Seed Propagation Technique of Atractylodes lancea in Maoshan, Jiangsu
2019-09-10WeizhongLIUZhijuanWANG
Weizhong LIU Zhijuan WANG
Abstract Due to over exploitation, the Atractylodes resources in such five counties and cities as Jurong, Jintan, Lishui, Liyang and Gaochun have been exhausted. This paper summarized the seed propagation technique of Atractylodes lancea in Maoshan, Jiangsu Province, aiming to provide reference for the restoration of A. lancea production in Maoshan, Jiangsu.
Key words Maoshan; Jiangsu; Atractylodes lancea; Seed; Seedling
Received: May 23, 2019Accepted: August 28, 2019
Weizhong LIU (1964-), male, P. R. China, associate researcher, devoted to research about organic agriculture development.
*Corresponding author. Email: liuweizhong168@126.com.
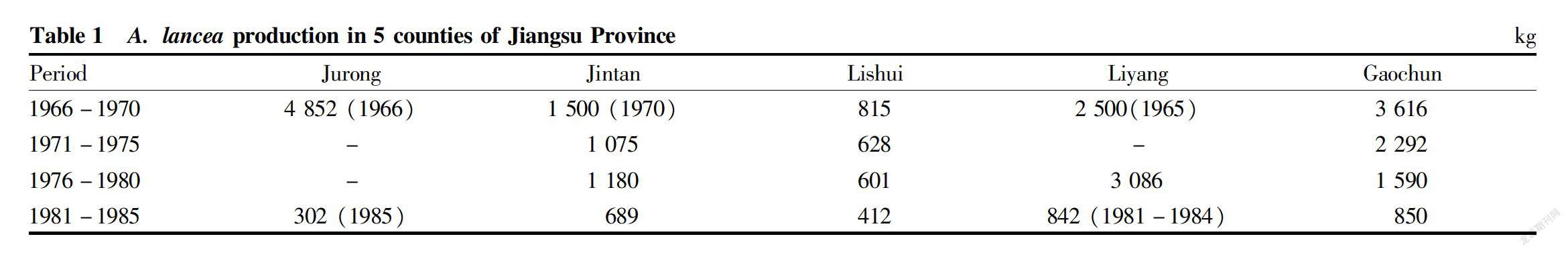
Atractylodes lancea is a plant in Compositae, which is widely distributed at 30°-32° north latitude, 111°-119° east longitude, and elevations of 60-1 000 m. Specifically, it is distributed in provinces such as Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shandong, Hubei and Sichuan[2]. A. lancea produced in Maoshan, Jiangsu Province has the best quality, hence the name “Mao Cangshu”[3]. According to the field investigations of He Shanan, He Huisheng, Lyu Wei, et al., since the 1960s, due to over exploitation, A. lancea resources in such five counties and cities as Jurong, Jintan, Lishui, Liyang and Gaochun have been exhausted (Table 1). In order to quickly recover the production of A. lancea in Maoshan, Jiangsu Province and to meet the needs of consumers, on the basis of years of research, the seed propagation technique of A. lancea in Maoshan, Jiangsu Province was summarized.
Seedbed preparation
Selection of seedbed
For the seedbed, yellowbrown loam with high organic matter content is selected. The soil is sandy soil, which is fertile and loose, and has flat terrain.
Ploughing
The soil is ploughed twice in middle to late September and 3-5 d before planting, respectively. The ploughing depth is about 25-30 cm, to facilitate weeding and loosening of soil. Before planting, the land is simultaneously applied with manure or compost at 15 000 kg/hm2 as the base fertilizer.
Preparation of seedbed
Before planting, ploughing is performed with a depth of 20-25 cm. The land is then raked to form ridges, which has a width of 120 cm and a height of 15 cm. The ridges are turtleshaped, and the groove width is about 30 cm. The ridge surface is smoothed, and stones and other debris are removed.
Seed Management
Seed treatment
In order to ensure the uniformity and consistency of the seedling emergence of A. lancea and facilitate seedling management, the seeds are graded by 1.43, 2 and 2.4 mm sieves before seeding, and the graded seeds are subpackaged with nylon mesh pockets with a pore size less than 1.4 mm, and soaked with 200 times EM bacterial liquid for 2 h[4]. Finally, the seeds are fished out. According to research by Zhang et al.[4], seed soaking with 200 times EM bacterial liquid can increase the emergence rate by more than 12%.
Seeding time
The sowing time of A. lancea can be carried out from the end of October to the end of December or from late March to early April, on a sunny day.
Seeding method
There are two kinds of sowing methods: strip sowing and hole sowing. When using strip sowing, the line is laid every 30 cm in ridges, and then the planting ditches about 3-4 cm in deepth and 10 cm in width are formed along the line. The row spacing is 30 cm. The sowing quantity is 45 kg/hm2, and the seeds are mixed with seed sand according to the ratio of 1∶5 and planted in the planting ditches. After sowing, the seeds are evenly covered with fine soil, and the thickness of the covering soil is about 1 cm[5], which is slightly compacted. A layer of straw is laid on the top, and watering is performed frequently. After emergence, the straw is removed. When adopting the hole sowing method, the hole spacing and the row spacing are both 20 cm, and each hole has a depth of about 3-4 cm and is sown with 4-6 seeds, which are evenly spread. After sowing, the seeds are covered with thin and fine soil with a thickness of about 1 cm[5]. The soil is covered with a layer of straw, and water is often sprinkled. After emergence, the straw is removed to facilitate emergence.
