Effects of Different Selenium Fertilizer Types on Selenium Content and Quality of “Lingfeng” Grapes
2019-09-10YanyanWUQinglanTIANJieyunLIUYongcaiHUANGWeihuaHUANGHaifeiMOUDaidongWU
Yanyan WU Qinglan TIAN Jieyun LIU Yongcai HUANG Weihua HUANG Haifei MOU Daidong WU
Abstract [Objectives] This study was conducted to choose a selenium rich foliar fertilizer suitable for the selenium rich fruit and vegetable industry in Guangxi.
[Methods] With "Lingfeng" wine grapes as test materials, such four kinds of selenium fertilizers as "Jufu Selenium" (JF), "Taishan Weed Fertilizer" (TS), "Zhongnong No. 6" (ZN) and "Kangxibao" (KX) were used as exogenous selenium for the experiment of selenium enriched grapes.
[Results] The selenium contents in the grape fruit applied with the selenium fertilizers increased by 1.2-16.8 times compared with the control (CK), and JF and ZN had a better selenium enriching effect and produced the fruit having the selenium contents reaching 75.85 and 45.79 μg/kg, respectively. Spraying selenium fertilizers can improve some quality indexes of grapes in that spraying JF on the leaves can significantly increase the total sugar content of the grapes while reducing the total acid content and spraying ZN significantly improved the vitamin C content of the fruit. With the delay of harvesting, the selenium content, total sugar content and total acid content of the "Lingfeng" grape fruit decreased, while the grapes sprayed with ZN showed the total sugar content increased slightly and the total acid decreased greatly.
[Conclusions] It is suggested that if you plan to harvest at the right time, you can use "Jufu Selenium" as the exogenous fertilizer for selenium enriched grapes; and if you want to postpone harvesting, you can use "Zhongnong No.6" as the selenium fertilizer.
Key words Selenium fertilizer; "Lingfeng" grapes; Quality; Yield
Selenium (Se) is one of the essential trace elements in humans. It has many physiological functions such as resisting cancer and aging and immune enhancement[1]. However, many countries are located in the low selenium areas in the world, and 22 provinces in China face the problem of selenium deficiency, which leads to the situation that about 100 million people are in low selenium status due to insufficient selenium content in the dietary structure[2]. Exogenous selenium supplement is a common supplement way for humans. The main research direction is to use animals, plants and microbes as carriers to form safe selenium enriched food by adding exogenous selenium. As a simple and safe development model, plant selenium enrichment has become a key research field. Relevant research shows that the application of selenium fertilizer by soil application or foliar application not only can improve the selenium content in crop product organs[1], but also can convert inorganic selenium into organic selenium through self metabolism of crops, thereby avoiding the harmful effects of inorganic selenium on the human body and achieving selenium enrichment[3]. As a snack after a meal, fruits and vegetables play an important role in daily life. Studies have shown that the application of selenium fertilizer not only can increase the total selenium content in fruits, but also has a significant effect on the accumulation of mineral elements in fruits[4]. Therefore, the development of selenium rich fruits and vegetables has a profound significance for humans to achieve exogenous selenium supplementation.
Guangxi has the characteristics of high temperature, more rain and short sunshine duration, and is thus a suitable area for grape planting. Due to improvements in cultivation techniques and breeding methods, this area has been transformed from a sub suitable area for traditional grape cultivation to a special advantageous planting area[5], and the yield has grown from 1 800 t in 1990 to 449 300 t in 2015. Also, the current cultivated area has exceeded 33 000 hm2[6]. The research on the production of selenium enriched grapes can not only improve the income level of local grape growers, but also strengthen the brand awareness of growers to promote the updating and optimization of grape industry in the area. As the local work on selenium enriched grapes in Guangxi has started, how to choose the right selenium enriching foliar fertilizer is the urgent task at present. In this study, the selenium enriching effect and quality of four commonly used exogenous selenium enriching fertilizers on "Lingfeng" wine grapes were investigated, aiming at providing reference for the development of selenium enriched grapes in this area.
Materials and Methods
Experimental materials
This experiment was carried out in the demonstration field (with a soil selenium content of 0.45 mg/kg) of Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences in 2017, using "Lingfeng" grapes as a test material and such four selenium fertilizers as"Jufu Selenium" (produced by Guilin Gui Zhu Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), "Taishan Weed Fertilizer" (produced by Taishan Jinpai Flower and Plant Fertilizer Research and Development Center), "Zhongnong No. 6" (produced by Anqiu Xinhai Bio fertilizer Co., Ltd.) and "Kangxibao" (produced by Guangxi Penshibao Co., Ltd.) as the exogenous selenium. For the convenience of statistical writing, the above selenium fertilizers were abbreviated as JF, TS, ZN and KX.
Experimental methods
The experiment was carried out with 3 plants as a treatment in 3 replicates, and 2 plants were used as a protection group between treatments. In the young fruit period (May 5) and the coloring period (May 27), foliar application was performed according to the concentrations recommended by the manufacturer (625 times for JF, 600 times for TS, 2 500 times for ZN, and 1 000 times for KX). Sampling was carried out on July 4 (normal harvesting date) and July 30 (delayed harvesting date). During sampling, 3 to 5 grains were collected from the upper, middle and lower clusters of each treatment, respectively, and all the grains from 30 clusters in total were mixed and sent to Guangxi Yipu Testing Co., Ltd. for testing. The contents of selenium and cadmium were determined after the steps of cleaning the grape samples with deionized water and grinding into pulp. The content of selenium was determined by hydride atomic fluorescence spectrometry. The contents of lead and cadmium were determined by graphite atomic absorption spectrometry. The total sugar content was determined by the direct titration method, and the total acid content was determined by the titration method. The vitamin C content was determined by the 2,6 dichlorphenolindophenol method.
Data processing
The data were preliminarily analyzed and processed by Excel2015. The variance analysis and correlation analysis were performed with SPSS18.0, and the sample mean values were subjected to multiple comparisons by the new multiple range method.
Results and Analysis
Effects of spraying selenium foliar fertilizers on selenium contents and heavy metal contents in grapes
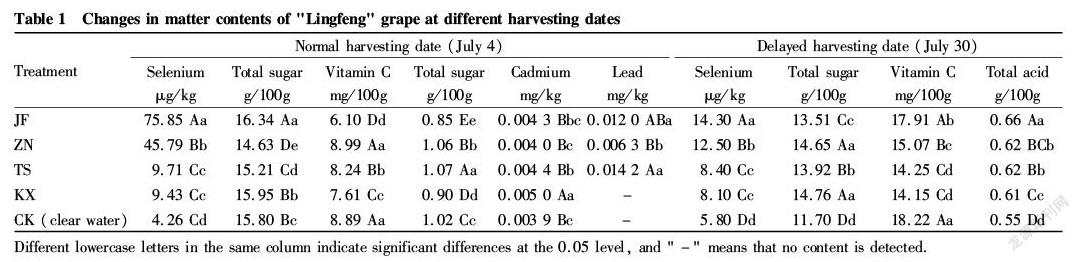
The results of the first sampling (July 4) are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from the table that the selenium content of the fruit was quite different in various treatments, ranging from 9.43 to 75.85 μg/kg. Compared with the control, the selenium content of the selenium applied grapes increased by 1.2 to 16.8 times. According to the recommended standard of selenium enriched grapes, the selenium range of the fruit was 10-100 μg/kg. The selenium enriching effects of the four kinds of selenium fertilizers ranked as JF > ZN > TS > KX. Among them, the selenium contents in the grape fruit of the JF and ZN treatments were significantly higher than other treatments, and the selenium contents reached the selenium rich standard, while TS and KX were relatively poorer, though their selenium contents were also close to the level of selenium enrichment. In addition, the lead and cadmium contents of the treatments all increased compared with the control. According to the GB2762 2012 standard, the lead and cadmium contents of the grapes in this study did not exceeded the standard, and the safe using amounts of the tested fertilizers need further study.
