一种新的基于超像素聚类的图像分割算法x
2019-10-08姜全春王宁李雷
姜全春 王宁 李雷


摘 要: 本文提出了一种使用具有噪声的基于密度的聚类方法进行超像素聚类来提高图像分割准确性的方法,首先以较低计算成本得到超像素分割,然后我们再利用密度聚类的原理将相关联的超像素聚集到一起,利用超像素对图像边缘信息的准确分割,来提高图像分割的准确性。我们在构建图形时使用局部邻域将算法应用于分割中,并利用DBSCAN既可以适用于凸样本集,也可以适用于非凸样本集的特性对超像素进行聚类分析。将所有各组紧密相连的样本划为各个不同的类别,则我们就得到了最终的所有聚类类别结果。该方法的一个重要特征是其能够在像素点密度大过某个阈值时,保留图像区域中的细节。
关键词: 密度聚类;图像分割;超像素分割;局部邻域
中图分类号: TP751 文献标识码: A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-6970.2019.06.010
本文著录格式:姜全春,王宁,李雷,等. 一种新的基于超像素聚类的图像分割算法[J]. 软件,2019,40(6):4448
【Abstract】: This paper proposes a method of using super-pixel clustering based on the density-based clustering method to improve the accuracy of image segmentation. Firstly, the super-pixel segmentation is obtained at a lower computational cost, and then we use the principle of density clustering. The associated superpixels are gathered together. and uses superpixels to accurately segment the edge information of the image to improve the accuracy of image segmentation. We use the local neighborhood to apply the algorithm to the segmentation when constructing the graph, and use DBSCAN to apply to both the convex sample set and the non-convex sample set to cluster the superpixel. By grouping all the closely connected samples into different categories, we get the final results for all cluster categories. An important feature of this method is its ability to preserve details in the image area when the pixel density is greater than a certain threshold.
【Key words】: Density clustering; Image segmentation; Superpixel segmentation; Local neighborhood
0 引言
在計算机视觉[1]上,图像分割的问题仍然是一个巨大的挑战。自从人工智能的显著发展,每时每刻都在产生海量图像。图像分割[2]在人类视觉感知中其重要作用,因为图像的类型和大小超出了传统的处理能力范围,聚类作为一种常见的无监督学习,得到了广泛的应用。聚类的原理就是将不同的数据点根据它们的差异程度分割成不同的簇,而且每个簇中的数据都具有相似的特征。聚类算法[3]很多,包括基于划分的聚类算法(如:k-means),基于层次的聚类算法(如:BIRCH),基于密度的聚类算法(如:DBSCAN),基于网格的聚类算法(如:STING)等等。郑金志等人[4]提出了基于优化初始聚类中心的改进WFCM图像分割算法,针对的是模糊C均值聚类算法的改进问题。
本文选择DBSCAN[5]作为我们的聚类算法,我们提出了一种基于超像素聚类的图像分割算法(SCIS)。超像素作为一种重要的处理技术已成功应用于许多视觉应用中,如图像分割和对象识别等。Felzenszwalb等人[6]采用了一种基于图形的图像分割,用于捕获感知上重要的区域,来达到一种高效的图像分割。Achanta等人[7,8]引入了一种简单线性迭代聚类方法,该方法产生具有较低计算复杂度的超像素,而且它们比较了SLIC与其他的流行方法[7]。在本文中,我们采用的是SLIC算法进行初始的超像素分割,之后根据DBSCAN原理将超像素进行聚类并应用于图像分割上,该算法既利用超像素保留了图像的细节特征,又基于密度融合原理提高了分割的精度。最后采用的伯克利BSDS300数据集进行验证。
1 SLIC算法和密度聚类理论
1.1 SLIC算法
Achanta等人提出的采用K均值算法生成超像素的简单线性迭代聚类(SLIC)方法。该算法通过将搜索空间限制为与超像素大小成比例的区域,显着地减少了优化中的距离计算的数量,并通过加权距离度量组合颜色和空间接近度,同时提供对超像素的尺寸和紧凑性的控制。
SLIC算法的本质是将基于划分的聚类算法用到超像素的聚类中,例如上面提到的K-means方法。
1.2 密度聚类方法
DBSCAN是基于一组邻域来描述样本集的紧密程度的,参数 用来描述邻域的样本分布紧密程度。其中, 描述了某一样本的邻域距离阈值,MinPts描述了某一样本的距离为 的邻域中样本个数的阈值。
3 实验结果分析
