林木参数监测多传感器的时空配准
2019-10-09王志楼邢涛
王志楼 邢涛


摘 要:本文基于多传感器集成以及时空配准技术, 实现林木的立体参数采集。采用自主研发的林木参数多传感器集成系统,在东北林业大学林场样地进行林木的数据采集,利用传感器间坐标系转换关系与双目视觉算法实现点云数据和图像数据的时空配准。对配准后数据提取标靶坐标与全站仪得到真实坐标进行比较,X、Y、Z三个方向的RMSE分别为0.074、0.117、0.153 m,RMSE平均值为0.115 m。结果表明该集成系统采集数据有效,配准效果良好。
关键词:林木参数监测;空间配准;时间配准
中图分类号:S757 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1006-8023(2019)05-0039-04
Abstract:Based on multi-sensor integration and spatial-temporal registration technology, this paper realizes the stereo parameter acquisition of forest trees. The self-developed forest parameter multi-sensor integrated system is used to collect the data of forest trees in the forest farm sample of Northeast Forestry University, and the spatial-temporal registration of point cloud data and image data is realized by the coordinate transformation relationship between sensors and the binocular vision algorithm. After the registration, the data extraction target coordinates are compared with the total station to obtain the real coordinates. The RMSE in the three directions of X, Y and Z are 0.074, 0.117, 0.153 m, respectively, and the average RMSE is 0.115 m. The results show that the data collected by the integrated system is valid and the registration effect is good.
Keywords:Forest parameter monitoring; space registration; time registration
0 引言
森林資源是全球资源重要的组成部分,在生态环境的恢复与重建、缓解全球气候变化以及促进社会和经济发展中具有重要作用[1]。林木参数监测系能够快速、准确、高质高效地获取多种空间、光谱和时间分辨率的森林资源现状及动态变化信息,在林业资源监测中发挥着重要作用。目前对于林业调查信息采集[2]及森林资源监测[3]的需求,需要研发三维激光扫描、CCD立体测量和林木健康检测等多传感器集成及其搭载技术,利用多源采集数据构建林木参数变化监测技术体系,形成移动式林木参数动态监测,实现对林木参数(林木胸径、树高、冠幅、林分郁闭度和林分生物量等参数)的动态监测,促进林业信息数字化发展进程以及作业精准化和科学管理,为大区域森林资源动态监测提供技术和数据支持[4]。
本文研发的林木参数监测采集系统是集成多种新型传感器的林木信息监测装置,系统的激光扫描仪可以采集林木的点云数据,单反相机可以采集林木的图像信息,通过点云和图像信息的融合,可以更全面的监测林木的树高、胸径、纹理和颜色,突破皮尺、胸径尺和测高仪等设备监测的单一和精确度低的限制。这套多传感器集成系统,传感器为1台三维激光扫描仪、3台单反摄像机、思拓力的S3Ⅱ RTK和SC200Ⅱ型GPS接收机、IMU惯性姿态仪,可以进行人工林的树木的点云数据采集、GPS定位和图像信息采集,提高林木点云数据和图像数据时间和空间配准[5-7],实现多传感器数据融合[8-10]预处理。
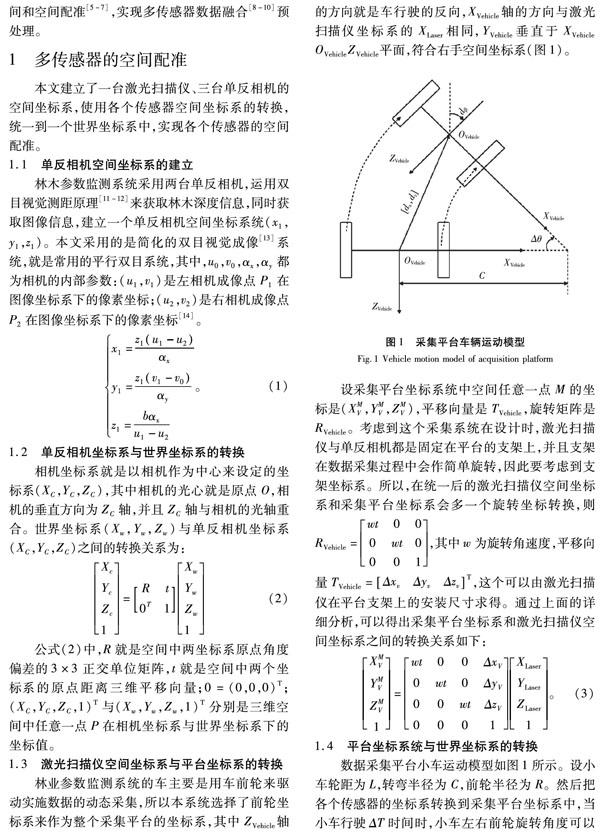
1 多传感器的空间配准
本文建立了一台激光扫描仪、三台单反相机的空间坐标系,使用各个传感器空间坐标系的转换,统一到一个世界坐标系中,实现各个传感器的空间配准。
1.1 单反相机空间坐标系的建立
林木参数监测系统采用两台单反相机,运用双目视觉测距原理[11-12]来获取林木深度信息,同时获取图像信息,建立一个单反相机空间坐标系统(x1,y1,z1)。本文采用的是简化的双目视觉成像[13]系统,就是常用的平行双目系统,其中,u0,v0,αx,αy都为相机的内部参数:(u1,v1)是左相机成像点P1在图像坐标系下的像素坐标;(u2,v2)是右相机成像点P2在图像坐标系下的像素坐标[14]。
从实验结果可以看出,本文所述的多传感器时空配准模型以及在配准过程中所用的方法,能够比较好的将各个传感器的坐标系准确的统一到世界坐标系中,并且能够把不同传感器采集的不同采样周期数据高精度的配准到同一个时间点上,比较好的解决了各个传感器之间不能准确同步的问题。
4 结论
本文设计的林木参数多传感器集成系统,能够有效的集成多传感器进行点云数据图像数据采集,并且能够高效的数据融合。通过各传感器间的坐标转换实现了多传感器的空间配准;借助GPS时间作为时间基准,不同频率数据进行内插、外推、BP神经网络算法处理,从而实现多传感器时间配准,经过实验证明,该系统有效的解决了多传感器时空配准问题,提高了点云采集精度。
【参 考 文 献】
[1]BUIZER M, HUMPHREYS D, JONG W D. Climate change and deforestation: the evolution of an intersecting policy domain[J]. Environmental Science & Police, 2014, 35:1-11.
