Main Components and Antioxidant Activity of Callisia repens Extracts
2019-08-26BoLENGShaoruCAI2XiuminLIJiafuHUANGYuXUEZhichaoLINWensongCHENChunxianLIYutianPAN
Bo LENG*, Shaoru CAI2, Xiumin LI, Jiafu HUANG, Yu XUE, Zhichao LIN, Wensong CHEN, Chunxian LI, Yutian PAN
1. Engineering Technological Center of Mushroom Industry, Minnan Normal University, Zhangzhou 363000, China; 2. School of Management, Xiamen University Tan Kah Kee College, Zhangzhou 363000, China
Abstract To study the main active components and antioxidant activity in vitro of extracts from Callisia repens, the contents of main active components such as total flavonoids, total anthocyanin and total sugar in the extracts were studied by spectrophotometry. The components and content of 18 kinds of metals were determined by ICP-MS mass spectrometry. Finally, the oxidative activity of the extract was evaluated by spectrophotometry. Results showed that the content of flavonoids, the total protein, the total sugar and the total anthocyanin in C. repens extract powder were 2.04%, 1.83%, 55.2% and 7.2%, respectively. Beneficial trace elements such as Ca, Mn, Mg in C. repens extracts were higher, while harmful heavy metals such as Pb, Hg, Ag, Co, Ge were very tiny or not detected at all. The IC50 of C. repens was 0.265 mg/mL for scavenging DPPH·, and 1.16 mg/mL for scavenging ·OH free radical, the total reducing power of 1 mg extract was equivalent to that of 39 μg of Vc, and the extract showed no regular chelating power to ferrous ions. In conclusion, C. repens extracts have high content of natural active components, but extremely low content of the harmful heavy metals, and C. repens extract has good antioxidant capacity. Its antioxidant activity is realized by a variety of active factors through a synergistic mechanism. Thus, C. repens extract has great potential for developing into functional foods.
Key words Callisia repens, Antioxidant activity, Total flavonoids, Total anthocyanin, Heavy metal
1 Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM), a common chronic lifelong disease, has become one of the three major diseases that seriously endanger human health[1]. According to statistics, by 2025, the number of diabetes patients in the world will exceed 333 million[2]. So far, the treatment methods of diabetes mainly include dietary therapy, physical therapy, and drug treatment, among which, drug treatment is an important method, and dietary therapy is the basis. The drug treatment has played a positive role in lowering blood sugar, but its stability and reproducibility need to be improved[3]. The thousands of years of TCM clinical practice shows that compared with the effect of western medicine in preventing and treating diseases, Chinese herbal medicines, as long as properly taking, will generally bring about obvious toxic and side effects, and have unique advantages such as moderate price, mild and lasting effect. In recent years, Japan, South Korea and many European and American developed countries have also set off a research upsurge in the search for natural active substances from Chinese herbal medicines[4]. According to the TCM theory, diabetes belongs to "consumptive thirst" disease. In the past, many famous physicians have provided many prescriptions for consumptive thirst. Therefore, it is a feasible approach to explore and develop hypoglycemic products from the treasure house of Chinese herbal medicines. In this treasure house, some Chinese herbal medicines are also foods and edible, they have both medical functions and edible functions. Thus, they are more reliable than western medicines in terms of safety. Accordingly, searching functional active substances from medical and edible Chinese herbal medicines is receiving more and more attention in recent years[5]. Homologous herbal medicines are popular in folk areas, and the efficacy and action mechanism of some herbal medicines have been proved. However, many herbal medicines are still not studied or reported,Callisiarepensis just an example.
C.repens(Commelinaceae family) is small evergreen plant widely applied in ornamental landscape. To date, the research onC.repenshas been concentrated on biological characteristics or green cultivation techniques[7-9], while there is still not report about its biological activities. In folk areas, especially the southern area of Fujian Province like Zhangzhou and Quanzhou, it is common to cookC.repenswith water to improve the condition of diabetes patients. According to some literature, Commelina communis belongs to the same family asC.repens, has the functions of clearing away the heat and detoxification, and lowering the blood sugar[10-11]. The previous study of our team has proved thatC.repenshas functions of lowering the blood sugar of Type II diabetes mice. In order to further screen main active components, we made a preliminary analysis on the active components and in vitro oxidative activity ofC.repensextract, so as to lay a certain foundation for future in-depth studies.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 MaterialsC.repenswas bought from flower market in Zhangzhou City. After washing and lyophilizing, it was stored at 2-4℃ for experiment. Main pharmaceutical reagents: α-Diphenyl-β-picrylhydrazyl, Ferrozine, EDTA, K3Fe(CN)6, rutin, FC chromogenic reagent, 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid were all analytically reagents and bought from Xiamen Tagene Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1Preparation the extract. Firstly,C.repenswas dried, cut into pieces and added with water for extraction. The protein was removed by Sevage method, filtered after boiling for 1 h, and the filtrate was lyophilized to obtain the extract for experiment.
