Competence investigation on insulation testing on electrosurgical instruments and needs analysis of training for Central Sterile Supply Department staff
2020-06-22XuWANGQingZHANGYiQinZHOU
Xu WANG, Qing ZHANG, Yi‑Qin ZHOU
1Department of Nursing, Yunnan Geriatric Hospital, Kunming,Yunnan; 2Central Sterile Supply Department, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China
ABSTRACT
Objective: The objective of this article is to investigate the competence of Central Sterile Supply Department (CSSD) staff in insulation testing on electrosurgical instruments, to analyze the needs of training for CSSD staff, and also to strengthen the effectiveness of monitoring the insulation testing on electrosurgical instruments for CSSD staff to provide a reference for the nursing safety training.
Materials and Methods: A total of 180 CSSD staff from 36 hospitals were enrolled as the research objects and investigated using“self‑assessment questionnaire of the competence in insulation testing on electrosurgical instruments and the needs of training".
Results: The overall self‑assessment score of competence in insulation testing on electrosurgical instruments for CSSD staff is 3.10 ± 0.42,including four dimensions which are attitude, system, cognition, and skills with the scores 3.31 ± 0.55, 2.80 ± 0.63, 2.74 ± 0.68, and 3.03 ± 0.36,respectively.Based on the survey of training needs for CSSD staff, the top three ranked training needs are trace management record of insulation testing on electrosurgical instruments (93.89%), disposal procedures for insulation damage of electrosurgical instruments (92.78%), and adverse events caused by leakage of electrosurgical instruments (80.55%).
Conclusion: The competence of insulation testing for CSSD staff is at a low level by overall.The competence of CSSD staff could be improved by analyzing the needs of training, establishing a systematic training system, and taking effective training action, thus ensuring the safety of patients and medical personnel.
Keywords: Electrosurgical instruments, insulation testing, competence, impact factor
INTRODUCTION
Electrosurgical instruments include high‑frequency electric knife, large‑vessel closure system, ultrasound knife, argon knife, loop electrosurgical excision procedure knife, endoscopic electric knife, and many other high‑frequency current surgical instruments.The cutting depth and coagulation speed during the operation are controlled by a computer.The insulating layer of electrosurgical instruments adopts the solid insulation method.The damage of the solid insulating layer is usually unavoidable.The abrasion during transportation, disinfection and sterilization, corrosion and friction when entering the human body will cause damage to the insulation layer,[1,2]which will cause relative damage of electricity leakage and potential safety hazards to doctors and patients.The failure of a power supply circuit may cause damage to other systems or lead to failure of the system.Moreover,the highest equipment failure rate lies in the power supply system.[3]The breakage of the insulating layer of the electrosurgical instruments, capacitance coupling as well as direct coupling may result in accidental burns.As the ratio is quite high in endoscopic surgery,[4]it is extremely significant and necessary to test the insulation performance for electrosurgical instruments.The competence of the Central Sterile Supply Department (CSSD) staff of the insulation testing on electrosurgical instruments is that the staff has the ability to conduct the insulation test for electrosurgical instruments based on attitude, system, cognition, and skills – four aspects.In this study, we investigated the current competence level of insulation test on electrosurgical instruments for CSSD staff and identified the impact factors to provide the evidence for the nursing safety training.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
General information
A total of 180 CSSD staff from 36 hospitals were randomly selected as the research objects, with 27 males and 153 females; 103 of them graduated from secondary school,61 from junior college, and 16 from undergraduates and 98 of them have worked <5 years, 55 worked 5–10 years, and 27 worked >10 years.All of them volunteered to participate in the investigation.Access standards were that they worked in CSSD and their CSSD centralized the disposal of electrosurgical instruments.
Ethic considerations
Before the questionnaire survey, the purpose and significance of this research were explained to the participants, we also promised that all information would just be used for research and be kept strictly confidential.
Investigation method
A self‑assessment questionnaire of the competence in insulation testing on electrosurgical instruments and the needs of training was used to evaluate the awareness of related knowledge, including relevant laws and regulations, causes of safety risks, and methods to reduce risks.The questionnaire includes 18 items in four dimensions.The four dimensions are attitude, system, cognition, and skill.The score of a single item ranges from 1 to 4: 1 indicates no knowledge, 2 indicates the knowledge of part, 3 indicates the knowledge of most, and 4 indicates the knowledge of all.At the end of the questionnaire,there listed the open‑ended question for training needs for insulation testing on electrosurgical instruments, emphasizing in the most desired topic or knowledge of the training.Then,by combining learning with practice, we could formulate reasonable and effective training programs and continuously followed up the training effect.
Statistical analysis
Chinese version SPSS 17.0 was used for statistical analysis.The measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation.T‑test was utilized and the counting data were expressed as a percentage (%).Chi‑square test was used and the difference was statistically significant whenP< 0.05.
