五味子乙素对人乳腺癌细胞MCF-7增殖和Notch-1信号通路的影响
2019-11-15赵炜赵志正
赵炜 赵志正
摘要:目的 觀察五味子乙素对人乳腺癌细胞增殖及Notch-1信号通路的影响,探讨其抑制乳腺癌发展的可能分子机制。方法 不同浓度五味子乙素(0、20、40、80 μmol/L)处理乳腺癌细胞MCF-7,作用24、48、72 h后,CCK-8法检测MCF-7细胞增殖。裸鼠皮下接种MCF-7细胞建立裸鼠乳腺癌移植瘤模型,随机分为对照组和五味子乙素组,每4 d测量肿瘤体积并绘制肿瘤生长曲线,32 d后取肿瘤称重。Western blot检测MCF-7细胞和肿瘤组织Notch-1及其下游分子Hes-1、Hey-1蛋白水平;免疫组化检测小鼠肿瘤组织Notch-1的表达。结果 与空白组比较,五味子乙素显著抑制MCF-7细胞生长,且抑制作用具有时间和浓度依赖性,同时显著降低MCF-7细胞Notch-1及其下游分子Hes-1、Hey-1蛋白的表达。与对照组比较,五味子乙素组裸鼠肿瘤体积及质量明显受抑制,且肿瘤组织Notch-1及其下游分子Hes-1、Hey-1蛋白表达显著降低。结论 五味子乙素可抑制乳腺癌发展,其机制可能与抑制乳腺癌细胞MCF-7及其裸鼠模型移植瘤的生长、降低Notch-1信号通路相关因子表达有关。
关键词:五味子乙素;细胞增殖;Notch-1;移植瘤;乳腺癌细胞MCF-7;小鼠
中图分类号:R285.5 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1005-5304(2019)10-0055-05
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-5304.2019.10.013 开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Abstract: Objective To explore the effects of schisandrin B on the growth of MCF-7 and Notch-1 signaling pathway in breast cancer; To explore possible molecular mechanism that inhibit the development of breast cancer. Methods Human breast cancer cell MCF-7 was treated with different concentrations of schisandrin B (0, 20, 40, 80 μmol/L) for 24, 48, 72 h. CCK-8 assay was used to detect cell growth. Nude mice breast cancer xenograft models were established by subcutaneous inoculation of MCF-7 cells in nude mice and were randomly divided into the control group and the schisandrin B treatment group. Tumor volume was measured every 4 days and the tumor growth curve was drawn. After 32 days, the tumor was weighed. The expressions of Notch-1, Hes-1, Hey-1 in MCF-7 cells and tumor tissues were detected by Western blot. Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of Notch-1 in tumor tissues. Results Compared with the blank group, schisandrin B significantly inhibited the growth of MCF-7 cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner, and significantly decreased the expression of Notch-1 and its downstream molecules Hes-1 and Hey-1 in MCF-7 cells. Compared with the control group, the tumor volume and quality of the schisandrin B treatment group were significantly inhibited, and the expression of Notch-1 and its downstream molecules Hes-1 and Hey-1 significantly decreased. Conclusion Schisandrin B can inhibit the growth of breast cancer, and its mechanism can be related to inhibiting the growth of breast cancer cells MCF-7 and its nude mouse model, and decreasing the expression of Notch-1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: schisandrin B; cell proliferation; Notch-1; xenografted tumor ; breast cancer cell MCF-7; mice
乳腺癌是发生在女性中最常见肿瘤之一,是女性癌症相关死亡的主要原因[1]。近年来,随着诊断学尤其是癌症分子生物学和基因组学领域的进步,乳腺癌检测发生了革命性的变化[2]。目前,治疗乳腺癌主要方法包括外科手术、化疗、放疗,大大改善了乳腺癌的预后,但仍有许多患者复发及在治疗过程中出现不良反应和耐药。因此,寻找有效治疗乳腺癌的药物,成为当前研究的重点。五味子乙素(Schisandrin B)是从五味子中分离得到的主要生物活性成分[3]。近年研究发现,五味子乙素在多种疾病中介导多种生物活性,包括抗炎、抗氧化和心血管保护作用[4-6]。有报道显示,五味子乙素可抑制胆管癌、肺腺癌、胶质瘤、胃癌细胞增殖[7-10],诱导细胞凋亡,减弱肿瘤的侵袭和转移[11]。本研究分别通过细胞与动物实验,观察五味子乙素对人乳腺癌细胞增殖及Notch-1信号通路表达的影响,探讨其可能的分子机制。
1 实验材料
1.1 动物
SPF级雌性Balb/C小鼠10只,6~8周,体质量18~20 g,购自广东省医学实验动物中心。饲养于温度(20±2)℃、相对湿度(50±5)%环境,日照时间12 h,自由摄食饮水。实验前小鼠适应性喂养7 d。
