农业生防昆虫黄猄蚁对3种农药的敏感性研究
2020-05-28吕晓艳张媛
吕晓艳 张媛
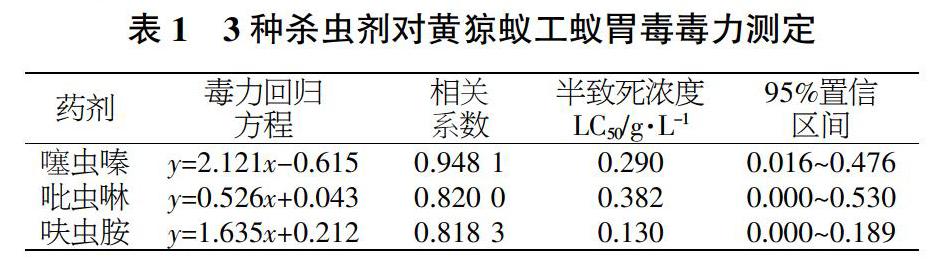
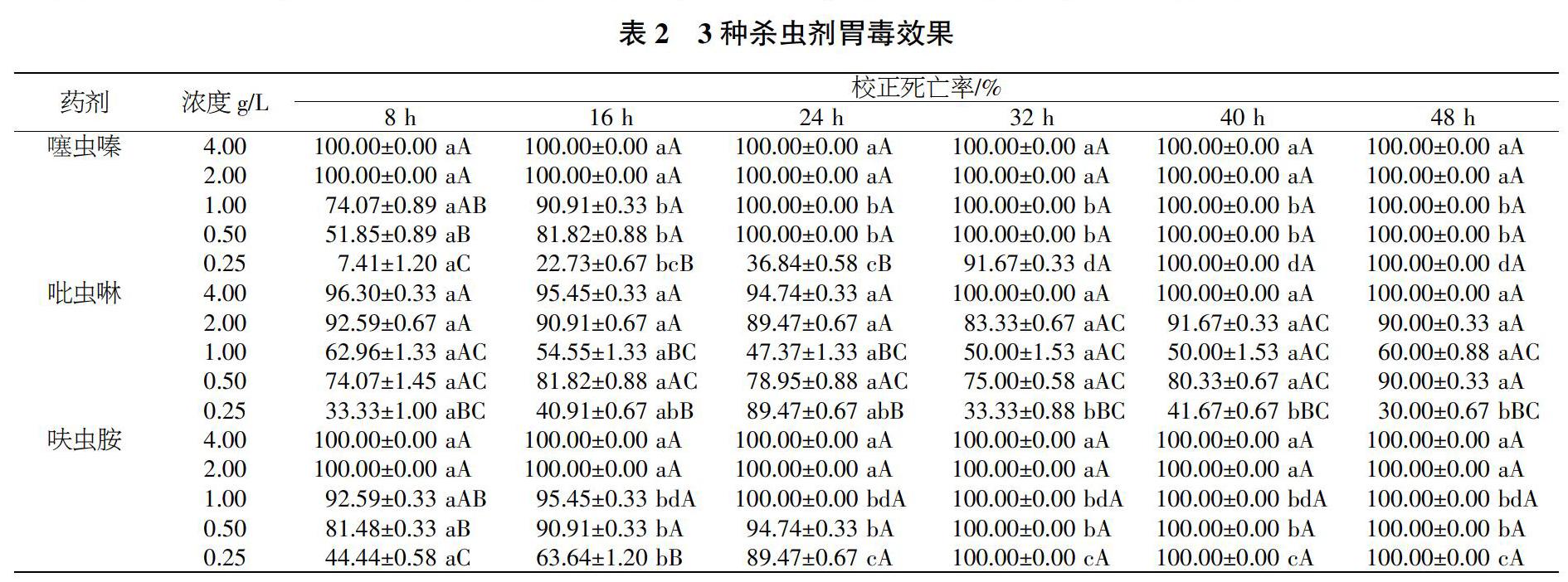
摘要 黄猄蚁(Oecophylla smaragdina)是最早用于农业生防的昆虫,目前已被证明能防治20多种农业害虫,对农林生产具有重要作用,但目前黄猄蚁对常见农药的药剂敏感性尚不清楚。本研究采集云南西双版纳地区的黄猄蚁,使用3种常见农药噻虫嗪、吡虫啉、呋虫胺对其进行毒力测定,并在培养皿中放置毒饵和黄猄蚁之后的8、16、24、32、40、48 h分别记录黄猄蚁的死亡情况。结果表明,黄猄蚁对不同药剂的敏感性存在差异,黄猄蚁对呋虫胺、噻虫嗪以及吡虫啉的16 h半数致死浓度(LC50)分别为0.130、0.290、0.382 g/L,差异显著;连续观察2 d后发现,不同农药对黄猄蚁的致死时间也存在差异,该研究可为黄猄蚁生防的利用和保护提供科学参考。
关键词 黄猄蚁;生物防治;药剂敏感性
中图分类号 S435 文献标识码 A
文章编号 1007-5739(2020)09-0095-02 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
Abstract Oecophylla smaragdina is the first insect to be used in agricultural biocontrol.It has been proved to be able to control more than 20 species of agricultural pests,which plays an important role in agriculture and forestry production,but the susceptibility of the ants to common pesticide is unclear.In this study,three common pesticides(thiamethoxam,imidacloprid and dinotefuran)were used to determine the virulence of Oecophylla smar-agdina collected from Xishuangbanna,Yunnan Province.The mortality of Oecophylla smaragdina was recorded at 8,16,24,32,40,48 hours after the baits and ants were placed in the petri dish.The results showed that the insecticide susceptibility is different to Oecophylla smaragdina among these 3 pesticides.The median lethal concentration(LC50)for dinotefuran,thiamethoxam,imidacloprid in 16 h were 0.130 g/L,0.290 g/L and 0.382 g/L respe-ctively,which is significant difference,and the lethal time of different pesticides on Oecophylla smaragdina is also different after 2-day observation.Our study could provide a scientific evidence on utilization in biocontrol and protection for Oecophylla smaragdina.
