Biological Characteristics of Aeromonas Strains in Nanchang Area
2019-09-10XinyiSHANDongxuWENXiaolanLIUWangmingTAOMengjuanZHANGWeiQIFengweiZHANGZhixiuZHU
Xinyi SHAN Dongxu WEN Xiaolan LIU Wangming TAO Mengjuan ZHANG Wei QI Fengwei ZHANG Zhixiu ZHU
Abstract [Objectives] This study was conducted to find effective measures to prevent and control Pelteobagrus fulvidraco hemorrhage.
[Methods] Typical disease materials were collected for bacterial isolation and culture and biological characteristics detection, and morphological characteristics were observed by pure culture method. Biochemical characteristics were identified by micro biochemical method. Molecular identification was performed by PCR amplification method. Drug resistance was detected by disk diffusion method. The agar diffusion method was used for the detection of in vitro inhibitory effect. The immunogenicity of the isolates was detected by subcutaneous immunoassay. The virulence factor was detected by spot inoculation. The intraperitoneal injection was used for the detection of pathogenicity.
[Results] The isolates were round, grayish white, and identified as Aeromonas. They fermented maltose, glucose, etc., did not ferment lactose, and were negative for urea and H 2S and positive for lysine and arginine. The target fragment appeared at 1 500, and the sequences shared the highest homology with Aeromonas. The isolates were highly susceptible to amikacin and gentamicin, and resistant to penicillin G and tetracycline. Eight lactic acid bacteria strains produced 1.1-1.9 cm of inhibition zone against the isolates. After the second vaccination, the titer reached 2 13 ; both hemolysin and protease were produced; and the test mice died within 24 h.
[Conclusions] The isolates are Aeromonas, and have strong drug resistance, immunogenicity and pathogenicity. Inactivated emusion oil vaccines of Aeromonas combined with the co use of lactic acid bacteria and susceptible drugs can prevent the outbreak of diseases caused by Aeromonas.
Key words Pelteobagrus fulvidraco; Aeromonas; Biological characteristics
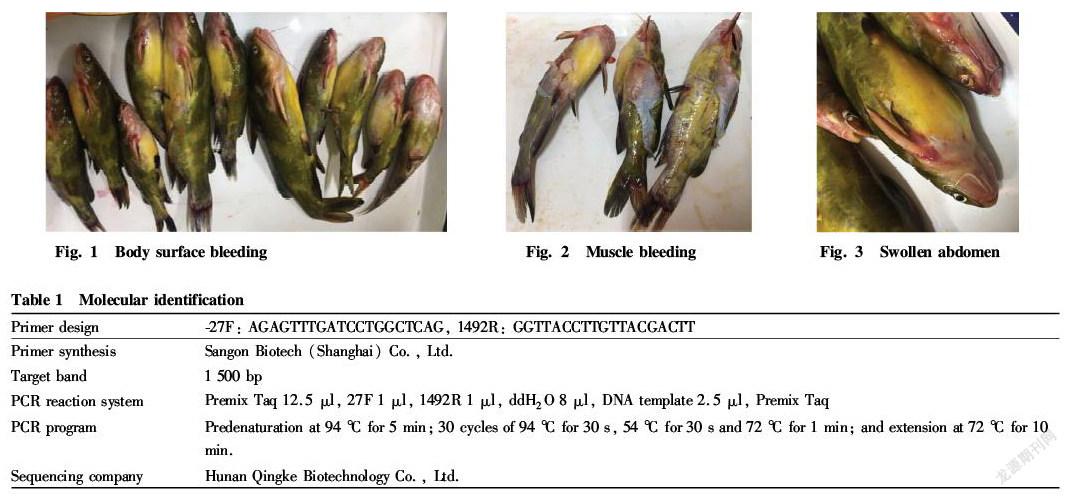
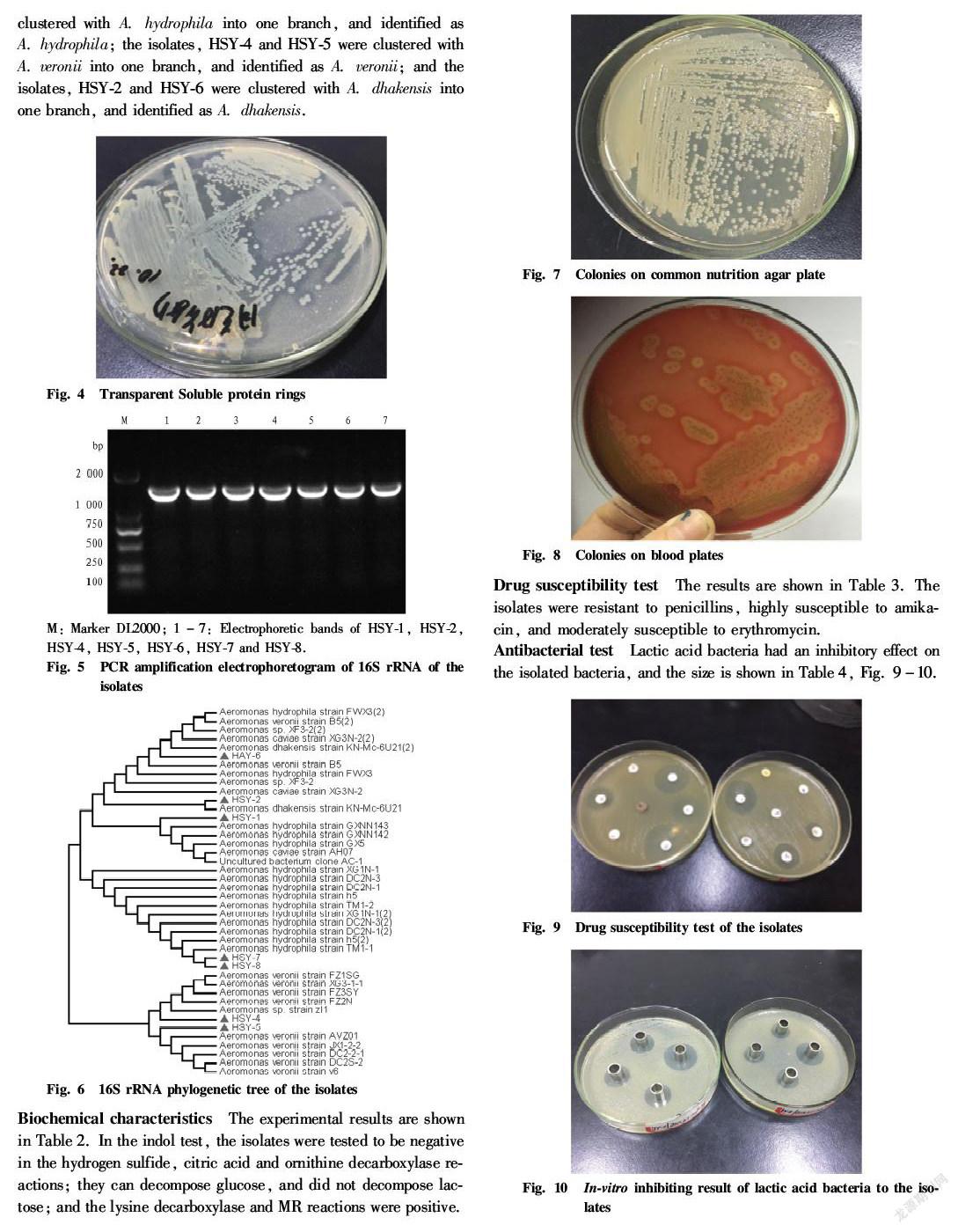
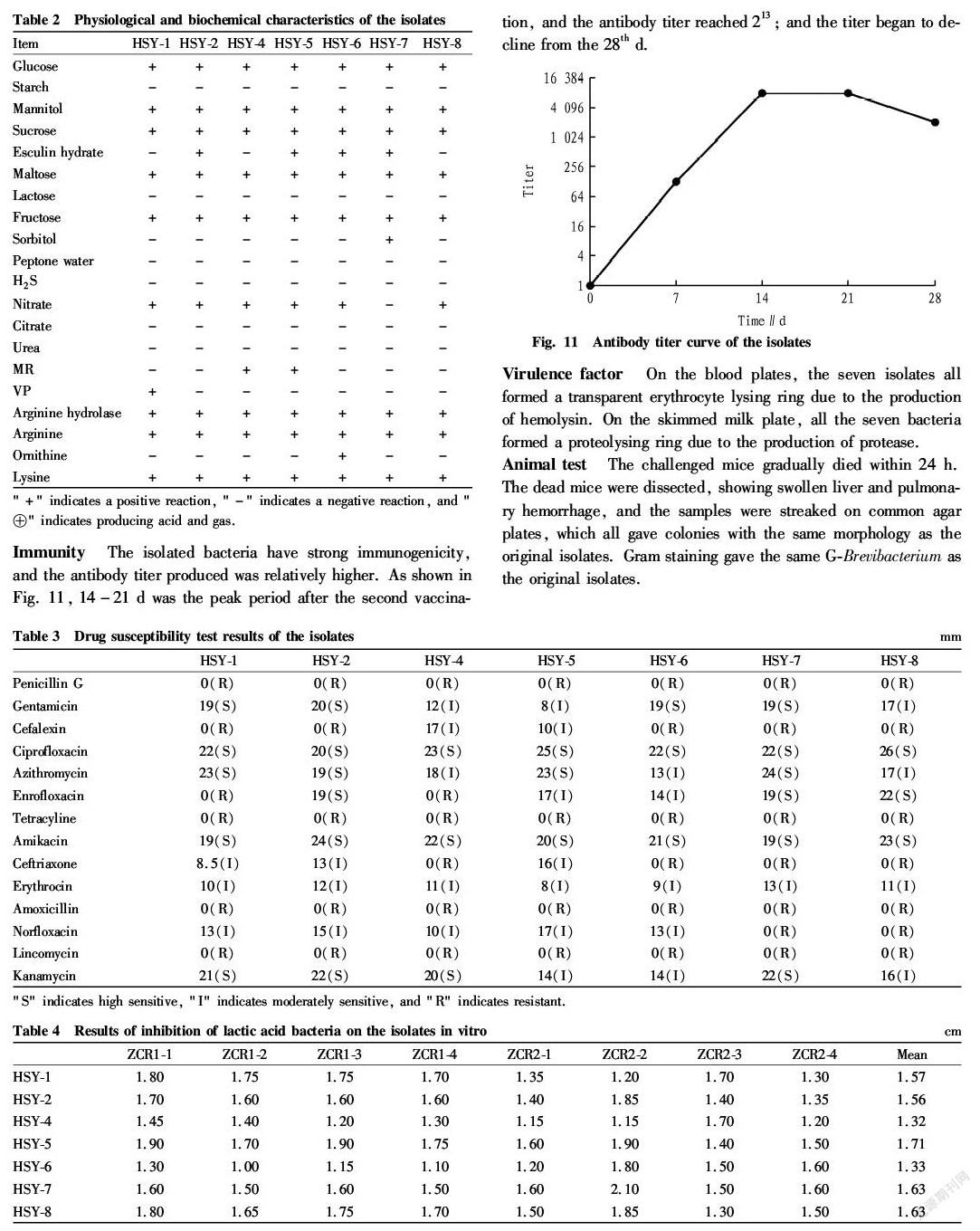
Pelteobagrus fulvidraco is a kind of bottom fish commonly found in Chinas freshwater system. Its meat is tender, delicate and delicious, and contains sufficient proteins and more mineral elements. It has the effect of strengthening the spleen, reducing swelling and facilitating diuresis. It is a middle and high grade precious variety which has a high economic efficiency. P. fulvidraco is highly resistant to diseases and easy to survive, but with the development of large scale farming, the diseases and pests of P. fulvidraco are becoming more and more[1-3]. In 2017, from April to October, there were many deaths of P. fulvidraco in some areas of Jiangxi Province, and the main symptoms of the diseased fish were body surface and muscle bleeding and abdomen swelling (Fig. 1 Fig. 3). In this study, typical disease materials were collected for bacterial isolation and culture and detection of biological characteristics, so as to find effective measures to prevent and treat P. fulvidraco bleeding and provide new ideas for clinical prevention and treatment of the disease.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Tested animals
Epidemic materials: P. fulvidraco died in some areas of Jiangxi Province; SPF laboratory mice: Animal Testing Center of Nanchang University Medical College (15-25 g/mouse).
Reagents
Blood plate, ordinary plate, common broth and skimmed milk plate, self prepared; 22 kinds of micro fermentation tubes and 14 kinds of drug sensitive paper discs, purchased from Hangzhou Tianhe Microbiology Co., Ltd.; lactic acid bacteria ZCR1 1, ZCR1 2, ZCR1 3, ZCR1 4, ZCR2 1, ZCR2 2, ZCR2 3 and ZCR2 4, preserved by the Preventive Veterinary Department, Jiangxi Agricultural University.
