Effect of Compound Treatment with Prochloraz and Chitosan on the Physicochemical Indexes of Refrigerated Citrus Gonggan
2019-09-10DongdiXIEDingliLU
Dongdi XIE Dingli LU

Abstract [Objectives] This study was conducted to investigate the synergized preservation effect of different concentrations of prochloraz and chitosan on citrus Gonggan, so as to prolong the sales period of Gonggan.
[Methods] "Zhongshan Gonggan" was used as a material. The Gonggan fruit was soaked with prochloraz (250, 300 and 350 mg/L) and then coated with different concentrations of chitosan (1.0% and 1.5%), respectively. The good fruit rate, weight loss rate and titratable acid (TA), reducing sugar, total soluble solids (TSS) and Vc contents were used as evaluation indexes to investigate the preservation effect of Gonggan during cold storage.
[Results] The treatment of prochloraz plus chitosan can significantly prolong the shelf life of Gonggan as it can inhibit the decline of good fruit rate, reduce the weight loss rate, and slow down the degradation and loss of titratable acid, reducing sugar, soluble solids and Vc. The 350 mg/L prochloraz+1.0% chitosan treatment was superior to other treatments.
[Conclusions] This study provides a theoretical basis for better prolonging the storage period of Gonggan.
Key words Zhongshan Gonggan; Chitosan; Prochloraz; Cold storage; Physicochemical indexes
Citrus Gonggan, a natural hybrid of Citrus sinensis and orange (Citrus reticulata), has the advantages of both C. sinensis and orange. It is also known as Shoubocheng, Guifeicheng, Huangdigan, which has the good fruit shape, golden color, thin skin, fewer seeds, crisp and slag free flesh, and tastes sweet with rich flavor due to high sugar and low acidity. It has won the title of "Chinese famous fruit". The fruit flesh contains vitamin C and citric acid, and has beautifying and anti fatigue effects. "Zhongshan Gonggan" is a geographical indication protection product of Zhongshan County, Hezhou City, Guangxi. It is produced in autumn (October November) and is mainly sold to Hong Kong, Macao and ASEAN countries. However, due to its short harvesting period and poor storage resistance, under normal temperature storage conditions, it usually shows obvious deterioration in 7-8 d[1], resulting in a short supply time which is difficult to meet market demand and consumers.
Chitosan (CTS) is an edible biological coating agent that reduces the respiration of the fruit after coating to preserve the freshness[2]. The authors have used chitosan to treat navel orange[2], water chestnut[3] and guava[4], and obtained a good preservation effect. In the research of fruit and vegetable coatings, the edible film has good barrier properties and a certain degree of gas permselectivity, but it is not good in microbial inhibition[5]. Chitosan combined with prochloraz can achieve the effect of synergized preservation[3]. During the storage of Gonggan, several diseases of citrus, such as stem end rot, green mold and blue mold are common. Prochloraz (PCR) is widely used in the preservation and postharvest storage of citrus fruits. It is often used as a high efficiency low toxic broad spectrum microbicide, which has a good control effect on stem end rot, green mold and blue mold of citrus fruits[6]. However, there is no research report on chitosan combined with prochloraz for preservation of Gonggan. In this study, the synergized preservation effect of the compound treatment with prochloraz and chitosan was investigated at (7±2) ℃, so as to prolong the sales period of Gonggan and provide reference for actual production of Gonggan.
Materials and Methods
Experimental Materials and Equipment
Zhongshan Gonggan, purchased from Zhongshan New Farm. The manufacturer of chitosan (deacetylation degree≥95%) is Shandong AK Biotech Ltd. The manufacturer of prochloraz (250 g/L emulsifiable concentrate) is Yixing Xingnong Chemical Products Co., Ltd.
VIS 722 visible spectrophotometer (Shanghai Spectrum Instruments Co., Ltd.); 80 1 sedimentation centrifuge (Jiangsu Jintan Huanyu Scientific Instrument Factory); centrifuge (Jiangsu Jintan Medical Instrument Factory); JYL C012 juice Machine (Shenzhen Caiyang Trading Co., Ltd.); Handheld Abbe Refractometer (ATAGO China Guangzhou Co., Ltd.).
Experimental methods
Compound treatment
A certain amount of chitosan was weighed, dissolved in 1% glacial acetic acid, and stirred in a warm water bath to completely dissolve it. Degassing was performed for 15 min (repeated 3 times), obtaining 1.0% and 1.5% chitosan solutions for later use.
Prochloraz (PCR, 250 g/L emulsifiable concentrate) was diluted with water to 250, 300 and 350 mg/L.
