猴子瘿袋化学成分研究
2019-09-10何小汝王雅琪徐柳云
何小汝 王雅琪 徐柳云
摘要 目的:研究波罗蜜属植物猴子瘿袋Artocarpus.Pithecogallus小枝的化学成分。方法:运用硅胶柱色谱、MCI gel树脂、LH-20葡聚糖凝胶(Sephadex LH-20)柱色谱、HPLC、ODS等色谱分离手段,对猴子瘿袋枝叶的95%乙醇提取物的乙酸乙酯部位进行分离纯化,通过其1H-NMR和13C-NMR数据与文献进行对照鉴定其结构。结果:共分离了六个三萜类化合物,分别鉴定为3,25-二羟基羊毛脂烷-8,23(E)-二烯-7,11-二酮(1),(24R)-环阿屯烷-25-烯-3β,24-二醇(2),(24R)-环阿屯烷-24,25-二醇-3-酮(3),熊果酸(4),桦木酸(5),白桦脂醇(6)。结论:化合物1、5和6为首次从菠萝蜜属植物中分离获得。
关键词 波罗蜜;猴子瘿袋;化学成分;分离;三萜;结构鉴定;熊果酸;白桦脂醇
Abstract Objective:To study the chemical constituents of the twigs of Artocarpus.Pithecogallus.Methods:Compounds were isolated and purified by the normal phase silica gel,MCI gel,Sephadex LH-20,HPLC and ODS chromatography.Their structures were identified by comparing the 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR data with those reported in literature.Results:Six triterpenoids were isolated from the ethyl-acetate fraction in 95% ethanol extract of A.Pithecogallus.All isolates were identified as 3,25-dihydroxy lanolin-8,23(E)-diene-7,11-dione(1),(24R)-cycloalkane-25-ene-3,24-diol(2),(24R)-cycloalkane-24,25-diol-3-one(3),ursolic acid(4),birch acid(5)and betulin(6).Conclusion:Compounds 1,5 and 6 were isolated from the genus Artocarpus for the first time.
Key Words Artocarpus; A.pithecogallus; Chemical constituents; Isolation; Triterpenoid; Structure identification; Ursolic acid; Betulin
中图分类号:R284.2 文献标识码:A doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2019.07.003
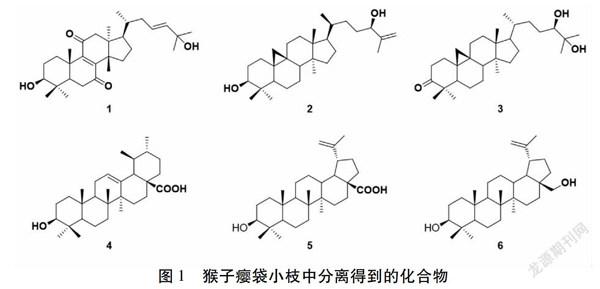
猴子瘿袋Artocarpus.pithecogallus為桑科(Moraceae)波罗蜜属常绿乔木植物,主要产自我国云南西双版纳地区,生长于海拔1 400~1 630 m湿润疏林中[1]。许多波罗蜜属植物在东南亚、中国作为传统民间用药[2-3],如在我国西南地区,白桂木A.hypargyreus Hance可用于治疗风湿、头痛和黄疸[4]。化学研究表明,菠萝蜜属植物富含各种异戊烯基取代的酚性化合物,这些成分多具有细胞毒活性[5-8]、抗炎[9-13]、抗真菌[14]、抗氧化[15-16]及酪氨酸酶抑制活性[17-18],具有很好的研究开发潜力。为了从波罗蜜属植物中发现新的活性有效成分,本课题组对该属植物牛李A.nigrifolius进行了系统的化学成分研究,从中发现了大量的三萜[19]及异戊烯基取代的黄酮和查尔酮[20],其中部分异戊烯基酚类化合物对人源宫颈癌HeLa细胞和胃癌SGC-7901细胞具有较强的细胞毒活性。为了进一步深入研究波罗蜜属植物的化学成分,促进药用资源的开发与利用,本课题采用多种色谱分离技术对猴子瘿袋的乙酸乙酯萃取部位进行了系统研究,分离得到了六个化合物(图1),经鉴定分别为3,25-二羟基羊毛脂烷-8,23(E)-二烯-7,11-二酮(1),(24R)-环阿屯烷-25-烯-3β,24-二醇(2),(24R)-环阿屯烷-24,25-二醇-3-酮(3),熊果酸(4),桦木酸(5)和白桦脂醇(6)。
