脑出血微创钻孔引流与尿激酶对颅内血块溶解的效果对比
2020-04-23王晶黄莉
王晶 黄莉

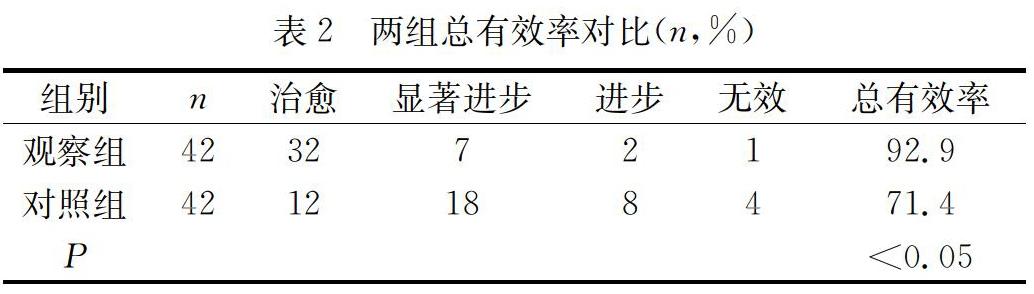

【摘 要】 目的 : 对比脑出血微创钻孔引流与尿激酶对颅内血块溶解的效果。方法 : 2018年4月至2019年4月选择在本院诊治的脑出血患者84例,随机分为两组。研究组给予微创钻孔引流治疗,对照组给予尿激酶治疗,记录颅内血块溶解效果。结果 : 治疗后观察組的总有效率显著高于对照组(P<0.05);治疗后观察组的血肿清除率显著高于对照组(P<0.05);治疗后两组的血清GFAP含量都显著低于治疗前,观察组也显著低于对照组(P<0.05);观察组闭管时间及引流时间都显著少于对照组(P<0.05)。结论 : 相对于尿激酶,微创钻孔引流在脑出血中的应用能促进颅内血块溶解,抑制血清GFAP的释放,减少闭管时间及引流时间,从而提高治疗效果。
【关键词】 微创钻孔引流;尿激酶;脑出血;颅内血块
Comparison of the effect of minimally invasive drilling drainage and urokinase on intracranial blood clot lysis in patients with cerebral hemorrhage
Wang Jing, Huang Li
Fourth People's Hospital of Tianshui, Tianshui, Gansu 741020
[Abstract] Objective:To compare the effects of minimally invasive drilling drainage and urokinase on intracranial blood clot lysis in patients with cerebral hemorrhage. Methods: From April 2018 to April 2019, 84 patients with cerebral hemorrhage were selected and divided into two groups. The study group was treated with minimally invasive drilling drainage, while the control group was treated with urokinase. The effect of intracranial blood clot dissolution was recorded. Results: After treatment, the total effective rate of the study group was significantly higher than that of the control group (P<0.05). After treatment, the hematoma clearance rate in the study group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.05). After treatment, the serum GFAP content in both groups was significantly lower than that before treatment, and the study group was also significantly lower than that in the control group (P<0.05). The closure time and drainage time of the study group were significantly less than those of the control group (P<0.05). Conclusion: Compared with urokinase, the application of minimally invasive drilling drainage in cerebral hemorrhage can promote the dissolution of intracranial blood clots, inhibit the release of serum GFAP, reduce the time of closure and drainage, and thus improve the therapeutic effect.
[Key words] Minimally invasive drilling drainage; Urokinase; Cerebral hemorrhage; Intracranial blood clot
脑出血是严重危害人类健康的常见病,具有高发病率、高致残率、高病死率等“三高”特征。流行病学显示我国脑出血患者占所有脑血管疾病患者的30.0%左右,1个月内的病死率接近20.0%[1]。特别是脑出血后引起机体和脑组织局部一系列病理性反应,包括脑内血肿的扩大,从而释放出大量的血管活性物质,诱发机体出现脑水肿,并可导致局部脑血流量减少[2]。随着医学技术的发展,微创技术在脑出血患者中的应用越来越多。其中脑出血微创钻孔引流具有操作简单、创伤小、并发症少、易于掌握、效果确切等优点,能减少因血肿占位、血肿毒性引发的脑组织损害,促进患者恢复[3]。而尿激酶经引流管注入可加速脑内血肿自引流管排出,也可促进血肿溶解液化,减少并发症的发生,有助于提高临床疗效,降低致死率、致残率。神经胶质纤维酸性蛋白(Glial fibrillary acidic protein,GFAP)是一种中间丝蛋白,被认为是 星形胶质细胞的特异性标志物,是星形胶质细胞的细胞骨架[4]。本文对比了脑出血微创钻孔引流与尿激酶对颅内血块溶解的效果,以明确其应用价值与机制。现总结报道如下。
参考文献
[1] 严鹏程.脑出血临床流行病学变化趋势分析[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2011.
[2] 谭卫国,孙晓欧.高血压脑出血破入脑室的外科临床治疗体会[J].养生保健指南,2019,(06):97.
[3] Gong X,Hu A,Li X,et al.Coordinated expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A and urokinase-type plasminogen activator contributes to classical swine fever virus Shimen infection in macrophages[J].BMC Vet Res,2019,15(01):82.
[4] Xu N,Meng H,Liu T,et al.Treatment of acute thromboembolic complication after stent-assisted coil embolization of ruptured intracranial aneurysm: a case report[J].Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat,2019,(15):69-74.
[5] 丽敏,于芳苹,张黎,等.盐酸法舒地尔对脑出血大鼠炎性反应及继发性脑损伤的影响研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2017,16(11):1081-1090.
[6] Zhang D,Zhang C,Lan S,et al.Near-Infrared Light Activated Thermosensitive Ion Channel to Remotely Control Transgene System for Thrombolysis Therapy[J].Small,2019,15(27):e1901176.
[7] 唐晓辉.尿激酶与重组组织型纤溶酶原激活剂超早期静脉溶栓治疗急性脑梗死的疗效和安全性比较[J].中国医师进修杂志,2012,35(25):59-61.
[8] 李显锋.穿刺引流術中应用尿激酶治疗老年高血压脑出血的疗效分析[J].世界复合医学,2019,05(02):121-123.
[9] 辛晓东,宋畅,郝万如.脑出血血肿穿刺引流术后颅内感染病原体分布及危险因素分析[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2019,17(05):794-796.
[10]Zhu C,Zhuo H,Qin Y,et al.Comparison of clear effect and the complications, and short and mid-term effects between ultrasound-guided and non-guided catheter-directed thrombolysis in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis of lower extremity[J].Vascular,2019,27(03):277-283.
