A Preliminary Study on Patent Application and Management of Agricultural Scientific Research Institutions
2019-10-24LizhenCHENXiuhuaWANGYonghuaLIUJianqiuYE
Lizhen CHEN, Xiuhua WANG, Yonghua LIU, Jianqiu YE
Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute, Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences, Haikou 571101, China
Abstract At present, there is a contradiction between the rapid growth of the number of patents declared and authorized by agricultural scientific research institutions and the decline of the efficiency of invention patents year by year, and the low conversion rate of patents. This paper discusses the patent application quantity, authorization quantity and patent efficiency of the Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute, Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences, analyzes the present situation of its work and the main problems existing in patent management, and puts forward the relevant suggestions.
Key words Agricultural scientific research institutions, Patent application, Patent management
1 Introduction
In recent years, with the construction of scientific and technological innovation platform of agricultural scientific research institutes and the increasing awareness of intellectual property protection, the patent application behavior of agricultural scientific research institutions has become more and more active, and the number of patent applications and authorizations has increased significantly. The patent license of Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences has developed steadily from scratch. By the end of December 2018, the total number of patents had reached 288, of which there are 204 valid patents, including 65 invention patents, 134 utility model patents and 5 design patents. The improvement of the quantity and quality of patents also puts forward new requirements for patent management. However, some of the promising patents failed to pay the annual fee on time because they did not have the support of special funds. This leads to the early invalidation of patents and the serious loss of intellectual property rights of institutions. Based on the analysis of the problems existing in the patent management of Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences, this paper puts forward some suggestions in order to provide a reference for the patent management of agricultural scientific research institutions.
