柑橘大实蝇NPC2基因的序列分析和组织表达模式
2020-08-25陈剑王兆祥杨岭叶海霞毛丽桂连友张国辉
陈剑 王兆祥 杨岭 叶海霞 毛丽 桂连友 张国辉

摘要 柑橘大实蝇是柑橘上的重要害虫,主要为害柑橘果实。NPC2是一种小分子蛋白,参与了脊椎动物的脂质代谢,最近有研究表明,NPC2有着类似于昆虫气味结合蛋白的功能,参与了昆虫的化学通讯。为了明确NPC2基因在柑橘大实蝇成虫组织中的分布,本研究从柑橘大实蝇转录组中,鉴定了NPC2基因,命名为BminNPC2。通过生物信息学方法分析了该基因序列特征并构建了系统进化树,采用实时荧光定量PCR技术研究了BminNPC2基因在柑橘大实蝇成虫组织中的表达模式。结果表明:BminNPC2基因开放阅读框为456 bp,编码151个氨基酸,等电点为6.10,分子量大小为16.66 kD,含有6个半胱氨酸。BminNPC2基因在柑橘大实蝇头部(去掉触角)和腹部表达量最高。据此结果我们在文中对BminNPC2基因功能进行了简要讨论。
关键词 柑橘大实蝇; NPC2基因; 序列分析; 组织表达模式
中图分类号: Q 966, S 436.66
文献标识码: A
DOI: 10.16688/j.zwbh.2019235
Sequence analysis and tissue expression pattern of Niemann-Pick type C2 gene in Bactrocera minax
CHEN Jian, WANG Zhaoxiang, YANG Ling, YE Haixia, MAO Li, GUI Lianyou, ZHANG Guohui*
(Institute of Entomology, College of Agriculture, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434025, China)
Abstract
Bactrocera minax, a major citrus pest, mainly damages citrus fruits. NPC2 is a type of small protein involved in lipid metabolism in vertebrates. Recent studies showed that NPC2s had the similar function to odorant binding proteins and participated in chemical communication of insects. In order to clarify the distribution of NPC2 gene in adult citrus flies, the NPC2 gene was obtained from B.minax through transcriptome analysis, which was named BminNPC2. The sequence characteristics of the NPC2 gene were analyzed using bioinformatics tools and a phylogenetic tree was generated to characterize the NPC2 gene. The tissue expression pattern of NPC2 gene was determined by the real-time PCR. The results showed that the open reading frame (ORF) of BminNPC2 was 456 bp in length, encoding 151 amino acid residues, with a deduced molecular weight (MW) of 16.66 kD and an isoelectric point (pI) of 6.10. It had six cysteines. The expression level of BminNPC2 gene in the head without antennae and abdomen was high. Based on these results, we briefly discussed the functions of BminNPC2 gene.