The three different concentrations of prochloraz solutions (250, 300 and 350 mg/L) were used to soak Gonggan for 5 min, respectively. The soaked Gonggan was then taken out and air dried. Each treatment was divided into two parts, which were soaked in 1.0% and 1.5% for 5 min, respectively, followed by taking out, drying o form a film and storing in a cold storage at (7±2) ℃ for 30 d. The good fruit rate and weight loss rate were recorded every 5 d, and the contents of titratable acid (TA), reducing sugar, vitamin C (Vc) and total soluble solid (TSS) in the flesh were determined. A total of six compound treatments were set as follows: T 1: 250 mg/L PCR+1.0% CTS, T 2: 300 mg/L PCR+1.0% CTS, T 3: 350 mg/L PCR+1.0% CTS, T 4: 250 mg/L PCR+1.5 % CTS, T 5: 300 mg/L PCR+1.5% CTS, and T 6: 350 mg/L PCR+1.5% CTS. A blank control group (CK) was also set by soaking in clear water for 5 min. Every treatment had three replicates.
Determination of indexes
Determination of good fruit rate: Fruit with intact skin free of mildew was regarded as good fruit, and the good fruit rate was calculated according to Good fruit rate=Good fruit number/Total fruit number×100%. Determination of weight loss rate: The weight loss rate was calculated by the weighing method[5] according to Weight loss rate=(Original quality of stored fruit Fruit quality after storage)/Original mass of stored fruit×100%. Determination of TSS content: An appropriate amount of Gonggan homogenate was filtered to remove the crude fiber in the homogenate with two layers of gauze, and the juice was measured with an Abbe refractometer. Determination of TA content: The TA content was determined by acid base neutralization titration[7]. Determination of reducing sugar: The reducing sugar content was determined by the direct titration method[8]. Determination of Vc content: It was determined by the 2,6 dichlorophenol indophenol titration method[8].
Results and Analysis
Effects of different treatments on the good fruit rate of Gonggan
It can be seen from Fig. 1 that the compound treatment of prochloraz and chitosan can reduce the decline of the good fruit rate of Gonggan. The reason might be that the compound treatment of prochloraz with chitosan causes the microbes on the surface of Gonggan to lose normal function due to the destruction of the plasticity and fluidity of the cell membrane, resulting in inhibition of the growth of the flora[3]. On the 5 th d of storage, there was no significant decrease in the good fruit rates of the CK and each compound treatment. After 10 d of storage, the good fruit rate of the CK group began to decrease significantly, and was always significantly lower than each compound treatment group. On the 10 th day of storage, except for the T 1 treatment, the good fruit rate did not change much in other composite treatment groups. On the 15 th d of storage, the good fruit rates of treatments T 1 and T 4 decreased significantly, while the good fruit rates of other compound treatment groups decreased, but the decrease was not obvious. After storage for 20 d, the good fruit rates of treatments T 1, T 2 and T 4 decreased significantly, while the values of treatments T 3, T 5 and T 6 were still higher; and on the 25 th d of storage, T 3 and T 6 had the highest good fruit rate, still above 95%. It can be seen that the compound treatments of 300 and 350 mg/L prochloraz and 1.5% chitosan had a better preservation effect.
Effects of different treatments on the weight loss rate of Gonggan during cold storage
After harvesting, Gonggan still undergoes respiration during storage, resulting in the loss of water, which leads to the loss of its freshness and mass, and even its commercial value. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that the weight loss rate of the compound treatment of prochloraz and chitosan in the storage process of Gonggan was lower than that of the CK, indicating that the compound treatment of prochloraz and chitosan can effectively inhibit the increase in weight loss rate during the storage of Gonggan. The reason is that the chitosan film acts as a semi permeable membrane, which slows the loss of moisture[2]. The experimental results also showed that the weight loss rate of the T 1 treatment group was always close to that of the CK group throughout the storage period. On the 5 th d of storage, the weight loss rates of all the test groups began to rise. On the 10 th d of storage, the weight loss rate of each treatment group showed a significant difference, and the weight loss rates of the CK and T 1 groups were higher. After 15 d of storage, the weight loss rates of the T 3, T 5, T 6 treatment groups and the CK group were significantly lower. Therefore, from the perspective of the weight loss rate, the suitable treatment groups for storing Gonggan were 350 mg/L prochloraz plus 1.0% chitosan, 300 mg/L prochloraz plus 1.5% chitosan and 350 mg/L prochloraz plus 1.5% chitosan.
