弓网系统降弓电弧电气特性仿真研究
2019-10-14周梦迪彭彦卿庄志坚
周梦迪 彭彦卿 庄志坚
摘 要: 基于Mayr電弧电路模型和Cassie电弧电路模型,考虑纵向气流吹弧效应,对电弧电压梯度[U]和电弧耗散功率[P0]进行修正,建立降弓电弧电路分析模型。研究降弓速度、降弓时刻以及降弓电弧电流对降弓电弧电压的影响。发现降弓电弧电压呈现近似线性的增长关系,降弓速度越高,降弓电弧电压增长得越快。降弓时刻对于电弧电压的影响主要体现在电弧电压出现的时刻差异,降弓电弧电压的波形基本一致。不同电弧电流情况下,电弧电压基本一致。文中的研究对于指导降弓操作、减轻弓网材料损失具有重要意义。
关键词: 弓网电弧; 降弓电弧; 降弓速度; 降弓时刻; 电弧电流; 电弧电压
中图分类号: TN710?34 文献标识码: A 文章编号: 1004?373X(2019)19?0159?05
Abstract: The dropping pantograph arc circuit model is established based on the Mayr arc circuit model and the Cassie arc circuit model. In the model, the arc voltage gradient [U] and the dissipation power [P0] are modified, and the longitudinal flow arc blowing effect is taken into consideration. The effects of the dropping speed, the dropping time and the arc current on the arc voltage are studied. It is found that the arc voltage increases linearly with time. The higher the dropping speed is, the faster the arc voltage increases. The effect of the dropping time on arc voltage is mainly reflected in the time difference of arc voltage, and the waveform of arc voltage is basically the same. The arc voltage is basically the same under different arc current conditions. The research in this paper is of great significance for guiding the operation of dropping pantograph and reducing the loss of pantograph?catenary material.
Keywords: pantograph?catenary arc; dropping pantograph arc; dropping pantograph speed; lowering time; arc current; arc voltage
0 引 言
随着国民经济的迅速发展,铁路运输向更高速度、更大运载量、更加安全稳定的方向发展,以满足人们对于运输时效性以及运输量的迫切需求。弓网系统作为列车获取电能的唯一途径,对于保证列车高速、安全、稳定运行十分重要[1?2]。然而,由于列车运行速度逐步提升导致振动加剧、接触线覆冰、升降弓操作等引起受电弓滑板与接触线分离,造成弓网之间的空气间隙被击穿而形成弓网电弧。弓网电弧不仅使车载电气设备承受高频振荡过电压,还会烧蚀受电弓滑板、接触网导线,轻者缩短弓网系统使用寿命,重者烧断接触导线,造成重大事故[3?5]。弓网离线电弧严重制约和影响了列车提速和运行安全。
文献[6]中根据瞬态热传导理论建立了弓网电弧烧蚀模型,分别对静态电弧和运动电弧在两种热流输入的情况下接触线的热过程进行了仿真计算,结果表明静态电弧比运动电弧对接触线的电气侵蚀程度更为严重。对于列车振动、接触线覆冰导致的弓网电弧,由于列车处于运行状态,弓网之间具有相对运动,电弧对于弓网材料的烧蚀较轻。而列车进行降弓操作时,列车处于静态,降弓导致的电弧对于弓网材料将会产生更为严重的损伤。因此,针对降弓电弧展开研究对于指导降弓操作、减轻弓网材料损失具有重要意义。


2.3 降弓电弧电流对降弓电弧电压的影响
为了分析降弓过程降弓电弧电流对降弓电弧电压的影响,研究不同降弓电弧电流对降弓电弧电压的影响。
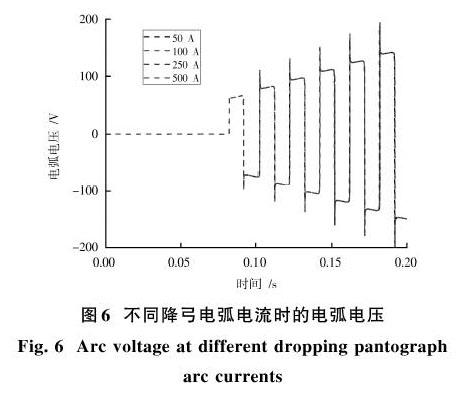
图5显示了降弓过程中降弓电弧电流的变化情况。由图可知,随着降弓过程的进行,降弓电弧电流的幅值逐渐减小,主要原因可能是电弧逐渐增长造成回路电阻值逐渐增大,使得回路的电流逐渐降低。
不同电弧电流时的降弓电弧电压如图6所示。由图6可知,不同电弧电流情况下,电弧电压基本一致。由电弧电压与电流的关系可知,1~50 A范围内电弧电压随着电弧电流的增大而逐渐减小,主要是因为电弧电流增大使得电弧温度升高,进而使得电弧电阻减小。而在电流大于50 A以后,电弧电压基本不变。
尽管电弧电流对于电弧电压的影响不大,但是电流的增大使得电弧的燃弧强度增强,对于弓网材料的威胁也会进一步加大。因此,应当避免大电流情况下的降弓操作。
3 结 论
本文研究了降弓电弧的电气特性,以及降弓速度、降弓时刻和降弓电弧电流对降弓电弧电压的影响,得出如下结论:
1) 基于Mayr电弧模型和Cassie电弧模型,将Mayr电弧模型与Cassie电弧模型进行串联,通过修正电弧电压梯度[U]和电弧耗散功率[P0],建立降弓电弧电路模型。
2) 研究不同降弓速度对电弧电压的影响,发现降弓电弧电压呈现近似线性的增长关系。降弓速度越高,降弓电弧电压增长得越快。通过增大降弓速度可以加快降弓电弧的熄灭速度,减轻电弧的损伤。
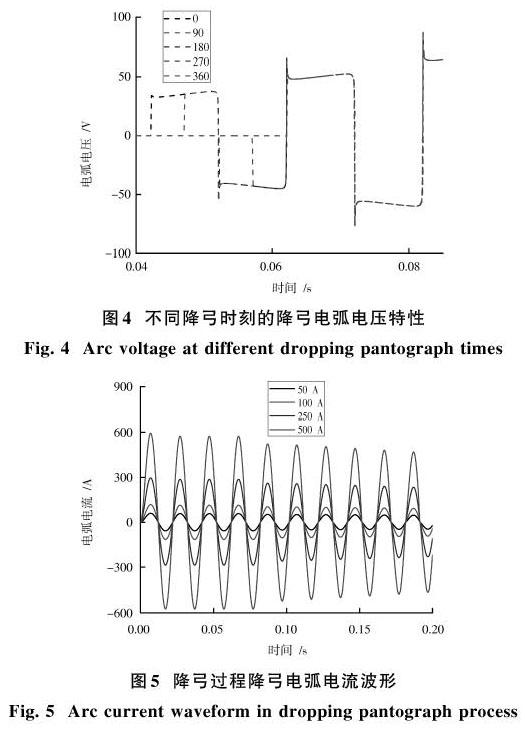
3) 降弓时刻对于电弧电压的影响主要体现在电弧电压出现的时刻差异,降弓电弧电压的波形基本一致。降弓时刻为0°时,电弧发生在0.042 s。降弓时刻从90°变化到360°时,电弧发生时刻也从0.047 s增长到了0.062 s。降弓时刻对应的接触网电压却有所不同,降弓产生的过电压将会严重威胁列车设备。因此,可以考虑采用选相降弓装置减轻降弓过电压的影响。
4) 不同电弧电流情况下,电弧电压基本一致。尽管电弧电流对于电弧电压的影响不大,但是电流的增大使得电弧的燃弧强度增强,对于弓网材料的威胁也会进一步加大。因此,应当避免大电流情况下的降弓操作。