Key words
Bactrocera minax; Niemann-Pick type C2 gene; sequence analysis; tissue expression pattern
柑橘大實蝇Bactrocera minax俗称“柑蛆”,属双翅目,实蝇科,大实蝇亚属[1],是柑橘生产上的主要害虫[2]。该虫广泛分布于中国、尼泊尔、印度和不丹的柑橘产区[1,3-4],严重影响了柑橘果实的产量与品质[5]。在柑橘大实蝇大暴发的年份给果农带来了巨大的经济损失。目前在柑橘大实蝇防治的实践中,化学杀虫剂起着主导作用。然而,杀虫剂的频繁使用导致了柑橘大实蝇抗药性的出现,并对人类和其他生物产生了不可预见的副作用[6-7]。利用嗅觉诱捕成虫,是高效控制柑橘大实蝇种群的绿色环保手段[8-9]。在近些年的研究中,发现某些昆虫NPC2蛋白参与了嗅觉通讯[10-11]。NPC2蛋白(niemann-pick type C2 proteins)又称为HE1,属于ML(MD-2-related lipid-recognition)家族,是人类附睾的一种主要分泌蛋白,可与胆固醇结合,在随后的研究中,发现NPC2也存在于牛奶、胆汁、精液中[12-14]。
在脊椎动物的不同物种中,NPC2序列一致性达到55%以上,具有高度保守性,这说明在脊椎动物中,NPC2可能有着相同的生理功能:主要用于结合胆固醇和脂质。在节肢动物的不同物种中,NPC2行使着不同的功能,如日本弓背蚁CjapNPC2结合部分疏水化合物:长链脂肪酸、芳樟醇等[11];家蚕NPC2参与了抑制细胞增殖,促进甘油三酯在BmN4细胞中的积累过程[15]。目前有关果蝇NPC2的研究有两个方面:Huang等在果蝇中鉴定了8个NPC2基因(NPC2a-h),同时对其进行了功能研究,发现NPC2a与NPC2b在调节甾醇稳态和蜕皮激素生物合成方面存在冗余作用[16]。随后,Shi等研究表明NPC2e和NPC2a可能在免疫缺陷(Imd)通路中发挥作用[17]。前人的研究证明NPC2在动物中起着重要的生理作用,但是目前对柑橘大实蝇NPC2功能还一无所知,因此本文开展了柑橘大实蝇NPC2基因研究。
本研究首次从柑橘大实蝇转录组中鉴定了NPC2基因,并对其进行了序列分析。同时采用荧光定量PCR技术研究了NPC2基因的组织表达模式,丰富了NPC2基因家族成员,也为后续的分子克隆和体外表达奠定了基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
供试昆虫:本研究所用的柑橘大实蝇成虫为长江大学农学院昆虫化学生态实验室人工饲养种群[18]。收集1~3日龄雌雄成虫的触角、头(去掉触角)、胸、腹、足、翅等组织,每个组织样本收集自30头成虫(不同日龄成虫各10头),3次生物学重复。最后,收集好的样品保存于-80℃备用。
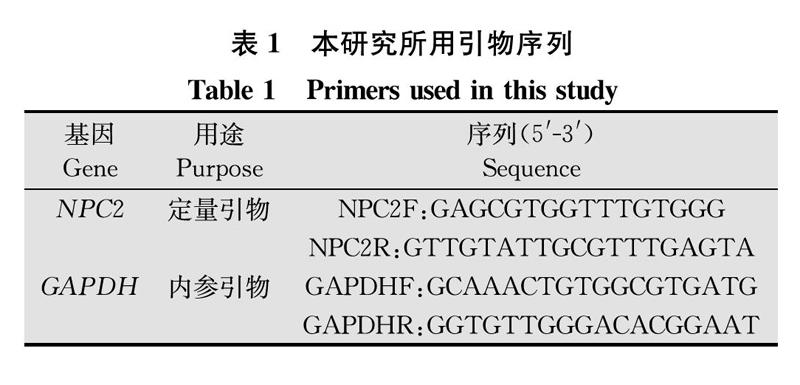
试剂:MiniBEST Universal RNA Extractin Kit、PrimeScriptTMRT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser、SYBR Premix Ex Taq II (Tli RNaseH Plus),均购自宝生物工程(大连)有限公司。定量和内参引物由武汉华大基因公司合成。
仪器:Bio-Rad CFX connect Real-Time System,美国Applied Biosystems公司。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 NPC2基因的鉴定与系统发育分析
利用关键字(NPC2)搜索转录组数据库,利用BLAST对NPC2基因进行鉴定。基于BLASTX对基因数据库的搜索,确定了NPC2候选基因。使用DNAstar软件(5.01版)进行开放阅读框(ORF)预测。信号肽采用SignalP5.0服务器进行预测(http:∥www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/)。氨基酸序列的多重比对由Clustal X软件(版本1.83)完成。利用MEGA 7.0软件中邻接法(NJ树)建立系统发育树,Bootstrap为1 000,分析不同目昆虫之间的进化关系。