2.2.2Determination of in vitro antioxidant capacity. For the determination of DPPH· scavenging capacity, referred to the literature[12]; for the determination of the reducing power, referred to the literature[13]; for the determination of chelating power to ferrous ions, referred to the method in the literature[14]; for the determination of hydroxyl radical scavenging rate, referred to the method in the literature[15].
2.2.3Determination of main active components. For the determination of total flavonoids, referred to the method of Ji Huijieetal.[16]; total protein content was determined by Kjeldahl method[17]; total anthocyanin content was determined with reference to the method in the literature[18], where DF dilution factor value was 5; total sugar was determined with reference to[19]; the heavy metal content was determined by ICP-MS mass spectrometry, and the content of 18 kinds of trace elements were determined with reference to[20].
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Analysis of components of the water extract ofC.repens
3.1.1Analysis of main active components. The extracted and preparedC.repenssolution was rose red, brighter than the red wine. It was sweet and fragrant. After lyophilizing to dry powder, the color and odor had little change, the sensory index of the finished product was good, thusC.repenshas good potential for development into commodities. Pharmacological analysis showed that the total protein content in dry powder ofC.repensextract was not high, but the total sugar content was up to 55.2%, which gave the product a sweet and fragrant flavor. Besides, both the total flavonoids and total anthocyanins in the dry powder were as high as 2.04% and 7.2%, respectively, and the total protein was 1.83%.
3.1.2Analysis of mineral elements in water extracts. According to Table 1, the concentration of Ca, Mg, and Mn in lyophilized powder ofC.repensextract was very higher, followed by the concentration of Fe and Zn. Ca is the most important metal element for human bones. Mg can catalyze or activate more than 300 enzyme systems. The lack of Mg will lead to a series of physiological disorder[21]. Mn plays a vital role in the physiological activities of the brain[ 22]. Zn can promote the physiological activity of a variety of enzymes[23]. The high quality of these beneficial elements is favorable for the exertion of the health-care