[2]黎曦,黃海虹,张新耐.林业调查信息采集处理平台技术研究[J].林业调查规划,2017,42(5):45-51.
LI X, HUANG H H, ZHANG X N. Platform and technology of forestry survey information collection and processing[J]. Forest Inventory and Planning, 2017,42(5):45-51.
[3]NEWNHAM G J, ARMSTON J, CALDERS K, et al. Terrestrial laser scanning for plot-scale forest measurement[J]. Current Forestry Reports, 2015, 1(4):239-251.
[4]TANG H, BROLLY M, ZHAO F, et al. Deriving and validating Leaf Area Index (LAI) at multiple spatial scales through lidar remote sensing: A case study in Sierra National Forest, CA[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 143(3):131-141.
[5]MAI X M, ZHU Z S, PENG X Y, et al. Position and orientation system for overhead power-line inspection using multi-sensor integrated unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2015, 23(1):20-23, 28.
[6]陈佳东.低空复杂环境多源时空配准方法与应用研究[D].西安:西安电子科技大学,2018.
CHEN J D. Method and application study of multi-source spatial and temporal registration in complex low-altitude environment[D]. Xian: Xidian University, 2018.
[7]LIN Q Y, YANG R Q, CAI K, et al. Real-time automatic registration in optical surgical navigation[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2016, 76:375-385.
[8]王胜平,周丰年,刘大伟,等.船载三维激光扫描数据时空配准方法研究[J].现代测绘,2015,38(3):7-10.
WANG S P, ZHOU F N, LIU D W, et al. Research on space-time registration method for shipborne 3D laser scanning data[J]. Modern Surveying and Mapping, 2015, 38(3):7-10.
[9]王伟.多传感器时空配准技术研究[D].北京:中国电子科学研究院,2014.
WAMG W. Multi-sensor space-time registration technology research[D]. Beijing: China Electronics Science Research Institute, 2014.
[10]夏家和,雷宏杰,李华,等.考虑时空基准差异的传递对准算法研究[J].导航定位与授时,2016,3(1):25-28.
XIA J H, LEI H J, LI H, et al. Study on transfer alignment algorithm considering space-time difference[J]. Navigation Positioning & Timing, 2016, 3(1):25-28.
[11]张如如,葛广英,申哲,等.基于双目立体视觉的三维重建方法[J].扬州大学学报(自然科学版),2018,21(3):5-10.
HANG R R, GE G Y, SHEN Z, et al. 3D reconstruction based on binocular stereo vision[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 21(3):5-10.
[12]李嘉琛,李晓晨,贠晓港,等.基于双目视觉的航空发动机受损叶片三维重建方法[J].科技与创新,2018,5(17):28-31.
LI J C, LI X C, DAI X G, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction method for damaged blade of aeroengine based on binocular vision[J]. Science and Technology & Innovation, 2018, 5(17):28-31.
[13]曹淞翔.基于双目视觉的三维重建[J].通讯世界,2018,25(12):236-238.
CAO S X. 3D reconstruction based on binocular vision[J]. Communication World, 2018, 25(12):236-238.
[14]JIA Z Y, YANG J H, LIU W, et al. Improved camera calibration method based on perpendicularity compensation for binocular stereo vision measurement system[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(12):15205-15223.
[15]杜思远.GNSS短时失锁下车载微惯导算法研究[D].太原:中北大学,2018.
DU S Y. Research on vehicle micro inertial navigation algorithm under GNSS short time unlock[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2018.
[16]斯海林,李标,邓天民.城市3D GIS实景采集中多传感器的时空配准研究[J].公路与汽运,2013,28(4):84-88.
SI H L, LI B, DENG T M. Spatio-temporal registration of multi-sensors in urban 3D GIS real-time acquisition[J]. Highways & Automotive Applications, 2013, 28(4):84-88.
[17]CHENT G, QIAN W X, CHEN Q, et al. Rapid head dectection method based on binocular stereo vision[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(1):150-155.
