D-D及FIB在危重症新生儿早期DIC诊断中的检测意义研究
2020-07-26张远朝冯荣波
张远朝 冯荣波
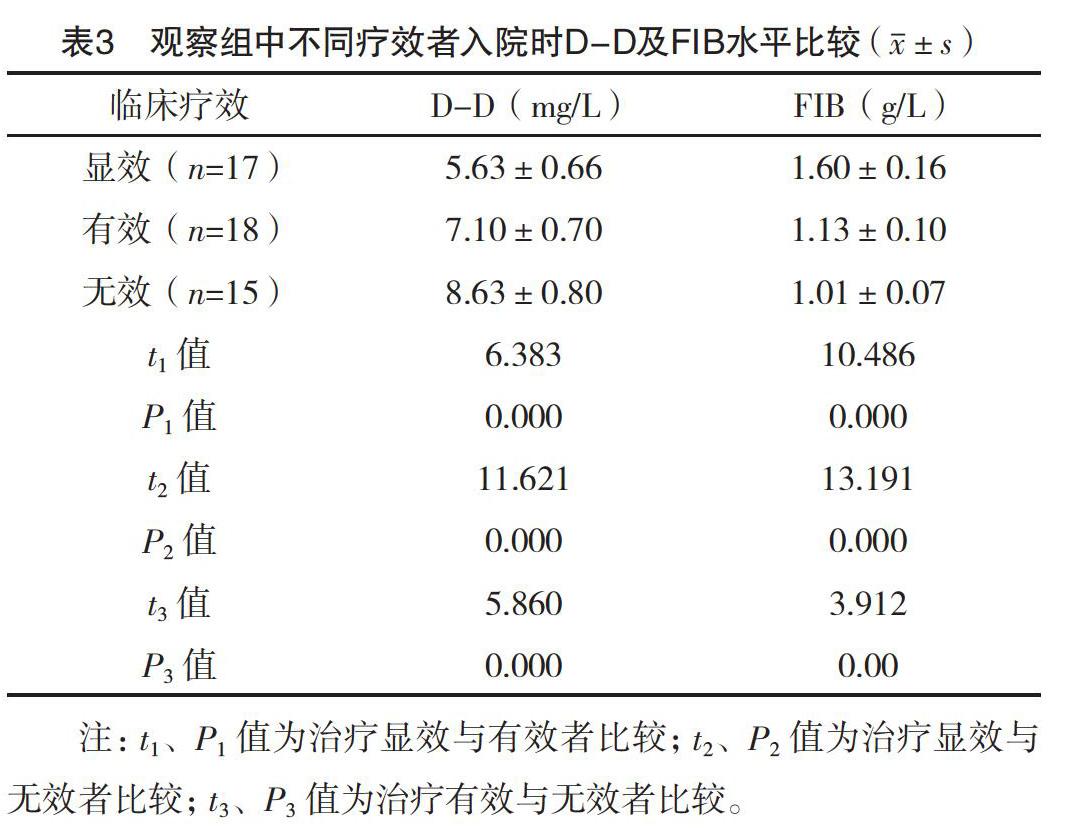
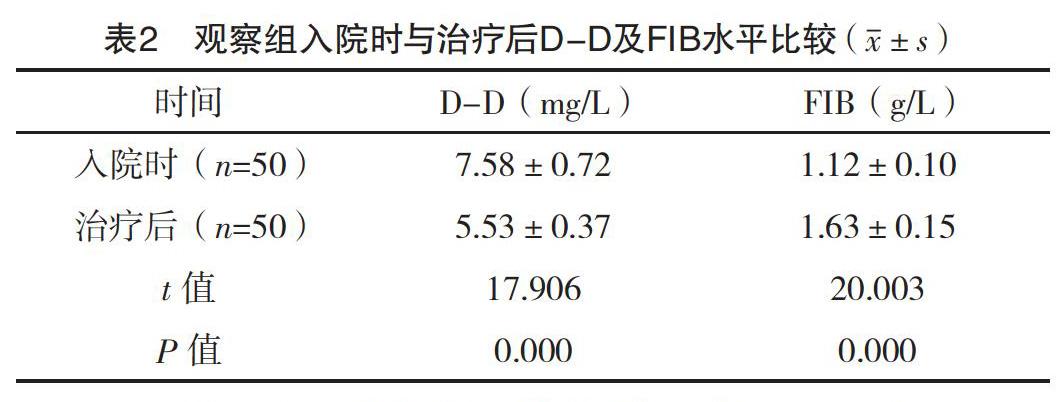
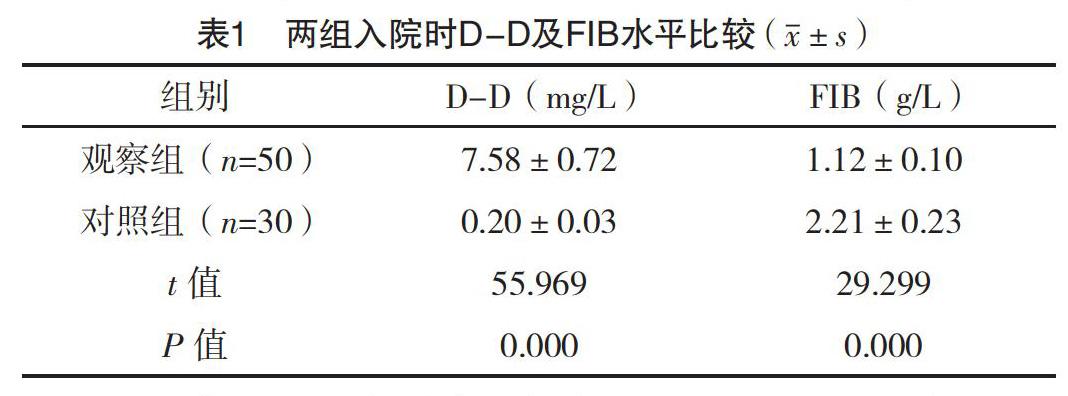
【摘要】 目的:探究D-二聚體(D-D)及纤维蛋白原(FIB)在危重症新生儿早期DIC诊断的检测意义。方法:选取2018年1月-2020年1月本院收治的50例早期DIC危重症新生儿为观察组,另选取同时期的30例健康新生儿为对照组。比较两组入院时D-D及FIB的检测结果,比较观察组入院时及治疗后的D-D及FIB的检测结果,并比较观察组中不同疗效者入院时D-D及FIB的检测结果。结果:观察组入院时D-D水平明显高于对照组,而FIB水平低于对照组(P<0.05)。观察组治疗后D-D水平低于入院时,而FIB水平高于入院时(P<0.05)。观察组治疗显效者入院时D-D水平低于治疗有效与无效者,且治疗有效者低于无效者(P<0.05)。观察组治疗显效者入院时FIB水平均高于治疗有效与无效者,且治疗有效者高于无效者(P<0.05)。结论:危重症新生儿早期DIC患儿的D-D水平升高,而FIB降低,D-D及FIB的检测有助于早期DIC的诊断,检测意义较高。
【关键词】 D-D FIB 危重症新生儿 早期DIC
[Abstract] Objective: To explore the detection significance of D-Dimer (D-D) and fibrinogen (FIB) in the diagnosis of critically ill neonates with early DIC. Method: A total of 60 critically ill neonates with early DIC from January 2018 to January 2020 were selected as the observation group, and another 30 healthy neonates in the same period were selected as the control group. The detection results of D-D and FIB at admission were compared between the two groups. The detection results of D-D and FIB of the observation group at admission and after treatment were compared. The detection results of D-D and FIB at admission of patients with different curative effects in the observation group were compared. Result: The D-D level of the observation group at admission was significantly higher than that of the control group, while the FIB level was lower than that of the control group (P<0.05). The D-D level in the observation group after treatment was lower than that at admission, while the FIB level was higher than that at admission (P<0.05). The D-D level at admission of the patients with obvious therapeutic effect in the observation group was lower than that of the patients with effective and ineffective treatment, and the D-D level of the patients with effective treatment was lower than that of the patients with ineffective treatment (P<0.05). The FIB level of the patients with obvious therapeutic effect in the observation group was higher than that in the patients with effective and ineffective treatment, and the FIB level of effective treatment was higher than that in the patients with ineffective treatment (P<0.05). Conclusion: The D-D level of critically ill neonates with early DIC is increased, while the FIB level is decreased, the detection of D-D and FIB was helpful to the diagnosis of early DIC, and the detection significance is high.