and pharmacological activity of theC.repensextract. In addition, the harmful trace elements such as Pb, Cu, Ni, Ag, and Ge were very tiny or not detected at all in theC.repensextract. Therefore, theC.repensextract is safe and non-toxic to the organism in terms of metal element composition, and has the potential to be developed into a functional food without heavy metal contamination.
Table 1 Content of 18 kinds of mineral elements inCallisiarepensextract
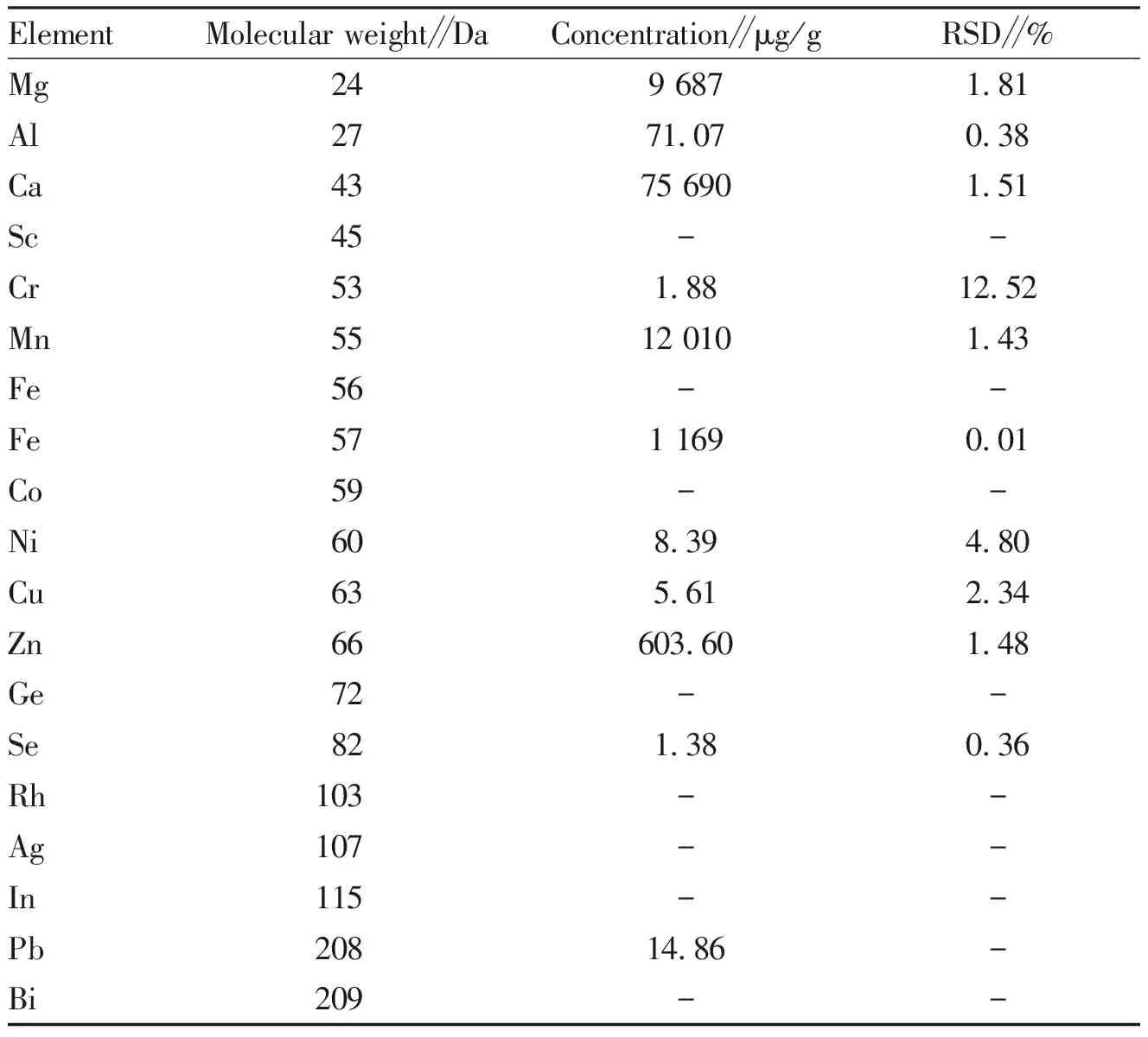
ElementMolecular weight∥DaConcentration∥μg/gRSD∥%Mg249 6871.81 Al2771.070.38 Ca4375 6901.51 Sc45--Cr531.8812.52 Mn5512 0101.43 Fe56--Fe571 1690.01 Co59--Ni608.394.80 Cu635.612.34 Zn66603.601.48 Ge72--Se821.380.36 Rh103--Ag107--In115--Pb20814.86-Bi209--
Note: "-" denotes not detected.
3.2 Analysis of antioxidant activity of the water extract ofC.repens
3.2.1DPPH free radical scavenging activity. Taking Vc as the reference standard, the DPPH·scavenging rate of theC.repensextract was shown in Fig.1. The linear regression equation for Vc scavenging DPPH· isy=4.039 3x+1.812,R2=0.999 6, and itsIC50=0.011 mg/mL. Different from Vc scavenging DPPH·linearity, the dose-effect relationship of theC.repenswater extract scavenging DPPH· is nonlinear, which is expressed as a polynomial relationship, and the formula for the fitted regression equation isy=0.000 04x3-0.020 2x2+3.023 8x-126.65,R2=0.999 4, and itsIC50=0.265 mg/mL. The above results indicate that there is a significant "S"-shaped dose-effect relationship between theC.repenswater extract content and DPPH free radical scavenging rate, similar to the synergistic action of hemoglobin transporting oxygen molecules, suggesting that the scavenging mechanism ofC.repenswater extract to DPPH free radicals may be the joint result of many active factors.
3.2.2Determination of total reducing ability. Taking Vc as the reference standard, the total reducing power of theC.repensextract was shown in Fig.2. The regression equation of Vc reducing powery=6.465x+0.040 5,R2=0.999 5. The reducing power ofC.repenswater extract increased with the increase of concentration, showing a good linear relationship. The correlation linear regression equation wasy=0.288 9x+0.010 5 andR2=0.999 9. Through calculation, it is known that the total reducing power of 1 mg ofC.repenswater extract is equivalent to the total reducing power of 39 μg of Vc.