1.2 药物
五味子乙素,南京道斯夫生物科技有限公司,溶于二甲基亚砜并配制成100 mmol/L贮备液保存。
1.3 细胞
人乳腺癌细胞株MCF-7,中国科学院上海细胞库提供,在本实验室进行培养。
1.4 主要试剂与仪器
杜尔伯科改良伊格尔(DMEM)培养基、胰蛋白酶和胎牛血清,美国Gibco公司;青/链霉素,美国Sigma公司;BCA法蛋白浓度检测试剂盒,上海碧云天生物技术公司;抗Notch-1抗体、抗Hes-1抗体、抗Hey-1抗体、抗β-actin抗体和辣根过氧化物标记的二抗,英国Abcam公司;CCK-8试剂盒,上海博谷生物科技有限公司。超低温冰箱(日本Sanyo公司),CO2细胞培养箱(美国Thermo公司),低速离心机(美国Thermo公司),电泳仪(北京六一生物科技有限公司),凝胶成像仪(美国Azure Biosystems公司)。
2 实验方法
2.1 细胞培养
MCF-7细胞培养于含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基,置于37 ℃、含5%CO2且湿度完全饱和的恒温培养箱中培养,定期取对数生长期细胞进行传代。
2.2 CCK-8实验
用于检测细胞增殖并计算增殖抑制率。100 μL对数生长期MCF-7细胞(1×105/孔)接种于96孔板,每组设置4个复孔,共4组,加入终浓度为0、20、40、80 μmol/L五味子乙素,培养24、48、72 h,每孔加入CCK-8试剂10 μL,继续培养4 h,使用分光光度计检测波长450 nm处吸光度,计算细胞增殖抑制率。细胞增殖抑制率(%)=(1-给药组A450÷对照组A450)×100%。
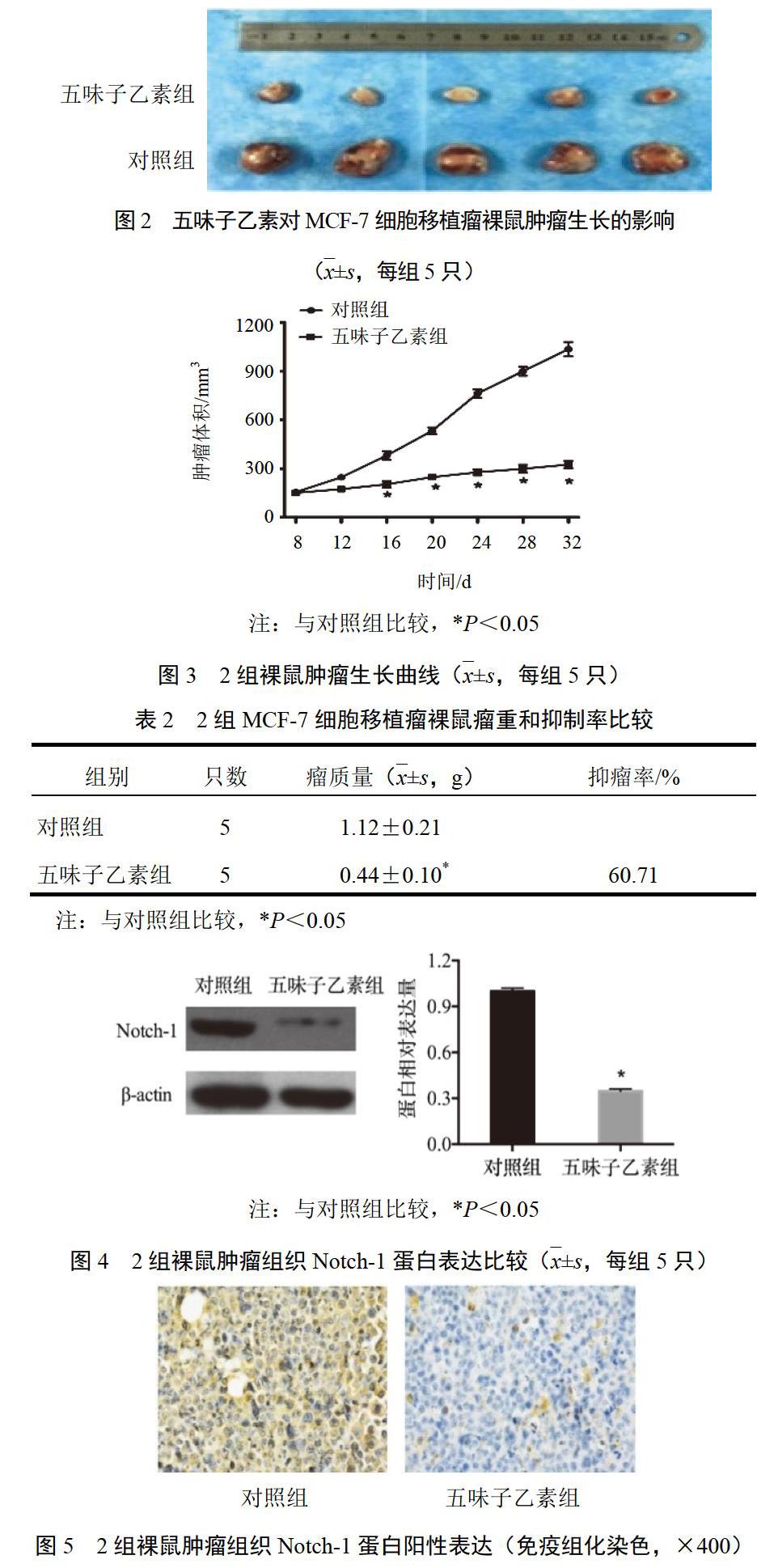
2.3 乳腺癌细胞移植瘤裸鼠模型建立
用PBS将对数期乳腺癌细胞MCF-7浓度调整为2×107/mL,取0.1 mL悬液注射于小鼠右后侧肢体皮下,接种后观察1周成瘤,将10只成瘤小鼠随机分为对照组和五味子乙素组,每组5只。五味子乙素组小鼠腹腔注射五味子乙素,每2 d注射1次,直至细胞接种后32 d,每次100 mg/kg,体积0.2 mL;对照组注射等体积PBS。每4 d用游标卡尺测量肿瘤长径和短径,肿瘤体积=长径×短径2÷2。细胞接种32 d,处死裸鼠,称取瘤重,计算抑瘤率。抑瘤率(%)=(对照组瘤体平均质量-给药组瘤体平均质量)÷对照组瘤体平均质量×100%。肿瘤组织置于液氮中保存備用。
2.4 Western blot检测
MCF-7细胞用预冷的细胞裂解液裂解15 min,4 ℃、12 000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液,收取蛋白。肿瘤组织先用液氮进行研磨,然后加入细胞裂解液,离心后获得肿瘤组织蛋白。BCA比色法计算蛋白浓度,通过SDS-PAGE将蛋白进行分离后,将蛋白转移至PVDF膜,随后用5%脱脂奶粉封闭液封闭2 h,根据说明书稀释一抗,利用封闭液将抗体稀释到所需浓度,4 ℃孵育过夜,用TBST洗涤3次×5 min,随后根据用量,稀释HRP标记的二抗,37 ℃孵育1 h。用TBST洗涤3次×5 min。用ECL化学发光检测,用Image J对图像进行灰度分析。
2.5 免疫组化检测
脱蜡、水化后切片,经1%Triton X-100处理15 min,再用3%H2O2处理10 min,随后加入Notch-1抗体孵育,置于湿盒4 ℃过夜,第2日清洗后孵育对应的二抗,室温30 min,最后进行染色封片。染色结果采用DAB显色法进行观察,使用苏木精进行对比染色。