Effects of spraying selenium foliar fertilizers on grape quality
It can be seen from Table 1 that the effects of different types of selenium fertilizers on total acid, vitamin C and total sugar in normal harvested grapes were not the same. The results of multiple comparisons showed that the four fertilizer treatments were significantly different from the control, indicating that the effects of the various treatments were obvious. Among them, the JF and KX treatments showed the total sugar contents of the fruit significantly higher than the control, which increased by 3.42% and 0.92%, respectively, while the contents of the TS and ZN treatments were significantly lower than that of the control (CK). However, the comparison results of the total acid with the CK were opposite to the total sugar. In addition, only the ZN treatment had the vitamin C content in the fruit higher than the CK. It can be seen from the effects of selenium fertilizers on grape quality that JF having a better selenium enriching effect can increase the total sugar content of grape fruit while reducing the total acid content to improve the quality of grapes.
Effects of different harvesting periods on changes of grape matter contents
Comparing and analyzing the grape sample data after harvesting in the normal harvesting date (July 4) and the delayed harvesting date (July 30) in Table 1, it can be seen that in each treatment, with the delay of harvesting, the selenium content, total sugar content and total acid content of the "Lingfeng" grape fruit were all reduced, while vitamin C was opposite, which increased significantly with the delayed harvesting.
The selenium content of the fruit in each treatment was compared between the two harvesting dates, and the contents of the delayed harvesting treatments were reduced by 13.49%-81.15% compared with those of the normal harvesting treatments. Among the various fertilizer treatments, JF had the highest decline, sequentially followed by ZN, KX, and TS which had the smallest drop. Secondly, the total sugar and total acid decreased by -0.001%-25.95% and 22.41%-45.47%, respectively. The total sugar reductions ranked as CK > JF > TS > KX > ZN; and the total acid reductions were in order of CK> TS > ZN > KX > JF. In addition, comparing the vitamin C contents of the two batches of harvested grape fruit, it can be seen that the contents of delayed harvesting treatments were 0.68-1.94 times higher than the normal harvesting treatments, and the increase rates ranked as JF > CK> KX > TS > ZN. Therefore, considering the effects of different harvesting dates on total sugar and vitamin C contents, the normal harvesting date should be matched with the JF treatment, while the delayed harvesting date should be accompanied by the ZN treatment.
Correlation between grape quality indexes after spraying selenium foliar fertilizers
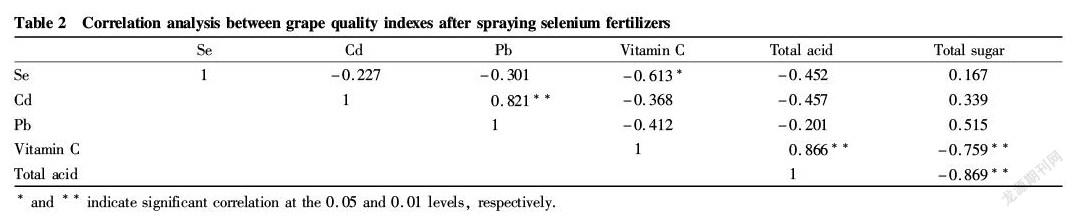
The correlation analysis was carried out between the indexes of the grapes sprayed with selenium fertilizers. It can be seen from Table 2 that the selenium content of the grape fruit was significantly negatively correlated with vitamin C content; the total sugar content was significantly negatively correlated with total acid and vitamin C contents; vitamin C had a significant positive correlation with total acid; and heavy metals cadmium and lead contents had a significant positive correlation therebetween, but no significant correlation with vitamin C, total acid and total sugar contents. Therefore, applying selenium fertilizers can increase the selenium content of the fruit while reducing the total acid content to improve the quality of the "Lingfeng" grape, but the addition of selenium fertilizers may lower the vitamin C content.