Key words Oecophylla smaragdina;biocontrol;insecticide susceptibility
黄猄蚁(Oecophylla smaragdina)是隸属蚁科(Formicidae)织叶蚁属(Oecophylla)的一种蚂蚁,广泛分布于亚洲和澳大利亚[1]。其由于具有很强的捕食能力,是世界上最早被用于以虫治虫的典型昆虫[2]。公元304年,嵇含在《南方草木传》中记载了用黄猄蚁防治柑橘害虫,公元304年之后又有多本古文书籍记载了用黄猄蚁防治多种经济作物上主要害虫的情况。由于其防治效果较好,后人将其连同蚁巢一起在市面出售[3-4],最终扩大了黄猄蚁的应用面积。扩大应用面积的同时,黄猄蚁从柑橘园被引迁到了荔枝、橘子、柚子园等,增加了黄猄蚁的应用范围[5]。直到现如今黄猄蚁的生防效果也不容小觑,其除了能够捕食柑橘、荔枝、柚子园主要害虫,还能控制芒果、可可、腰果和樟子松等经济树木上的主要害虫,如红带蓟马(Selenothrips rubrocinctus)和蝽象(Cyclopelta si-ccifolia)等20多种有害生物[6-7],对农林业生产具有非常重要的作用。在一些东南亚国家,黄猄蚁可被传统医学应用于治疗人体疾病、可作为饲喂鸟的珍贵饲料以及作为重要的食用昆虫在市场上进行交易等[8]。此外,在农业发展的需要下,人类长期施用农药,一些有害生物产生抗药性,而大量类似黄猄蚁的害虫天敌被农药杀死,导致害虫再猖獗、粮食作物农药残留的现象[9]。随着人类健康、环保意识的提升,生物防治越来越受重视,19世纪以来,生物防治在很多国家迅速发展起来[10],黄猄蚁作为生物防治历史最长且有效的昆虫,其在当代农业生产中扮演着越来越重要的角色。但是,由于农药的大量广泛使用,黄猄蚁也不可避免地遭到农药的毒害,而目前针对农药对黄猄蚁毒性的研究基本为空白。本研究拟选择噻虫嗪(Thiamethoxam)、吡虫啉(Imidacloprid)和呋虫胺(Dinotefuran)3种新烟碱类杀虫剂,研究其对黄猄蚁的毒性。这3种农药由于具有高效低毒、杀虫广谱以及对人畜、作物和环境安全的特点,在农业生产中被广泛使用[11-12]。使用这3种农药进行黄猄蚁的毒性研究符合实际应用,也可为保护黄猄蚁提供依据。
[1] JAMES K W.Geographic distribution of the African weaver ant,Oecoph-ylla smaragdina[J].Transactions of the American Entomological Society,2017,143(2):501-510.
[2] VAN MELE P.A historical review of research on the weaver ant Oecoph-ylla in biological control[J].Agricultural and Forest Entomology,2008,10(1):13-22.
[3] 虞國跃.黄猄蚁:忠实的卫士[J].森林与人类,2008(1):91-95.
[4] 杨沛.黄猄蚁史料及其用于柑橘害虫防治的研究[J].中国生物防治,2002,18(1):28-32.
[5] 张祖兵,高世德,周明,等.黄猄蚁对柚子花期害虫的影响[J].生态学杂志,2010,29(2):329-332.
[6] HOSETTI B B,RUDRESH B S.Studies on Oecophylla smaragdina as a bio-control agent against pentatomid bug infesting on Pongamia tree[J].Journal of Environmental Biology,2012,33:1103-1106.
[7] MORALES H,PERFECTO I.Traditional knowledge and pest management in the Guatemalan highlands[J].Agriculture and Human Values,2000,17:49-63.
[8] PIERRE E M,IDRIS A H.Studies on the predatory activities of Oecophy-lla smaragdina(Hymenoptera:Formicidae)on Pteroma pendula(Lepido-ptera:Psychidae)in oil palm plantations in Teluk Intan,Perak(Malaysia)[J].Asian Myrmecology,2012,5:161-174.
[9] 祁力钧,傅泽田,史岩.化学农药施用技术与粮食安全[J].农业工程学报,2006,18(6):203-206.
[10] 万方浩,叶正楚,郭建英,等.我国生物防治研究的进展及展望[J].昆虫知识,2000,37(2):65-74.
[11] MAIENFISCH P,ANGST M,BRANDL F,et al.Chemistry and biology of thiamethoxam:A second generation neonicotinoid[J].Pest Manage Scie-nce,2001,57(10):906-913.
[12] JURASKE R,CASTELLS F,VIJAY A,et al.Uptake and persistence of pesticides in plants:Measurements and model estimates for imidacloprid after foliar and soil application[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,165(1):683-689.
[13] AZUMA N,KIKUCHI T,OGATA K,et al.Molecular phylogeny among local populations of weaver ant Oecophylla smaragdina[J].Zoolog Scien-ce,2002,19:1321-1328.
[14] 王亮,张锦堂,李宗波,等.蚂蚁与植物的互惠共生关系研究进展[J].西南林业大学学报,2020,40(1):181-188.