3 统计学方法
采用SPSS17.0统计软件进行分析。实验数据以—x±s表示,用方差分析进行比较,两组间比较用t检验。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
4 结果
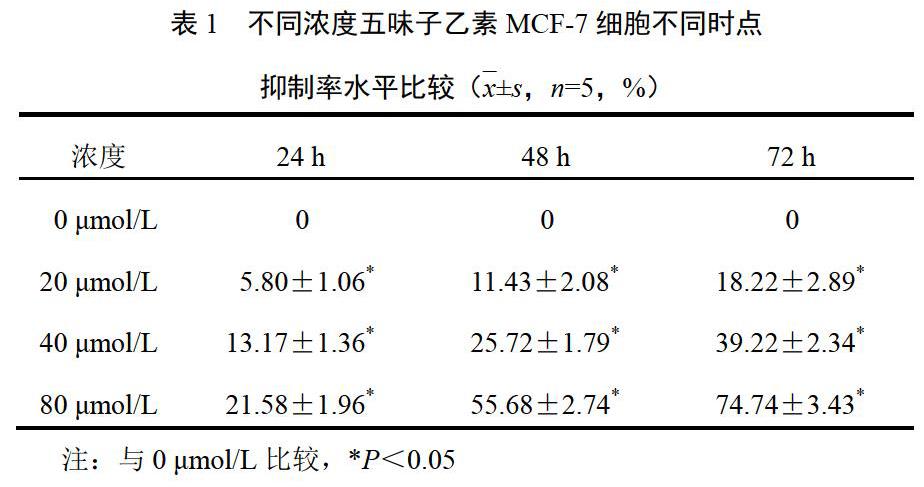
4.1 五味子乙素对乳腺癌MCF-7细胞增殖的影响
经不同浓度五味子乙素(0、20、40、80 μmol/L)处理的乳腺癌MCF-7细胞,其对乳腺癌MCF-7细胞增殖的抑制作用具有时间和浓度依赖性,细胞抑制率随五味子乙素浓度增加和处理时间的延长而增加。结果见表1。
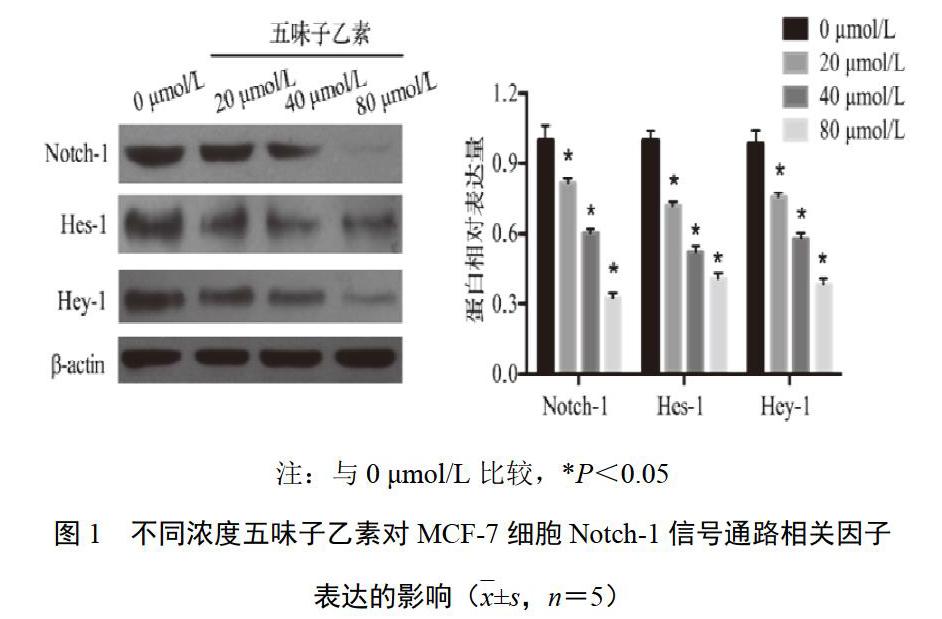
4.2 五味子乙素对乳腺癌MCF-7细胞Notch-1信号通路相关因子表达的影响
[6] THANDAVARAYAN R A, GIRIDHARAN V V, ARUMUGAM S, et al. Schisandrin B prevents doxorubicin induced cardiac dysfunction by modulation of DNA damage, oxidative stress and inflammation through inhibition of MAPK/p53 signaling[J]. PLoS One,2015,10(3):e0119214.
[7] JIANG Y, ZHANG Q, BAO J, et al. Schisandrin B suppresses glioma cell metastasis mediated by inhibition of mTOR/MMP-9 signal pathway[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2015,74:77-82.
[8] LV X J, ZHAO L J, HAO Y Q, et al. Schisandrin B inhibits the proliferation of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells by inducing cycle arrest and apoptosis[J]. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine,2015,8(5):6926-6936.
[9] YANG X, WANG S, MU Y, et al. Schisandrin B inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human cholangiocarcinoma cells[J]. Oncology Reports,2016,36(4):1799-1806.
[10] LIU X N, ZHANG C Y, JIN X D, et al. Inhibitory effect of schisandrin B on gastric cancer cells in vitro[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology,2007,13(48):6506-6511.
