腺苷脱氨酶水平与类风湿关节炎关系的荟萃分析
2020-04-20蔡昕添朱晴吴婷
蔡昕添 朱晴 吴婷
[摘要] 目的 系统评价腺苷脱氨酶(ADA)水平与类风湿关節炎(RA)的关系。 方法 在PubMed、Embase、Cochrane Library、Web of Science、中国知网、万方数据库检索已发表的关于ADA水平与RA相关性的文献,检索时间从建库至2019年6月1日。中文检索词:腺苷脱氨酶、腺苷氨基水解酶、类风湿关节炎、类风关;英文检索词:ADA,Adenosine Deaminase,Adenosine Aminohydrolase,RA,Rheumatoid Arthritis。由2名研究人员独立进行文献筛选、质量评价及数据提取,若存在争议,由双方协商或由第三方协助裁定解决。采用GetData Graph Digitizer 2.22软件对入选文献中的数据进行数字化转换提取,Stata 12.0软件进行数据合并、敏感性分析及发表偏倚评估。 结果 共纳入16篇文献,包含病例组784例,对照组711例。荟萃分析显示,病例组ADA水平显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(SMD = 1.37,95%CI:1.00~1.74,P < 0.05)。剔除6篇对荟萃分析结果影响较大的文献后,病例组ADA水平显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(SMD = 1.14,95%CI:0.90~1.38,P < 0.05)。Begg检验与Egger检验结果提示研究间不存在明显发表偏倚(P = 0.631,0.629)。 结论 RA患者关节滑液及血清中ADA水平较正常人明显增高,血清及关节滑液中ADA水平有望成为诊断、评估RA病情活动的一种重要指标。
[关键词] 类风湿关节炎;腺苷脱氨酶;关系;荟萃分析
[中图分类号] R593.22 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2020)03(a)-0081-05
[Abstract] Objective To systematically evaluate the association between adenosine deaminase (ADA) level and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Methods Published literatures on the correlation between ADA level and RA in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China national knowledge infrastructure and wanfang database were searched. The retrieval time was from the database construction to June 1, 2019. Chinese keywords were adenosine deaminase, adenosine amino hydrolase, rheumatoid arthritis, wind–lik. English keywords were ADA, Adenosine Deaminase, Adenosine Aminohydrolase, RA, Rheunatoid Arthritis. Two researchers shall independently conduct literature screening, quality evaluation and data extraction in accordance. In case of any dispute, both parties shall negotiate or a third party shall assist in adjudication and settlement. GetData Graph Digitizer 2.22 software was used to digitally convert and extract the data in the selected literature and Stata 12.0 software was used to merge the data, sensitivity analysis and publication bias evaluation were carried out. Results A total of 16 articles were enrolled, including 784 cases in the case group and 711 cases in the control group. Meta-analysis showed that the levels of ADA in the case group were significantly higher than those in the control group (SMD = 1.37, 95%CI:1.00-1.74, P < 0.05). After the exclusion of 6 literatures with significant influence on the results of meta-analysis, ADA levels in the case group were significantly higher than those in the control group, with statistically significant differences (SMD = 1.14, 95%CI: 0.90-1.38, P < 0.05). The results of Begg test and Egger test showed that there was no significant publication bias between the studies (P = 0.631, 0.629). Conclusion The levels of ADA in synovial fluid and serum of patients with RA are significantly higher these those of normal people. The levels of ADA in serum and synovial fluid are expected to become an important factor for the diagnosis and evaluation of the disease activity of RA.
