基于模拟多曝光融合的低照度图像增强方法
2019-08-27司马紫菱胡峰
司马紫菱 胡峰


摘 要:针对部分低照度图像整体亮度偏暗、对比度差和视觉信息偏弱等问题,提出一种基于模拟多曝光融合的低照度图像增强方法。首先,利用改进的变分Retinex模型和形态学的结合产生基准图来保证曝光图像集中的主体信息;其次,结合Sigmoid函数和伽马矫正构造新的光照补偿归一化函数,同时提出了一种基于高斯引导滤波的反锐化掩模算法,用于调整基准图的细节;最后,分别从亮度、色调和曝光率设计曝光图集的加权值,通过多尺度融合得到最终增强结果,有效地避免了增强结果中的光晕和颜色失真。在不同的公开数据集上的实验结果表明,与传统的低照度图像增强方法进行相比,所提方法降低了亮度失真率,提升了视觉信息保真度。该方法能够有效地保留视觉信息,有利于实现低照度图像增强的实时性应用。
关键词:低照度图像;Retinex理论;曝光融合;细节调整;图像增强
中图分类号: TP391.41图像识别及其装置
文献标志码:A
Abstract: Aiming at the problems of low luminance, low contrast and poor visual information, a low-light image enhancement method based on simulating multi-exposure fusion was proposed. Firstly, the improved variational Retinex model and morphology were combined to generate the reference map to ensure the subject information in the exposed image set. Then, a new illumination compensation normalization function was constructed by combining Sigmoid function and gamma correction. At the same time, an unsharp masking algorithm based on Gaussian guided filtering was proposed to adjust the details of the reference map. Finally, the weighted values of exposed image set were designed from luminance, chromatic information and exposure rate respectively, and the final enhancement result was obtained through multi-scale fusion with effective avoidance of halo phenomenon and color distortion. The experimental results on different public datasets show that, compared with the traditional low-light image enhancement method, the proposed method has reduced the lightness distortion rate and increased the visual information fidelity. The proposed method can effectively preserve visual information, which is conducive to the real-time application of low-light image enhancement.
Key words: low-light image; Retinex theory; exposure fusion; detail adjustment; image enhancement
0 引言
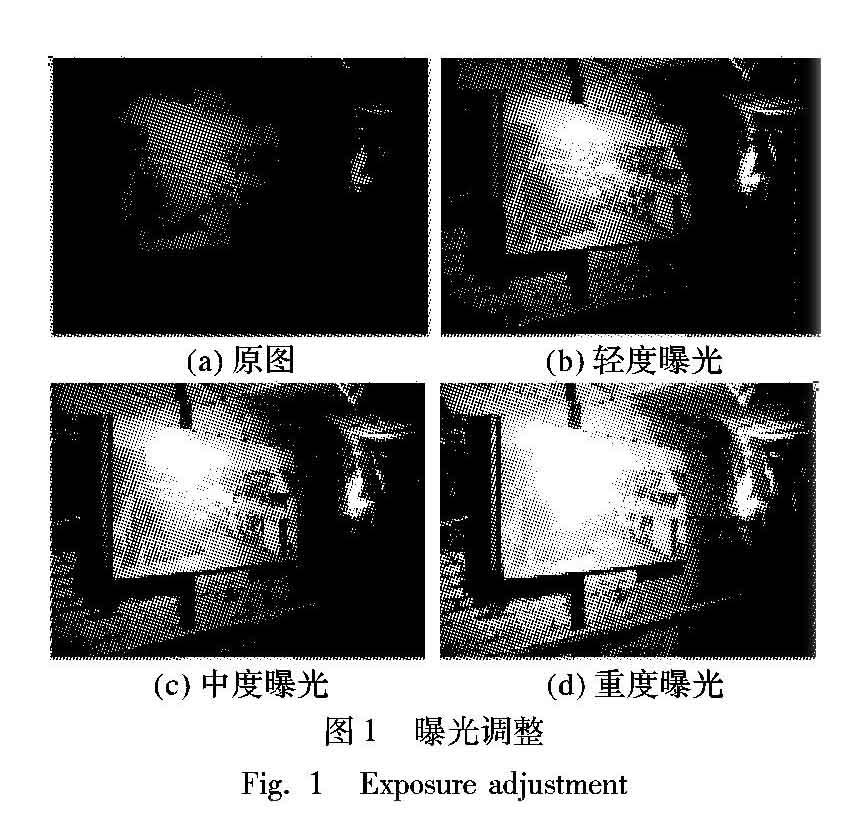