1.2.2 利用实时定量PCR技术对NPC2基因进行组织表达分析
各组织的总RNA用MiniBEST Universal RNA Extraction Kit提取;使用PrimeScriptTMRT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser合成第一链cDNA;每个组织的RNA/cDNA提取/合成重复3次。表1为实时定量PCR中使用的基因特异性引物,以GAPDH作为内参。采用BioRad CFX connect Real-Time System和試剂SYBR Premix Ex Taq II (Tli RNaseH Plus)检测NPC2的组织表达水平。实时PCR采用25 μL的反应体系,包含12.5 μL SYBR Premix Ex Taq II (Tli RnaseH Plus), 上下游引物各1 μL(10 μmol/L), 2 μL cDNA样品, 8.5 μL ddH2O。PCR条件为95℃,30 s;95℃ 5 s,55℃ 30 s,72℃ 30 s,40个循环。用熔解曲线分析扩增产物,所有试验样品均进行了3次技术重复。采用2-△△CT法进行相对定量分析[19]。
1.2.3 数据分析
采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)和Tukeys HSD检验分析不同组织间的差异,显著性水平为0.05。所有数据均采用SPSS 17.0软件进行分析(SPSS Inc,Chicago,IL,USA)。
2 结果与分析
2.1 柑橘大实蝇NPC2基因的序列分析
通过对柑橘大实蝇头部转录组数据进行分析,得到了1个NPC2基因,命名为BminNPC2。BminNPC2开放阅读框为456 bp,编码151个氨基酸,N端有一个21个氨基酸残基组成的信号肽,成熟肽由130个氨基酸残基组成,含有6个半胱氨酸(图1,图2)。BminNPC2等电点为6.10,分子量大小为16.66 kD。
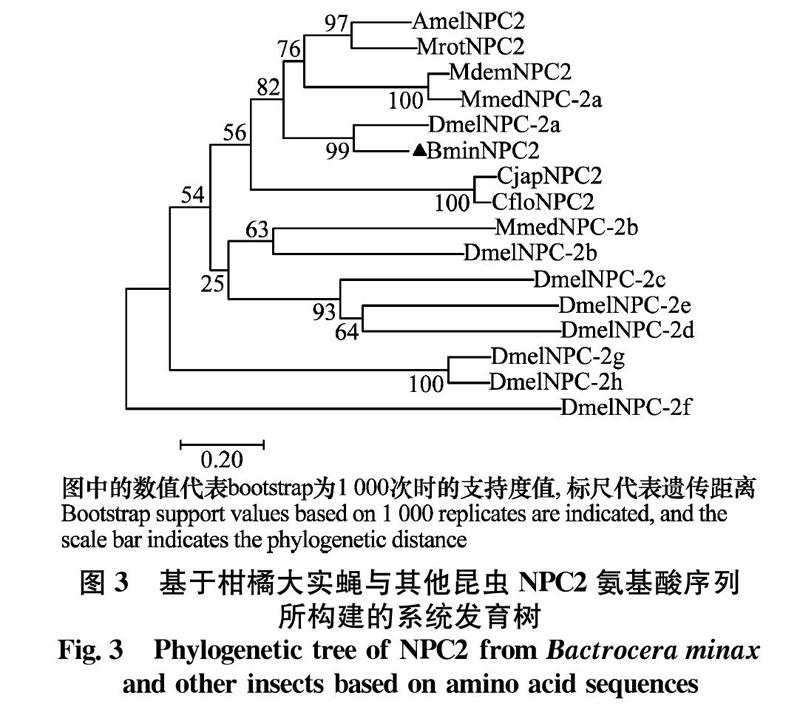
2.2 BminNPC2系统进化分析
利用BLAST对BminNPC2的同源蛋白进行搜索,搜索结果进行氨基酸序列的多重比对(图2),同时构建了NPC2s系统进化树(图3),结果表明,柑橘大实蝇NPC2蛋白氨基酸与黑腹果蝇Drosophila melanogaster NPC-2a蛋白氨基酸序列一致性最高(71.97%),与其他的NPC2蛋白氨基酸序列一致性为(22%~57%)。
2.3 BminNPC2 组织表达模式
使用2-△△Ct相对定量法,以柑橘大实蝇雄虫足中NPC2基因的表达量为基准,采用实时荧光定量PCR法测定了NPC2基因的组织表达谱(图4)。结果显示,BminNPC2在所有组织中都有表达,在头部(去掉触角)和腹部表达量最高,在翅中表达量次之,在触角、胸、足3个部位表达量最低,且BminNPC2在雌雄成虫组织中的表达量基本一致,无差异性。
3 讨论
柑橘大实蝇BminNPC2基因序列分析显示,BminNPC2具有NPC2基因家族的典型特征:开放阅读框为456 bp,编码151个氨基酸,其N端具有21个氨基酸残基组成的信号肽,成熟肽由130个氨基酸残基组成,含有6个半胱氨酸(图1)[11,20]。说明柑橘大实蝇BminNPC2属于NPC2基因家族。
在节肢动物中,NPC2基因在同一物种和不同物种中高度分化,根据构建的系统进化树分析可知,柑橘大实蝇NPC2氨基酸与黑腹果蝇D.melanogaster NPC-2a氨基酸序列一致性最高(71.97%),与其他的NPC2氨基酸序列一致性为22%~57%,这可能是为了适应外在的环境压力而产生的复制或分化的结果[21]。节肢动物NPC2基因的组织表达模式的不同可能与其对应的生理功能有关,例如,日本弓背蚁CjapNPC2在触角中相对高表达[11],中红侧沟茧蜂的MmedNPC-2a同样在触角中相对高表达[10],这两者都能结合挥发性的气味分子。对黑腹果蝇的NPC2研究中,发现DmeNPC-2e和DmeNPC-2a可能在免疫缺陷(Imd)通路中发挥作用[17],以及DmeNPC-2a和DmeNPC-2b参与了调节甾醇类物质稳态和蜕皮激素生物合成[16]。柑橘大实蝇BminNPC2基因在所有的组织中都有表达,这与中红侧沟茧蜂的MmedNPC-2a表达模式一致,但是BminNPC2基因并没在触角中高表达,而BminNPC2和DmelNPC-2a序列一致性较高,我们推测BminNPC2可能不参与嗅觉通讯功能,而是具有和DmelNPC-2a相似的功能。
