肺结节早期诊治中应用中医体质学说干预72例分析
2019-08-19叶钢福
叶钢福
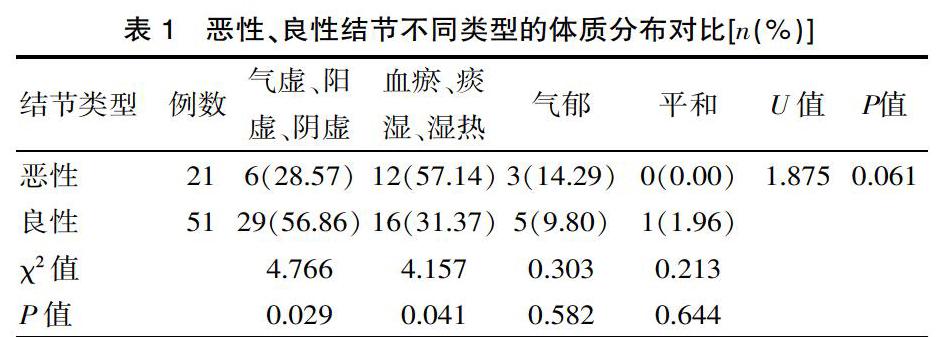


[摘要] 目的 分析中醫体质在肺结节早期诊治中的应用效果。 方法 该研究采取整群抽样方法抽取2015年4月—2016年4月,该院呼吸科住院及门诊确诊72例肺结节,纳入观察组;2013年1月—2015年3月,抽取该院住院及门诊确诊了192例早期肺结节,纳入对照组。观察组中采用影像联合体质辨识诊断良性肺结节而进行保守治疗的患者41例,按照确诊顺序分组,分为常规组(n=20)、干预组(n=21),分别采用常规治疗以及在此基础上联合体质管理治疗。结果 观察组72例对象,其中恶性21例、良性51例,恶性结节的对象气虚、阳虚、阴虚体质占比28.57%低于良性对象56.86%,差异有统计学意义(χ2=4.766、P=0.029<0.05)。观察组联合体质分析诊断诊断特异度、阳性预测值、符合率分别为98.04%、95.00%、95.83%,高于对照组86.03%、71.64%、85.94%,差异有统计学意义(χ2=5.601、4.747、5.091,P=0.018、0.029、0.024<0.05)。治疗后,干预组CRP(7.11±2.48)mg/L低于常规组(9.27±1.81)mg/L、ALB(46.56±1.97)g/L高于常规组(44.24±3.12)g/L,干预组结节吸收消失率42.86%、病理体质转为平和体质率38.10%高于常规组5.00%、0.00%,差异有统计学意义(t/χ2=3.172、2.862、7.961、9.466,P=0.003、0.007、0.005、0.002<0.05)。结论 在肺结节早期诊治中的应用中医体质分析,可以降低假阳性率;对于良性保守治疗的对象,进行体质管理,可以提升疗效,加速结节吸收消失。
[关键词] 肺结节;体质;管理;治疗
[中图分类号] R259 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2019)05(b)-0153-03
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the application effect of TCM constitution in the early diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary nodules. Methods The study adopted a cluster sampling method, from April 2015 to April 2016, 72 cases of pulmonary nodules were diagnosed in the hospital for admission and outpatients in our hospital. From January 2013 to March 2015, 192 cases of early pulmonary nodules were diagnosed in the hospital and outpatient clinics, and were included in the control group. 41 patients in the observation group who underwent conservative treatment with benign pulmonary nodules by imaging combined with physical identification were divided into the normal group (n=20) and the intervention group (n=21) according to the order of diagnosis. On this basis, combined with physical management treatment. Results Of the 72 patients in the observation group, 21 were malignant and 51 were benign. The proportion of qi deficiency, yang deficiency and yin deficiency was 28.57%, which was lower than that of benign subjects of 56.86%, the difference was statistically significant (χ2=4.766, P=0.029<0.05). The diagnostic specificity, positive predictive value and coincidence rate of the observation group combined with physical analysis were 98.04%, 95.00%, and 95.83%, respectively, which were higher than the control group (86.03%, 71.64%, and 85.94%). The difference was statistically significant (χ2=5.601, 4.747, 5.091, P=0.018, 0.029, 0.024<0.05). After treatment, the intervention group had a lower CRP (7.11±2.48) mg/L than the conventional group (9.27±1.81) mg/L and ALB (46.56±1.97) g/L, which was higher than the conventional group (44.24±3.12) g/L. The disappearance rate of nodules was 42.86%, the pathological constitution was flat and the body mass rate was 38.10% higher than that of the conventional group (5.00%, 0.00%), and the difference was statistically significant (t/χ2=3.172, 2.862, 7.961, 9.466, P=0.003, 0.007, 0.005,0.002<0.05). Conclusion The application of TCM constitution analysis in the early diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary nodules can reduce the false positive rate. For the benign conservative treatment, physical management can improve the curative effect and accelerate the disappearance of nodule absorption.