[Key words] D-D FIB Critically ill neonates Early DICFirst-authors address: Xinyi Peoples Hospital, Xinyi 525300, Chinadoi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2020.18.026
综上所述,危重症新生儿早期DIC患儿的D-D水平升高,而FIB降低,D-D及FIB的检测有助于早期DIC的诊断,检测意义较高。
参考文献
[1]徐晓敏,林晓君,刘玲莉,等.止凝血功能指标检测对新生儿DIC的诊断价值[J].中国农村卫生事业管理,2016,36(1):133-134.
[2]罗素云.APTT、PT、FIB与D-D水平在新生儿早期凝血功能障碍中的诊断价值分析[J].中国实用医药,2019,14(16):69-70.
[3]韩永才,张彤,牛俊红,等.分析新生儿重症肺炎与普通肺炎患者抗凝血酶Ⅲ和D-二聚体、降钙素原等指标水平差异[J].中国社区医师,2019,35(34):129-130,132.
[4]陶格斯,牛瑞兵,张雅蓉.血浆D-二聚体、FDP、FM检测在早期DIC诊断中的应用研究[J].当代医学,2017,23(31):86-87.
[5]夏洪艳,苏庸春,温贤浩.新生儿期纤维蛋白原降低研究进展[J].儿科药学杂志,2019,25(6):63-64.
[6]周真珍.D-二聚体、FDP联合检测对早期DIC的诊断价值[J].医学新知杂志,2017,27(6):645-646.
[7]何静.D-二聚体检测在DIC诊断及治疗中的应用效果[J].医学信息,2019,32(z2):178-179.
[8]吕欣,韩悦,唐雅琼,等.纤维蛋白原对DIC患者疾病诊断及预后的价值[J].中国血液流变学杂志,2018,28(3):261-267.
[9]郝淑娟,韩建存,常晓丹.胎盘早剥新生儿的纤维蛋白原、D-D、APTT、PT水平指标变化对患儿凝血功能的早期监测价值研究[J].中国妇幼保健,2019,34(17):3990-3993.
[10] Amanda W,Mark W,Jawed F,et al.International Normalized Ratio Relevance to the Observed Coagulation Abnormalities in Warfarin Treatment and Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation[J].Clin Appl Thromb Hemost,2018,24(7):1033-1041.
[11] Morita N,Nakahara K,Morita R,et al.Efficacy of Combined Thrombomodulin and Antithrombin in Anticoagulant Therapy for Acute Cholangitis-induced Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation[J].Intern Med,2019,58(7):907-914.
[12]蔡锦梅,黄雪珍,张瑞雄,等.血浆D-二聚体及纤维蛋白原检测在诊断弥散性血管内凝血方面疾病的临床意义[J].中国当代医药,2018,25(9):114-116.
[13]付禹.分析止凝血功能指标检测诊断新生儿弥散性血管内凝血(DIC)的临床价值[J].当代医学,2018,24(4):104-105.
[14]杨庆宝.新生儿DIC应用微剂量肝素治疗的效果研究[J].基层医学论坛,2019,23(11):1499-1500.
[15]关莹.凝血检验指标在弥散性血管内凝血诊断中的价值[J].中国现代药物应用,2019,13(23):78-79.
[16] Ding R,Wang Z,Lin Y,et al.Comparison of a new criteria for sepsis-induced coagulopathy and International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis disseminated intravascular coagulation score in critically ill patients with sepsis 3.0:a retrospective study[J].Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis,2018,29(6):551-558.
[17] Junko U,Liangcheng W,Hiroyoshi K,et al.Rupture of hidden abnormal myometrial vessels during cesarean delivery of a patient with subserosal leiomyoma:A possible pathogenesis of sudden-onset disseminated intravascular coagulation[J].Clin Case Rep,2018,6(9):1747-1750.
[18]李婉影,劉会,高清平.出凝血分子标志物对脓毒血症合并弥散性血管内凝血的早期诊断和预后评估的价值[J].内科急危重症杂志,2019,25(1):31-34.
[19]彭捷,陈韡.D-体和抗凝血酶联合检测在弥散性血管内凝血诊断中的应用价值分析[J].临床合理用药杂志,2018,11(32):147-148.
[20]张福敏,苏秦,邓益斌.新生儿败血症合并弥散性血管内凝血临床相关因素分析[J].医学理论与实践,2018,31(21):3180-3182.
(收稿日期:2020-04-09) (本文编辑:田婧)