[Key words] Rheumatoid arthritis; Adenosine deaminase; Association; Meta-analysis
类风湿性关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)是一种以慢性关节炎为主要临床特征的自身免疫性疾病[1-3]。腺苷脱氨酶(adenosine deaminase,ADA)是嘌呤代谢过程中一种重要的酶,被认为是细胞免疫的重要标志物[4]。近年来发现ADA可反映系统性红斑狼疮等自身免疫性疾病炎症状态下单核-巨噬细胞的活性,因而关于ADA与自身免疫性疾病间相互关系的研究已经成为当下研究的热点[4-5]。但国内外关于ADA与RA相关性的各项研究差异较大,部分研究认为ADA水平与RA发生发展密切相关,另一部分则认为两者间并无显著相关[6-7]。且关于ADA水平与RA病情活动程度的研究结论目前仍存较大争议[8-9]。因此,为综合评估ADA与RA及其疾病活动程度之间的关系,本研究拟通过对国内外公开发表的有关ADA水平与RA相关性的文献进行薈萃分析,综合评估研究间异质性从而得出一个更可靠的结论。
1 资料与方法
1.1 文献检索
在PubMed、Embase、Cochrane Library、Web of Science、中国知网、万方数据库检索已发表的关于ADA水平与RA相关性的文献,检索时间从建库至2019年6月1日。中文检索词:腺苷脱氨酶、腺苷氨基水解酶、类风湿关节炎、类风关;英文检索词:ADA,Adenosine Deaminase,Adenosine Aminohydrolase,RA,Rheu-matoid Arthritis。纳入标准:①研究对象:病例组RA诊断符合1987年美国风湿病学会标准[10]或2010年欧洲抗风湿病联盟诊断标准[11];对照组为非RA人群,包括健康对照组、骨关节炎组等。活动期与非活动期评价采用DAS28-ESR评分[12],DAS28-ESR评分>2.6分为活动期。②研究类型:所选文献为公开发表的原创性、观察性研究。③语种限制为中文或英文,且可获取全文。③测量指标:能获取样本量、均数与标准差或中位数与四分位数间距。排除标准:①文献仅为动物实验、病例报告等;②文献研究设计不严谨、关键数据缺失且无法转换与修正。
1.2 文献筛选与资料提取
2位研究人员独立进行文献检索与去重。逐篇阅读题目、摘要与关键词进行初筛,对可能符合标准的文献再逐篇全文阅读。纳入文献数据提取内容主要包括作者姓名、病例组与对照组ADA水平等。部分研究未直接提供均数与标准差,而是以散点图形式表示,采用GetData Graph Digitizer 2.22软件对图中数据进行数字化转换与提取[13]。如果文章未提供重要的原始数据,将通过电子邮件联系通讯作者而获取数据。所提取信息由双方交叉、独立核对,如存在争议,由双方协商或由第三方协助裁定解决。
1.3 文献质量评价
采用渥太华量表(NOS)[14]对纳入文献进行质量评价。评分项由8项构成,满分为9分,≥6分视为较高质量研究,<6分视为低研究质量。
1.4 统计学方法