1 材料
Bruker AX-600型核磁共振波谱仪(瑞士布鲁克公司),安捷伦1200型高效液相色谱仪(美国Agilent公司),Sephadex LH-20凝胶(美国GE Healthcare公司),MCI GEL CHP 20P(75~150 M)精细分离树脂(日本Mitsubishi公司),反相硅胶ODS-A gel(12 nm,S-75 M)(日本YMC公司),YMC-Pack ODS半制备柱(10 mm×250 mm,5M,日本YMC公司),薄层硅胶板(烟台江友硅胶开发有限公司),柱层析硅胶(青岛海洋化工有限公司,100-200目,200-300目),色谱纯甲醇和乙腈(百灵威公司),其他试剂均为市售分析纯(西陇化工股份有限公司)。
本实验药材采自云南省勐腊县,经中科院西双版纳热带植物园许又凯教授鉴定为猴子瘿袋A.pithecogallus,凭证标本(AP201409)保存于南昌大学药学院标本馆。
2 提取与分离
取晾干的猴子瘿袋小枝5 kg,粉碎后于室温下用95%乙醇反复提取3次,每次浸泡7 d,所得提取液减压浓缩,得粗浸膏553.1 g。加入适量的水于粗浸膏中,并在超声条件下搅拌混悬,用等体积的乙酸乙酯与悬浮液萃取4次,而后将有机相合并,浓缩得油状浸膏246.0 g。将油状浸膏通过MCI柱色谱分离,以甲醇/水(0∶ 100→100∶ 0,v/v)梯度洗脱,合并浓缩后得到6个组分(Fr.1~Fr.6)。组分Fr.3(19.8 g)经ODS反相色谱(甲醇-水 35∶ 65→40∶ 60)和高效液相色谱(乙腈-水60∶ 40)洗脱得到单体化合物5(2.2 mg)和6(1.6 mg)。组分Fr.5(2.9 g)经Sephadex LH-20柱色谱(甲醇),由ODS反相色谱(甲醇-水 70∶ 30→80∶ 20)和高效液相色谱(乙腈-水 95∶ 5)洗脱得到单体化合物1(5.0 mg)和4(1.3 mg)。组分Fr.6(10.9 g)经ODS反相色谱(甲醇-水 80∶ 20→95∶ 5)和高效液相色谱(乙腈-水 35∶ 65)洗脱得到化合物2(7.0 mg)和3(14.0 mg)。
3 结构鉴定
化合物1:白色固体;1H-NMR(400MHz,CDCl3):δH 3.30(1H,dd,J=10.4,6.0 Hz,H-3),5.58(2H,m,H-23,H-24),0.86(3H,d,J=6.4 Hz,H-21),0.90(3H,s,H-29),0.94(3H,s,H-18),1.02(3H,s,H-28),1.08(3H,s,H-30),1.30(3H,s,H-19),1.30(3H,s,H-26),1.30(3H,s,H-27);13C-NMR(100 MHz,CDCl3):δC 34.0(C-1),27.5(C-2),78.1(C-3),38.7(C-4),48.6(C-5),35.4(C-6),200.0(C-7),149.9(C-8),154.9(C-9),38.2(C-10),201.9(C-11),51.5(C-12),45.3(C-13),48.0(C-14),31.9(C-15),28.1(C-16),48.9(C-17),18.8(C-18),17.9(C-19),35.9(C-20),18.9(C-21),37.9(C-22),125.0(C-23),140.0(C-24),70.9(C-25),30.1(C-26),30.1(C-27),27.7(C-28),15.2(C-29),24.2(C-30)。以上数据与文献报道基本一致[21],故鉴定该化合物为3β,25-二羟基羊毛脂烷-8,23(E)-二烯-7,11-二酮。