Experimental instruments
HH. BII.420BS electrothermal constant temperature incubator, Shanghai Yuejin Medical Instruments Co., Ltd.; LDZX 40BI vertical automatic electric steam sterilizer , Shanghai Shenan Medical Instrument Factory; COCI optical microscope, Chongqing Optical Instrument Factory; Motic digital microscope, Motic China Group Co., Ltd.; WP750 microwave oven, Guangdong Galanz Company; UV752 UV Vis Spectrophotometer, Shanghai Aucy Technology Instrument Co., Ltd.; horizontal electrophoresis tank, electrophoresis instrument, PCR instrument, Bio Rad Company.
Methods
Separation and purification
In the sterile ultra clean workbench, the dead P. fulvidraco with typical natural symptoms was wiped with 75% ethanol cotton balls. The typical lesions were aseptically hooked, and streaked and cultured on skimmed milk tryptone plates at 37 ℃ for 24 h. The growth state of the colonies was observed, and the dominant bacterial communities with the same morphology were picked for purification culture.
Molecular identification
Molecular identification is shown in Table 1.
Biological characteristics
Culture characteristics of isolates
The isolated and purified bacteria were streaked into blood plates and normal agar plates, and cultured in an incubator at 37 ℃ for 24 h. The morphology and size of the colonies were observed, and single typical colonies were picked for Gram stain microscopy to observe the morphological characteristics of the colonies.
Biochemical characteristics of isolates
The isolates were inoculated into micro biochemical reaction tubes of sucrose, mannitol, lactose, maltose, glucose, citrate, phosphate glucose peptone water, nitrate, hydrogen sulfide, arginine hydrolase, arginine decarboxylase, gelatin, ornithine decarboxylase, esculin hydrate and lysine decarboxylase, respectively, and were cultured in an incubator at 37 ℃ for 24 h. The growth changes were observed according to the instructions of the micro biochemical reaction tubes.
Drug tolerance
The isolated broth cultures were smeared on common plates. Then, 14 kinds of drug sensitive paper discs were attached to the surface of the medium according to the agar diffusion method, and after culturing at 37 ℃ for 24 h, the inhibitory zone diameter (in mm) was measured.
Antibacterial test
The isolate cultures were applied to two ordinary agar medium plates, respectively, and on each plate, four Oxford cups were placed equidistantly. Onto one plate, lactic acid bacteria ZCR1 1, ZCR1 2, ZCR1 3 and ZCR1 4 fermentation broths were added, respectively, and on the other plate, lactic acid bacteria ZCR2 1, ZCR2 2, ZCR2 3 and ZCR2 4 fermentation broths were added, respectively. The bacteria were cultured at 37 ℃ in an incubator for 24-48 h to observe the size of the inhibitory zone diameter.
Immunity
The HSY 1 medium was inactivated with 0.5% formaldehyde, centrifuged at 3 000 r/min for 15 min, and emulsified with Freunds adjuvant at a ratio of 1∶1 to prepare an HSY 1 oil emulsion vaccine. Rabbits were immunized intraperitoneally twice (2 ml, 5 ml) (at an interval of 15 d/time), and blood was collected for immunological serum antibody detection.
Virulence factor
The isolated bacteria were spotted on blood plates and skimmed milk plates at 37 ℃ for 24 h. Then, the changes in the colony morphology were observed.
Animal test
The isolates were inoculated into common broth and cultured at 37 ℃ for 24 h. Then, seven groups of white mice, 5 mice/groupk were intraperitoneally injected at a dose of 0.5 ml/mouse , and a control was also set up to observe the death. The dead mice were used for the isolation of bacteria, which were cultured in time for staining microscopy.
Results and Analysis
Separation and purification results
On the skimmed milk tryptone medium, there were a large number of colonies with uniform morphology, smooth surface, neat edges and clear transparent protein soluble circles (Fig. 4). The seven strains with single morphology were purified as HSY 1. HSY 2, HSY 4, HSY 5, HSY 6, HSY 7 and HSY 8. The purified strains were transferred to the common nutrient agar slant, and preserved in a refrigerator at 4 ℃ for subsequent experiments.
Molecular identification
Agarose gel electrophoresis showed that the amplified 16S rRNA gene fragments of the seven isolates were approximately 1 500 bp (Fig. 5), which was consistent with the expected fragment size. The gene sequences of the isolates were cut using seqman software. The truncated fragments were subjected to homology comparison using the National Center for Biotechnology Information. The results showed that the homology between the isolates and the Aeromonas reference sequence in GenBank was above 99.6% . The extracted samples were subjected to phylogenetic analysis using MEGA6 software (Fig. 6), which showed that HSY 1, HSY 7 and HSY 8 were clustered with A. hydrophila into one branch, and identified as A. hydrophila ; the isolates, HSY 4 and HSY 5 were clustered with A. veronii into one branch, and identified as A. veronii; and the isolates , HSY 2 and HSY 6 were clustered with A. dhakensis into one branch, and identified as A. dhakensis .