NPC2在脊椎动物体内的生理功能已较为熟悉(如胆固醇脂質结合和转运)[22-23],但是NPC2在非脊椎动物中的生理功能我们所知甚少,因此NPC2在无脊椎动物中的生理功能值得我们去深入研究。近年来,随着我们对NPC2基因的研究,越来越多的NPC2基因在无脊椎动物中相继被发现,在螯肢动物中,美洲钝眼蜱Amblyomma americanum、蓖子硬蜱Ixodes ricinus、蜈蚣Strigamia maritima等都发现了NPC2基因[24-26];在昆虫纲中,棉铃虫Helicoverpa armigera、佛罗里达弓背蚁Camponotus floridanus等昆虫中都含有NPC2基因[27-28]。在本研究中,我们首次在柑橘大实蝇的头部转录组中鉴定了一个NPC2基因,并对其作了序列和组织表达分析,这为昆虫NPC2家族增加了新的成员,将有助于进一步研究BminNPC2在相关类群中的功能和进化关系。
参考文献
[1] 汪兴鉴, 罗禄怡. 桔大实蝇的研究进展[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 1995, 32(5): 310-315.
[2] 陈世骧, 谢蕴贞. 关于桔大实蝇的学名及其种征[J]. 昆虫学报, 1955, 5(1): 123-126.
[3] DORJI C, CLARKE A R, DREW R A I, et al. Seasonal phenology of Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Tephritidae) in western Bhutan [J]. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 2006, 96(5): 531-538.
[4] DREW R A I, DORJI C, ROMIG M C, et al. Attractiveness of various combinations of colors and shapes to females and males of Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Tephritidae) in a commercial mandarin grove in Bhutan [J]. Journal of Economic Entomology, 2006, 99(5): 1651-1656.
[5] 王小蕾, 张润杰. 桔大实蝇生物学、生态学及其防治研究概述[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2009, 31(1): 73-79.
[6] MARGARITOPOULOS J T, SKAVDIS G, KALOGIANNIS N, et al. Efficacy of the pyrethroid alpha-cypermethrin against Bactrocera oleae populations from Greece, and improved diagnostic for an iAChE mutation [J]. Pest Management Science, 2010, 64(9): 900-908.
[7] DESNEUX N, DECOURTYE A, DELPUECH J M. The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods [J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 2007, 52(1): 81-106.