化合物2:白色固体;1H-NMR(400 MHz,CDCl3):δH 4.93(1H,s,H-26a),4.83(1H,s,H-26b),4.02(1H,t,J=6.0 Hz,H-24),3.28(1H,dd,J=10.8,4.0 Hz,H-3),0.33(1H,d,J=4.0 Hz,H-19),0.54(1H,d,J=4.0 Hz,H-19),1.72(3H,s,H-27),0.96(6H,s,H-18,H-29),0.88(3H,d,J=5.6 Hz,H-21),0.87(3H,s,H-28),0.80(3H,s,H-30)。13C-NMR(100 MHz,CDCl3):δC 32.1(C-1),30.5(C-2),79.0(C-3),40.6(C-4),47.2(C-5),21.3(C-6),28.3(C-7),48.1(C-8),20.1(C-9),26.2(C-10),26.2(C-11),33.0(C-12),45.4(C-13),49.0(C-14),35.7(C-15),26.6(C-16),52.3(C-17),18.2(C-18),30.0(C-19),36.1(C-20),18.5(C-21),32.0(C-22),31.8(C-23),76.5(C-24),147.9(C-25),111.1(C-26),17.7(C-27),19.5(C-28),25.6(C-29),14.1(C-30)。以上数据与文献报道基本一致[22],故鉴定该化合物为(24R)-环阿屯烷-25-烯-3β,24-二醇。
化合物3:白色固体;1H-NMR(400 MHz,CDCl3):δH 3.29(1H,dd,J=10.0,1.6 Hz,H-24),0.78(1H,d,J=4.0 Hz,H-19a),0.57(1H,d,J=4.0 Hz,H-19b),1.22(3H,s,H-26),1.16(3H,s,H-27),1.09(3H,s,H-29),1.04(3H,s,H-18),0.99(3H,s,H-28),0.90(3H,s,H-30),0.89(3H,d,J=6.4 Hz,H-21);13C-NMR(100 MHz,CDCl3):δC 33.5(C-1),37.5(C-2),216.8(C-3),50.3(C-4),48.4(C-5),21.5(C-6),28.1(C-7),47.9(C-8),21.1(C-9),26.0(C-10),25.9(C-11),35.6(C-12),45.3(C-13),48.7(C-14),32.8(C-15),26.7(C-16),52.3(C-17),18.1(C-18),29.6(C-19),36.4(C-20),18.4(C-21),33.4(C-22),28.7(C-23),79.6(C-24),73.3(C-25),23.2(C-26),26.6(C-27),19.3(C-28),22.2(C-29),20.8(C-30)。以上数据与文献报道基本一致[23],故鉴定该化合物为为(24R)-cycloartane-24,25-diol-3-one。
化合物4:熊果酸;白色固体;1H-NMR(400 MHz,CDCl3):δH 5.25(1H,t,J=3.2 Hz,H-12),3.22(1H,dd,J=10.8,4.4 Hz,H-3),1.08(3H,s,H-27),0.98(3H,s,H-23),0.94(3H,d,J=6.8 Hz,H-29),0.92(3H,s,H-26),0.86(3H,d,J=6.8 Hz,H-30),0.78(3H,s,H-24),0.77(3H,s,H-25);13C-NMR(100 MHz,CDCl3):δC 38.9(C-1),28.2(C-2),79.2(C-3),39.0(C-4),55.4(C-5),18.5(C-6),33.1(C-7),33.8(C-8),47.7(C-9),36.8(C-10),23.4(C-11),125.8(C-12),138.5(C-13),42.2(C-14),27.4(C-15),24.3(C-16),48.0(C-17),53.1(C-18),39.2(C-19),39.6(C-20),30.8(C-21),37.1(C-22),28.3(C-23),17.1(C-24),15.6(C-25),15.8(C-26),23.7(C-27),180.9(C-28),17.2(C-29),21.3(C-30)。以上數据与文献报道基本一致[24],故鉴定该化合物为熊果酸。
化合物5:白色固體;1H-NMR(400 MHz,CD3OD):δH 4.64(1H,brs,H-29a),4.52(1H,s,H-29b),3.06(1H,dd,J=11.2,4.8 Hz,H-3),1.63(3H,s,H-30),0.94(3H,s,H-27),0.90(3H,s,H-23),0.88(3H,s,H-26),0.79(3H,s,H-25),0.68(3H,s,H-24);13C-NMR(150 MHz,CDCl3):δC 38.5(C-1),27.0(C-2),79.2(C-3),38.5(C-4),55.0(C-5),17.9(C-6),34.8(C-7),40.7(C-8),50.3(C-9),37.3(C-10),22.3(C-11),25.9(C-12),37.3(C-13),43.0(C-14),27.0(C-15),32.3(C-16),57.8(C-17),45.4(C-18),49.6(C-19),149.7(C-20),29.0(C-21),37.4(C-22),27.6(C-23),15.2(C-24),16.0(C-25),16.2(C-26),15.2(C-27),181.1(C-28),109.1(C-29),19.7(C-30)。以上数据与文献报道基本一致[25],故鉴定该化合物为桦木酸。