采用Stata 12.0软件进行数据分析。所纳入研究的测量指标均为连续性变量但对于ADA的测量方法与计量单位不尽相同,因此效应指标采用标准化均数差(SMD),各效应量均计算95%置信区间(CI)。当I2≤50%时可认为其异质性较低,当I2>50%时则认为其异质性较高。当P > 0.1,I2≤50%时,其异质性在可接受范围,合并效应量常采用固定效应模型;如P < 0.1,I2>50%,则需进一步分析原因,寻找异质性来源,对可能造成异质性的因素行亚组分析,排除可能存在异质性的因素后I2仍>50%者则采用随机效应模型。通过敏感性分析探讨单一研究对合并效应量的影响,以评估其稳定性。通过绘制漏斗图并做Begg检验、Egger检验判断是否存在发表偏倚及其大小。
2 结果
2.1 文献检索结果
最终纳入文献16篇,其中英文15篇,中文1篇;病例组784例,对照组711例。见图1。
2.2 文献质量评价
16篇[6-9,15-26]文献均为高质量研究。见表1。
2.3 荟萃分析结果
2.3.1 两组ADA水平比较 16篇[6-9,15-26]文献存在较明显的异质性(I2 = 88.9%,P < 0.001),采用随机效应模型进行分析。结果显示病例组ADA水平显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(SMD = 1.37,95%CI:1.00~1.74,P < 0.05)。见图2。
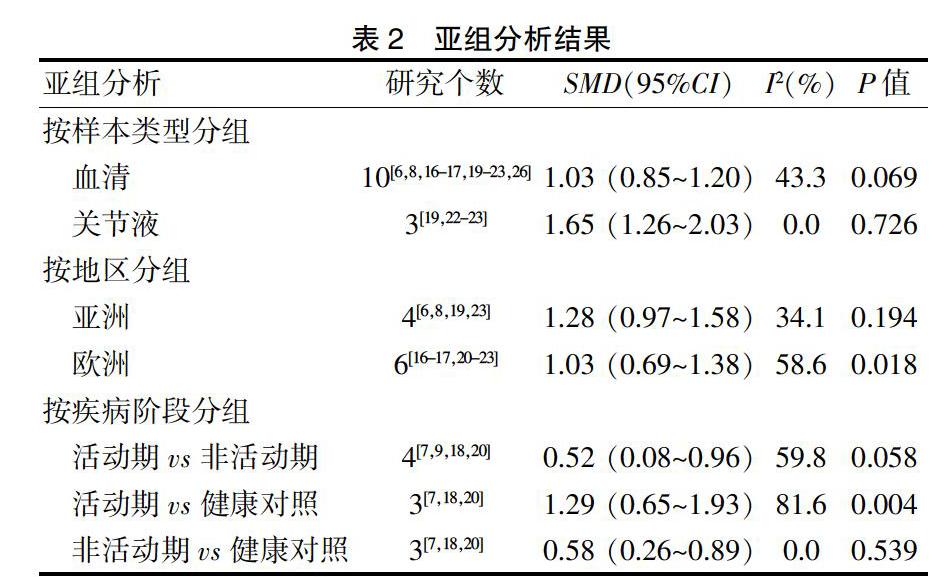
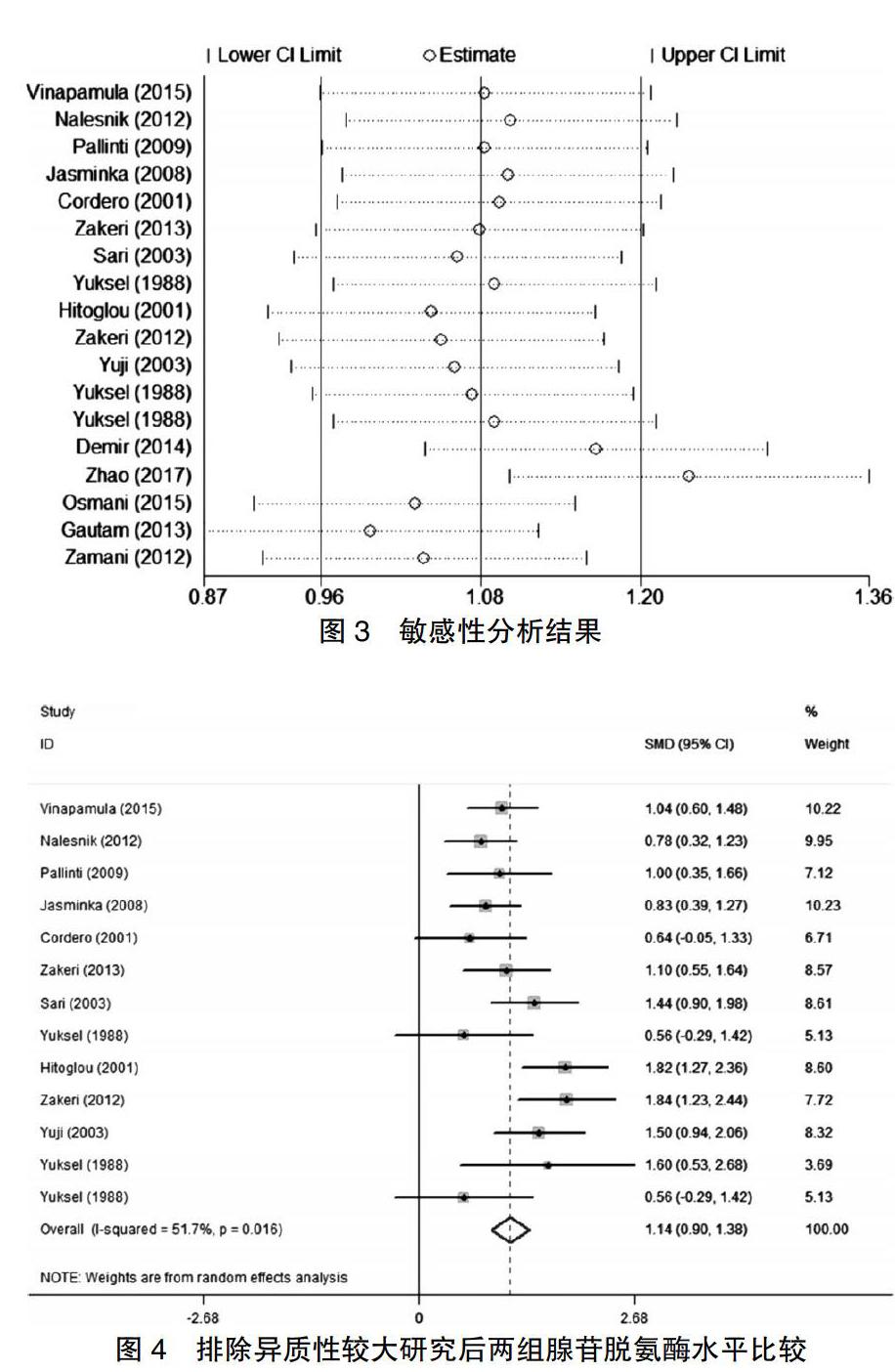
2.3.2 敏感性分析 6文献[7,9,15,18,24-25]对荟萃分析结果影响较大,见图3。剔除后文献异质性显著降低(I2 = 51.7%,P = 0.016),采用随机效应模型进行分析,结果显示病例组ADA水平显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(SMD = 1.14,95%CI:0.90~1.38,P < 0.05),见图4。
2.3.3 亚组分析 亚组分析结果示以关节滑液为样本的研究中其合并效应的异质性较亚组分析前大大降低(I2 = 0.0%,P = 0.726);以血清为样本的研究中其合并效应的异质性较亚组分析前也有所降低(I2 =43.3%,P = 0.069),其结果显示,无论是血清还是关节液样本,RA患者ADA水平均显著高于对照组(P < 0.05)。不同地区的亚组分析结果显示,无论是来自亚洲还是来自欧洲,RA患者ADA水平均高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。纳入研究中,有4项研究[7,9,18,20]报道了活动期与非活动期ADA水平的相关性,3项研究[7,18,20]报道了活动期与对照组、非活动期与对照组ADA水平的相关性。合并后结果显示活动期血清ADA水平高于非活动期,活动期、非活动期ADA水平均高于健康对照,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。见表2。
[8] Pallinti V,Ganesan N,Anbazhagan M,et al. Serum biochemical markers in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Indian J Biochem Biophys,2009,46(4):342.