Effects of different treatments on the soluble solid content of Gonggan
Total soluble solids (TSSs) refer to a general term for all water soluble compounds in plant tissues. The change in its content reflects to some extent the amount of sugar and other solids in the tissue, and is also related to the water retention capacity of tissue cells[1]. During storage, the smaller the amplitude of the soluble solid of Gonggan, the better the preservation effect. It can be seen from Fig. 3 that the change of the soluble solid content of Gonggan in the storage process generally increased at first and then decreased. The reason might be that the harvested Gonggan is not fully mature, and the Gonggan gets mature and tend to aging over time during storage[8]. During the whole storage process, the soluble solid content in each treatment group was always higher than that in the CK group, and the differences were obvious on the 20 th to 25 th d. It indicated that the compound treatment of prochloraz and chitosan significantly inhibited the degradation of soluble solids. During the first 20 d of storage, except for the abnormal fluctuation of treatment T 5, the soluble solids of other compound treatment groups basically showed an upward trend, and the flavor of Gonggan was well maintained. Among them, 350 mg/L prochloraz plus 1.5% chitosan was a better combination to control the degradation of soluble solids.
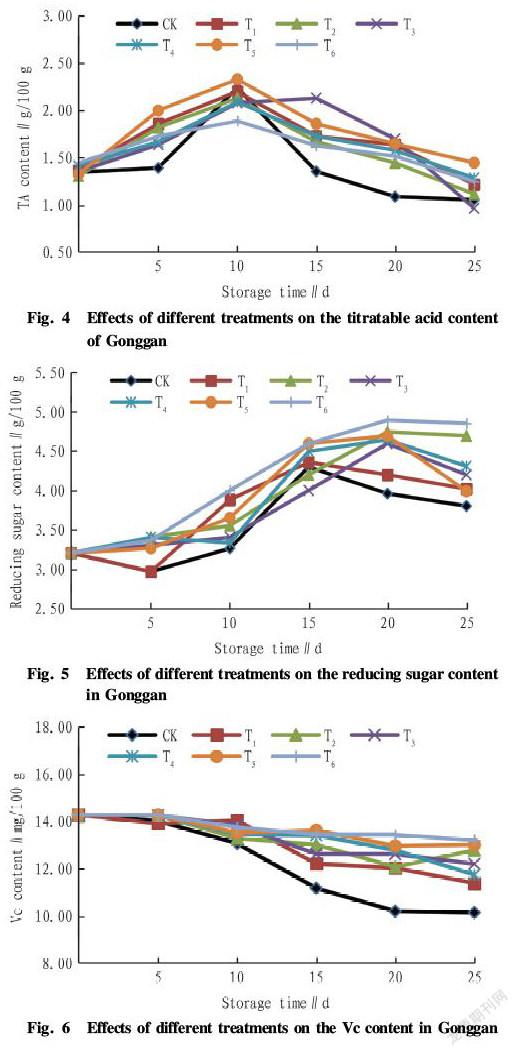
Effects of different treatments on the titratable acid content of Gonggan during cold storage
The titratable acid (TA) content is one of the important factors determining the taste of Gonggan, and it is an important index to judge the quality of Gonggan. The acids in Gonggan are mainly organic acids such as citric acid, and the greater the loss of acids is, the greater the influence it has on Gonggan flavor[6]. It can be seen from Fig. 4 that the titratable acid contents of the Gonggan in the compound treatments and the CK treatment showed an inverted "V" change, but the titratable acid content of the CK group fluctuated greatly. The titratable acid content of each compound treatment group showed an upward trend within the first 10 d of storage, peaked at the 10 th or 15 th d after storage, and then decreased, indicating that the compound treatment can effectively reduce the after ripening speed of Gonggan. The titratable acid content in the CK group was reduced to a minimum at 20 d of storage. On the 25 th d of storage, the T 3 treatment had the lowest titratable acid content, followed by the T 2 treatment. Taken together, the T 6 treatment among the compound treatments exhibited a more gentle change in titratable acid content, so the compound treatment of 350 mg/L prochloraz and 1.5% chitosan can be the optimal combination for controlling titratable acid content.
Effects of different treatments on the reducing sugar content in Gonggan
The reducing sugars in Gonggan are mainly glucose, fructose, etc., and their content is one of the important factors that determine the nutritional value and taste of the fruit, as well as one of the important indicators for judging the quality of Gonggan. It can be seen from Fig. 5 that the reducing sugar content in Gonggan treated with prochloraz plus chitosan increased at first and then decreased basically, while in the CK control group and T 1 treatment, it decreased at first, then increased and finally decreased. The reason might be that after harvesting, the compound treatment affects the after ripening speed of Gonggan. On the 10 th d of storage, the reducing sugar content in each compound treatment was higher than that in the CK group; the CK group and T 1 treatment peaked earlier on the 15 th d; and other treatment groups reached the peak on the 20 th d. It showed that the compound treatment slowed down the after ripening process to a certain extent. On the 20 th and 25 th d, the difference in reducing sugar content of Gonggan was more obvious in each treatment group, while the reducing sugar content in the Gonggan of treatment T 6 was still higher (4.86 g/100 g). Therefore, the compound treatment of 350 mg/L prochloraz and 1.5% chitosan was a better combination that maintained a good reducing sugar content.