RESULTS
The scores of the competence on four dimensions ranked from high to low as attitude factor, skill factor, system factor,and cognitive factor, as shown in Table 1.The competence scores of the CSSD staff on the electrosurgical instrument insulation testing are shown in Table 2.According to the self‑assessment of competency, the staff addressed the training needs, as shown in Table 3.The qualified ratio of the training effect for the CSSD staff on the insulation testing of electrosurgical instruments is shown in Table 4,and the differences were statistically significant before and after training regarding the qualified ratio of various training contents (P< 0.01).
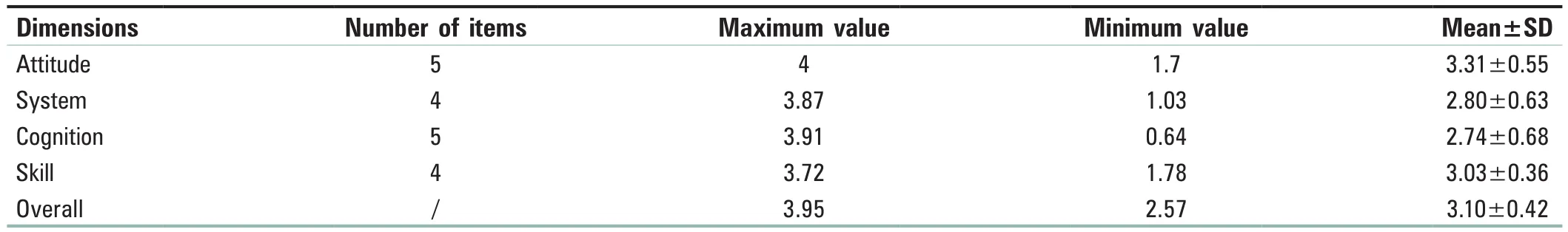
Table 1: Competency score on four dimensions for insulation testing of electrosurgical instruments for Central Sterile Supply Department staff (n=180)

Table 2: Score of each item of competence of electrosurgical instruments insulation testing for Central Sterile Supply Department Staff (n=180)
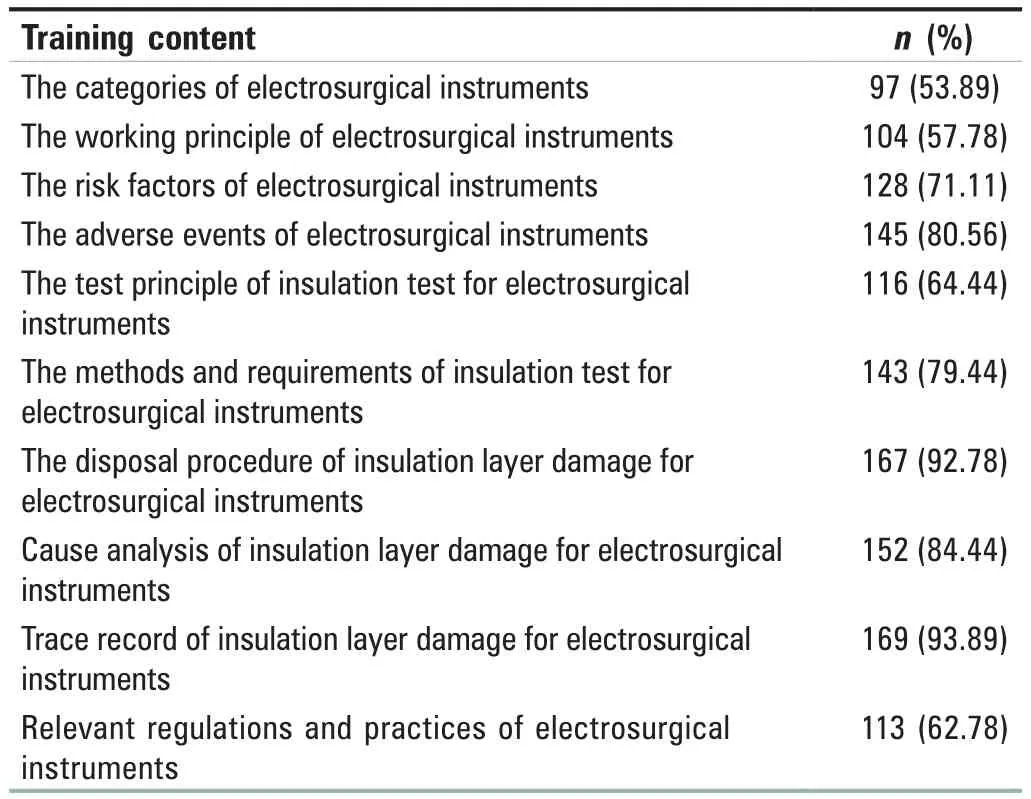
Table 3: Requirements of personnel in Central Sterile Supply Department for insulation testing and training of electrosurgical instruments (n=180)
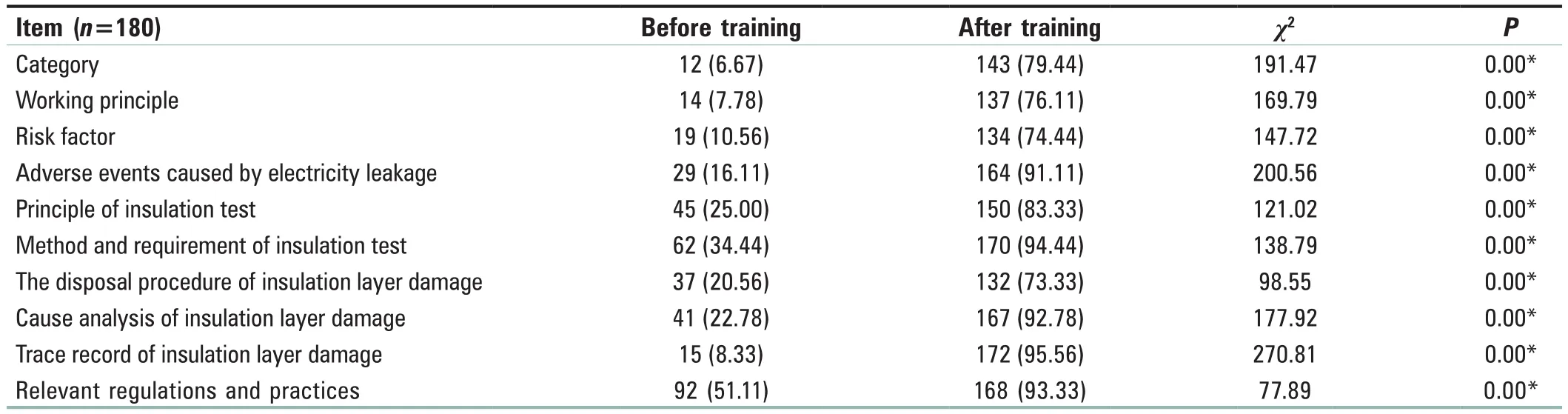
Table 4: Comparison of qualified ratio of training on electrosurgical instruments insulation testing among Central Sterile Supply Department staff n (%)
DISCUSSION
Facing the diversity, complexity, and dynamicity of electrosurgical instruments, the CSSD staff should have not only solid professional knowledge but also the excellent practical ability and innovative ability in the process of disposal.By evaluating the competence of CSSD staff for the insulation testing of the electrosurgical instruments, the advantages and disadvantages of them were clarified.The overall score of the competence for the insulation testing of the electrosurgical instruments in the CSSD was 3.10 ± 0.42.As per four separate dimensions, the highest score ranked in attitude factor, which reflected the high level of safety consciousness of CSSD staff, showing that the patient safety is put in the first place and the CSSD staff keep an initiative and active working style, and the lowest score ranked in the system factor and cognitive factor, indicating that the CSSD staff have vague grasp of the qualified ratio and intact ratio of the insulating test of the electrosurgical instrument.[5]Hence,how to formulate relevant system norms, standards as well as procedures and how to use the monitoring results should be further developed and refined.By building an equal,sharing, mutual‑assistance platform while starting the linkage mechanism between operating rooms, user departments,equipment departments, and equipment manufacturers, we can find the joint point and establish a security system.At the same time, we should do a good job in communication and early warning release aspects, keep knowledge and practice in one, and strive for practical results.