[11] DAI X, YIN C, GUO G, et al. Schisandrin B exhibits potent anticancer activity in triple negative breast cancer by inhibiting STAT3[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology,2018, 358:110-119.
[12] NIE J, ZHAO C, DENG L, et al. Efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine in treating cancer[J]. Biomedical Reports,2016,4(1):3-14.
[13] LI X, TSAUO J, GENG C, et al. Ginsenoside Rg3 decreases NHE1 expression via inhibiting EGF-EGFR-ERK1/2-HIF-1α pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma:A novel antitumor mechanism[J]. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine,2018,46(8):1915-1931.
[14] ZHOU R, CHEN H, CHEN J, et al. Extract from Astragalus membranaceus inhibit breast cancer cells proliferation via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2018,18(1):83.
[15] LI Q, LU X H, CAI L, et al. Antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing activity of schisandrin B against human glioma cells[J]. Cancer Cell International,2015,15(1):12.
[16] WU Y F, CAO M F, GAO Y P, et al. Down-modulation of heat shock protein 70 and up-modulation of Caspase-3 during schisandrin B-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology,2004,10(20):2944.
[17] XIANG S S, WANG X A, LI H F, et al. Schisandrin B induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of gallbladder cancer cells[J]. Molecules,2014,19(9):13235-13250.
[18] LIU Z, ZHANG B, LIU K, et al. Schisandrin B attenuates cancer invasion and metastasis via inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. PLoS One,2012,7(7):e40480.