隨着科技的进步与发展,图像采集的方式越来越丰富,人们对图像的质量要求也越来越高。然而图像在获取的过程会受到很多因素的影响,特殊光照环境下,光学成像设备因为光照不均匀,从而可能使获得的图像曝光不均匀、场景细节损失、弱小目标识别不清。由于拍摄设备的动态范围是有限度的,如果仅仅调整设备曝光率,还是不能解决某些区域出现过度曝光或者过度饱和等问题。从图1可以看出,随着曝光率的增加,原来曝光不足的区域趋向于正常显示,而原来正常的区域趋向于过度曝光,导致无法正常显示区域信息。针对这个问题,学者们进行了大量研究。目前主流的方法主要分为两类:基于直方图增强和基于Retinex图像增强[1]。基于直方图的方法通过修改直方图的分布来增强图像,该方法因为简单有效而被广泛应用于各个领域,然而该方法对噪声敏感,在其改变图像亮度的同时可能出现过度增强的现象。近年来围绕这一问题,学者们提出了一系列优化算法。Lee等[2]通过寻找二维直方图分层之间的差异性提出了一种新的对比度增强算法;Celik等[3]尝试寻找一个最大灰度差来重新映射直方图;Gu等[4]将质量评估模型应用于直方图参数的优化中,有效地处理了过度增强的问题。但这些方法关注的是对比度增强,并没有充分利用图像的真实亮度,存在过度增强或者未被增强的风险。
基于Retinex的方法将图像看作是由光照分量和反射分量构成。传统的Retinex方法通过对光照分量的估计和移除,将反射分量看作是最后的增强结果[5-6],但是往往会出现增强结果不自然和过度增强等问题。Wang等[7]设计了亮度滤波器对亮度进行估计,然后使用双对数变换修整亮度,但是不能很好地处理细节。王小明等[8]提出了利用快速二维卷积和多尺度连续估计的算法,降低了多尺度Retinex算法的运算复杂度,但该方法可能会因为光照分量的结构性导致部分增强区域失去自然性。Fu等[9]通过最大后验概率来估计光照分量和反射分量,将两者进行伽马校正后重新调整图像,得到最后的增强结果,虽然增强效果较为理想,但仍会在纹理丰富的区域丢失细节信息。
上述方法可以获得较好的主观质量,但这些结果并不能准确地反映场景的真实信息。因此,基于单幅低照度图像的增强仍然是一个具有挑战性的问题。为了改善上述情况,基于Retinex的图像增强方法,本文提出了一种基于模拟多曝光融合的低照度图像增强方法,基本框架如图2所示。
1)首先将原来的低照度图像由RGB(Red,Green,Blue)颜色模式转化为HSV(Hue,Saturation,Value)模式,然后将HSV图像的V通道进行变分Retinex和形态学操作,得到变分增强后的基准图E1。
2)将变分增强后的基准图E1通过Sigmoid函数和伽马矫正构造新的归一化函数来实现图像的光照补偿,并得到基准图E2。
3)再通过基于高斯引导滤波的反锐化掩模算法对基准图E1进行细节调整,得到调整后的基准图E3。
4)将三幅基准图E1、E2、E3基于图像的亮度、曝光率和色调设计三幅曝光图的加权值,为曝光良好的像素分配较大的权值,曝光不足的像素分配较小的权值,得到图像集W1、W2、W3。
5)最后将加权后的图像集和基准图像集通过多尺度融合的方式结合,实现最后的增强,输出增强后的图像。
1 基于变分Retinex的增强方法
在模拟曝光之前,需要确定曝光图像的数量。为了同时兼顾图像的亮度和细节信息,本文选择三幅曝光图像,其中一幅为基准图像,另外两幅曝光图是在基准图E1的基础上,分别基于细节和亮度调整而产生。所以基准图E1是整个曝光图集的核心,E1的估计不足将会严重影响着其余两幅图的内容调整。Retinex理论是基于人眼视觉系统所提出的图像增强理论,因此基于Retinex理论产生基准图,其数学模拟如下:
5 结语
针对低照度图像,本文提出了一种基于模拟多曝光融合的图像增强方法。首先,利用形态学和改进的变分模型产生曝光图像集的基准图,以此保证增强结果的主体信息;为了模拟多曝光,分别以亮度和细节为目的,在基准图的基础上产生另外两幅曝光图;然后,分别基于亮度、曝光度和色调设计曝光图集的加权值,为曝光良好的像素分配较大的权值,为曝光不足的区域分配较小的权值;最后,采取多尺度融合图像集的方式,避免增强结果中的光晕,得到了最终增强的图像。将本文的方法和已有的低照度图像增强方法在四个公开的数据集上进行测试对比,实验结果表明,本文的方法具有较小的亮度失真和对比度失真,能够有效地保留图像本身的视觉信息。但是因为本文采取了交替求解策略,迭代次数增加了算法的复杂度,因此在接下来的工作中,如何提高算法的效率将是下一步的研究重点。
参考文献 (References)
[1] YUE H J, YANG J Y, SUN X Y, et al. Contrast enhancement based on intrinsic image decomposition [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(8): 3981-3994.