2 Patent status
2.1 Application statusThe overall number of patents applied for by the Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences showed a trend of first rising, then falling and then rising. 2013 was the peak period of patent application by the Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences, with the number of applications reaching 80, 10 times that of 2009. It was followed by a total of 78 patents declared in 2015. In 2014, 61 patent applications ranked third. The number of patent applications declined gradually after 2015 and increased slightly by 2018 (Table 1).
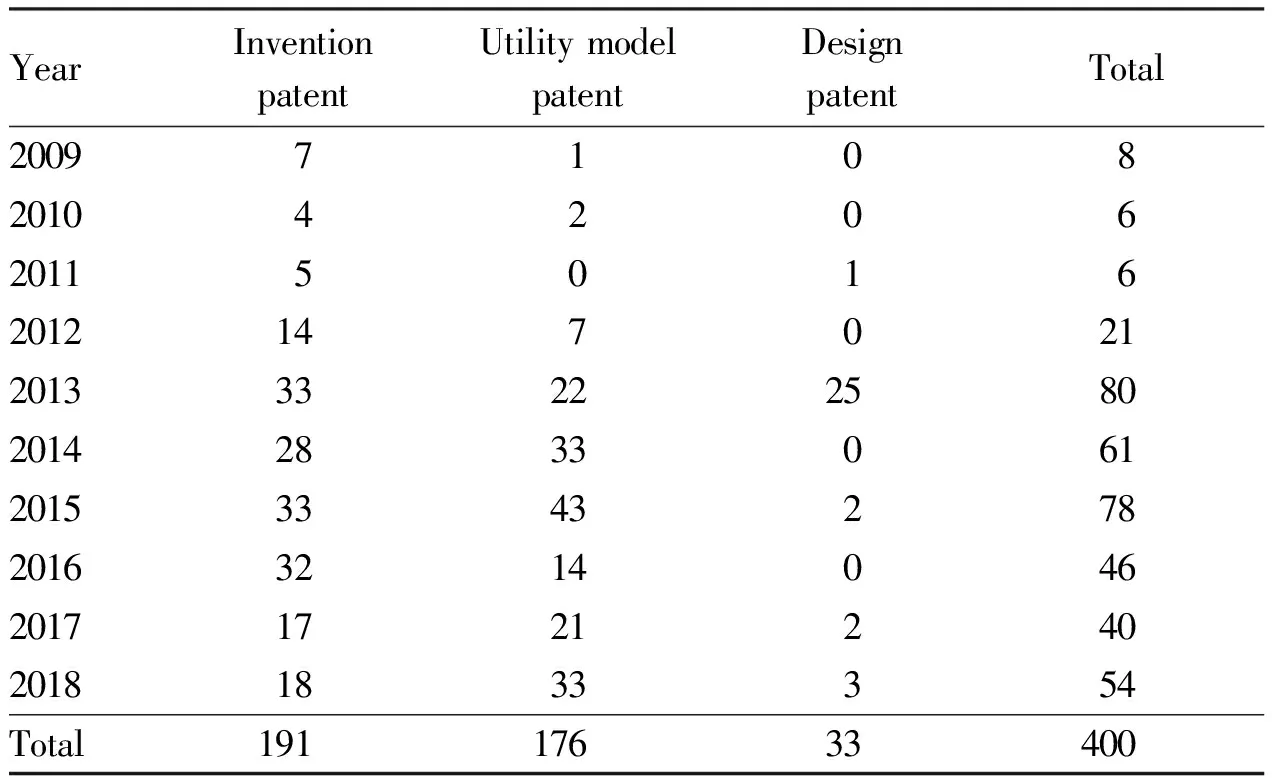
Table 1 Patent application of Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences during 2009-2018 (pcs)
2.2 Authorization statusThe number of authorized patents by Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences is increasing year by year. In 2018 and 2016, the number of patents accounted for more than 50% of the total, and there was the largest number of patents authorized in 2018, with a total of 73 patents, accounting for 25.35% of the total number of licensed patents. In 2016, the number of patents authorized was 54, accounting for 18.75% of the total number of patents authorized. The number of patents authorized in 2018 was 73 times that in 2009 and 2.023 times the sum of patents in the five years from 2009 to 2013. Most of authorized patents by Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences were utility model patents, with a number of 193, accounting for 67.01% of the total; there were 85 invention patents, accounting for 29.51% of the total; there were 10 design patents, accounting for 3.47% of the total. Over the past 10 years, the number of authorized patents by Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences has achieved a quantitative leap (Table 2).
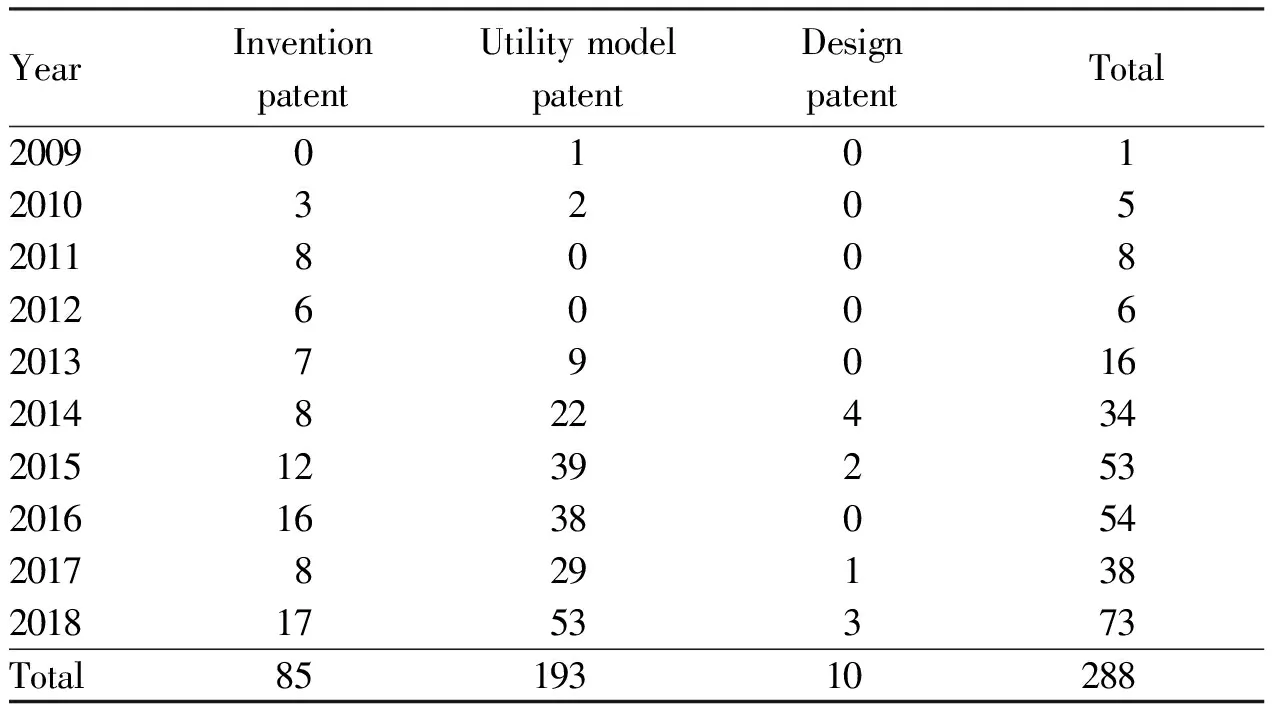