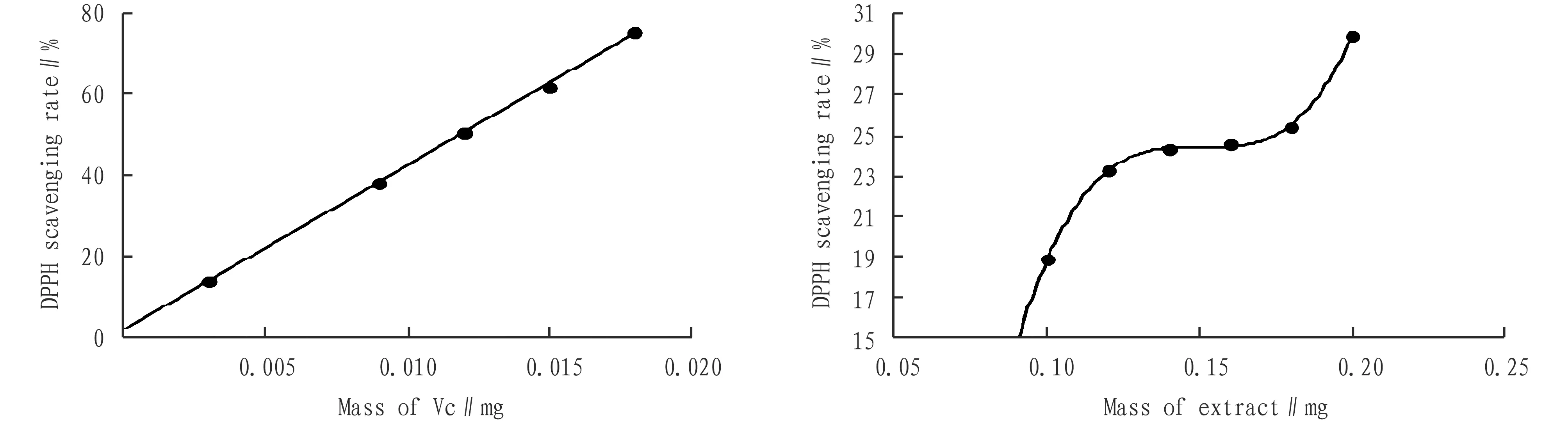
Fig.1 DPPH· scavenging rate of Vc and water extract ofCallisiarepens
3.2.3Chelating power to ferrous ions. From Fig.3, it can be known that EDTA has high chelating power to ferrous ions, and its linear regression equation isy=1 199.1x+8.145 5,R2=0.996 6. The water extract ofC.repenshas no regular chelating power to ferrous ions, indicating that it may not have ion chelating power.
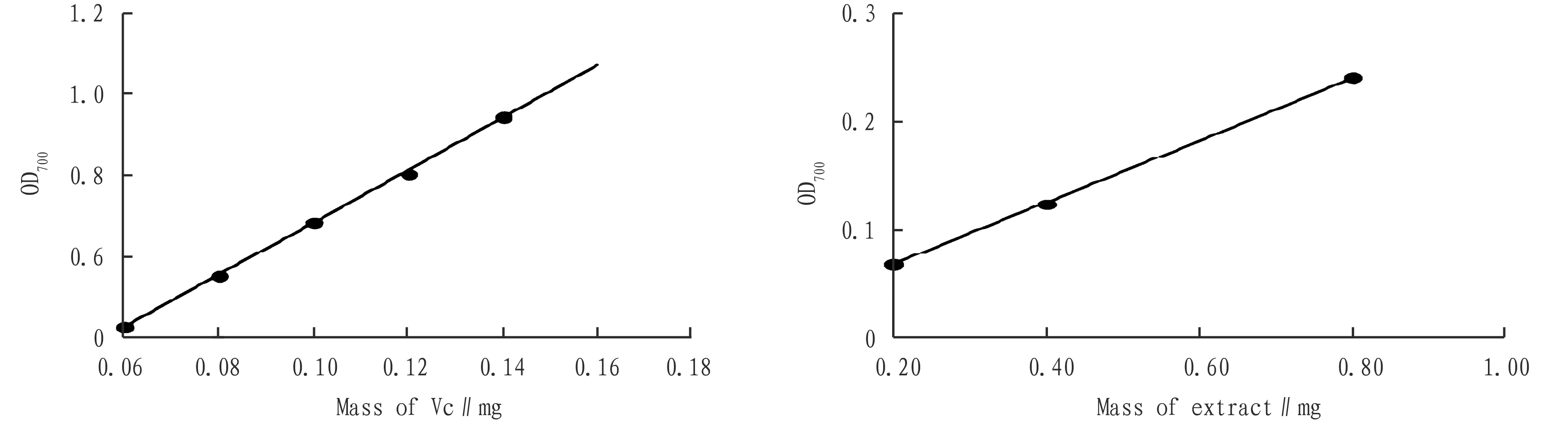
Fig.2 Total reducing power of Vc and water extract ofCallisiarepens
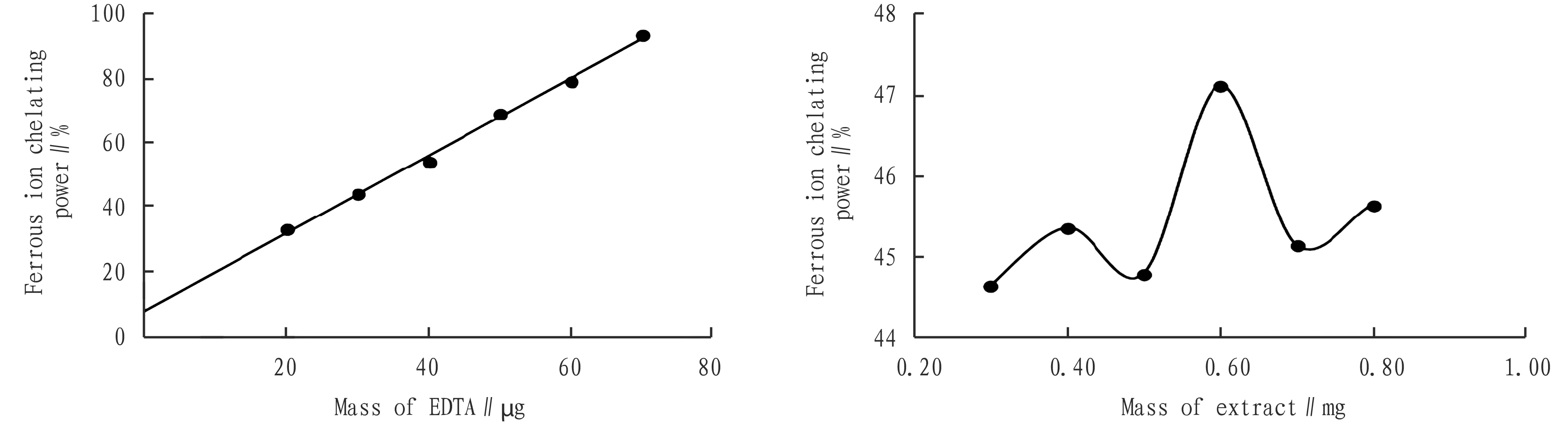
Fig.3 Ferrous ion chelating power of EDTA and water extract ofCallisiarepens
3.2.4Hydroxyl free radical scavenging activity ofC.repensextract. Taking Vc as the reference standard, the hydroxyl free radical scavenging rate of theC.repensextract was shown in Fig.4. The action of Vc scavenging hydroxyl free radical shows a typical linear dose-effect relationship, and its linear regression equation isy=2 762.8x+3.401 2,R2=0.979 5, and itsIC50=0.017 mg/mL. The hydroxyl free radical scavenging action ofC.repenswater extract shows no linear relationship, but obvious logarithmic relationship. The fitted regression equation isy=21.06ln(x)+46.948,R2=0.999 5,IC50=1.16 mg/mL. Similar to its scavenging effect on DPPH free radicals, it is further indicated that there may be multiple active factors in the water extract ofC.repens, and the hydroxyl free radicals are scavenged through synergistic action.