[9] Salesi M,Ghazvini RA,Farajzadegan Z,et al. Serum adenosine deaminase in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate [J]. J Res Pharm Pract,2012,1(2):72-76.
[10] Balbaloglu O,Ozcan SS. Is pentraxin 3 level an effective biomarker in disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis? [J]. Arch Med Sci,2020,16(1):81-86.
[11] Boer AC,Boeters DM,van der Helm-van Mil AHM. The use of MRI-detected synovitis to determine the number of involved joints for the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for Rheumatoid Arthritis - is it of additional benefit? [J]. Ann Rheum Dis,2018,77(8):1125-1129.
[12] Xie W,Li J,Zhang Z. The impact of different criteria sets on early remission and identifying its predictors in rheumatoid arthritis:results from an observational cohort(2009-2018)[J]. Clin Rheumatol,2020,39(2):381-389.
[13] Zhu B,Zhu Q,Li N,et al. Association of serum/plasma high mobility group box 1 with autoimmune diseases:A systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Medicine(Baltimore),2018,97(29):e11531.
[14] Schuch FB,Stubbs B,Meyer J,et al. Physical activity protects from incident anxiety:A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies [J]. Depress Anxiety,2019,36(9):846-858.
[15] 趙冠华,郜赵伟,董珂,等.血清腺苷脱氨酶检测在几种自身免疫性疾病中的临床意义研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2017,17(4):672-675.
[16] Nalesnik M,Nikoli■ JM,Jandri■ S. Adenosine deaminase and C-reactive protein in diagnosing and monitoring of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Medicinski Glasnik,2011,8(1):163-168.
[17] Cordero OJ,Salgado FJ,Mera-Varela A,et al. Serum interleukin-12,interleukin-15,soluble CD26,and adenosine deaminase in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Rheumatol Int,2001,21(2):69-74.
[18] Zamani B,Jamali R,Jamali A. Serum adenosine deaminase may predict disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Rheumatol Int,2012,32(7):1967-1975.
[19] Zakeri Z,Izadi S,Niazi A,et al. Comparison of adenosine deaminase levels in serum and synovial fluid between patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis [J]. Int J Clin Exp Med,2012,5(2):195-200.
[20] Sari RA,Taysi SO,Bakan N. Correlation of serum levels of adenosine deaminase activity and its isoenzymes with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol,2003,21(1):87-90.
[21] Hitoglou S,Hatzistilianou M,Gougoustamou D,et al. Adenosine deaminase activity and its isoenzyme pattern in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Clin Rheumatol,2001,20(6):411-416.
[22] Yuksel H,Ako■lu TF. Serum and synovial fluid adenosine deaminase activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis,osteoarthritis,and reactive arthritis [J]. Ann Rheum Dis,1988,47(6):492-495.
[23] Yuji N,Koshiba M,Nakazawa T,et al. Specific increase in enzymatic activity of adenosine deaminase 1 in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts [J]. Arthritis Rheum,2003,48(3):668-674.
[24] Osmani AM,Sayeed D,Ali GM,et al. Study of serum adenosine deaminase and alkaline phosphatase in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Evol of Med and Dent Sci,2015,49(4):312-318.
[25] Gautam N,Archana J,Kumar R,et al. Serum total adenosine deaminase activity in Nepalese patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [J]. Asian of Med Sci,2013,4(2):30-35.
[26] Jasminka MN,Jasenka LM,Milada SN,et al. Citrullinated peptide antibodies,adenosine deaminase activity and other potential biomarkers for predicting and monitoring rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Med Bio,2008,27(3):383-388.
[27] da Silva J,Passos DF,Bernardes VM,et al. ATP and adenosine:Role in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Immunol Lett,2019,214:55-64.
(收稿日期:2019-09-03 本文編辑:刘明玉)