[8] DONG Yongcheng, WAN Lun, PEREIRA R, et al. Feeding and mating behaviour of Chinese citrus fly Bactrocera minax (Diptera, Tephritidae) in the field [J]. Journal of Pest Science, 2014, 87(4): 647-657.
[9] LIU Lu, ZHOU Qiong. Olfactory response of female Bactrocera minax to chemical components of the preference host citrus volatile oils [J]. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 2016, 19(3): 637-642.
[10]ZHENG Yao, WANG Shanning, PENG Yong, et al. Functional characterization of a Niemann-pick type C2 protein in the parasitoid wasp Microplitis mediator [J]. Insect Science, 2018, 25(5): 765-777.
[11]ISHIDA Y, TSUCHIYA W, FUJII T, et al. Niemann-pick type C2 protein mediating chemical communication in the worker ant [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2014, 111(10): 3847-3852.
[12]KIRCHHOFF C, OSTERHOFF C, YOUNG L. Molecular cloning and characterization of HE1, a major secretory protein of the human epididymis [J]. Biology of Reproduction, 1996, 54(4): 847-856.
[13]NAURECKIENE S. Identification of HE1 as the second gene of Niemann-pick C disease [J]. Science, 2000, 290(5500): 2298-2301.
[14]KLEIN A, AMIGO LRETAMAL M J, MORALES M G, et al. NPC2 is expressed in human and murine liver and secreted into bile: potential implications for body cholesterol homeostasis [J]. Hepatology, 2010, 43(1): 126-133.
[15]ADACHI T, ISHII K, MATSUMOTO Y, et al. Niemann-pick disease type C2 protein induces triglyceride accumulation in silkworm and mammalian cell lines [J]. Biochemical Journal, 2014, 459(1): 137-147.
[16]HUANG Xun, WARREN J T, BUCHANAN J, et al. Drosophila Niemann-pick type C-2 genes control sterol homeostasis and steroid biosynthesis: a model of human neurodegenerative disease [J]. Development, 2007, 134(20): 3733-3742.
[17]SHI Xiuzhen, ZHONG Xue, YU Xiaoqiang. Drosophila melanogaster NPC2 proteins bind bacterial cell wall components and may function in immune signal pathways [J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2012, 42(8): 545-556.
[18]杜田華, 华登科, 何章章, 等. 柑橘大实蝇成虫对板栗挥发物的行为反应[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2018, 40(2): 247-257.
[19]LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method [J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408.
[20]INOHARA N, NUEZ G. ML—a conserved domain involved in innate immunity and lipid metabolism [J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2002, 27(5): 219-221.
[21]ZHU Jiao, WANG Guirong, PELOSI P. Plant transcriptomes reveal hidden guests [J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2016, 474(3): 497-502.
[22]STORCH J, XU Zhi. Niemann-pick C2 (NPC2)and intracellular cholesterol trafficking [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 2009, 1791(7): 671-678.
[23]PELOSI P, IOVINELLA I, FELICIOLI A, et al. Soluble proteins of chemical communication: an overview across arthropods [J/OL]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2014, 5: 320. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00320.
[24]RENTHAL R, MAGHNANI L, BERNAL S, et al. The chemosensory appendage proteome of Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) reveals putative odorant-binding and other chemoreception-related proteins [J]. Insect Science, 2017, 5(24): 730-742.
[25]IOVINELLA I, BAN Liping, SONG Limei, et al. Proteomic analysis of castor bean tick Ixodes ricinus: a focus on chemosensory organs [J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2016, 78: 58-68.
[26]CHIPMAN A D, FERRIER D E K, BRENA C, et al. The first myriapod genome sequence reveals conservative arthropod gene content and genome organisation in the centipede Strigamia maritime [J/OL]. PLoS Biology, 2014, 12(11): e1002005. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002005.
[27]ZHU Jiao, GUO Mengbuo, BAN Liping, et al. Niemann-pick C2 proteins: A new function for an old family [J/OL]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2018, 9: 52. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00052.
[28]BONASIO R, ZHANG Guojie, YE Chaoyang, et al. Genomic comparison of the ants Camponotus floridanus and Harpegnathos saltator [J]. Science, 2010, 329(5995): 1068-1071.
(责任编辑:田 喆)
