糖尿病患者采用生酮饮食效果的Meta分析
2020-05-21钟冬赐詹思延
钟冬赐 詹思延

[摘要] 目的 系统评价国内外采用生酮饮食治疗糖尿病患者的效果,从而更好地为糖尿病患者的饮食管理和综合治疗提供循证依据。 方法 通过检索PubMed、Cochrane Library、EMbase、Sinomed、万方医学网、维普网等数据库,收集国内外对糖尿病患者使用生酮饮食治疗的随机对照试验(RCT),试验组给予低碳生酮饮食,对照组给予低卡路里食物或者平板健康餐,对所纳入的文献采用Jadad评分进行质量评价,使用Review Manager5.3软件进行Meta分析。将试验组和对照组的糖化血红蛋白含量、体重、甘油三酯水平等结局指标进行比较。 结果 该次Meta分析共纳入文献7篇,其中试验组200例病例,对照组155例病例。Meta分析结果显示,试验组糖化血红蛋白含量低于对照组[MD=-0.50,95%CI(-0.70,-0.30),P<0.01];试验组体重低于对照组[MD=-8.07,95%CI(-10.73,-5.40),P<0.01];试验组甘油三酯水平低于对照组[MD=-29.05,95%CI(-45.50,-12.71),P<0.01]。 结论 生酮饮食是一种能够有效降低糖尿病患者糖化血红蛋白含量,减轻体重,降低甘油三酯水平的膳食疗法。
[关键词] 糖尿病;生酮饮食;Meta分析
[中图分类号] R587.2 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1672-4062(2020)01(b)-0032-05
[Abstract] Objective To systematically evaluate the efficacy of ketogenic diet in the treatment of diabetic patients at home and abroad, so as to provide evidence-based evidence for dietary management and comprehensive treatment of diabetic patients. Methods A randomized controlled trial (RCT) of ketogenic diet for diabetic patients was collected by searching PubMed, Cochrane Library, EMbase, Sinomed, Wanfang Medical Network, and VIP. The trial group was given a low-carbon ketogenic diet. The control group was given low-calorie food or flat-table healthy meal, and the included literature was evaluated by Jadad score, and the review was performed using Review Manager5.3 software. The outcome measures such as glycated hemoglobin content, body weight, and triglyceride levels in the test group and the control group were compared. Results A total of 7 articles were included in the meta-analysis, including 200 cases in the experimental group and 155 cases in the control group. Meta-analysis showed that the glycated hemoglobin content of the experimental group was lower than that of the control group [MD=-0.50, 95% CI(-0.70, -0.30), P<0.01]; the weight of the experimental group was lower than that of the control group [MD=-8.07, 