Therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of heat-sensitive moxibustion for adjuvant treatment of depression in Parkinson disease
2020-02-28WangXiaomei王笑媚RongChunjiao荣春娇
Wang Xiao-mei (王笑媚), Rong Chun-jiao (荣春娇)
Lishui Second People’s Hospital, Zhejiang 323000, China
Abstract
Keywords: Moxibustion Therapy; Moxa Stick Moxibustion; Heat-sensitive Moxibustion; Quality of Life; Mental Status and Dementia Tests; Parkinson Disease; Depression
Parkinson disease (PD) is a chronic and progressive neurodegenerative disease pathologically characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and the dysfunction of dopamine (DA) pathway in the striatum, and clinically characterized by bradykinesia, myotonia, tremor, abnormal posture and gait[1].As the disease progresses, non-motor symptoms of PD also gradually occur, among which, depression is more common, with the incidence rate as high as 35%-50%[2].Parkinson disease with depression (PDD)can lead to the decrease of cognitive ability, the decrease of daily quality of life and the increase of suicide rate, which has a very negative impact on families and society[3].For PDD, DA receptor agonists,tricyclic antidepressants, and 5-hydroxytryptamine(5-HT) reuptake inhibitors are mainly used in clinic, and appropriately combined with cognitive behavioral therapy, electric shock therapy, psychotherapy and other auxiliary therapies[4].However, the efficacy of drug is limited, the action is slow, the treatment course is long, the cost is high, and the adverse reactions are obvious, while the curative effect is not stable.The auxiliary therapies lack of professionals, and its clinical popularization rate needs to be improved[5].
PDD belongs to tremor syndrome and depression syndrome in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).TCM has a certain effect in treating PDD[6-7], and patients have better compliance.As one kind of the TCM therapies, moxibustion has been reported in many clinical studies in the treatment of PD and depression[8-9], and its safety has been widely recognized.However, there are few reports on the clinical efficacy and mechanism of moxibustion for PDD.
In this study, we observed the clinical efficacy of heat-sensitive moxibustion for the treatment of PDD,and its effects on the levels of neurotransmitters and inflammatory factors.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Case selection
1.1.1 Diagnostic criteria in Western medicine
Met the diagnostic criteria of PD in theChinese Guideline for Treatment of Parkinson Disease(3rd edition)[10].Met the diagnostic criteria of depression in the 3rd edition ofChinese Classification and Diagnosis of Mental Diseases(Classification of Mental Disorders)[11].
1.1.2 Criteria for syndrome differentiation of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)
Syndrome differentiation classification referred to the criteria of syndrome of qi and blood depletion in theGuiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines[12].Primary manifestations: tremor of head or limbs, less movement, over-thinking and being anxious, palpitations and timidity.Secondary manifestations: hypomimia, dim complexion, dizziness and spiritlessness, anorexia, a pale teeth-printed tongue with white coating, deep pulse or weak pulse.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Those who met the above diagnostic criteria of PD in Western medicine and syndrome of qi and blood depletion for syndrome differentiation of TCM; aged 40-80 years; Hamilton depression scale-17(HAMD-17) >13 points[13]; agreed to participate in this trial and signed informed consent.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Patients with non-PD diseases such as hepatolenticular degeneration, hepatic encephalopathy,essential tremor; those with severe diseases of heart,brain, liver or kidney; women during pregnancy or lactation; those were unconscious or unable to cooperate with the trial; those who were allergic to the medication.
1.4 Statistical methods
All data were statistically analyzed by the SPSS version 20.0 statistical software.Chi-square test was applied to the comparison of counting data.Measurement data were first tested for normality and homogeneity of variance.Those in normal distribution and had homogeneous variance were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s), andt-test was applied.T’-test was applied for data with uneven variance.If data did not meet the normal distribution,non-parametric test was applied.P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
1.5 General data
A total of 80 patients who met the inclusion criteria of PDD were enrolled from our hospital between September 2016 and January 2019.All patients were randomly divided into an observation group and a control group by the random number table, with 40 cases in each group.There was no dropout case during the study.The patients in the observation group were aged between 48 and 80 years, with the shortest duration of 9 months and the longest of 93 months.The patients in the control group were aged between 51 and 80 years, with the shortest duration of 6 months and the longest of 92 months.There were no significant differences in the data of gender, age and duration of disease between the two groups (allP>0.05), indicating that the two groups were comparable (Table 1).

Table 1.Comparison of general data between the two groups
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Control group
Patients in the control group received conventional symptomatic treatment of Western medicine, and the efficacy was observed after continuous 2-month treatment.
Anti-PD treatment: Oral levodopa and benserazide hydrochloride tablets (national drug registration number: H10930198, Shanghai Roche Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China), starting at 0.125 g per time, three times a day.Added 0.125 g per week after starting the medicine, and maintained the dosage after the symptoms improved.
Antidepressant treatment: Oral paroxetine tablets(national drug registration number: H10950043,Sino-American Tianjin Shike Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,China), 20 mg, once a day.
2.2 Observation group
2.2.1 Medications
The observation group received the same medications as the control group.
2.2.2 Heat-sensitive moxibustion
Acupoints: Qihai (CV 6) and bilateral Xuehai (SP 10),Zusanli (ST 36), Xinshu (BL 15) and Pishu (BL 20).
Moxa stick specifications: Hwato Brand pure moxa sticks of 1.8 cm in diameter and 20 cm in length were used for moxibustion (Nanyang Wolong Chinese Medicine Moxa Factory, China).
Methods: Acupoint locations referred to theScience of Meridians and Acupoints[14].The heat-sensitive moxibustion operation referred to theAcupoint Heatsensitization Moxibustion:A New Moxibustion Therapy[15].The patient took a supine position, exposing the acupoints.After receiving moxibustion at frontal points, the patient changed to the prone position.The physician sought heat-sensitized points first, which was to apply circling moxibustion and mild moxibustion to the acupoints with an ignited moxa stick 3-5 cm away from skin.When patient felt heat penetration, heat expansion, heat transmission or heat in distant area but not in local area, that would be the heat-sensitized point.Then the physician continued to perform mild moxibustion at this heat-sensitized point till the disappearance of the heat sensitization.The physician repeated the above steps until the selected acupuncture points were completed for moxibustion in turn.The heat-sensitive moxibustion was performed once a day for 2 months.
3 Observation of Curative Efficacy
3.1 Observation items
3.1.1 HAMD-17 score
HAMD-17 was scored before and after treatment for the two groups by the same neurologist not knowing about grouping.The HAMD-17 score ranges from 0 to 53 points, and higher scores indicate more severe depressive symptoms.PD patients with a HAMD-17 score >13 points were considered to be depressed.HAMD-17 has high sensitivity and specificity that can be used for screening and severity assessment of PDD[13].
3.1.2 Unified Parkinson's disease rating scale (UPDRS)
UPDRS was scored before and after treatment for the two groups by the same neurologist not knowing about grouping.UPDRS consists of Ⅰ (mind, behavior and emotion), Ⅱ (activities of daily living), Ⅲ (motor examination) and Ⅳ (complications).The total score is 199 points, and the higher the score, the more severe the condition of PD patients[16].
3.1.3 Parkinson's disease quality of life questionnaire-39 (PDQ-39)
Before and after treatment, patients in both groups filled the PDQ-39 according to their actual situation in the last month.PDQ-39 consists of 8 dimensions,including physical activity, daily behavioral activities,mental health, humiliation, social support, cognition,communication and physical discomfort, with a total of 39 subjects and a score ranging from 0 to 156 points.The higher the score, the worse the quality of life[17].
3.1.4 Neurotransmitter and inflammatory factors detection
The fasting venous blood in the morning was collected before and after treatment.The serum DA,5-HT, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6(IL-6) levels of the two groups were measured before and after treatment by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
3.2 Criteria of curative efficacy
The reduction rate of HAMD-17 score was used as the criteria of efficacy evaluation[18].
HAMD-17 reduction rate = (Score before treatment -Score after treatment) ÷ Score before treatment ×100%.
Cured: The main symptoms basically disappeared.HAMD-17 reduction rate ≥90%.
Marked effect: The main symptoms were significantly improved.HAMD-17 reduction rate ≥60%, but <90%.
Effective: The main symptoms were improved.HAMD-17 reduction rate ≥30%, but <60%.
Invalid: The main symptoms were not obviously improved or even worse.HAMD-17 reduction rate<30%.
3.3 Results
3.3.1 Clinical efficacy
The total effective rate was 95.0% in the observation group and 72.5% in the control group.The total effective rate of the observation group was higher than that of the control group (χ2=7.44,P=0.006), (Table 2).

Table 2.Comparison of clinical efficacy between the two groups (case)
3.3.2 HAMD-17 score
There was no significant difference in the HAMD-17 score between the two groups before treatment(P>0.05).After treatment, the HAMD-17 scores in both groups decreased obviously (bothP<0.05), and the HAMD-17 score in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group(P<0.05), (Table 3).
3.3.3 UPDRS score
There were no significant differences in the UPDRS component and total scores between the two groups before treatment (allP>0.05).After treatment, the UPDRS component and total scores in both groups decreased significantly (allP<0.05), and all the scores in the observation group were lower than those in the control group (allP<0.05), (Table 4).
Table 3.Comparison of the HAMD-17 score between the two groups (±s, point)

Table 3.Comparison of the HAMD-17 score between the two groups (±s, point)
Note: Compared with the same group before treatment, 1)P<0.05; compared with the control group after treatment, 2)P<0.05
Group n Before treatment After treatment Observation 40 21.75±5.55 14.43±4.961)2)Control 40 21.55±5.61 17.78±4.421)
Table 4.Comparison of UPDRS scores between the two groups (±s, point)
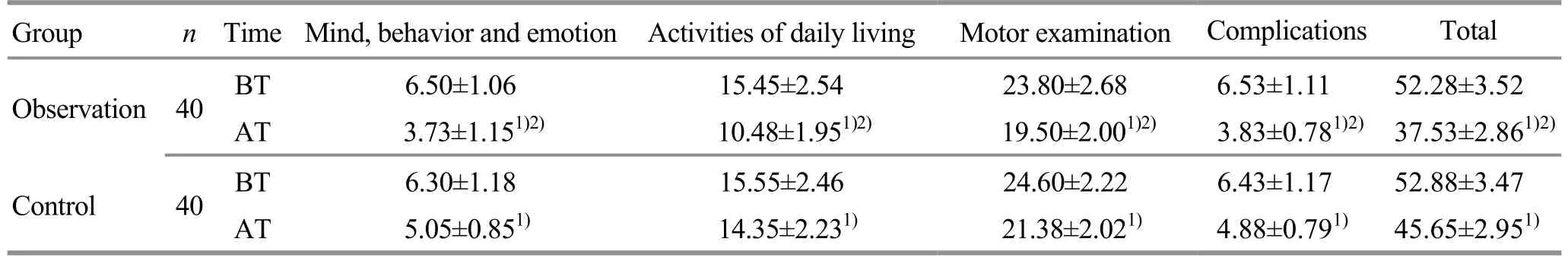
Table 4.Comparison of UPDRS scores between the two groups (±s, point)
Note: BT=Before treatment; AT=After treatment; compared with the same group before treatment, 1) P<0.05; compared with the control group after treatment, 2) P<0.05
Motor examination Complications Total 23.80±2.68 6.53±1.11 52.28±3.52 19.50±2.001)2) 3.83±0.781)2) 37.53±2.861)2)24.60±2.22 6.43±1.17 52.88±3.47 21.38±2.021) 4.88±0.791) 45.65±2.951)
3.3.4 PDQ-39 score
There was no significant difference in the PDQ-39 score between the two groups before treatment(P>0.05).After treatment, the PDQ-39 scores in both groups decreased significantly (bothP<0.05), and the PDQ-39 score in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group (P<0.05), (Table 5).
3.3.5 Serum DA and 5-HT levels
There were no significant differences in the serum DA and 5-HT levels between the two groups before treatment (bothP>0.05).After treatment, the DA and 5-HT levels in the observation group increased significantly (bothP<0.05), and were higher than those in the control group (bothP<0.05), (Table 6).
Table 5.Comparison of the PDQ-39 score between the two groups (±s, point)

Table 5.Comparison of the PDQ-39 score between the two groups (±s, point)
Note: Compared with the same group before treatment, 1)P<0.05; compared with the control group after treatment, 2)P<0.05
Observation 40 65.98±8.69 48.35±8.401)2)Control 40 64.10±7.96 56.20±7.591)
Table 6.Comparison of the serum DA and 5-HT levels between the two groups (±s)
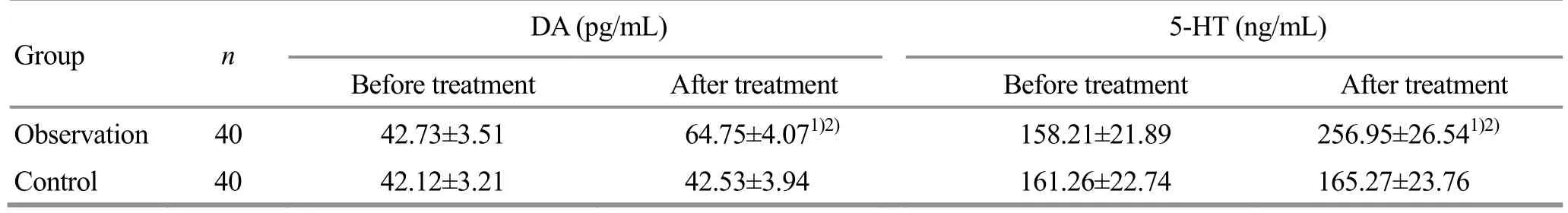
Table 6.Comparison of the serum DA and 5-HT levels between the two groups (±s)
Note: Compared with the same group before treatment, 1) P<0.05; compared with the control group after treatment, 2) P<0.05
Group n DA (pg/mL) 5-HT (ng/mL)Before treatment After treatment Before treatment After treatment Observation 40 42.73±3.51 64.75±4.071)2) 158.21±21.89 256.95±26.541)2)Control 40 42.12±3.21 42.53±3.94 161.26±22.74 165.27±23.76
3.3.6 Serum TNF-α and IL-6 levels
There were no significant differences in the serum TNF-α and IL-6 levels between the two groups before treatment (bothP>0.05).After treatment, the TNF-α and IL-6 levels in the observation group decreased significantly (bothP<0.05), and were lower than those in the control group (bothP<0.05), (Table 7).
3.3.7 Adverse reactions
During the treatment, there were 2 cases of mild diarrhea, 2 cases of nausea and vomiting and 3 cases of dizziness in the control group.There was 1 case of vomiting occurred in the observation group.The incidence of adverse reactions in the control group was 17.5%, which was significantly higher than that in the observation group (2.5%,χ2=5.00,P=0.025).The adverse reactions in the two groups were minor and all self-relieved within a short time.After treatment, there were no obvious abnormal changes in blood, urine,stool, liver and kidney function in all participants.
Table 7.Comparison of the TNF-α and IL-6 levels between the two groups (±s, pg/mL)

Table 7.Comparison of the TNF-α and IL-6 levels between the two groups (±s, pg/mL)
Note: Compared with the same group before treatment, 1) P<0.05; compared with the control group after treatment, 2) P<0.05
Group n TNF-α IL-6 Before treatment After treatment Before treatment After treatment Observation 40 432.93±59.48 333.87±45.241)2) 26.96±3.08 18.90±3.351)2)Control 40 445.98±53.86 430.06±49.03 26.28±2.86 25.74±3.08
4 Discussion
The pathogenesis of PDD is not clear.At present, it is believed that it is mainly caused by endogenous biological factors and exogenous psychological factors.Study showed that there was no significant correlation between the severity of depression and the progress of PD, and some of the depression symptoms appeared before motor symptoms, some occurred at the same time, and some after medications[19].It was clear that although bad mind and emotions such as delusion,despair and inferiority caused by the aggravation of motor dysfunction and the decline of social function and adaptability could indeed lead to the occurrence of depressive symptoms, the endogenous biological factors were the most primary cause of PDD.
Abnormalities in neurotransmitters such as DA and 5-HT play an important role in the occurrence and progress of PDD.DA is a neurotransmitter involved in the regulation of both motor function and emotional activity.The main biochemical change of PD is the significant decrease of DA content in the brain.The typical motor symptoms of PD only occur when the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra is reduced by more than 50% and DA content in the basal ganglia is reduced by more than 80%.Decreased DA neurons in the central system can also lead to reduced or lost happiness, apathy and the decrease of consciousness activities.Both PD patients and patients with depression have corpus striatum DA system dysfunction.Depression symptoms are one of the basic manifestations of PD patients with impaired dopaminergic pathways in the central frontal cortex[20].In addition to dopaminergic system, PD with depression is also related to abnormal 5-HT system.Clinical study showed that the serum 5-HT level was significantly reduced in patients with PD and depression, and 5-HT receptor antagonists could improve depressive symptoms in PD patients[19].5-HT transporters are also related to PDD, and can reflect the functional status of 5-HT neurons.It was found that the marker signal of 5-HT transporter in the nucleus raphes dorsalis was significantly reduced in the brain specimens of PD patients, indicating that there was 5-HT neuron dysfunction in PD patients[21].In addition, the feedback mechanism of 5-HT on DA is also involved in pathogenic process of PDD.Under physiological conditions, 5-HT inhibits the release of DA, while with the decrease of the DA level, the 5-HT level decreases, leading to the onset of PDD.
Recent studies suggested that inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-6 might also cause depression in PD patients.It was found that the serum TNF-α and IL-6 levels in PDD patients were significantly lower than those in healthy participants.After treatment, the levels of inflammatory factors were corrected to some extent[22], which suggested that the levels of inflammatory factors might be related to cognitive dysfunction in patients with PDD and might reflect the severity of cognitive impairment.Inflammatory cytokines may induce dopaminergic neuron cell damage by stimulating microglia, and also lead to apoptosis by combining with dopaminergic neuron cells and participate in the pathogenesis of PD[23].At the same time, over-expressed inflammatory cytokines aggravate immune damage, affect the expressions of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal cortex axis hormones and neurotransmitters such as DA and 5-HT, and induce emotional disorders such as depression[24].
According to the clinical manifestation of PDD, it falls under the category of tremor syndrome and depression syndrome in TCM.There is no consensus on pathogenesis and TCM pattern.For example, Song QY[25]advocated that it should be divided into three patterns:yin deficiency of liver and kidney, internal stirring of deficient wind; yang deficiency of spleen and kidney,internal blockade of phlegm stagnation; deficiency of both qi and blood, static blood blocking collaterals.However, study on TCM pattern showed that syndrome of qi and blood depletion was one of the most common syndromes in PD patients[26], and syndrome of qi and blood depletion of heart and spleen was a common pattern in patients with depression[27].PD patients with emotional disorders were more likely to have qi deficiency[28].It is clear that deficiency of both qi and blood syndrome is one of common syndromes in clinic.Therefore, the treatment principles should be benefiting qi for promoting production of blood and invigorating heart and spleen.
The heat-sensitive moxibustion is a new therapy characterized by applying suspended moxibustion to heat-sensitized acupoints.It has effects of traditional moxibustion such as warming for unblocking, warming for invigoration and mutual application of unblockinginvigorating.It is also suitable for deficiency syndrome,cold syndrome and meridian qi and blood blockage syndrome.In addition, the heat-sensitive moxibustion pays more attention to the transmission of meridian provoked by moxibustion, so that qi can reach the disease location, thus producing a more significant therapeutic effect compared with the traditional moxibustion.
In this study, Qihai (CV 6), Xuehai (SP 10), Zusanli(ST 36), Xinshu (BL 15) and Pishu (BL 20) were selected for moxibustion.Qihai (CV 6) is the Yuan-Primary point of Huang (the region around the navel), the sea of qi generation and the gathering place of primordial qi.Moxibustion at Qihai (CV 6) has the effect of benefiting qi and regulating qi flow.Xuehai (SP 10) can activate blood and resolve stasis, replenish and nourish blood,and lead blood back to the channel.For treating blood-related diseases, combination of Xuehai (SP 10)and Qihai (CV 6) has the effects of replenishing and nourishing blood, moving qi and activating blood, and promoting meridians and dissipating stasis.Zusanli(ST 36) is the He-Sea point of the Stomach Meridian and the Lower He-Sea point of stomach, with the effect of invigorating spleen and stomach, harmonizing qi and blood, strengthening vital qi and primordial energy.Xinshu (BL 15) and Pishu (BL 20) are the Back-Shu points of heart and spleen, respectively.They can invigorate heart and spleen and promote the derivation of qi and blood.They are the key points to treat diseases of heart and spleen.The combination of the above five acupoints can produce the effect of benefiting qi and activating qi flow, nourishing blood and promoting blood circulation, and invigorating spleen for benefiting heart.
Results of this study showed that the clinical effective rate of the observation group was significantly higher than that of the control group.After treatment, the HAMD-17 score, the UPDRS component and total scores in the observation group were improved obviously, and superior to those in the control group.The PDQ-39 score in the observation group decreased obviously after treatment, and was lower than that in the control group.The serum DA and 5-HT levels in the observation group increased significantly after treatment, and the TNF-α and IL-6 levels decreased significantly, which were all significantly different from those in the control group.The above results indicated that heat-sensitive moxibustion had certain assistant effect in treating PDD that could significantly improve clinical symptoms.It had obvious antidepressant effect,and could improve quality of life of patient, which may be related to the up-regulation of DA and 5-HT levels and the down-regulation of TNF-α and IL-6 levels.
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Initiation mechanisms of acupuncture effect: a literature review of basic studies
- Manipulation parameter optimization in Liu’s back tuina therapy for kids’ cough variant asthma in remission stage
- Clinical observation of sinew-regulating bone-setting manipulations plus exercise therapy for chronic non-specific low back pain
- Observation on therapeutic efficacy of tuina plus cupping for chronic fatigue syndrome
- Therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of heat-sensitive moxibustion for vascular dementia
- Clinical study on Jin’s three-needle therapy for post-stroke cognitive impairment