化合物6:白色固体;1H-NMR(400 MHz,CDCl3):δH 4.67(1H,d,J=1.6 Hz,H-29a),4.57(1H,m,H-29b),3.78(1H,brd,J=10.8 Hz,H-28a),3.31(1H,brd,J=10.8 Hz,H-28b),3.17(1H,dd,J=11.2,5.2 Hz,H-3),2.38(1H,td,J=10.8,5.6 Hz,H-13),1.67(3H,s,H-30),1.01(3H,s,H-27),0.97(3H,s,H-26),0.96(3H,s,H-23),0.81(3H,s,H-24),0.75(3H,s,H-25);13C-NMR(150 MHz,CDCl3):δC 38.8(C-1),27.5(C-2),79.1(C-3),39.0(C-4),55.4(C-5),18.4(C-6),34.4(C-7),41.0(C-8),50.5(C-9),37.3(C-10),21.0(C-11),25.3(C-12),37.4(C-13),42.8(C-14),27.2(C-15),29.3(C-16),47.9(C-17),49.9(C-18),48.9(C-19),150.6(C-20),29.9(C-21),34.1(C-22),28.1(C-23),15.5(C-24),16.2(C-25),16.1(C-26),14.9(C-27),60.6(C-28),109.8(C-29),19.2(C-30)。以上数据与文献报道基本一致[26],故鉴定该化合物为白桦脂醇。
本论文对波罗蜜属植物猴子瘿袋的小枝进行了系统的化学成分研究,从中分离得到六个三萜1-6,其中化合物1、5和6为首次从菠萝蜜属植物中分离获得。
参考文献
[1]中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会编.中国植物志[M].23卷.北京:科学出版社,1998:46.
[2]Chen C C,Huang Y L,Ou J C,et al.Three new prenylflavones from Artocarpus altilis[J].J Nat Prod,1993,56:1594-1597.
[3]Hakim E H,Asnizar,Yurnawilis,Aimi N,et al.Artoindonesianin P,a new prenylated flavone with cytotoxic activity from Artocarpus lanceifolius[J].Fitoterapia,2002,73:668-673.
[4]Yu M H,Zhao T,Yan G R,et al.New isoprenylated flavones and stilbene derivative from Artocarpus hypargyreus[J].Chem Biodivers,2012,9(2):394-402.
[5]Ko H H,Lu Y H,Yang S Z,et al.Cytotoxic prenylflavonoids from Artocarpus elasticus[J].J Nat Prod,2005,68:1692-1695.
[6]Wang Y H,Hou A J,Chen L,et al.New isoprenylated flavones,artochamins A-E,and cytotoxic principles from Artocarpus chama[J].J Nat Prod,2004,67:757-761.
[7]Wang Y H,Hou A J,Chen D F,et al.Prenylated stilbenes and their novel biogenetic derivatives from Artocarpus chama[J].Eur J Org Chem,2006(15):3457-3463.