95 %CI(-10.73,-5.40), P<0.01]; the triglyceride level in the test group was lower than that in the control group [MD=-29.05, 95% CI(-45.50, -12.71), P<0.01]. Conclusion ketogenic diet is a dietary therapy that can effectively reduce glycated hemoglobin levels, reduce body weight, and lower triglyceride levels in diabetic patients.
[Key words] Diabetes; Ketone diet; Meta-analysis
糖尿病作為一组以高血糖为特征的代谢性疾病,现在已经逐渐发展成为全球三大导致过早死亡的健康危害因素之一[1]。糖尿病的发病原因和发生机制较为复杂,其并发症较多,且后果较为严重[2-3],因此糖尿病患者非常需要早期治疗和早期干预。现在糖尿病的治疗方式包括药物治疗、运动治疗、生活方式干预、饮食治疗等。尽管今年来在药物治疗方面取得了较大的进展,药物的不良反应和潜在危害仍然使得人们对药物治疗的安全性保持很大的警惕。非药物治疗方案也逐渐受到人们的欢迎,比如采用低碳水化合物、高脂肪、适量蛋白质组成的生酮饮食(ketogenic diet)治疗。生酮饮食作为难治性癫痫[4-5](refractory epilepsy,RE)疾病的非药物治疗方式之一,已有近百年的应用历史。近年来,生酮饮食[6]开始被尝试着用于糖尿病患者的治疗,取得了一定的治疗效果。目前大部分研究指出,生酮饮食能够有效地降低糖尿病患者的糖化血红蛋白含量,减轻他们的体重,降低其甘油三酯水平[7]。但是各个研究的样本量都相对较小,试验结果的可信度不够高。因此,该研究拟采用Meta分析的方法,系统评价入选的几篇随机对照试验研究,研究糖尿病患者采用生酮饮食治疗的效果,为糖尿病的非药物疗法提供新的科学依据。
1 方法
1.1 文献纳入标准
①包含结局指标:糖化血红蛋白(glycosylated hem- oglobin content,HbA1c);体重(weight);甘油三酯水平(triglyceride levels);②各纳入文献为RCT研究;③试验组和对照组资料具有可比性;
1.2 文献排除标准
①干预措施不是采用生酮饮食;②原始研究数据资料不全;③动物试验。
1.3 资料检索
检索数据库为:PubMed、Cochrane Library、EMbase、Sinomed、万方医学网、维普网等数据库。检索时间不限。英文关键词:Diabetes mellitus、Ketogenic diet、Atkins diet.中文关键词:糖尿病、生酮饮食。文献纳入内容为:第一作者姓名和发表年限、干预组和治疗组参与人数、治疗手段和持续时间、终点指标等
1.4 质量评价
根据Jadad评分量表内容:①随机化序列的产生是否恰当;②随机化隐藏是否恰当;③盲法是否恰当;④撤退与退出描述是否清楚,两名数据提取员对上述7篇文献的质量进行评价,当意见相左时,相互讨论是否有合理的达成一致的方法。
1.5 统计方法
将纳入的7篇文献里的数据根据Cochrane系统评价手册进行合并,使用ReView Manager5.3软件对上述各项研究进行Meta分析。对7篇研究的异质性采用I2检验,Cochrane手册I2值将异质性分成4个程度:①0%~40%为轻度异质性;②40%~60%为中度异质性;③50%~90%为较大的异质性;④75%~100%为很大的异质性。Meta分析中效应模型的选择根据异质性检验结果而定(若异质性<50%,则采用固定效应模型;若异质性≥50%,则采用随机效应模型)。使用均数差(x±s)来描述资料中的连续性变量。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 文献检索结果
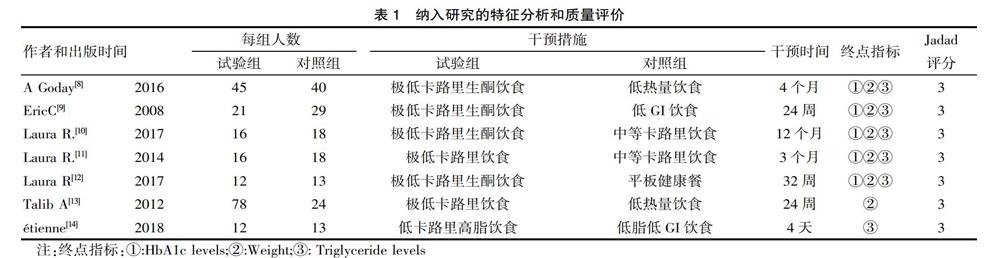
初次检索出249篇文献(英文:243篇中文:27篇,去除重复文献16篇,通过阅读题目和摘要排除掉209篇,最后通过阅读全文筛选出7篇符合标准的英文文献,各文献研究类型均为随机对照试验,且研究对象均为人类。总的筛选流程图见图1。
2.2 文獻质量评价
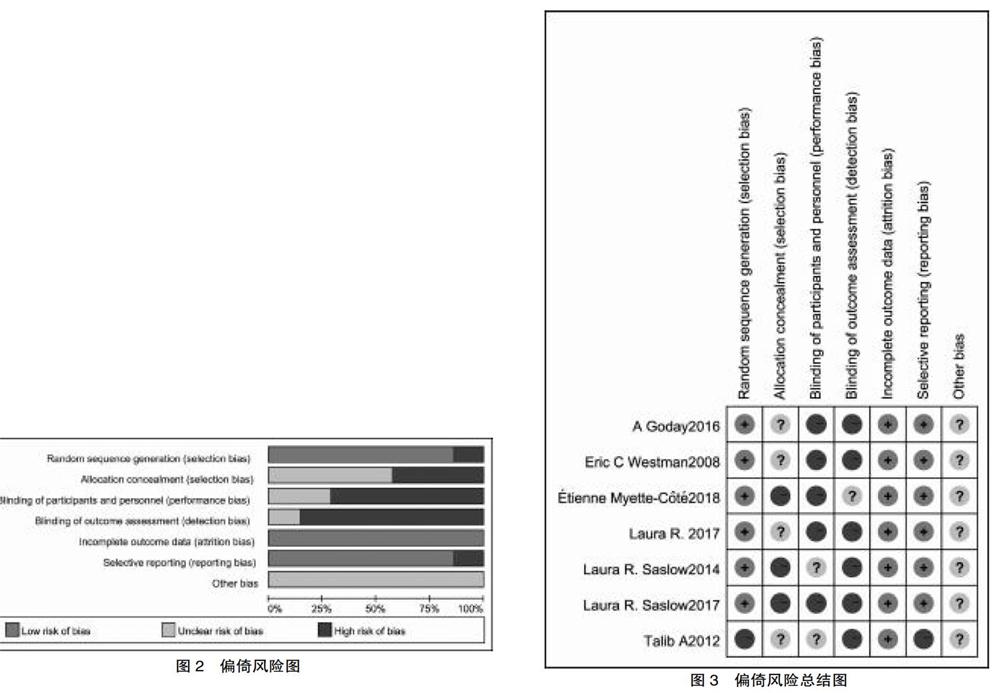