Seedling Management
Weeding
Weeds should be removed in the seedling stage, once every 2-3 weeks in the growing season. When loosening the soil during the period from April to the beginning of the hottest part of summer, hilling is performed at the same time. After entering the hottest part of summer, the hightemperature highhumidity climate is not suitable for weeding. Every time when we hoe the grass, we cant get too close to the A. lancea seedlings, so as not to hurt the roots of A. lancea; and for the weeds that are close to the seedlings, the root part of A. lancea should be pressed with one hand, the weeds can be removed with the other hand. Each time, the weeding is combined with hilling up and clearing the ditches. The soil is smashed and loosened along the A. lancea rows, and the weeds are removed at the same time.
Thinning
Thinning is performed when the seedlings grown by direct seeding have 2-3 true leaves thereon. Seedlings are remained according to the plant spacing of 3 cm for strip sowing, and 1-2 plants are remained in each hole for hole sowing. The seedlings pulled out could be filled in the gaps and transplanted.
Fertilization
It is necessary to perform topdressing 3 times a year. Faecal matter is applied at the first time in May at a rate of 15 000 kg/hm2 in the seedling stage; at the second time, faecal matter is applied at 18 750 kg/hm2 or ammonium sulphate is applied at 75 kg/hm2 in June; and at the third time, faecal matter is applied in August at 15 000-18 750 kg/hm2, and plant ash and superphosphate are also applied.
Drainage
In the seedling stage, the drainage ditch should be dredged, and after heavy rain, the accumulated water should be drained in time to ensure that there is no water on land surface.
Control of Pests and Diseases
According to the law of occurrence and development of pests and diseases, comprehensive prevention and control measures such as biological control, physical control and chemical control are adopted. The use of pesticides implements the NY/T3932000 Green food—Guideline for application of pesticide. The pests of A. lancea are mainly aphids, which are the most harmful in spring and summer. The yellow boards for sticking pests can be used to trap aphids at a height of 0.5 m above the ground, which can kill a large number of winged aphids. It can also be controlled by natural enemies, such as ladybugs and lacewing flies. Aphid sex pheromones can also effectively trap aphids. Using pesticides to control aphids, it is recommended to use highefficiency, lowtoxic, lowresidue agents, such as 2 000 times dilution of 10% imidacloprid WP for spraying, 3 000 times dilution of 1.8% avermectin for spraying, 500-1 000 times dilution of 10% nicotine EC for spraying, and 2 500 times dilution of 50% pirimicarb WP for spraying. The main diseases are black spot, ring spot, blight, soft rot, southern blight, root knot nematode disease and so on. 70% thiophanatemethyl, 25% carbendazim and 50% Kangkuling can effectively prevent black spot, ring spot, blight and soft rot by root irrigation and foliar spray. The root knot nematode disease can be effectively prevented by using 5% Kexianling at 7 500 g/hm2. Southern blight can be bettered controlled with 50% thiophanatemethyl and 20% tolclofosmethyl[6-7].
References
[1] Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese pharmacopeia[S]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2010. (in Chinese)
[2] FENG WX, GU W, KONG LJ, et al. Study on HOLC fingerprint of Atractylodes lancea in different producing areas[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2010(10): 434-435. (in Chinese)
[3] XIA QS, CHEN QY, LIU MM, et al. Establishment of the method for determining the chroma range of Atractylodes lancea[J]. Hubei Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015(4): 45-47. (in Chinese)
[4] ZHANG HZ. Study on Key Techniques of seedling raising of Atractylodes lancea[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2016. (in Chinese)
[5] HOU HR, CHAO JG, GU W, et al. Effects of environmental factors on seed germination of Atractylodes lancea[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2017(3): 33-34. (in Chinese)
[6] YANG XZ, CHI XM. Summary of high quality, high yield and pollutionfree artificial cultivation techniques of Atractylodes lancea[J]. Yunnan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica, 2007, 28(9): 21-23. (in Chinese)
[7] ZHANG HZ, SU SH, WANG M, et al. Control of dark leaf spot disease on Atractylodes lancea in seedling stage[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2011(7): 2671-2675.
杂志排行
农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Observation on Cardiac Opening of the Inferior Vena Cava in Goat Fetuses
- Evaluation on Application and Spraying Effect of AirAssisted Sprayer in Apple Orchard with Dwarfing Rootstocks
- Problems in the Development of Traditional Chinese Medicinal Materials Planting Industry in Shiyan City and Countermeasures
- Study on Practical Mature Age of Individual Pinus thunbergii×P. densiflora
- Effects of Different Densityreducing Methods on Canopy Microenvironment, Tree Growth and Fruit Quality in Closed Apple Orchard
- Development of Whole Potato Flour Fish Noodles