[8]Zheng Z P,XuY,Qin C,et al.Characterization of antiproliferative activity aonstituents from Artocarpus heterophyllus[J].J Agric Food Chem,2014,62:5519-5527.
[9]Lin J A,Fang S C,Wu C H,et al.Anti-inflammatory effect of the 5,7,4′-trihydroxy-6-geranylflavanone isolated from the fruit of Artocarpus communis in S100B-induced human monocytes[J].J Agric Food Chem,2011,59(1):105-111.
[10]Fang S C,Hsu C L,Yen G C,et al.Anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic compounds isolated from the fruits of Artocarpus heterophyllus[J].J Agric Food Chem,2008,56(12):4463-4468.
[11]Wei B L,Weng J R,Chiu P H,et al.Antiinflammatory flavonoids from Artocarpus heterophyllus and Artocarpus communis[J].J Agric Food Chem,2005,53(10):3867-3871.
[12]Chung M I,Ko H H,Yen M H,et al.Artocarpol A,a novel constituent with potent anti-inflammatory effect,isolated from Artocarpus rigida[J].Helv Chim Acta,2000,83(6):1200-1204.
[13]Lu Y H,Lin C N,Ko H H,et al.Two novel and anti-inflammatory constituents of Artocarpus rigida[J].Helv Chim Acta,2002,85(6):1626-1632.
[14]Jayasinghe L,Balasooriya B,Padmini W C,et al.Geranyl chalcone derivatives with antifungal and radical scavenging properties from the leaves of Artocarpus nobilis[J].Phytochemistry,2004,65(9):1287-1290.
[15]Lin K W,Liu C H,Tu H Y,et al.Antioxidant prenylflavonoids from Artocarpus communis and Artocarpus elasticus[J].Food Chem,2009,115(2):558-562.
[16]Jamil S,Sirat H M,Jantan I,et al.A new prenylated dihydrochalcone from the leaves of Artocarpus lowii[J].J Nat Med,2008,62(3):321-324.
[17]Nguyen N T,Nguyen M H,Nguyen H X,et al.Tyrosinase Inhibitors from the wood of Artocarpus heterophyllus[J].J Nat Prod,2012,75(11):1951-1955.
[18]Likhitwitayawuid K,Sritularak B.A new dimeric stilbene with tyrosinase inhibitiory activity from Artocarpus gomezianus[J].J.Nat.Prod,2001,64(11):1457-1459.
[19]刘曦,王勇,况晓东,等.牛李化学成分分离鉴定[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2018,24(4):56-65.
[20]Liu Xi,Kuang X D,He X R,et al.Prenylflavonoids from the twigs of Artocarpus nigrifolius[J].Chem Pharm Bull,2018,66(4):434-438.
[21]Wang L Y,Wang N L,Yao X S,et al.Euphane and tirucallane triterpenes from the roots of Euphorbia kansui and their in vitro effects on the cell division of Xenopus[J].J Nat Prod,2003,66(5):630-633.
[22]Escobedo-Martinez C,Concepcion L M,Hernandez-Ortega S,et al.1H and 13C NMR characterization of new cycloartane triterpenes from Mangifera indica[J].Magn Reson Chem,2012,50(1):52-57.
[23]Inada A,Murayta H,Inatomi Y,et al.Cycloartane triterpenes from the leaves of Aglaia-Harmsiana[J].J Nat Prod,1995,58(7):1143-1146.
[24]Gnoatto S C,Dassonville-Klimpt A,Da N S,et al.Evaluation of ursolic acid isolated from Ilex paraguariensis and derivatives on aromatase inhibition[J].Eur J Med Chem,2008,43(9):1865-1877.
[25]Khaliq S,Volk F J,Frahm A W.Phytochemical investigation of Perovskia abrotanoides[J].Planta Medica,2007,73(1):77-83.
[26]魏華,何春年,彭勇,等.川木香化学成分研究[J].中国中药杂志,2012,37(9):1249-1253.
(2019-06-05收稿 责任编辑:徐颖)