各文献基本特征及Jadad评分结果如图1所示。根据Cochrane手册准则,7篇纳入文献的偏倚风险图2及图3所示。
2.3 Meta分析结果
2.3.1 Weight森林图 在对糖尿病患者的HbA1c变化水平进行比较方面,共有5篇文献研究了该指标,由于I2=0%,判定纳入研究之间没有异质性,使用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示,干预组治疗前后HbA1c下降水平大于对照组[MD=-0.50,95%CI(-0.70,-0.30),P<0.01]。见图4。
2.3.2 Weight森林图 在对糖尿病患者的Weight变化水平进行比较方面,共有6篇文献研究了该指标,由于I2=0%,判定纳入研究之间没有异质性,使用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示,干预组治疗前后Weight下降水平大于对照组[MD=-8.07,95%CI(-10.73,-5.40),P<0.01]。见图5。
2.3.3 Triglyceride森林图 在对糖尿病患者的Triglyceride变化水平进行比较方面,共有6篇文献研究了该指标,由于I2=0%,判定纳入研究之间没有异质性,使用固定效应模型进行分析。结果显示,干预组治疗前后Triglyceride下降水平大于对照组[MD=-28.61,95%CI(-46.66,-10.56),P<0.01],见图6。
2.4 敏感性分析
改用随机效应模型后,Meta分析结果与修改前比较异质性变化不大。逐篇剔除各文献后,Meta分析结果显示,异质性与剔除前相比变化不大,说明结果较为稳健。
2.5 发表偏倚检验
采用绘制漏斗图方式对Meta分析结果进行发表偏倚检验,分别绘制关于HbA1c、Weight、Triglyceride levels的漏斗图,观察图形发现,这三者的漏斗图结果基本对称,显示发表偏倚较小,见图7、8、9。
3 讨论
近年来,人们的生活水平不断提高,不良的饮食习惯和繁重的都市压力使得糖尿病的发病率越来越高,如果糖尿病得不到长期适当的综合治疗[15],延缓其进展,那么其近期和远期并发症的发生率将越来越大,会严重危害人们的健康。在糖尿病的治疗手段中,饮食管理和膳食治疗有可能成为治疗糖尿病的[16]经济有效的一种非药物治疗手段[17-18]。生酮饮食[19]作为一种非药物性的替代性饮食疗法,相对安全有效。
该研究主要从HbA1c、Weight、triglyceride levels这3个方面来评价生酮饮食治疗糖尿病患者的有效性:①HbA1c:HbA1c是指血液红细胞中的血红蛋白通过糖化反应与血中葡萄糖结合的产物,一般反应人体8~12周的总体血糖水平,人体糖化血红蛋白水平一般跟血浆葡萄糖的浓度成正比,是检测血糖变化过程中的一个有效指标。在该研究中,试验组HbA1c水平明显低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),说明生酮饮食治疗糖尿病患者有一定效果。②Weight:糖尿病患者往往都伴有肥胖,而体重的减轻能够改善糖尿病患者的胰岛素抵抗。在该次研究中,试验组采用生酮饮食治疗后,明显减轻了体重,说明了其有效性。③triglyceride levels:生酮饮食[20]能够降低糖尿病患者甘油三酯水平,改善其脂质代谢,减轻其体重,从而改善糖尿病患者病情。
虽然该研究异质性较小,敏感性分析后异质性很低,结果相对可靠,能够未临床医师在对糖尿病患者采取治疗措施的时候提供循证医学依据。但是该研究也存在很多不足:①纳入的研究比较少;②纳入的病例数量不是很多;③纳入的问文献全是英文文献,由于各地区人种,饮食习惯和生活环境的不同,生酮饮食治疗糖尿病患者效果方面可能存在差異,因此该研究对国内糖尿病患者提供治疗依
据时可能存在较大局限性。④分析的7篇文献均为已发表的文献,未发表的文献和其他来源(比如会议、报纸等)真实可靠,具有借鉴意义的资料,因此可能存在一定的发表偏倚。
[参考文献]
[1] Tiruneh SA.Factors influencing diabetes self-care practice among type 2 diabetes patients attending diabetic care follow up at an Ethiopian General Hospital, 2018[J].J Diabetes Metab Disord,2019,18(1):199-206.