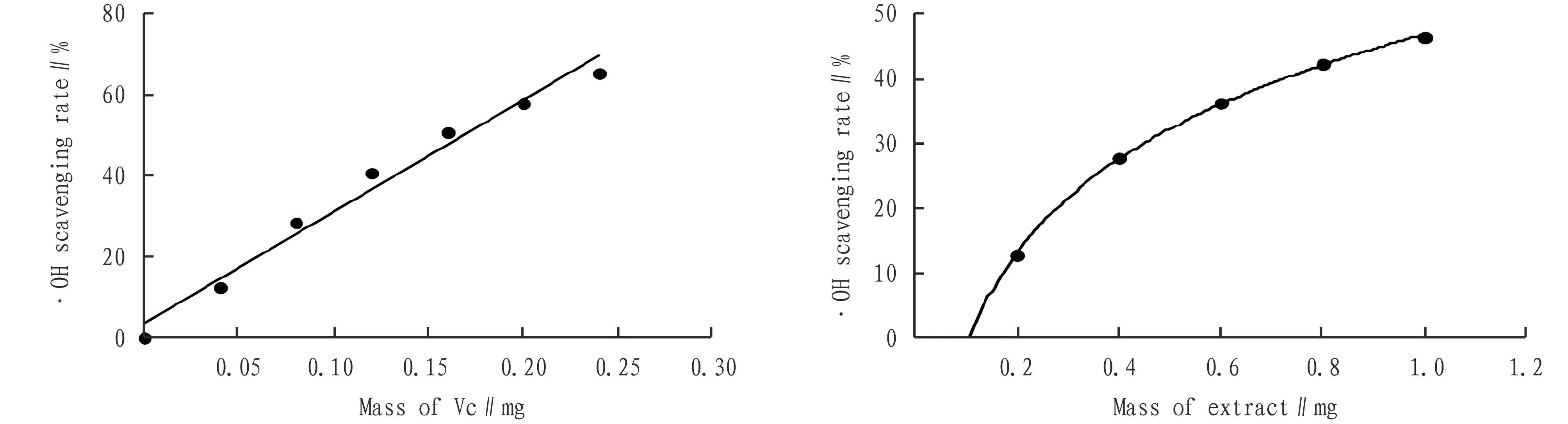
Fig.4 Hydroxyl free radical scavenging of Vc and water extract ofCallisiarepens
4 Conclusions
C.repensis a common edible Chinese herbal medicine for lowering the blood sugar in southern folk areas of Fujian Province. In previous study, we have proved that its water extract has strong blood sugar lowering effect, but the active components and action mechanism are still not clear. At present, most of the biologically active components of Chinese herbal medicines, especially edible Chinese herbal medicines, are polysaccharides, flavonoids, and anthocyanins[24]. Most of the components with hypoglycemic properties generally have strong antioxidant activity[25-27]. DPPH free radical scavenging capacity, reducing power and hydroxyl radical scavenging capacity are the most important and most commonly used indicators for measuring the antioxidant capacity of these biologically active substances. Absorbing and enriching various mineral elements in the soil through roots is one of the most basic physiological characteristics of plants. Different plants have different adsorption and enrichment preferences for different minerals. If heavy metals reach high concentration, it will inevitably exert a great impact on product quality and safety. Through this experiment, main active components ofC.repenswater extract such as polysaccharides, flavonoids, anthocyanins, and beneficial mineral elements are high, while the harmful trace elements are tiny or not detected at all, thusC.repenshas excellent potential for developing into health-care functional food. The experimental results also showed thatC.repenswater extract may contain a variety of antioxidant active factors, which show a strong ability to scavenge DPPH free radicals and hydroxyl radicals through a synergistic mechanism. TheC.repenswater extract used in this study is a crude extract that has not been purified by high precision. The relative content of active polysaccharides, total flavonoids and anthocyanins is relatively low. With the improvement of extraction method, further separation and purification, the active component content of unit mass extract will increase, and the physiological activity such as antioxidant capacity will be greatly improved.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Effects of Tillage Methods on Soil Available Phosphorus and Available Potassium in the Loess Plateau
- Poverty Alleviation in the Poor Mountainous Areas of Western China by Supporting Industry: A Case Study of Xundian Hui and Yi Autonomous County in Yunnan Province
- Analysis on Mechanical Grain Harvesting Characteristics of Different New Maize Varieties
- Poverty Alleviation through Employment Promotion in Extreme Poverty-stricken Areas in Western China: A Case Study of Targeted Poverty Alleviation through Employment Promotion in Awang Town, Dongchuan District
- The Poverty Alleviation Model for Poor Nationalities in the Mountainous Areas of Western China: A Case Study of “Promotion for the Entire Lisu Nationality” in Naimu Danxia Village Group
- Impact of Ningbo Port Logistics on Regional Economic Development of Zhejiang Province