Table 2 The number of authorized patents by Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences from 2009 to 2018 (pcs)
2.3 Invalidation situationPatents can be divided into three types: invention patents, utility model patents and design patents. Among them, the protection period of invention patent is 20 years, and the protection period of utility model patent and design patent is 10 years. The patents from 2009 to 2018 are all in the period of protection, and the number of authorized patents is increasing year by year, but the number of invalid patents is also increasing year by year. From the analysis of Fig.1, it can be seen that the overall trend of authorized patents is on the rise, and the overall trend of invalid patents is rising at first and then falling. By the end of December 2018, of the 53 patents authorized in 2015, 32 had expired, with the largest number of patent failures. Of the 34 patents authorized in 2014, 21 had expired, with the second largest number of patent failures. The total number of invalid patents in 2014 and 2015 accounted for more than 50% of the total number of invalid patents. Of these, 38.10% were invalid patents in 2015 and 25% in 2014. The reason for the invalidation of the patent is the non-payment of the annual fee (Table 3).
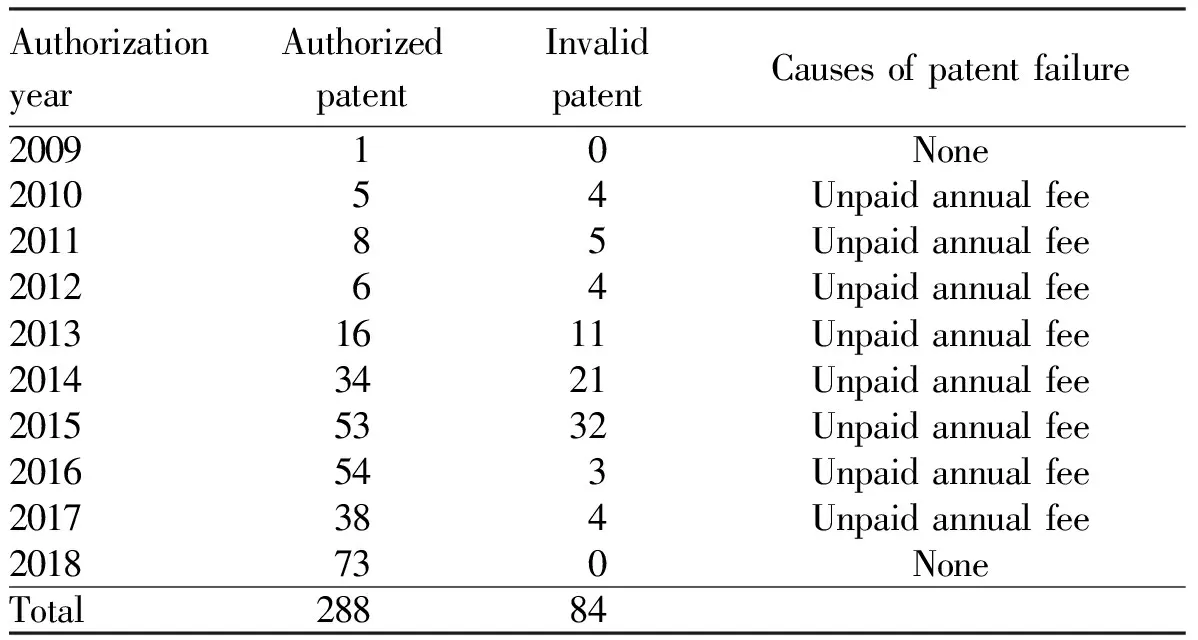
Table 3 Invalidation of patents in Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences (by the end of December 2018) (pcs)
3 Existing problems and cause analysis
3.1 Low patent conversion rate due to orientation of scientific research evaluation system and scientific research policy
(i) The patents of agricultural research institutes mainly come from the achievements of scientific research projects. Most of the purposes of patent applications are required for the conclusion of project acceptance, scientific and technological awards, scientific research assessment and professional title evaluation, and are not guided by market demand. Before the application of many patents, it is lacking in the market research, resulting in the disconnection between patents and market demand, so it is difficult to get the favor of enterprises.
