomaterial Scaffolds for Improving Vascularization During Skin Flap Regeneration
- A Case of Coexistence of Aplasia Cutis Congenita and Giant Congenital Melanocytic Nevus:Coexistence of Two Rare Skin Diseases
- Pedicled or Free Flap from Contralateral Breast for Autologous Breast Reconstruction
- A Novel Method for the Prenatal Diagnosis of Cleft Palate Based on Amniotic Fluid Metabolites
- Comprehensive Strategy for Keloid Treatment:Experience at Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital
