基于GIS的浙江省安吉县生态敏感性与适宜性评价
2019-12-10肖惠珍
肖惠珍
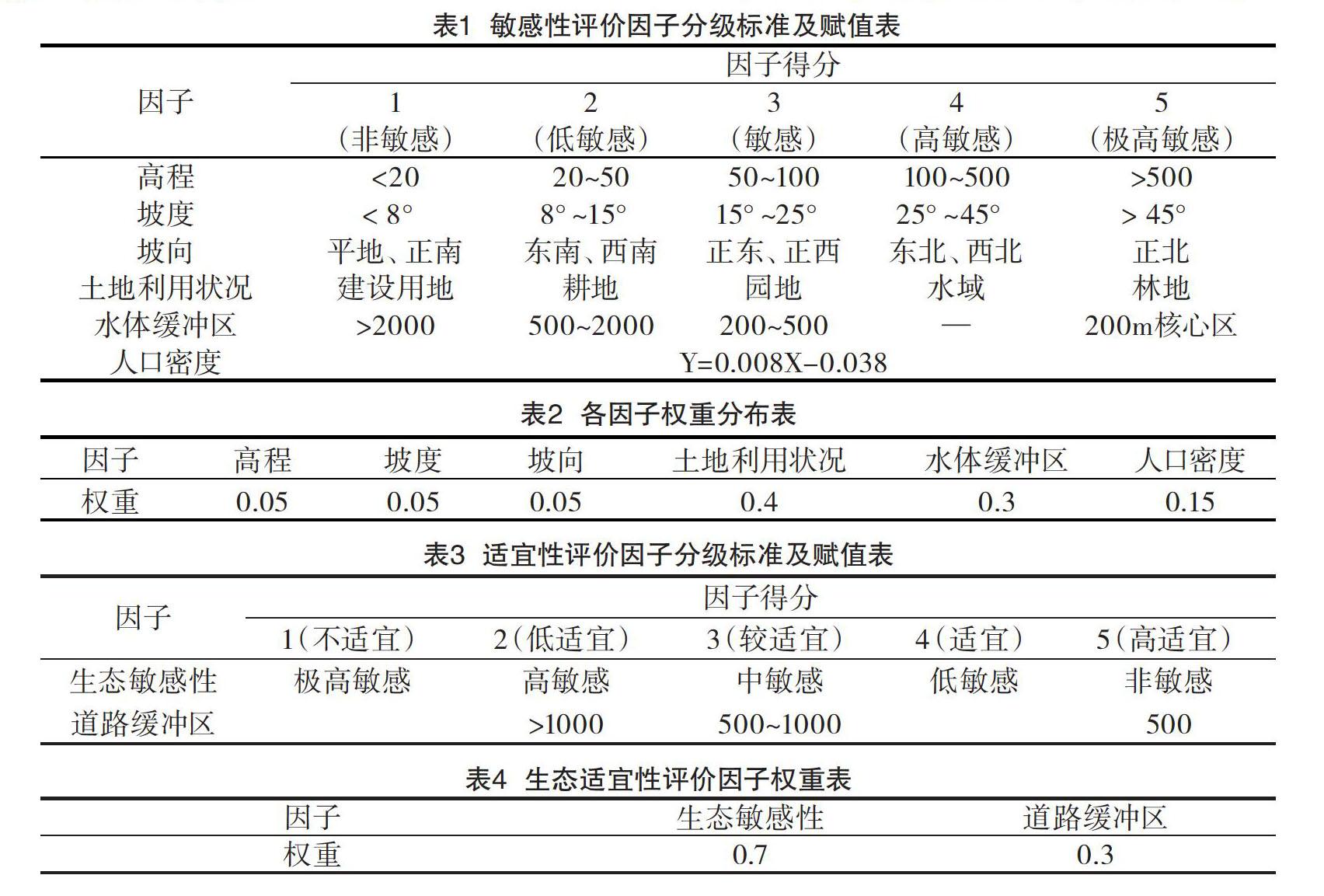
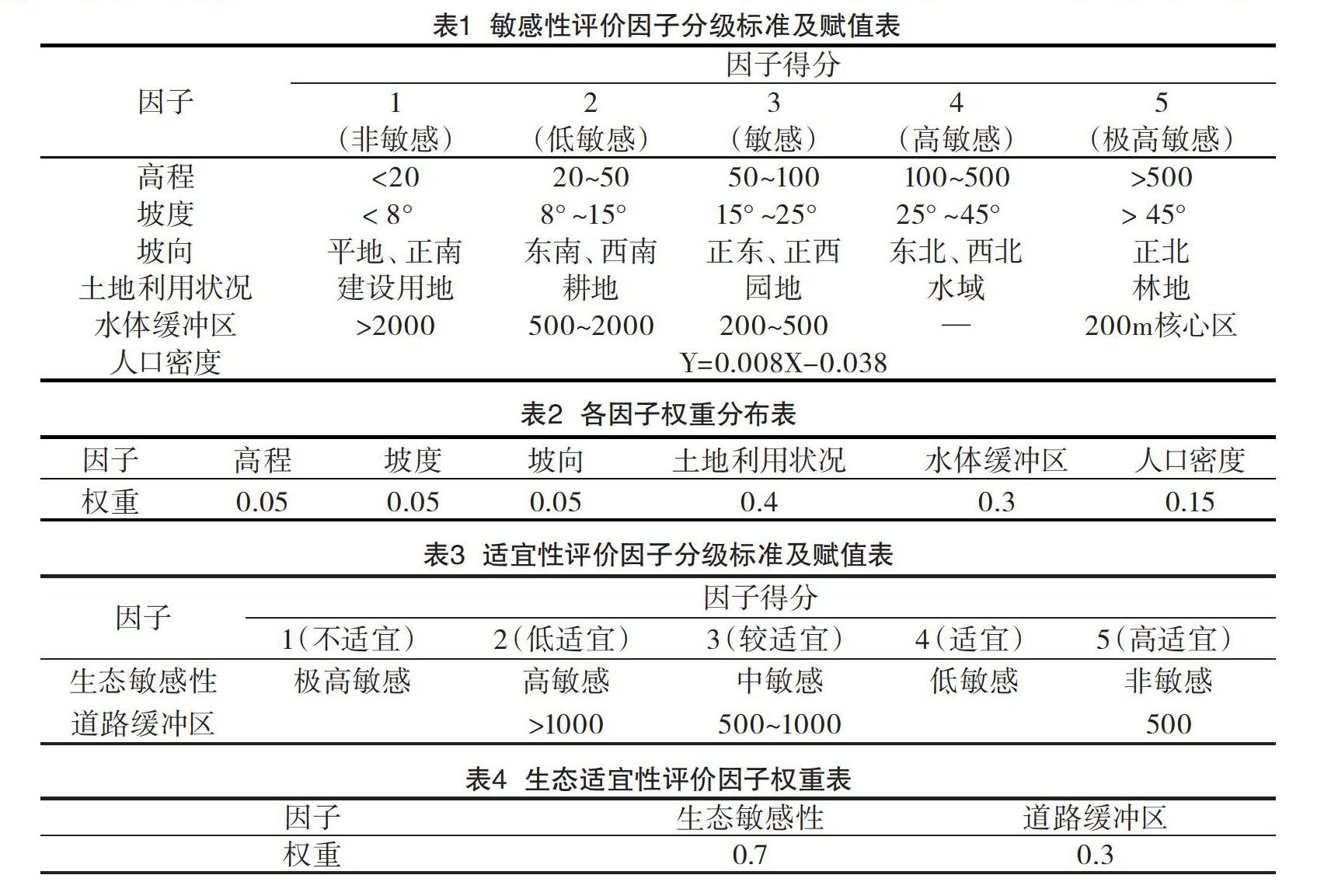
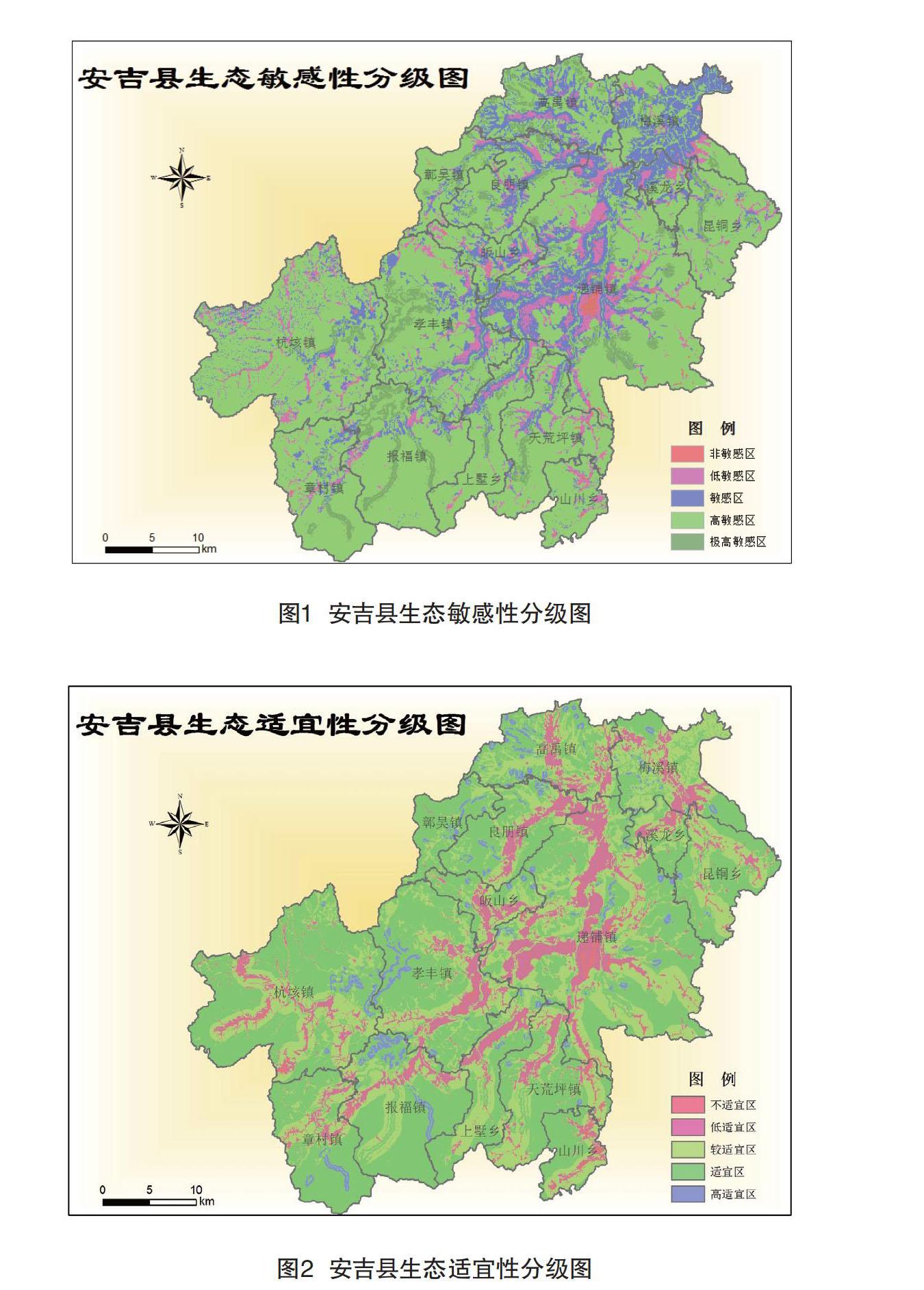
摘 要:生态健康是一个地区可持续发展的重要指标。该文以生态调查为基础,基于GIS技术的生态敏感性与生态适宜性分析,以因子加权叠加法为基本分析方法,运用GIS的空间分析功能进行分析。结果表明:(1)极高敏感区主要分布在高程高,坡度大且邻近水域的区域;高敏感区分布在研究区森林覆盖的大部分面积;敏感区集中分布在坡度不大的耕地和园地区域;低敏感区和非敏感区分布在坡度较缓,植被较单一的区域。(2)高适宜用地主要为现有居民点聚居区域及建筑用地,无自然植被;适宜用地一般坡度平缓,且交通便利,植被较差;较适宜用地离道路交通较远,坡度高程适中,经一定的工程措施和环境补偿措施后也可作为建设用地;低适宜用地主要为森林覆盖区域,以及引用水源及周边区域;不适宜用地植被景观优良,生态敏感性强,完全不适宜作为建设用地。
关键词:GIS 生态敏感性 生态适宜性
中图分类号:X826 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-3791(2019)10(b)-0178-04