Effects of different treatments on the Vc content in Gonggan during cold storage
The citrus fruits are rich in nutrients such as Vc in the ripening process. The Vc content in the tissue directly affects the nutritional value of the fruit, and also affects the taste and flavor of the fruit. It is also one of the important indicators used to judge the storage quality of Gonggan. It can be seen from Fig. 6 that the Vc contents in the compound treatments of prochloraz and chitosan and the CK group showed a decline, overall. There was no significant difference in the decrease of Vc content between the various treatments within the first 10 d of storage. On the 15 th d of storage, the decrease in the Vc content of Gonggan was accelerated, and the differences between the prochloraz and chitosan compound treatments and the CK group were significant. Among the various compound treatments, treatments T 5 and T 6 showed a higher Vc content, and their Vc contents decreased at a lower rate. On the 25 th d of storage, the Vc content in the T 6 treatment was the highest (13.21 mg/100 g), followed by treatment T 5. In conclusion, the Vc content of Gonggan in the CK group was basically at a lower level. It showed that the combination of prochloraz and chitosan slowed down the loss of Vc in Gonggan. Taken together, 350 mg/L prochloraz and 1.5% chitosan had a good effect.
Conclusions and Discussion
The experimental data showed that under the cold storage condition of (7±2) ℃, immersing Gonggan fruit in a certain concentration of prochloraz followed by coating with a certain concentration of chitosan effectively inhibited the decline of good fruit rate and the increase in weight loss rate, and reduced the loss of soluble solids, titratable acid and Vc, thereby prolonging the storage period of Gonggan. According to the analysis of various indexes, the storage effect of the 350 mg/L prochloraz and 1.5% chitosan treatment group was the best, followed by the 300 mg/L prochloraz and 1.5% chitosan treatment group. This is superior to the preservation of Gonggan by Xie et al.[1] with single chitosan, indicating that the treatment of prochloraz has a synergistic effect on the preservation effect of chitosan. The reason is that prochloraz is a broad spectrum high efficiency imidazole microbicide, which makes microbes lose their normal function by inhibiting the plasticity and fluidity of the microbial cell membrane and destroys the cell membrane function of the microbes to reduce the degree of fruit spoilage. Chitosan can form a transparent film on the surface of Gonggan fruit, which can effectively inhibit the respiration of the fruit, slow down the consumption of various substances caused by respiration and inhibit transpiration, thereby reducing water loss[3].
In summary, it can be seen that the combination of 350 mg/L prochloraz and 1.5% chitosan had the best storage effect, and on the 25 th d of storage, its good fruit rate, weight loss rate, soluble solid content, titratable acid content, reducing sugar content and the vitamin C content were 96%, 10.09%, 11.9%, 1.25 g/100 g, 4.86 g/100 g and 13.21 mg/100 g, respectively.
References
[1] XIE YH, LUO YH, XIE DD, et al. Effects of different concentrations chitosan coating on storage quality of Gonggan[J]. Food Research and Development, 2017, 38(22): 209-213. (in Chinese)
[2] XIE DD. Study on Mechanism and effect of chitosan coating preserving fuchuan navel orange[J]. Journal of Hezhou University, 2006(3): 125-127. (in Chinese)
[3] XIE DD, QIN LD. Application of prochloraz plus additives in postharvest storage[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(17): 179-182. (in Chinese)
[4] XIE DD. Effect of pre harvest boron spraying and post harvest chitosan filming on the storage of sugar apple[J]. South China Fruits, 2007, 36(1): 25-27. (in Chinese)
[5] LUO F. Study on chitosan composite coating film and its application in preservation of Jinqiu pear[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2009. (in Chinese)
[6] WANG HH, ZHOU HJ, CHEN ZL, et al. Effects of prochloraz emulsion in water on storage quality and disease of gongchuan orange[J]. Food & Machinery, 2010(1): 44-47. (in Chinese)
[7] China Import and Export Commodity Inspection Bureau. Citrus inspection[M]. Beijing: China International Business and Economics Press, 1984. (in Chinese)
[8] REN YF, LIU C, HE JY, et al. Effect of Coptis chinensis Franch chitosan film on preservation of Valencia orange fruits[J]. Food Science, 2012(1): 291-296. (in Chinese)
杂志排行
农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Study on Chemical Composition of the Ethyl Acetate Extract of Pratia
- Effects of Different Selenium Fertilizer Types on Selenium Content and Quality of “Lingfeng” Grapes
- Protoplast Culture and Its Application in Fruit Breeding
- Indexes of Tree Structure of Cylindrical Pear Orchards at the Sapling Stage
- Carbon Storage and Distribution of the Mature Pinus massoniana Plantation in Northwest Guangxi
- Pollution and Quality Control of Mycotoxins in Foods and Feeds