[2] Dambha-Miller H.Association Between Primary Care Practitioner Empathy and Risk of Cardiovascular Events and All-Cause Mortality Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Prospective Cohort Study[J].Ann Fam Med,2019,17(4):311-318.
[3] Davies MJ.Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association(ADA)and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes(EASD)[J].Diabetes Care,2018,41(12):2669-2701.
[4] Sheng GM.Optimized mid-long term management of ketogenic diet in children with refractory epilepsy[J].J Biol Regul Homeost Agents,2019,33(3):913-918.
[5] Fan Y.Crosstalk between the Ketogenic Diet and Epilepsy: From the Perspective of Gut Microbiota[J].Mediators Inflamm,2019:8373060.
[6] Joshi S, RJ Ostfeld, M McMacken.The Ketogenic Diet for Obesity and Diabetes-Enthusiasm Outpaces Evidence[J].JAMA Intern Med, 2019.
[7] Stocker RK.[Ketogenic Diet and its Evidence-Based Therapeutic Implementation in Endocrine Diseases][J].Praxis (Bern 1994), 2019,108(8):541-553.
[8] Goday A.Short-term safety, tolerability and efficacy of a very low-calorie-ketogenic diet interventional weight loss program versus hypocaloric diet in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Nutr Diabetes,2016,6(9):e230.
[9] Westman EC.The effect of a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-glycemic index diet on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Nutr Metab (Lond),2008,5:36.
[10] Saslow LR.Twelve-month outcomes of a randomized trial of a moderate-carbohydrate versus very low-carbohydrate diet in overweight adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus or prediabetes[J].Nutr Diabetes,2017,7(12):304.
[11] Saslow LR.A randomized pilot trial of a moderate carbohydrate diet compared to a very low carbohydrate diet in overweight or obese individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus or prediabetes[J].PLoS One,2014,9(4):e91027.
[12] Saslow LR.An Online Intervention Comparing a Very Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations Versus a Plate Method Diet in Overweight Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial[J].J Med Internet Res,2017,19(2):e36.
[13.] Hussain TA.Effect of low-calorie versus low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet in type 2 diabetes[J].Nutrition,2012,28(10):1016-1021.
[14] Myette-Cote E.The effect of a short-term low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet with or without postmeal walks on glycemic control and inflammation in type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial[J].Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol,2018,315(6):R1210-r1219.
[15] Petersmann A.Definition, Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus[J].Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes, 2018. 126(7):406-410.
[16] Shestakova MV IA Sklyanik, Dedov, II.Is it possible to achieve sustained remission or cure of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the 21st century[J].Ter Arkh,2017,89(10):4-11.
[17] Wei JP.Research Progress on Non-Drug Treatment for Blood Glucose Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus[J].Chin J Integr Med,2018,24(10):723-727.
[18] Corona G.Sexual Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes at Diagnosis: Progression over Time and Drug and Non-Drug Correlated Factors[J].PLoS One, 2016,11(10):e0157915.
[19] Boison D.New insights into the mechanisms of the ketogenic diet[J].Curr Opin Neurol,2017,30(2):187-192.
[20] Westman EC.Implementing a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab,2018,13(5):263-272.
(收稿日期:2019-10-15)