Abstract: Ecological health is an important indicator of sustainable development in a region. Based on the ecological survey, based on GIS technology of the ecological sensitivity and ecological suitability analysis, the factor weighted superposition method as the basic analysis method, using the spatial analysis function of GIS to analyze. The results show that: (1)the highly sensitive areas are mainly located in the areas with high elevation, large slope and adjacent waters; the highly sensitive areas are distributed in most areas covered by forest in the study area; the sensitive areas are concentrated in cultivated land and garden areas with small slope; the low sensitive areas and non-sensitive areas are distributed in areas with gentle slope and single vegetation. (2)Highly suitable land use is mainly existing residential areas and construction land without natural vegetation; suitable land use is generally gentle slope, convenient transportation and poor vegetation; more suitable land is far away from road traffic, moderate slope elevation, after certain engineering measures and environmental compensation measures, it can also be used as construction land; low suitable land use is mainly forest-covered areas, as well as introduction. Water sources and surrounding areas; unsuitable land for construction because of its excellent vegetation landscape and strong ecological sensitivity.
Key Words: GIS; Ecological sensitivity; Ecological suitability
在現代化城市建设的过程中,生态环境保护问题越来越受到重视,人们逐渐意识到“先破坏,后恢复”是不能确保可持续发展的,比经济利益更重要的是生态环境的保护和建设。随着计算机技术的发展,地理信息系统的出现也为城市规划提供了一个有效的手段。安吉县作为新农村建设中的领头羊,对安吉县土地利用空间格局以及驱动力因子进行研究,将会对其他一些正在起步建设新农村和一些比较落后的乡镇提供理论指导意义和标榜作用,有助于其他乡镇在新农村建设中对土地利用的合理规划和使用。该研究以浙江省安吉县为例,通过生态敏感性和生态适宜性分析,以求为解决城市规划中的问题解决新思路,对改善安吉县自身的生态环境、保护其土地资源、促进区域土地生态系统和推动经济环境的可持续发展也同样具有极其重要的意义。
1 研究区概况
安吉位于长三角腹地,是浙江省湖州市的市属县。与浙江省的长兴县、湖州市吴兴区、德清县、杭州市余杭区、临安市和安徽省的宁国县、广德县为邻。在东经119°14′~119°53′和北纬30°23′~30°53′之间,面积1885.71km2。
天目山脉自西南入境,分东西两支环抱县境两侧,呈三面环山,中间凹陷,东北开口的“畚箕形”的辐聚状盆地地形。地势西南高、东北低,县境南端龙王山是境内最高山,海拔1587.4m,也是浙北的最高峰。山地分布在县境南部、东部和西部,丘陵分布在中部,岗位分布在中北部,平原分布在西苕溪两岸河漫滩,各占面积11.5%、50%、13.1%和25.4%。盛产竹子,为全国著名的“中国竹乡”。