注:本文通讯作者为彭彦卿。
参考文献
[1] GAO G, ZHANG T, WEI W, et al. A pantograph arcing model for electrified railways with different speeds [J]. Procee?dings of the institution of mechanical engineers, Part F: journal of rail and rapid transit, 2017, 232(6): 1731?1740.
[2] WEI W, WU J, GAO G, et al. Study on pantograph arcing in a laboratory simulation system by high?speed photography [J]. IEEE transactions on plasma science, 2016, 44(10): 2438?2445.
[3] 杨志鹏,李华伟,孙忠国,等.基于弓网电弧模拟试验装置的电弧参数测量及分析[J].北京交通大学学报,2012,36(2):111?115.
YANG Zhipeng, LI Huawei, SUN Zhongguo, et al. Electric parameters measurement and harmonics analysis for the pantograph?catenary arcing prototype [J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2012, 36(2): 111?115.
[4] 李运良.弓网电弧对覆冰接触网的影响研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2017.
LI Yunliang. Study on the influence of pantograph?catenary arc on ice covered catenary [D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017.
[5] BUCCA G, COLLINA A. Electromechanical interaction between carbon?based pantograph strip and copper contact wire: A heuristic wear model [J]. Tribology international, 2015, 92: 47?56.
[6] 吴积钦,钱清泉.弓网系统电弧侵蚀接触线时的热分析[J].铁道学报,2008,30(3):31?34.
WU Jiqin, QIAN Qingquan. Thermal analysis of arc erosion of contact wire of the pantograph & catenary system [J]. Journal of the China railway society, 2008, 30(3): 31?34.
[7] YANG Z H, ZHANG Y Z, ZHAO F, et al. Dynamic variation of arc discharge during current?carrying sliding and its effect on directional erosion [J]. Tribology international, 2016, 94: 71?76.
[8] 王英,刘志刚,范福强,等.弓网电弧模型及其电气特性的研究进展[J].铁道学报,2013,35(8):35?43.
WANG Ying, LIU Zhigang, FAN Fuqiang, et al. Review of research development of pantograph?catenary arc model and electrical characteristics[J]. Journal of the China railway society, 2013, 35(8): 35?43.
[9] 范福强.基于改进Habedank电弧模型的弓网离线过电压研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2014.
FAN Fuqiang. Study on separation between the pantograph and catenary based on improved Habedank arc model [D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014.
[10] 王英.弓网电接触热流和电流传导及影响规律研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2015.
WANG Ying. Studies on the heat distribution and current conduction of pantograph?catenary electric contact and their inf?luence laws [D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015.
[11] 陈旭坤.高速列车弓网电弧动态模型研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2015.
CHEN Xukun. Study on the dynamic model of the pantograph?catenary arc of the high?speed train [D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015.
[12] 乔凯,刘文正,张坚,等.基于改进Mayr模型的弓网离线电弧仿真分析[J].铁道标准设计,2018,62(5):138?142.
QIAO Kai, LIU Wenzheng, ZHANG Jian, et al. Simulation analysis of pantograph?catenary arc based on improved Mayr model [J]. Railway standard design, 2018, 62(5): 138?142.