[2] LEE C, LEE C, KIM C S. Contrast enhancement based on layered difference representation of 2D histograms [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(12): 5372-5384.
[3] CELIK T, TJAHJADI T. Contextual and variational contrast enhancement [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(12): 3431-3441.
[4] GU K, ZHAI G T, LIN W S, et al. The analysis of image contrast: from quality assessment to automatic enhancement [J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(1): 284-297.
[5] JOBSON D J, RAHMAN Z, WOODELL G A. Properties and performance of a center/surround Retinex [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(3): 451-462.
[6] 劉茜,卢心红,李象霖.基于多尺度Retinex的自适应图像增强方法[J].计算机应用,2009,29(8):2077-2079.(LIU Q, LU X H, LI X L. Adaptive image enhancement method based on multi-scale Retinex algorithm [J].Journal of Computer Applications, 2009, 29(8): 2077-2079.)
[7] WANG S H, ZHENG J, HU H M, et al. Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(9): 3538-3548.
[8] 王小明,黄昶,李全彬,等.改进的多尺度Retinex图像增强算法[J].计算机应用,2010,30(8):2091-2093.(WANG X M, HUANG C, LI Q B, et al. Improved multi-scale Retinex image enhancement algorithm [J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2010, 30(8): 2091-2093.)
[9] FU X Y, LIAO Y H, ZENG D L, et al. A probabilistic method for image enhancement with simultaneous illumination and reflectance estimation [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 4965-4977.
[10] WANG Y F, WANG H Y, YIN C L, et al. Biologically inspired image enhancement based on Retinex [J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 177(C): 373-384.
[11] GUO X J, LI Y, LING H B. LIME: low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(2): 982-993.
[12] FU X Y, ZENG D L, HUANG Y, et al. A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation [C]// Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2016: 2782-2790.
[13] KIMMEL R, ELAD M, SHAKED D, et al. A variational framework for Retinex [J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2003, 52(1): 7-23.
[14] GOLDSTEIN T, OSHER S. The split bregman method for L1-regularized problems [J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(2): 323-343.
[15] DENG G. A generalized unsharp masking algorithm [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(5): 1249-1261.
[16] ANCUTI C O, ANCUTI C. Single image dehazing by multi-scale fusion [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(8): 3271- 3282.
[17] ANCUTI C O, ANCUTI C, de VLEESCHOUWER C, et al. Single-scale fusion: an effective approach to merging images [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(1): 65-78.
[18] ANCUTI C, ANCUTI C O, HABER T, et al. Enhancing underwater images and videos by fusion [C]// Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2012: 81-88.
[19] ANCUTI C O, ANCUTI C, BEKAERT P. Enhancing by saliency-guided decolorization [C]// CVPR 2011: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2011: 257-264.
[20] CHOI L K, YOU J, BOVIK A C. Referenceless prediction of perceptual fog density and perceptual image defogging [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3888-3901.
[21] JOBSON D J, RAHMAN Z, WOODELL G A. A multiscale Retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(7): 965-976.
[22] XU H T, ZHAI G Z, WU X L, et al. Generalized equalization model for image enhancement [J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2014, 16(1): 68-82.
[23] SHAN Q, JIA J Y, BROWN M S. Globally optimized linear windowed tone mapping [J]. IEEE transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2010, 16(4): 663-675.
[24] YING Z Q, LI G, REN Y R, et al. A new image contrast enhancement algorithm using exposure fusion framework [C]// CAIP 2017: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, LNCS 10425. Cham: Springer, 2017: 36-46.
[25] LI M D, LIU J Y, YANG W H, et al. Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust Retinex model [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(6): 2828-2841.
[26] MA K, ZENG K, WANG Z. Perceptual quality assessment for multi-exposure image fusion [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3345- 3356.
[27] SHEIKH H R, BOVIK A C. Image information and visual quality [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(2): 430-444.
[28] LI Z G, ZHENG J H, ZHU Z J, et al. Weighted guided image filtering [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(1): 120-129.
[29] AYDIN T O, MANTIUK R, MYSZKOWSKI K, et al. Dynamic range independent image quality assessment [C]// SIGGRAPH 2008: Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGGRAPH. New York: ACM, 2008: Article No. 69.
[30] WANG Q H, FU X Y, ZHANG X P, et al. A fusion-based method for single backlit image enhancement [C]// ICIP 2016: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2016: 4077-4081.
[31] YING Z Q, LI G, REN Y R, et al. A new low-light image enhancement algorithm using camera response model [C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2017: 3015-3022.
[32] 王晨,湯心溢,高思莉.基于人眼视觉的红外图像增强算法研究[J].激光与红外,2017,47(1):114-118.(WANG C, TANG X Y, GAO S L. Infrared image enhancement algorithm based on human vision [J]. Laser and Infrared, 2017, 47(1): 114-118.)