(ii) The evaluation index of scientific research work is set with emphasis on quantity rather than quality, emphasis on form rather than application. In the application and conclusion policies of all kinds of scientific research projects, the number of patents obtained through the project research is an important factor affecting whether the project can be established and concluded.
(iii) The patent evaluation standards in project acceptance, science and technology awards, scientific research assessment and professional title evaluation are still based on the number of applications and authorizations. It only emphasizes the quantity but not the conversion rate of patent achievements, resulting in the situation of low level of patent technology and difficult transformation of achievements. Policy orientation causes researchers to count only quantity and ignore quality when applying for patents. After obtaining the patent license, because there is no relevant policy incentive, the patent certificate is "put on the shelf", so that the patent is reduced to "the right lying on the certificate". As Professor Liu Yongpei[1]said, "For enterprises, if they only own patents and do not convert them into actual products to enter the market, the economic value of patents is also pleasure in the mirror." The same is true for scientific research institutions.
3.2 Lack of highly skilled professional teams and effective managementAccording to the management level of intellectual property rights, it can be divided into three categories: intellectual property business management, tactical management and strategic management[2]. At present, many agricultural scientific research institutions do not have a separate intellectual property management office, and patent management work is mainly taken charge of by the unit science and technology department or achievement transformation office. Taking Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences as an example, patent management is mainly attached to the department of science and technology and achievement transformation office. The relevant business of patent application, authorization and maintenance is the responsibility of the department of science and technology, and the achievement transformation office is responsible for the conversion business of the patent. Patent management is only part of the business of these two departments, and managers work part-time. The management level can be classified as business management, and the management mode adopts the way of administrative management, with simple content and single method. Daily work is mainly for the formulation of relevant management policies, registration of patent declaration and authorization, management of patent-related affairs, it almost cannot provide professional management and services, and managers do not have such capabilities. Due to the lack of professional knowledge, it results in the absence of effective management in the whole process of patent application, authorization, maintenance and transformation, the patent application cannot be given professional guidance. As a result, it is difficult for patent applications and licenses to realize a process from quantitative change to qualitative change. The reasons mainly include two aspects: First, China’s agricultural scientific research institutions lack experience in effective intellectual property management, basically emphasizing management over service. Second, the management system is not perfect, there is no top-level design of a set of incentive policies to promote the transformation of patent achievements and mobilize the enthusiasm of staff. This has led to a shortage of patent management personnel, especially fewer people who understand the market, technology and management, which in turn leads to a weaker and weaker management power in intellectual property rights.
3.3 Lack of special financial support and declining patent efficiency year by yearThe term of protection of invention patents is 20 years, and that of utility model patents and design patents is 10 years. The annual maintenance fee of invention patent is 82 300 yuan, and that of utility model patent and design patent is 11 200 yuan. The annual fee of patent is increasing year by year. The annual fee of invention patent is 4 000 yuan in the 10th-12th year, 6 000 yuan in the 13th-15th year and 8 000 yuan in the 15th year. Some patents have no financial support after the acceptance of the project. In addition, with the expiration of the period of professional title evaluation and scientific and technological awards, many patent inventors have put the patents on the shelf and no longer carry out maintenance. This has led to a decline in patent efficiency year by year (Table 4-6).