Conclusions and Discussion
Foliar application of selenium fertilizers is a relatively simple and effective method of applying selenium fertilizers. Previous studies have also confirmed that the foliar application of selenium fertilizers can significantly improve the yield of grape per plant[8] and selenium content in the fruit flesh[9], and also can significantly improve the soluble sugar and vitamin C contents of grape fruit[10]. However, due to the wide variety of selenium fertilizers, and different varieties of grapes tested in various regions, the results cannot provide direct reference for local growers. The results of this study showed that the selenium content of grape fruit was significantly higher than that of the CK after spraying the four kinds of selenium fertilizers on "Lingfeng" grape, and such two selenium fertilizers as "Jufu Selenium" and "Zhongnong No. 6" produced the grapes reaching the selenium rich standard and thus had the best selenium enriching effects. In addition, spraying selenium fertilizers can improve some quality indexes of the fruit. After spraying "Jufu Selenium" on the foliar surface, the total sugar content of the fruit was significantly improved, and the total acid content was reduced. Spraying "Zhongnong No. 6" significantly improved the vitamin C content of the fruit.
Grape harvesting period has a certain impact on grape quality traits. With the delay of the picking date, the selenium content, total sugar content and total acid content of the "Lingfeng" grape fruit decreased, and the vitamin C content increased, while the ZN treatment showed the total sugar content slightly increased and the total acid decreased greatly. Considering the combination of fertilizer type and harvesting period, according to the inconsistent harvesting period of the growers, combined with the contradictory characteristics of total sugar, total acid, vitamin C and other factors, it is recommended to adopt "Jufu Selenium" as the exogenous fertilizer when harvesting at the appropriate harvest time and to select "Zhongnong No. 6" when postponing the picking time.
References
[1] LIU QL, HAO YY, WU GL, et al. Effects of exogenous selenium on fruit quality and selenium content of Dangshan crisp pear[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 44(8): 113-117. (in Chinese)
[2] WANG Q, LIU YH, YANG JN, et al. Analysis on the distribution of selenium resources and its relationships with soil properties of Ili District, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(6): 555-559. (in Chinese)
[3] ZHENG XC, WANG HB, WANG XD, et al. Researches on selenium absorption and distribution in Kyoho grape[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2016(4): 128-132. (in Chinese)
[4] LIU QL, HAO YY, HAO GW, et al. Effect of spraying selenium on the mineral elements content and the storage properties of the pear fruits[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2015, 51(5): 655-660. (in Chinese)
[5] SUN X, LI HY, LI XP, et al. One year two harvest cultivation pattern and cultivation techniques of Guangxi grapes[J]. Sino Overseas Grapevine & Wine, 2015(3): 45-50. (in Chinese)
[6] HE JJ, WANG B, CHEN AJ, et al. Study on the cultivation and division of one year two harvest grape in different ecological regions in Guangxi[J]. Southern Hornticulture, 2016, 27(5): 6-8. (in Chinese)
[7] CHEN JX, YANG BZ, FAN LH, et al. A research on the selenium limit in the selenium rich grape[J]. Fujian Analysis & Testing, 2013, 22(4): 31-33. (in Chinese)
[8] SUN HQ, PANG ZR, LI XY, et al. Application effects of selenium fertilizers on Otilia seedless grapes[J]. Journal of Library and Information Sciences in Agriculture, 2011(5): 27. (in Chinese)
[9] QUE XF, SI WH, XU L, et al. Application effect of foliar fertilizer enriching selenium on Weike grape[J]. Horticulture & Seed, 2012(6): 84-86. (in Chinese)
[10] ZHENG XC, WANG HB, WANG XD, et al. Effects of selenium amino acid chelate on the fruit and leaf quality of outdoor cropping Kyoho[J]. Sino Overseas Grapevine & Wine, 2013(3): 15-17. (in Chinese)
杂志排行
农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Study on Chemical Composition of the Ethyl Acetate Extract of Pratia
- Protoplast Culture and Its Application in Fruit Breeding
- Indexes of Tree Structure of Cylindrical Pear Orchards at the Sapling Stage
- Carbon Storage and Distribution of the Mature Pinus massoniana Plantation in Northwest Guangxi
- Pollution and Quality Control of Mycotoxins in Foods and Feeds
- Effect of Compound Treatment with Prochloraz and Chitosan on the Physicochemical Indexes of Refrigerated Citrus Gonggan