Conclusions and Discussion
Aeromonas includes 20 species including A. veronii, A. hydrophila and A. caviae, widely distributed in nature. They can grow at 0-45 ℃, optimally at 30 ℃ and can cause diseases such as enteritis and sepsis in mammals (humans, domestic animals, etc.) and cold blooded animals (frogs, fish, snakes, etc.), and are thus typical human beast fish common pathogens[6].
P. fulvidraco in some areas of Jiangxi dies from April to October, which is the period with suitable temperature for the growth of Aeromonas, and the clinical bleeding symptoms are consistent with Aeromonas septicaemia. The isolated colonies are smooth and round on ordinary agar plates, which are G Brevibacterium, which is consistent with Jia et al.[6-7]. They decomposed glucose and did not decompose lactose, which is consistent with Hu et al.[8-10], but inconsistent with the result of Zhang et al.[11] that the colonies decomposed lactose, which may be caused by differences in strains. According to"Bergeys manual of Determinative Bacteriology", the newly diagnosed isolates were Aeromonas. The 16S rRNA sequencing results showed that HSY 1, HSY 7 and HSY 8 were A. hydrophila , HSY 4 and HSY 5 were A. veronii, and HSY 2 and HSY 6 were A. dhakensis.
The isolates of this study were resistant to drugs such as penicillin G, highly susceptible to gentamicin, and moderately susceptible to erythromycin. Huang et al.[12-14] reported that the isolates are highly resistant to penicillin and novobiocin and susceptible or highly susceptible to azithromycin and ciprofloxacin, which is basically the same as the results of this study. Li et al.[15] and Zhang et al.[11] reported that the isolates were highly susceptible to neomycin, ceftriaxone and tetracycline, which does not accord with the results of this study, which might be caused by clinical medication or strain differences and regional differences.
Due to the clinical abuse of antibiotics, Aeromonas is becoming more and more resistant to the drugs, and it is extremely urgent to find biopharmaceuticals to reduce or replace antibiotics. Zhang et al.[16] found that five kinds of Chinese herbal medicines including Schisandra chinensis, Rhus chinensis Mill. and Coptis chinensis Franch. can be used to control Aeromonas diseases in tilapia. Zhu et al.[17-18] reported that Bacillus amyloliquefaciens has a better antagonistic effect on A. veronii. In this study, the lactic acid bacteria had a strong inhibitory effect on Aeromonas, which can be used for the prevention and treatment of diseases caused by Aeromonas.
According to references[19-20], the inactivated vaccine of A. hydrophila has good immunogenicity. In this study, the mice produced the titer reaching 213 after the second vaccination, suggesting strong immunogenicity, which is consistent previous studies[19-20]. According to Yan et al.[21], the inoculation of A. veronii ghost vaccine can increase the serum antibody titer of carps, and the overall immune effect is better than that of formaldehyde inactivated vaccine. Therefore, the development of a new bacteria ghost vaccine still needs further experiments.
According to the report of Bi et al.[22-23], the extracellular product of A. veronii contains lipase, amylase and protease and has hemolytic activity, which is consistent with the result of this study that the isolates produced hemolysin and protease and had strong pathogenicity and accords with the symptom in this study that the test mice died within 24 h.
From April to October every year which is the high incidence period of Aeromonas, in order to prevent its outbreak, it is recommended to immunize the fish body and add lactic acid bacteria to the culture water area regularly accompanied with the use of sensitive drugs.