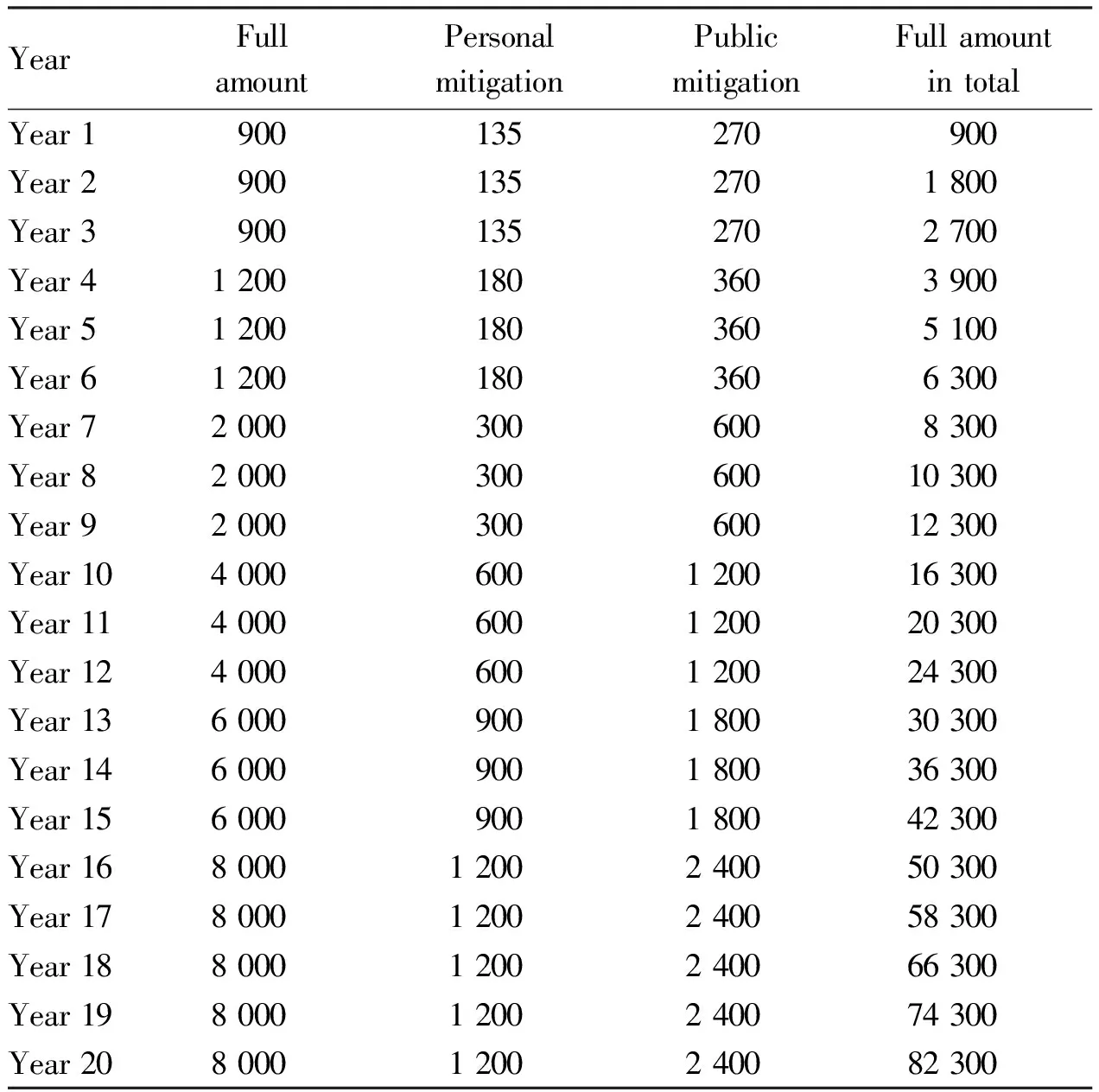
Table 4 List of annual fees for invention patents (yuan)
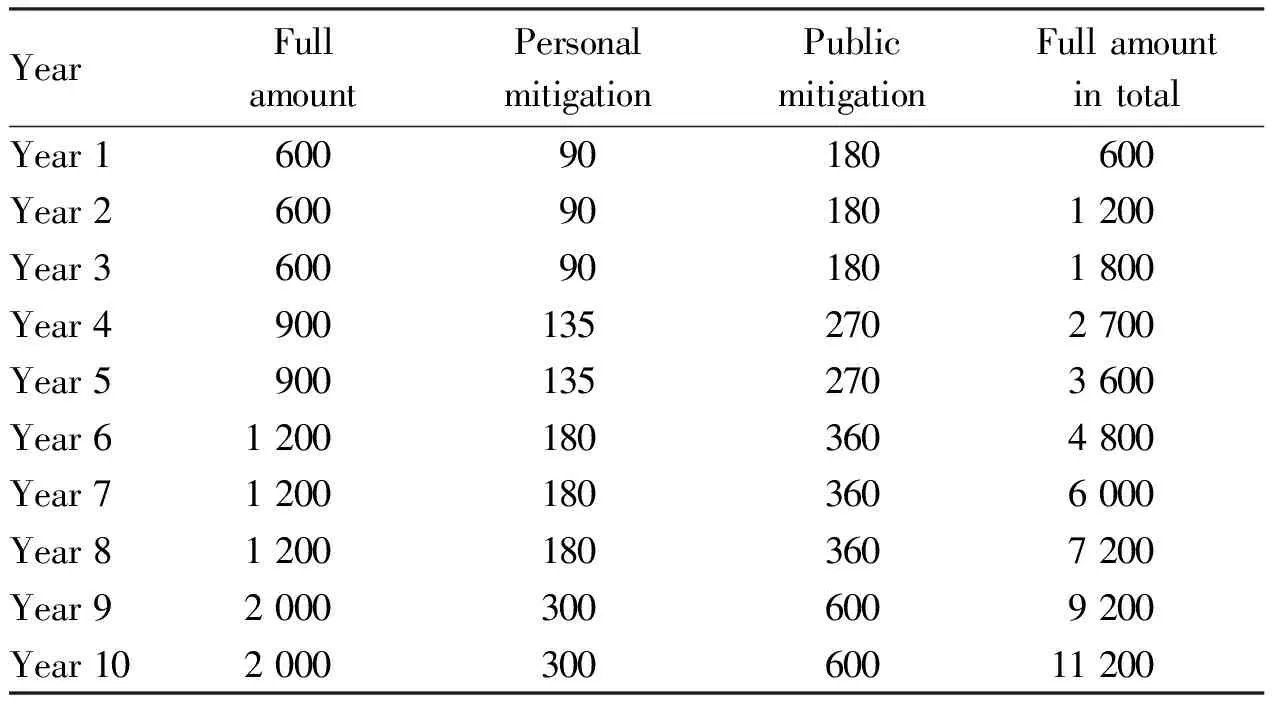
Table 5 List of annual fees for utility model patents (yuan)

Table 6 List of annual fees for design patents (yuan)
3.4 Imperfect patent management rules and regulationsIn 2011, Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences formulated Patent Management Regulations of the Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences. It is mainly related to the ownership of the patentee, the reward of the patent, the declaration, authorization and transfer of the patent. However, with the increase of the number and type of patents, higher requirements have been put forward for patent management. At present, the patent management of Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences is still in the administrative stage. The main reason is that the managers implement part-time management, the study of patent laws and regulations is not deep enough, the understanding of patent policy is not accurate and deeper, resulting in imperfect patent management rules and regulations.
4 Recommendations
4.1 Increasing incentives and improving the proportion of invention patentsScientific and reasonable incentive policies should be formulated to guide and encourage scientific and technological personnel to sprint to invention patents with higher scientific and technological content. The direction of patent development of agricultural scientific research institutions should be "distribution by quantity and success by quality". For example, the scientific and technological personnel who obtained authorized invention patents can be rewarded in cash; the proportion of the score of the invention patent should be increased in the aspects of professional title evaluation, scientific research assessment, post appointment, and so on; the unit should