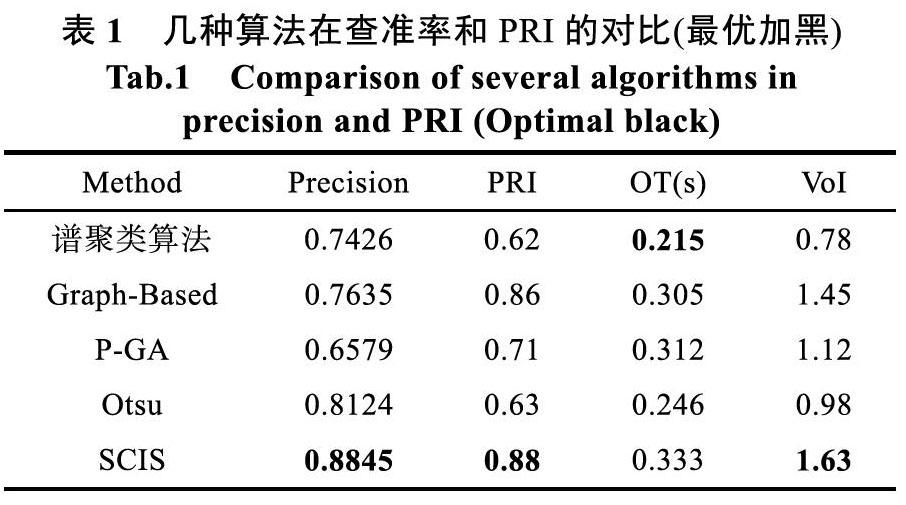
从实验结果和表1可以得出,SCIS算法所使用的超像素聚合方法与其他两种方法都比较相近,所以我们的算法有很高的可行性;我们定量的评估算法的性能[14]在查准率(Precision)、概率边缘指标(PRI)和信息变化(VoI)等平均值都有效的提升,而且得到了更好的分割结果。
4 结论
本文借鉴了经典的DBSCAN算法和SLIC方法,提出了一种基于超像素聚合的图像分割方法(SCIS)。该算法既融合了SLIC算法对图像的边缘特征的提取,又体现了聚类算法对图像整体的把握。我们首先将图像分割成许多精确的小区域,然后根据合并函数将他们逐渐聚集成所需要的超像素块(区域)。本研究所采用的DBSCAN聚类算法弥补层次聚类算法和划分式聚类算法往往只能发现凸型的聚类簇的缺陷,还可以相对抗噪音图像,能处理任意形状和大小的图像簇。从实验结果可以看出,SCIS是一提高图像分割的有效方法。算法精度提高了22%。
参考文献
[1] Bay H, Ess A, Tuytelaars T, et al. Speeded-Up Robust Features (SURF)[J]. Computer Vision and Image Unders-tanding, 2008, 110(3): 346-359.
[2] 丁亮, 張永平, 张雪英. 图像分割方法及性能评价综述[J]. 软件, 2010, 12: 78-83.
[3] 孙吉贵, 刘杰, 赵连宇. 聚类算法研究[J]. 软件学报, 2008, 19(1): 48-61.
[4] 郑金志, 郑金敏, 汪玉琳. 基于优化初始聚类中心的改进WFCM图像分割算法[J]. 软件, 2015, 04: 136-142.
[5] Mihael Ankerst, Markus M. Breunig, Hans-Peter Kriegel, and J?rg Sander. 1999. OPTICS: ordering points to identify the clustering structure[J]. In Proceedings of the 1999 ACM SIGMOD international conference on Management of data (SIGMOD '99), 1999, 28(2): 49-60.
[6] Felzenszwalb P F, Huttenlocher D P. Efficient Graph-Based Image Segmentation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 59(2): 167-181.
[7] Achanta R, Shaji A, Smith K, Lucchi A, Fua P, Süsstrunk S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2274-2282.
[8] Liu M Y, Tuzel O, Ramalingam S, Chellappa R. Entropy-rate clustering: cluster analysis via maximizing a submodular function subject to a matroid constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(1): 99-112.
[9] Zhu Song, Cao Danhua, Wu Yubin, Jiang Shixiong. Improved accuracy of superpixel segmentation by region merging method[J]. Frontiers of Optoelectronics, 2016, 9(4): 633-639.
[10] Wu Z, Leahy R M. An Optimal Graph Theoretic Approach to Data Clustering: Theory and Its Application to Image Segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1993, 15(11): 1101-1113.
[11] Perona P, Freeman W. A factorization approach to grouping [C]. European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1998.
[12] Liu F, Gleicher M. Region Enhanced Scale-Invariant Saliency Detection[C]. Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, ICME 2006, July 9-12 2006, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. IEEE, 2006.
[13] 贾耕云, 赵海英, 刘菲朵. 基于超像素的Graph-Based图像分割算法[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2018, 41(3): 46-50.
[14] Vendramin, L., Campello, R. J., Hruschka, E. R. Relative clustering validity criteria: a comparative overview. Stat. Anal. Data Min, 2010, 3(4): 209-235.