References
[1] WANG M, ZHOU FJ, ZHANG TH, et al. Isolation and identification and Chinese herbal medicine sensitivity test of Aeromonas sobria from Pelteobagrus fulvidraco[J]. Scientific Fish Farming, 2017(6): 63-64. (in Chinese)
[2] ZHU CK, LIU GJ, ZHANG ZS, et al. Establishment of a duplex PCR assay based on Aha and gyrB genes for detection of Aeromonas veronii[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2017(10): 810-815. (in Chinese)
[3] SHAN XF, KANG YH, XU Y, et al. Screening of in vivo induced genes of Aeromonas veronii from yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco)[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2015(11): 842-845. (in Chinese)
[4] BUCHANAN RE, GIBBONS NE, et al. Bergeys manual of determinative bacteriology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984. (in Chinese)
[5] CHE XZ, CAI MY, et al. Common bacterial system identification manual[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007: 320-418. (in Chinese)
[6] JIA JP, KANG YH, ZHANG DX, et al. Isolation, identification and drug resistance analysis of pathogenic Vicva sinensis in brocaded crucian[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 40(1): 19-23. (in Chinese)
[7] ZHU RL, MA T, CHEN L, et al. Isolation, identification and virulence genes detection of Aeromonas veronii from Aristichthys nobilis[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2017, 44(2): 229-233. (in Chinese)
[8] HU XC, SUN JH, SUN JF, et al. Isolation, identification and antibiotic sensitivity analysis of Aeromonas veronii biovar Sobria from diseased butterfly tail goldfish[J]. Journal of Hydroecology , 2018, 39(01): 105-110. (in Chinese)
[9] ZHU Zx, XU Tl, DENG SZ. Isolation, identification and antimicrobial test in vitro of Aeromonas from Hemibarbus maculatus Bleeker[J]. Agricultural Science&Technology, 2017, 18(1): 156-160
[10] TIAN T, ZHANG JM, DU HJ. Isolation and identification of Aeromonas veronii from Chinese sturgeon and its antibiotic sensitivity[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2017, 44(6): 1010-1016. (in Chinese)
[11] ZHANG XM, CUI WY, DING SQ, et al. Isolation, identification and antibiotic sensitivity of Aeromonas veronii from Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Microbiology China, 2017, 44(12): 2795-280. (in Chinese)
[12] HUANG JL, TAN XC, PENG SH, et al. The resistance to antibiotics of 109 Aeromonas veronii isolated from Ctenopharyngodon idellus[J]. Journal of Foshan University: Natural Science Edition, 2017,35(2):66-70. (in Chinese)
[13] ZHU NY, ZHENG XY, CAO FF, et al. Preliminary study on drug resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila from turtle[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2017, 29(9): 1445-1450. (in Chinese)
[14] ZHANG DF, LIU C, KE XL, et al. Isolation, identification and antimicrobial resistance of a multidrug resistant Aeromonas schubertii isolated from snakehead fish[J], Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 2017, 39(12): 981-986. (in Chinese)
[15] LI ZQ, ZHANG K, LIN M, et al. Isolation and identification of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii from Pseudosciaena crocea[J]. Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(1): 139-146. (in Chinese)
[16] ZHANG ZX, SHI QM, WU TL, et al. In vitro antibacterial test of single flavored Chinese herbal medicine against tilapia Aeromonas veronii[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2017(1): 147-149. (in Chinese)
[17] ZHU ZX, JIANG XH, DENG SZ, et al. Isolation, Identification and in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii from soft shelled turtles[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology, 2016(4): 804-809. (in Chinese)
[18] HE T, ZOU S, GONG L, et al. Isolation of pathogenic strain AvX005 and screening of its antagonistic bacteria in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus[J]. Fisheries Science, 2018,37(1):15-23. (in Chinese)
[19] ZHANG L, DING YM, AI XH. Protecting soft shelled turtle from fatal Aeromonas hydrophila infection by immunization with Aeromonas hydrophila emusion oil vaccine[J]. Microbiology China, 2010(12): 1793-1797.
[20] LUO F, ZHANG QZ, FENG HR, et al. Changes of peripheral blood immune indexes of Spinibarbus sinensis immunized with inactivated vaccine[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2010(4): 626-634.
[21] YAN BB, JIANG N, LUO L, et al. Effect of injection immunization with Aeromonas veronii ghosts on immunological responses and hepcidin gene expression in common carp[J]. Microbiology China, 2017(6): 1395-1404.
[22] BI JF, CHEN L, KANG YH, et al. Analysis of enzyme activity and immunogenicity of the extracellular products from Aeromonas veronii TH0426[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2017, 37(10): 1896-1899.
[23] XIONG J, LAI XJ, YU Q, et al. Comparison of extracellular products of virulence gene of seven strains of pathogenic Aeromonas sp. from eel[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2017, 36(1): 76-85.
杂志排行
农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Study on Chemical Composition of the Ethyl Acetate Extract of Pratia
- Effects of Different Selenium Fertilizer Types on Selenium Content and Quality of “Lingfeng” Grapes
- Protoplast Culture and Its Application in Fruit Breeding
- Indexes of Tree Structure of Cylindrical Pear Orchards at the Sapling Stage
- Carbon Storage and Distribution of the Mature Pinus massoniana Plantation in Northwest Guangxi
- Pollution and Quality Control of Mycotoxins in Foods and Feeds