establish and perfect the incentive mechanism, fully mobilize the enthusiasm of researchers for invention and creation. For example,MeasuresfortheAwardofScientificandTechnologicalAchievementsofTropicalCropsGeneticResourcesInstituteoftheChineseAcademyofTropicalAgriculturalSciences(Interim) (2013) introduced by Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences clearly stipulates that for the authorized invention patent, the institute will reward 3 000 yuan/item; for the utility model patent, the institute will reward 1 500 yuan/item; for the design patent, the institute will reward 1 000 yuan/item.MeasuresfortheAwardofScientificandTechnologicalAchievementsofTropicalCropsGeneticResourcesInstituteoftheChineseAcademyofTropicalAgriculturalSciences(Interim) (2019) clearly stipulates that if we apply for the title of researcher based on applied technology research and development, the person-in-charge obtaining three national invention patents can be used as one of the performance conditions.
4.2 Building a platform for the transformation of scientific and technological achievements and strengthening industry-university-research cooperationInOutlineofthe13thFive-YearPlanforNationalEconomicandSocialDevelopmentofthePeople’sRepublicofChinaissued in 2016, it is clearly stated that it is necessary to construct an institutional mechanism to encourage innovation and remove the institutional obstacles that bind innovation and the transformation of achievements, improve the mechanism for the transformation of scientific and technological achievements and the distribution of benefits, and increase the proportion of income sharing in the transformation of scientific and technological achievements. This shows that China is strengthening the transformation of scientific and technological achievements and guiding the transformation of scientific and technological achievements in policy.
Therefore, agricultural scientific research institutions should keep up with the pace of national policy, actively build a platform for the transformation of achievements, and break down this "barrier" between scientific research institutions and society. It is necessary to fully release the innovative elements such as "talent, capital, information, and technology" among scientific research institutions, enterprises, and markets, and vigorously promote the timely transfer and implementation of patents. It is necessary to strengthen cooperation with enterprises, and the implementation of scientific research projects should be carried out in cooperation with enterprises, so that scientific research projects can be closely integrated with industrial development. It is necessary to strengthen publicity and promotion, authorize patents to actively participate in technology exhibitions, increase the possibility of trading technology products, maintain communication and exchanges with enterprises and manufacturers, and promote the transformation of patent achievements. The management department should improve the quality of service, actively connect enterprises with researchers, let enterprises understand the creativity of scientific and technological personnel, and let scientific and technological personnel understand the needs of the market and enterprises. It is necessary to invent patents that are closer to the market, more practical and valuable, and then promote the maturity of patented technology with the help of the enterprise platform, so as to push the achievements to the market more quickly.
4.3 Strengthening the construction of professional management team and regulating patent managementTalent is the foundation of patent technology innovation, we must adhere to the strategy of "talent first", not only to train patent technology experts, but also to train all-around talents with overall patent consciousness[4]. In order to improve the quality of patent application and promote the effective transformation of patents, agricultural scientific research institutions shall set up independent intellectual property management agencies or cooperate with relevant patent agencies to provide professional guidance to researchers before patent declaration, so as to avoid repetitive research, and improve the success rate of declaration. In the process of project demonstration and research and development, it is necessary to carry out the necessary tracking and retrieval in order to determine the patent declaration type and technical focus. The number of patents cited is currently recognized as an effective measure of patent quality. Through the data mining of patent information, patent managers should discover the formation characteristics of highly cited patents in order to guide the patent application of scientific researchers.
4.4 Establishing and improving the patent management system and optimizing the intellectual property management system and mechanismWithin the unit, it is necessary to formulate a patent management system with patent management as the core, in line with the market economy and national laws and regulations. It is necessary to guide, encourage and strengthen the procedures in terms of policy, so that patent activities can be raised from the spontaneous requirements of scientific and technological personnel to the stage at which the management departments consciously and actively guide, manage, and provide services, and change passive services into active services. In the mode of operation, the work related to patent transformation can be operated in a market-oriented mode, that is, the project responsibility system. The remuneration of project staff should be closely related to the market value generated by patent conversion, so as to provide incentives for project staff to engage in patent conversion[5]. It is necessary to define the distribution of benefits in the transformation of intellectual property rights and establish a reasonable distribution mechanism among units, management agencies, and inventors. For scientific research personnel, we should adopt an encouraging attitude and distribute the benefits reasonably[6]so as to maximize the interests of scientific and technological personnel in order to improve the enthusiasm of scientific research personnel.
5 Conclusions
To sum up, patent management is an important part of the management of agricultural scientific research institutions. It is necessary to strengthen the patent management of agricultural scientific research institutions, which can not only enhance the scientific and technological innovation ability and competitiveness of agricultural scientific research institutions, but also promote the rapid development of social science, technology and economy, and enhance China’s comprehensive national strength and international competitiveness.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Poverty Alleviation by Helping the Disabled in Impoverished Mountainous Areas of Western China: Taking Luquan Yi and Miao Autonomous County in Yunnan Province as an Example
- Research on Scientifically and Rationally Promoting the Fallow of Cultivated Land under the Strategy of Rural Revitalization
- Study on the Effect of "Crayfish-Rice Continuous Cropping" on Grain Production: A Case Study of Hubei Province
- Integrated Development of Rural Tourism and Rural Poverty Alleviation in the Context of Rural Revitalization: A Case Study of Enshi Prefecture, Hubei Province
- Groundwater Nitrate Contamination and Driving Forces from Intensive Cropland in the North China Plain
- Development of Rural E-commerce from the Perspective of Agricultural New Kinetic Energy Cultivation: Based on Survey on the "E-commerce Entering Villages and Households" Project of Jurong City