Difficulties exist in the implementation and management of insulation testing for surgical instruments.According to the self‑assessment of the competency of the electrosurgical instrument insulation testing in CSSD, the training needs of CSSD staff were investigated.The current situation is that there is a process already for the insulation test of the electrosurgical instrument, but there is no trace management.When it is found that the insulation layer is damaged, there are no perfect disposal process and no root cause analysis, which confuse employees on the significance and effectiveness of the detection.In view of this situation,we took adverse events as the breakthrough point and implemented training.The training, combined with the requirements of laws and regulations, was focused on the cause analysis, disposal process, and traces records.In this way, the training could make it possible for CSSD staff to master basic knowledge and skills and expand knowledge and solid professional level as well as practical ability.[6]Based on risk awareness, we have established a standardized,systematic, and scientific training mode till now to carry out a series of specific training for CSSD staff[7]and have created a security system while ensuring the data integrity and security needs to ensure the safety of patients and medical personnel.
CONCLUSION
The competence of insulation testing for CSSD staff is at a low level by overall.The competence of CSSD staff could be improved by analyzing the needs of training, establishing a systematic training system, and taking effective training action, thus ensuring the safety of patients and medical personnel.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflict of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Integrative Nursing的其它文章
- The relationship between diabetes‑related distress and self‑management in empty‑nest elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: The mediating effect of self‑efficacy
- Impact of the emigration of nurses on health care delivery system in selected hospitals, Benin‑City, Edo State, Nigeria
- A bibliometric analysis of nursing research in COVID‑19 in China
- Effect of flapping‑meridians combined with thunder‑fire moxibustion on upper limb dysfunction after stroke
- Clinical effect of scraping therapy in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis
- Establishment and management of neurosurgery emergency observation ward during the COVID‑19 epidemic period
